Cheilopora sincera ( Smitt, 1868 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5125.2.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:6DDA279A-FA5F-4993-98DD-FC40133292BB |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6425473 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03825422-2A39-4450-8A9F-F9482DDDFC4D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Cheilopora sincera ( Smitt, 1868 ) |
| status |
|
Cheilopora sincera ( Smitt, 1868) View in CoL
( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 ; Table 6)
Discopora sincera Smitt, 1868: 28 , pl. 27, figs 178–180.
Cheilopora sincera: Levinsen 1909: 353 View in CoL , pl. 24, fig. 4a.
not Cheilopora sincera: Grischenko et al. 2007: 1125 View in CoL View Cited Treatment , fig. 31. Material examined. Lectotype (designated here) SMNH-Type-1733, North Atlantic Ocean , Finnmark, northern Norway, encrusting a bivalve shell. Leg. S. Lovén.
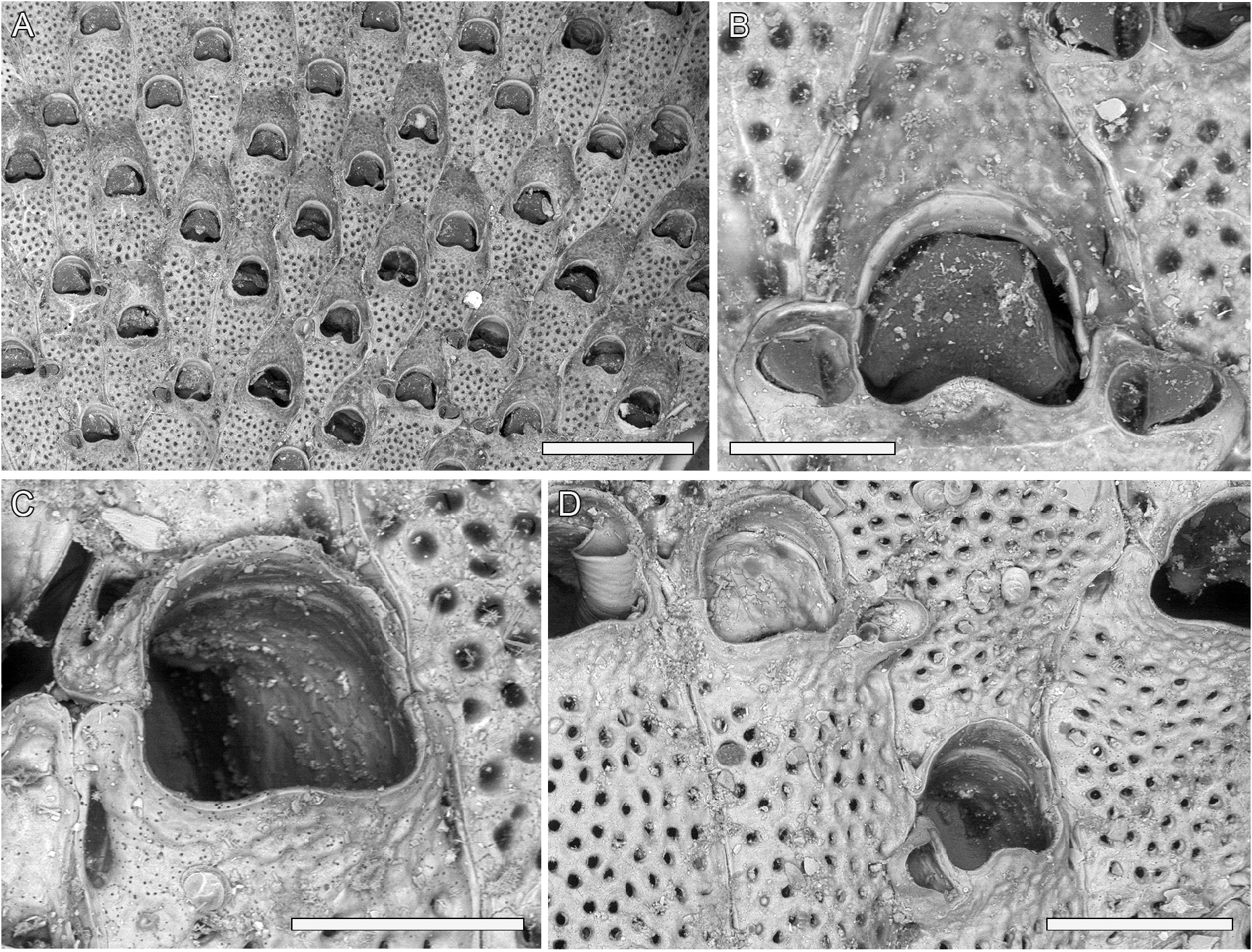
Description. Colony encrusting, multiserial, uni- to multilaminar, extensive, encrusting a fragment of a bivalve shell on both sides.
Autozooids arranged in alternating, longitudinal rows ( Fig. 8A View FIGURE 8 ), distinct with narrow, shallow grooves and a thin rim of raised calcification, elongate rectangular sometimes acutely tapering proximally, twice as long as wide (mean L/ W 2.12).
Frontal shield flat proximally, slightly convex centrally and distally raised as a pointed ( Fig. 8A View FIGURE 8 ), rounded ( Fig. 8B View FIGURE 8 ) or anvil-shaped ( Fig. 8D View FIGURE 8 ) suboral process, nodular and finely granular, densely and evenly perforated by circular or funnel-shaped pseudopores, 20–25 µm in diameter, except for the suboral area and the raising peristome ( Fig. 8A–C View FIGURE 8 ); marginal areolae distinguishable from pseudopores by being larger and elliptical to drop-shaped, about 80 µm long, placed lateral to the orifice (budding sites for avicularia) and at proximal corners ( Fig. 8C View FIGURE 8 ).
Orifice cormidial, formed by two or more autozooids (e.g. the zooid to which it belongs plus the distal neighbour as seen in Fig. 8C View FIGURE 8 or also the lateral neighbours as in Fig. 8D View FIGURE 8 ), bell-shaped, slightly larger in ovicellate zooids; oral spines absent; closure plates, nodular as the frontal shield, observed sealing the orifice ( Fig. 8D View FIGURE 8 ).
Adventitious avicularia rare, single or paired, budded from the latero-oral marginal areolae, elliptical to pearshaped; rostrum slightly raised, rounded, directed laterally, indenting the frontal shield of the lateral neighbours; crossbar lacking; mandible semi-elliptical ( Fig. 8B View FIGURE 8 ).
Ovicells endozooidal, flat to slightly convex, formed by an elongation of the proximal frontal shield of the next distal zooid ( Fig. 8A View FIGURE 8 ); ooecium rounded trapezoidal or triangular, nodular as the frontal shield but much less pseudoporous ( Fig. 8B View FIGURE 8 ).
Ancestrula not observed.
Remarks. Smitt (1868) described this species as Discopora sincera based on the material collected by Prof. Lovén in Finnmark, Norway, and found between 19–60 m depth encrusting ascidians, bivalve shells (as the studied syntype), and volcanic rocks.
Levinsen (1909) introduced the genus Cheilopora to accommodate, in addition to Smitt’s species, four further species, i.e. Hippoporina circumcinta Neviani, 1896 , Mucronella praelucida Hincks, 1884 , Mucronella praelonga Hincks, 1884 , and Lepralia grimaldii Jullien, 1903 in Jullien & Calvet (1903). Of these species only two, namely C. sincera and C. praelucida , can be confirmed as belonging to Cheilopora , while Neviani’s species became the type of Cheiloporina Canu & Bassler, 1923 , and Jullien’s species has been accepted as its junior synonym (see Reverter-Gil & Fernández-Pulpeiro 1999, p. 43).? Cheilopora praelonga is only tentatively placed in this genus. Levinsen (1909), however, did not indicate a type species for his new genus; the selection was made a few years later by Canu & Bassler (1917).
The Japanese material described and illustrated in Grischenko et al. (2007, fig. 31) as Cheilopora sincera does not correspond with the type specimen. In addition to the absence of avicularia, which could be lacking for developmental or environmental reasons, the main difference is in the ovicell. In the Japanese species, the ovicell is hyperstomial and occupies most of the frontal surface of the next distal autozooids which appear packed and squat. In the type specimen, ovicells are endozooidal and flat, do not occupy the frontal of the neighbour zooid but seem to elongate it ( Fig. 8A, B View FIGURE 8 ). Nevertheless, Bassler (1936) proposed the family Cheiloporinidae to accommodate genera with endozooidal ovicells, such as Cheiloporina and Cheilopora , initially placed in the Hippopodinidae , the type species of which had hyperstomial ovicells. A better fit for the Japanese specimen seems to be Cyclicopora Hincks, 1884. The type species, C. longipora ( MacGillivray, 1882) lacks avicularia, the ovicells are large, hyperstomial and globular ( Cook et al. 2018, p. 208, fig. 3.158), and some zooids can also develop a pointed mucro (see also SEM image of the type specimen NMV F45691 View Materials available from Bock (2022) at http://bryozoa.net/cheilostomata/ cyclicoporidae/cyclicopora_longipora.html).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Schizoporelloidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Cheilopora sincera ( Smitt, 1868 )
| Martino, Emanuela Di 2022 |
Cheilopora sincera :
| Levinsen, G. M. R. 1909: 353 |
Discopora sincera
| Smitt, F. A. 1868: 28 |