Chvalaea yolkamini, Jaume-Schinkel & Soares & Barros, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4748.3.12 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:346382B1-71E8-4BD9-92A0-8E7678EFEB18 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3705869 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03818780-DC51-FFB7-689B-5AF403B2BA61 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Chvalaea yolkamini |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Chvalaea yolkamini View in CoL sp. nov.
( Figs 1–18 View FIGURES 1–4 View FIGURES 5–10 View FIGURES 11–13 View FIGURES 14–18 )
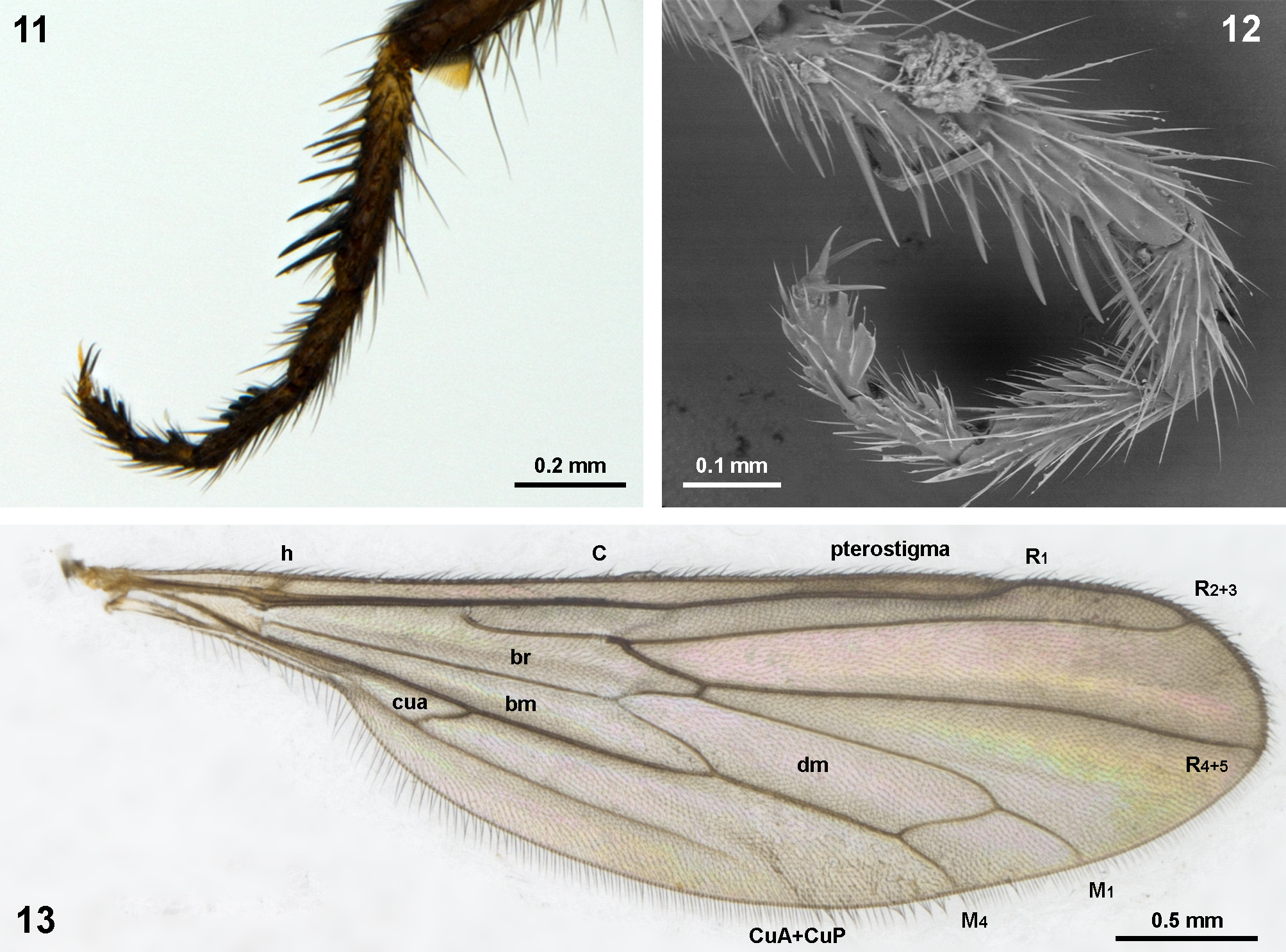
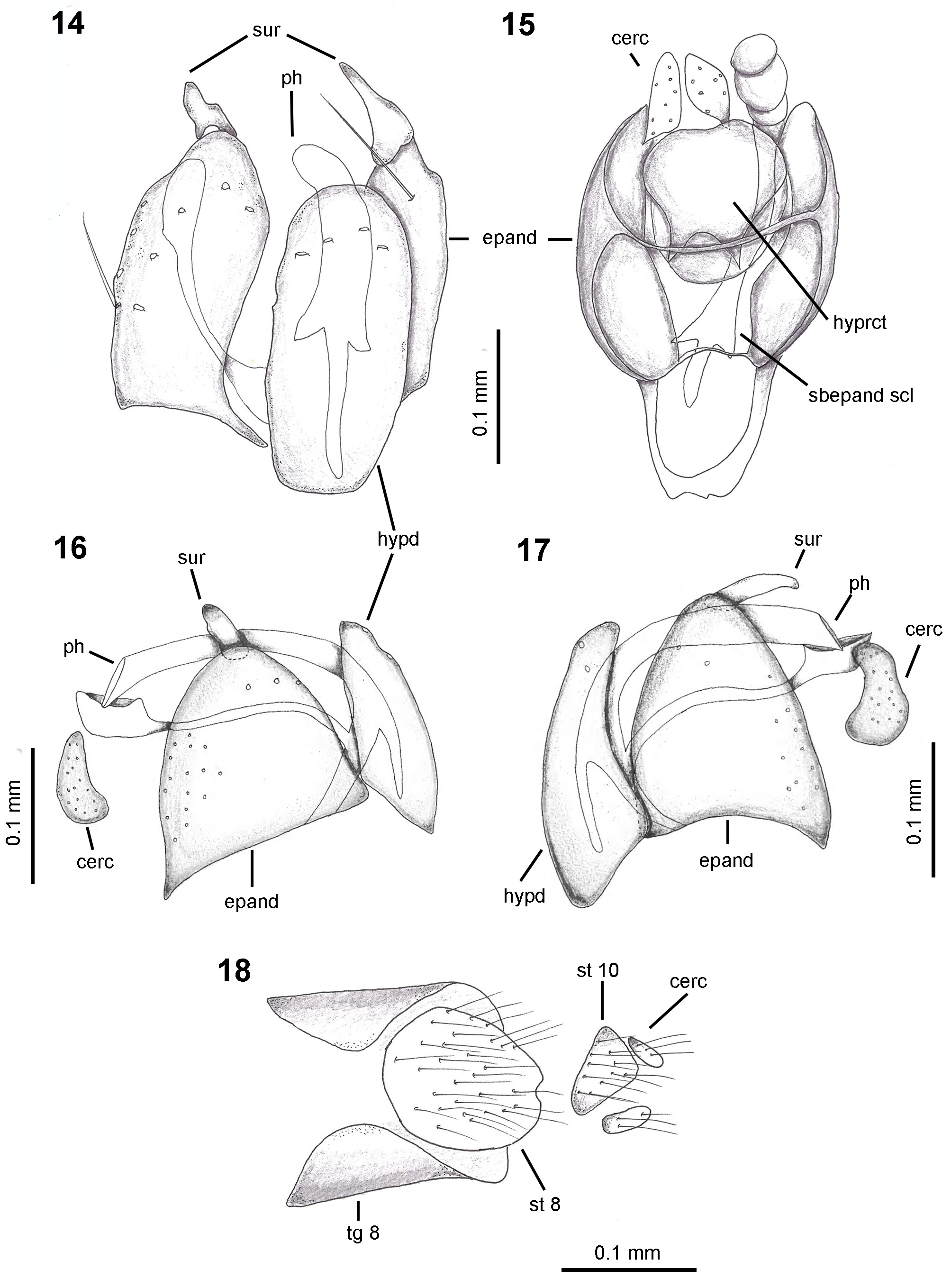
Diagnosis. Frons narrow at mid-length, narrower than width of anterior ocellus ( Figs 7 View FIGURES 5–10 ). Postpedicel 1.5 times length of scape and pedicel combined ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 5–10 ). Scutum dark brown, with light brown region near postpronotal lobe ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 5–10 ). Pleura orange-brown, except anepisternum and anterior half of katepisternum somewhat darker brown ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 5–10 ). Wing veins M 1 and M 4 reaching wing margin ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 11–13 ). Fore and mid tarsomere 1 pale yellow with dark apex ( Figs 5–6 View FIGURES 5–10 ). Hind tarsomeres 3–5 with short, blunt black spine-like ventral setae ( Figs 11–12 View FIGURES 11–13 ). Hypandrium narrow, oval about 2 times longer than wide, with 4 long setae near apex, arranged in trapezoidal pattern ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 14–18 ).
Description. Male ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 5–10 ). Body length 3.5 mm. Wing length 3.8 mm. Head. Frons narrow at mid-length (narrower than width of anterior ocellus) ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 5–10 ). Antenna dark brown ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 5–10 ). Postpedicel 1.5 times length of scape and pedicel combined ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 5–10 ); postpedicel 345 µm length, 36 µm width, pubescent, with 1 outstanding dorsal seta on basal third; stylus arista-like, more than twice length of postpedicel; 1 pair of proclinate ocellar setae. Proboscis pale brown, very short; palpus yellow, with slender yellow setae. Postocular row of 8 strong black setae. Thorax. Covered with yellow pruinosity. Pronotum dark brown ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 5–10 ). Scutum dark brown, with light brown region near postpronotal lobe ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 5–10 ); postalar callus light brown ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 5–10 ). Pleura extensively orange-brown, except anepisternum and anterior half of katepisternum brown; anterior thoracic spiracle dark brown ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 5–10 ). Scutellum brown, 1 pair of thin apical and convergent setae, 1 pair of short and thin lateral setae, about half length of apical. Mediotergite brown. Acrostichals biseriate and dorsocentrals uniseriate, short, slender and sparse; notopleuron with 1 long and strong seta; 1 anterior postalar seta very short, slender and 1 long, strong posterior postalar seta, shorter than notopleural seta ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 5–10 ). Wing ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 11–13 ). Light brown; cell cua shorter than half length of cell bm; veins M 1 and M 4 reaching wing margin; CuA+CuP not reaching wing margin; pterostigma slightly darker than rest of wing; halter with dark brown knob, stem yellow and pale ( Figs 5–6, 9 View FIGURES 5–10 ). Legs. All coxae ground color pale yellow, except anterior surface of fore coxa slightly darker than mid and hind coxae; femora pale yellow on basal 1/3, darker at junction of tibiae; fore and mid tibiae pale brown, darker near apex; hind tibia dark brown, paler near base; fore and mid tarsomere 1 pale yellow with dark apex, remaining fore and mid tarsomeres dark brown, hind tarsomeres dark brown, except extreme base. Chaetotaxy: mid and hind femora with 1 long and strong seta on anteroventral surface near apex. Fore tibia with 1 long and strong anteroventral seta near middle; mid tibia with 1 anterodorsal, 1 dorsal and 1 posterodorsal strong setae near junction with femur, 1 long and strong anterodorsal seta near middle, 1 long and strong anterodorsal seta on apical 1/4; 1 long and strong anterodorsal and 1 long and strong posteroventral seta near junction with tarsomeres. Hind tibia with 1 dorsal, 1 posterodorsal, 1 anterodorsal and 1 posteroventral setae on the basal 1/3; 1 strong posterodorsal seta at mid-length; 1 strong dorsal and 1 strong posterodorsal seta near apex. Fore and mid tarsomeres with no remarkable setae. Hind tarsomere 1 with anteroventral row of long, strong, black spine-like setae; tarsomere 2 with 3 short strong ventral setae; tarsomeres 3–5 with short, blunt spine-like ventral setae ( Figs 11–12 View FIGURES 11–13 ). Abdomen. Black, shiny, slender, slightly curved downwards, covered with thin pale setae ( Figs 5 View FIGURES 5–10 ). Segment 8 about as broad as length, 1 row of stronger setae near posterior margin, concolorous with abdomen. Terminalia. Left cercus (lateral view) shorter, slender at apex; right cercus slightly longer than left, broader at base. Left epandrial lamella subtriangular, as long as wide; right epandrial lamella subtriangular, 1.4 times longer than width. Surstyli long, subequal in length, narrowed at apex. Phallus elongate; phallic shaft gradually arched, cylindrical, without protuberances. Hypandrium narrow, elongate and oval, 2 times longer than wide, apical margin convex with 4 setae arranged in trapezoidal pattern ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 14–18 ); subepandrial sclerite basal margin sinuate and apical margin truncate ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 14–18 ); hypoproct about as long as wide, with apex slightly sinuate in middle, lateral margins round, basal margin strongly concave in middle, almost triangular in shape ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 14–18 ). Female ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 5–10 ). Similar to male. Terminalia ( Fig. 18 View FIGURES 14–18 ). Lateral margins of tergite 8 extending ventrally; sternite 8 large, about as long as wide, suboval, slightly concave at distal margin; sternite 10 short, triangular; cercus short, shorter than sternite 10.
Variation. Stored specimens in alcohol present a more evident contrast in coloration on the scutum, general coloration brown, paler near the postpronotal lobes, pinned specimens tend to have less evident coloration, resembling a scutum homogeneously brown.
Distribution. This species is only known to occur in Mexico (Veracruz).
Type material. HOLOTYPE ♂, labelled: Mexico, Veracruz, Xalapa, Ecological Park Francisco Javier Clavi- jero (19°30′52″N, 96°56′12″W), 1344–1372 m, 31.viii.2019, posing in branch tips, Sweeping, S. JAUME-SCHIN- KEL col GoogleMaps .; HOLOTYPE, Chvalaea yolkamini Jaume-Schinkel, Soares & Barros [red label] ( IEXA) . Holotype condition: good, terminalia dissected. PARATYPES: same data as holotype, except 3.viii.2018 (1 ♂, 2 ♀, INPA) ; 19.iii.2018 (1 ♀, IEXA) ; 12.x.2019 (1 ♀, IEXA) ; 19.x.2019 (1 ♀, IEXA) ; 17.xi.2019 (6 ♀, IEXA) ; 3.xii.2019 (2 ♂, 2 ♀, IEXA; 2 ♂, 3 ♀, INPA) .
Additional examined material. Same data as holotype except, 31.viii.2019 (1 ♂, IEXA); 17.xi.2019 (1 ♀, IEXA).
Etymology. Yolkamini in Nahuatl, a native language in Mexico, means hunter, in reference to the predatory habits of this species of Chvalaea .
Remarks. Chvalaea yolkamini sp. nov. is similar to C. sinclairi on the basis of the short postpedicel, about 1.5 times the length of scape and pedicel combined, apical pair of convergent scutellar setae thin and short, and short, blunt, black spine-like ventral setae absent on hind tarsomere 2. But the new species differs by the narrow hypandrium, about 2 times longer than wide, hypoproct with apex slightly sinuate in the middle in C. yolkamini sp. nov., while the apex is truncate in C. sinclairi and fore and mid tarsomere 1 pale yellow with dark apex in C. yolkamini sp. nov., while all fore and mid tarsi are pale brown in C. sinclairi .
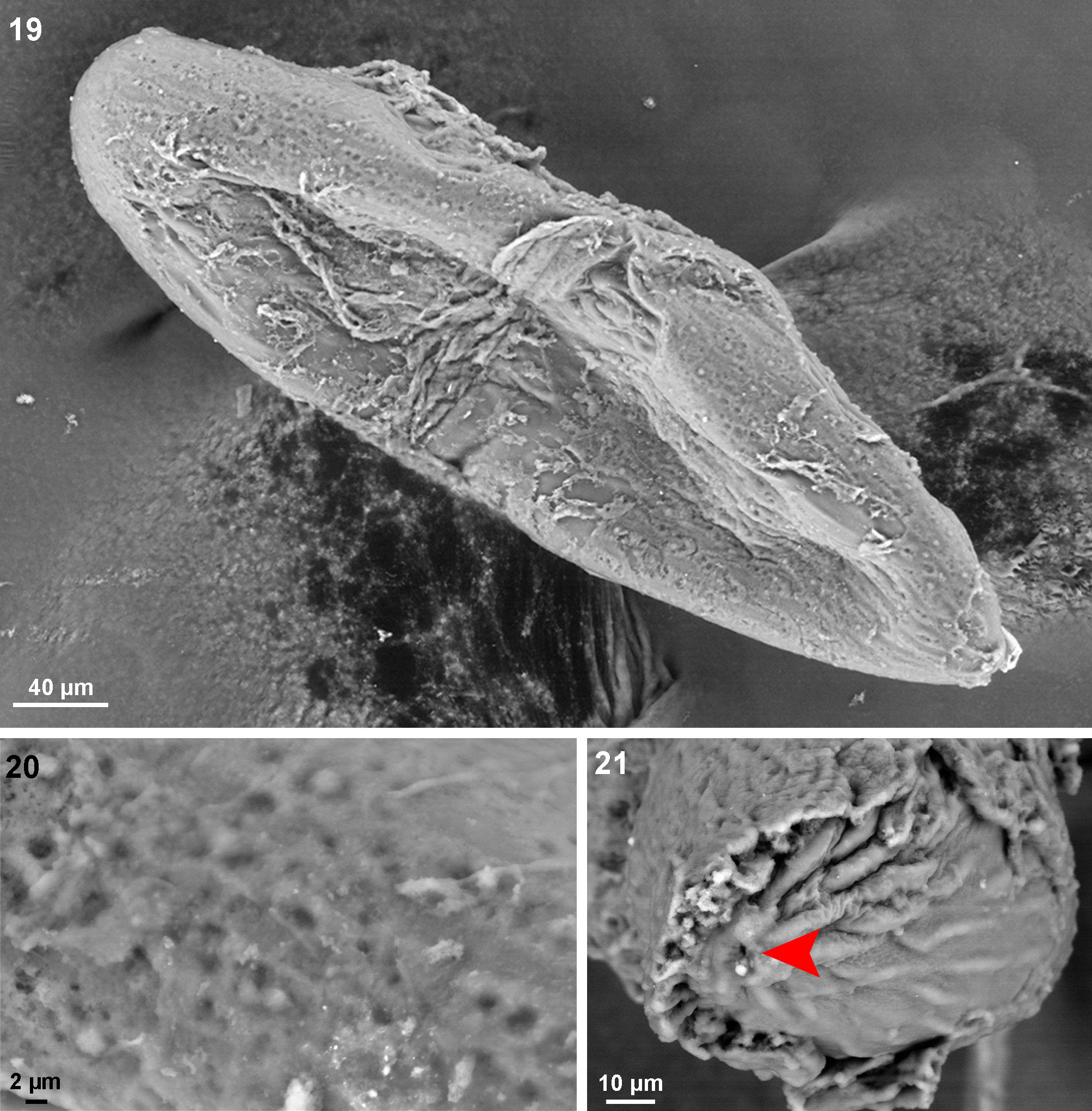
Egg description (n=2) ( Figs 19–21 View FIGURES 19–21 ). Egg measurement: 443.57 ± 2.5 μm long, 137.14 ± 3.8 μm wide (mid area). Eggs are creamy yellow, ellipsoidal, narrower towards anterior pole. Surface of entire egg smooth, with pitting, orange peel-like surface; without distinct ornamentation. Micropyle located at anterior pole preceded by more corrugated chorionic surface, followed by smooth rim around micropyle.
| INPA |
Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas da Amazonia |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.