Cloridina albatrossae, Ahyong, Shane T., 2004
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.169642 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6272118 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0380974E-AE58-2436-5272-FCF1CB40F8C1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Cloridina albatrossae |
| status |
sp. nov. |
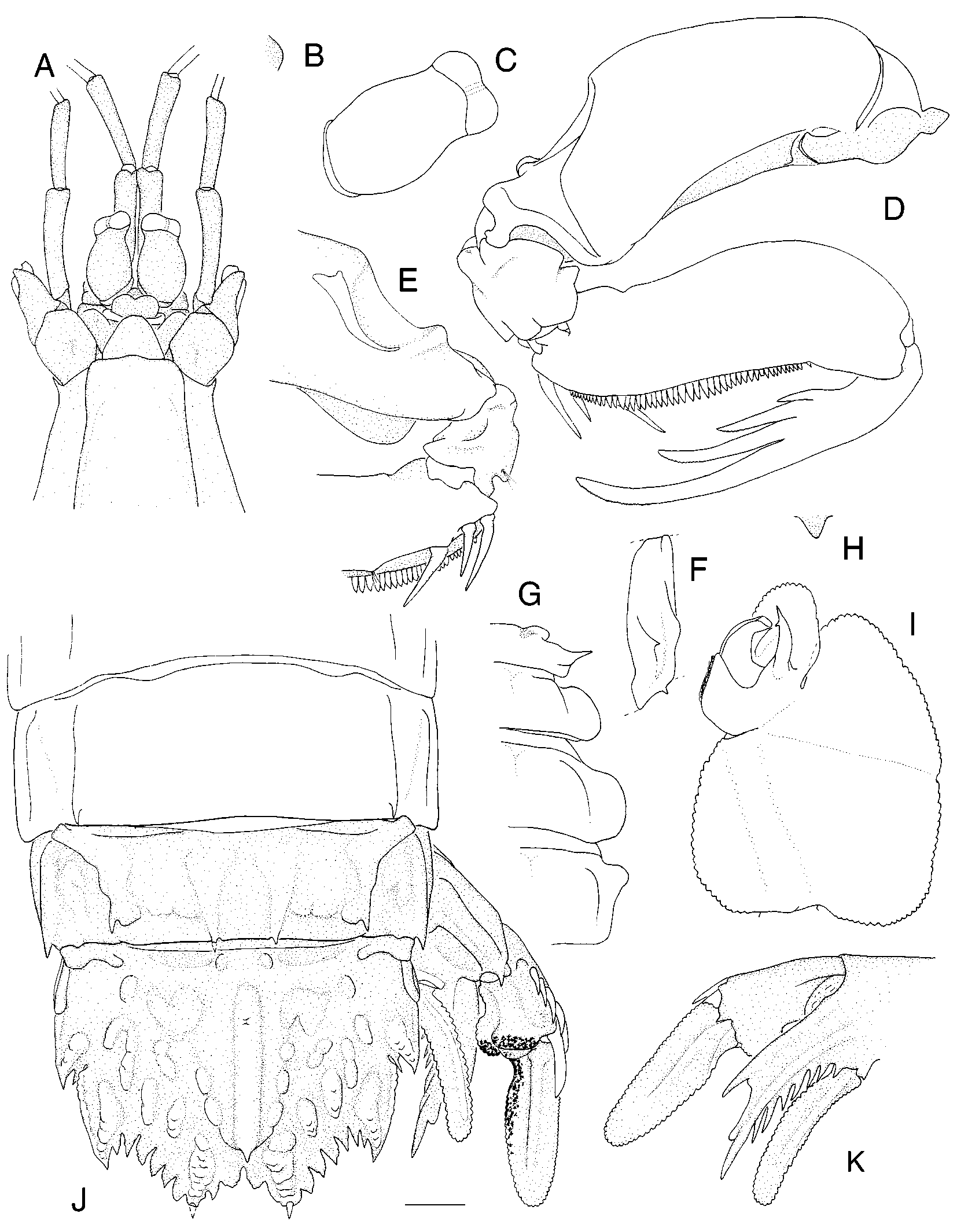
Cloridina albatrossae sp. nov. ( Figure 4 View FIGURE 4 )
Material examined. HOLOTYPE: USNM 77931, male (TL 61 mm), Tawitawi, Tinakta Island, Sulu Archipelago, 5°11’50”N, 119°54’00”E, 18 m, coarse sand, oyster dredge, Albatross stn 5159, R. P. Bigelow, 21 Feb 1908.
Diagnosis. Antennular somite dorsal processes with low, rounded apices. Rostral plate broader than long. Raptorial claw dactylus proximal margin obtusely angular, lacking basal notch or large lobes. TS5 lateral process a short, slender spine, directed laterally. TS6–7 lateral process broadly rounded, unarmed posterolaterally. Telson ventral surface without postanal or supplementary carinae.
Description. Dorsal integument smooth. Eye small, elongate, extending slightly beyond midlength of A1 segment 1; cornea width almost half eye length. Ophthalmic somite anterior margin rounded. Ocular scales fused, rounded laterally; emarginate medially.
A1 somite dorsal processes with apices low, rounded; A1 peduncle length 0.90 CL. A2 scale length unknown.
Rostral plate triangular, broader than long, apex broadly rounded; without dorsal carina.
Carapace anterior width 0.42 CL; anterolateral spines not extending to base of rostral plate; lacking carinae except for reflected marginal carinae; posterior margin straight.
Raptorial claw dactylus with 4 teeth, with outer proximal margin obtusely angular; propodus distal margin unarmed; carpus dorsal carina undivided; merus outer inferodistal angle unarmed.
Mandibular palp 2segmented (distal segment damaged on right side). MXP1–4 each with epipod. MXP5 basal segment lacking ventrally directed spine.
Pereopods 1–3 basal segment unarmed; endopod segments fused, slender, entire margin setose.
TS6–8 each without submedian carinae; with intermediate carinae. TS5 lateral process a short, slender spine, directed laterally; ventral spine small. TS6–7 lateral process broadly rounded. TS8 anterolateral margin rounded; sternal keel conical.
AS 1–5 without submedian carinae; intermediate, lateral and marginal carinae distinct. AS 6 with ventrolateral spine anterior to uropodal articulation. Abdominal carinae spined as follows: submedian 6, intermediate 5–6, lateral 6, marginal unarmed.
Telson broader than long; submedian, intermediate and lateral teeth short, traingular; prelateral lobe shorter than margin of lateral tooth; margin of intermediate tooth proximally crenulate; dorsolateral surface irregular, with 4 irregular, inflated carinae posterolaterally. Telson denticles triangular, each lacking dorsal tubercle; submedian 1–2, intermediate 6, lateral 1. Telson ventral surface lacking postanal or supplementary carinae; ventrolateral carina rudimentary, not extending posteriorly to base of lateral tooth.
Uropodal protopod terminating in 2 slender spines, inner longer, outer margin smooth; inner margin with 7 or 8 slender spines; with blunt ventral tubercle anterior to endopod articulation; protopod terminal spines with lobe on outer margin of inner spine rounded, deflected dorsally, narrower than adjacent spine, proximal margin concave.
Uropod exopod proximal segment unarmed dorsally; inner margin with broad, round distal lobe; outer margin with 6 movable spines, distalmost slender with acute apex, not reaching midlength of distal segment; distal margin with short ventral spine lateral to articulation with distal segment. Exopod distal segment longer than proximal segment; with black patch at articulation of exopod segments.
Colour in alcohol. Almost completely faded, except for some dark pigment at the articulation of the uropodal exopod segments, extending onto the inner half of the distal segment.
Etymology. Named for the U.S. Fisheries Steamer Albatross, from which the holotype was collected.
Measurements of holotype. TL 61 mm, CL 12.25 mm, cornea width 1.20 mm, anterior carapace width 5.1 mm, A1 peduncle length 11.05 mm.
Remarks. Cloridina albatrossae sp. nov. can be distinguished from its congeners by the combination of the rounded dorsal processes of the antennular somite, short rostral plate and spiniform lateral process of TS5. Cloridina albatrossae resembles C. chlorida ( Brooks, 1886) in the spiniform lateral process of TS5, but differs in bearing slightly less inflated eyestalks, blunt instead of sharp dorsal processes of the antennular somite, unarmed lateral carinae anterior to AS 6, unarmed marginal carinae on all abdominal somites, and in bearing a narrower lobe between the terminal spines of the uropodal protopod. Note, however, that the last mentioned feature might prove unreliable because it is known to vary in width in species of some other squillid genera (e.g., Oratosquillina Manning, 1995 , Quollastria Ahyong, 2001 ) (Ahyong 2001).
Distribution. Known only from Tinakta Island, the Philippines, at 18 m depth on coarse sand substrate.
| USNM |
Smithsonian Institution, National Museum of Natural History |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |