Halozercon tigerek, Marchenko, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4568.3.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3350BF32-11E9-4C7E-917D-AEC26AFE50AC |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5928681 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038D87AF-E042-A524-A7EB-FC450F89F82E |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Halozercon tigerek |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Halozercon tigerek sp. n.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:23434AB2-5324-4713-B98E-143C87C607CA
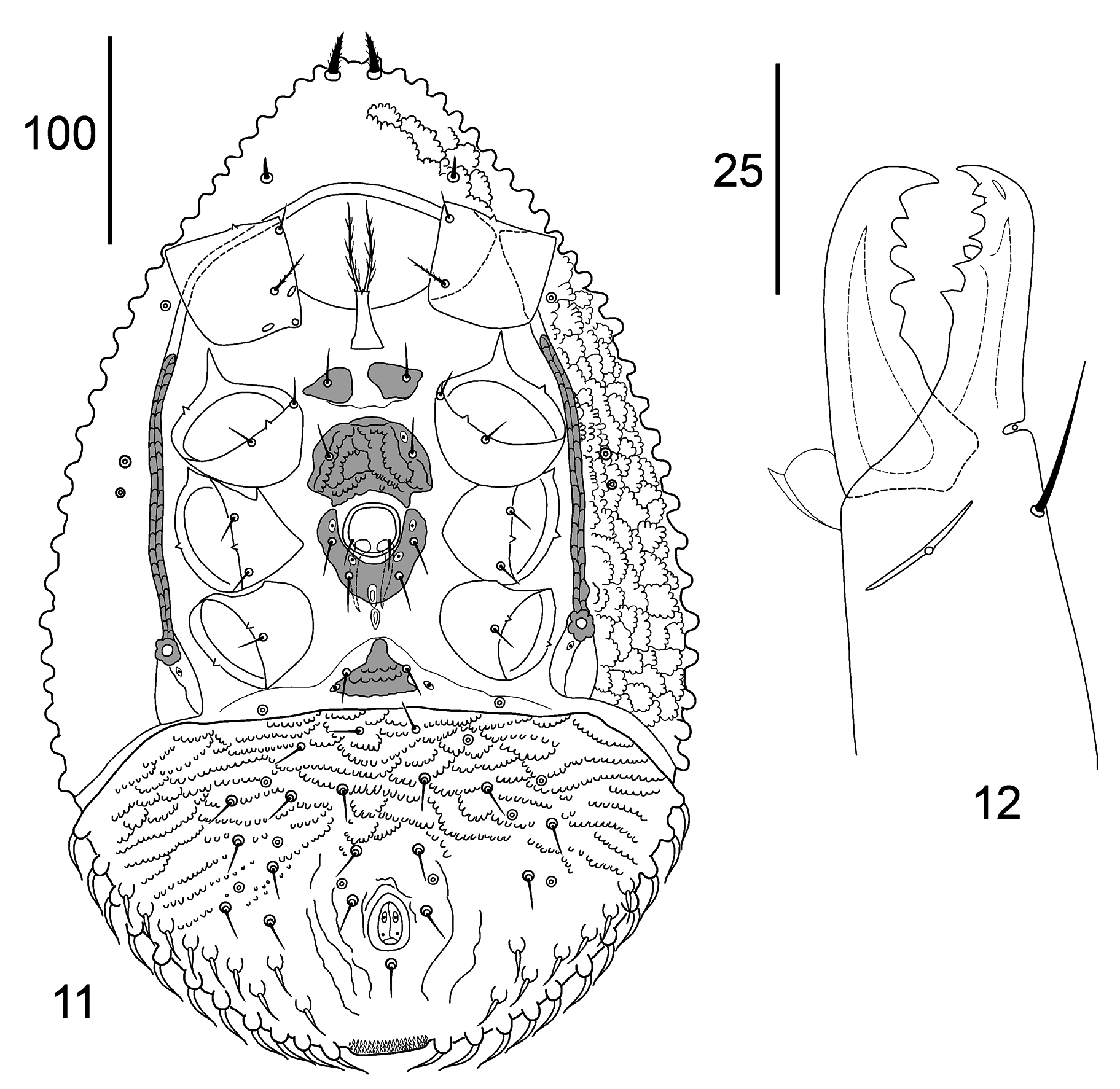
Diagnosis. Vertex with two pairs of setae j1 and z1, pore-like structures ip1 absent. Podonotum ornamented by small tubercles and festoon reticulation over the entire surface. Dorsal shields neotrichous. Many dorsal setae lanceolate or leaf-shaped. Median region of opisthonotum with 17–22 setae of J series, with slightly linear reticulation. First sternal platelet entire with pair of lyrifissures iv2. Metapodal shields large. Soft cuticle between genital and ventri-anal shields with two pairs of setae Jv1, Zv1 and two lightly sclerotised plates. Adults peritremes long, reaching level of spine top of coxae II anteriorly; in deutonymph peritremes shorter, reaching middle level of coxae II. Ventri-anal shield entire. Adult chelicera without sexual dimorphism.
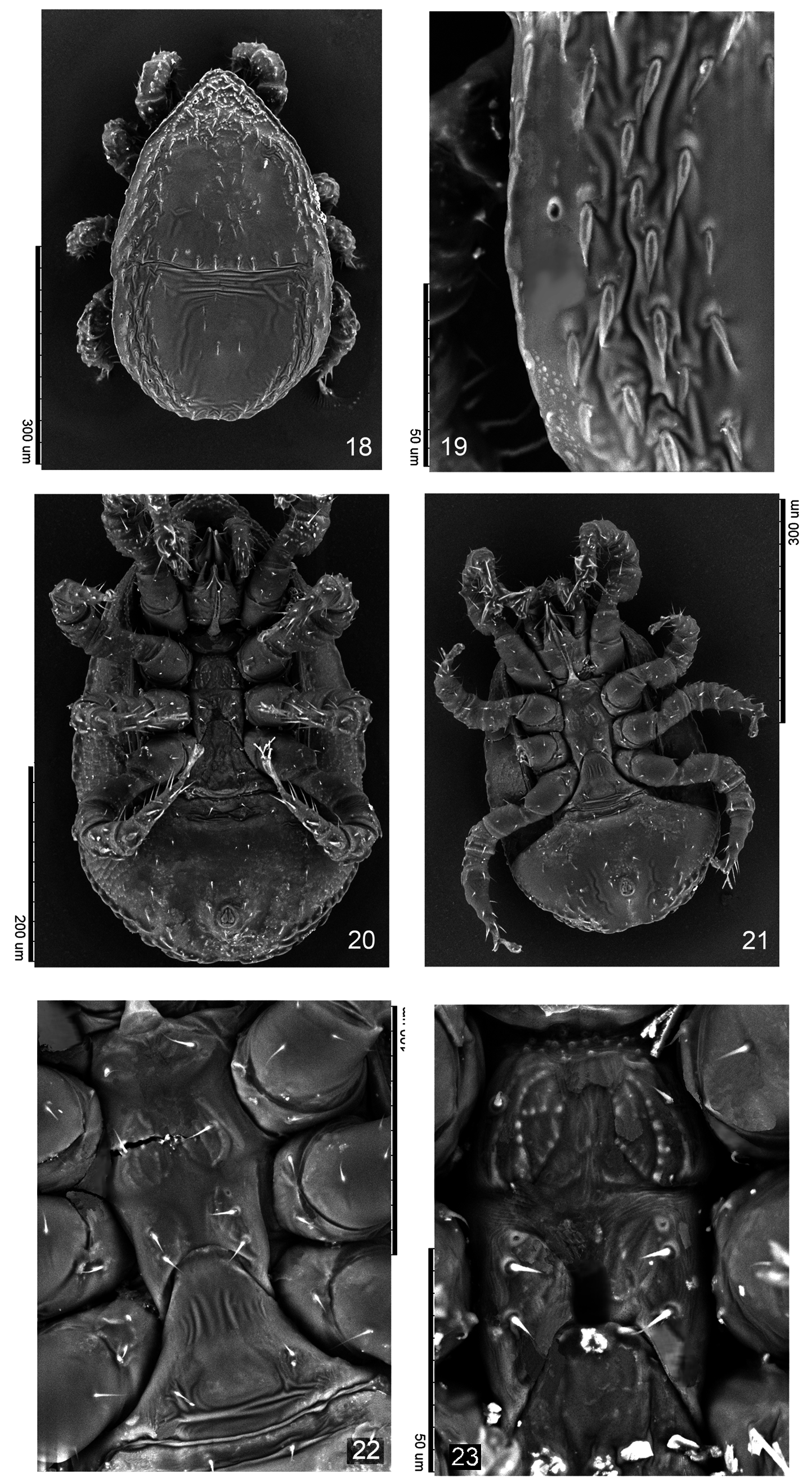
Description. Female ( Figs 1–10 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURES 2–5 View FIGURES 6–9 View FIGURE 10 , 18–27 View FIGURES 18–23 View FIGURES 24–29 and 30–41 View FIGURES 30–41 , n=10)
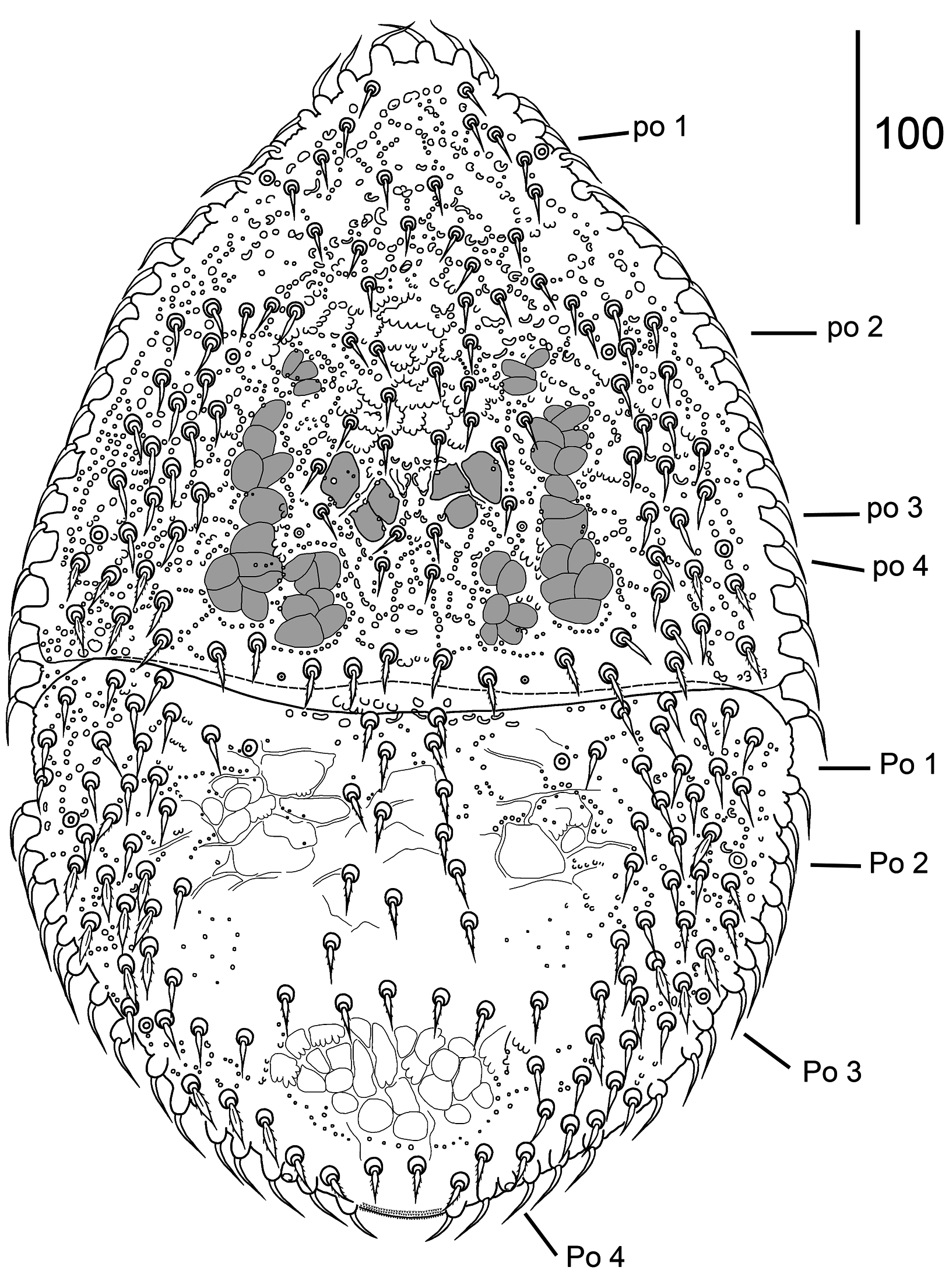
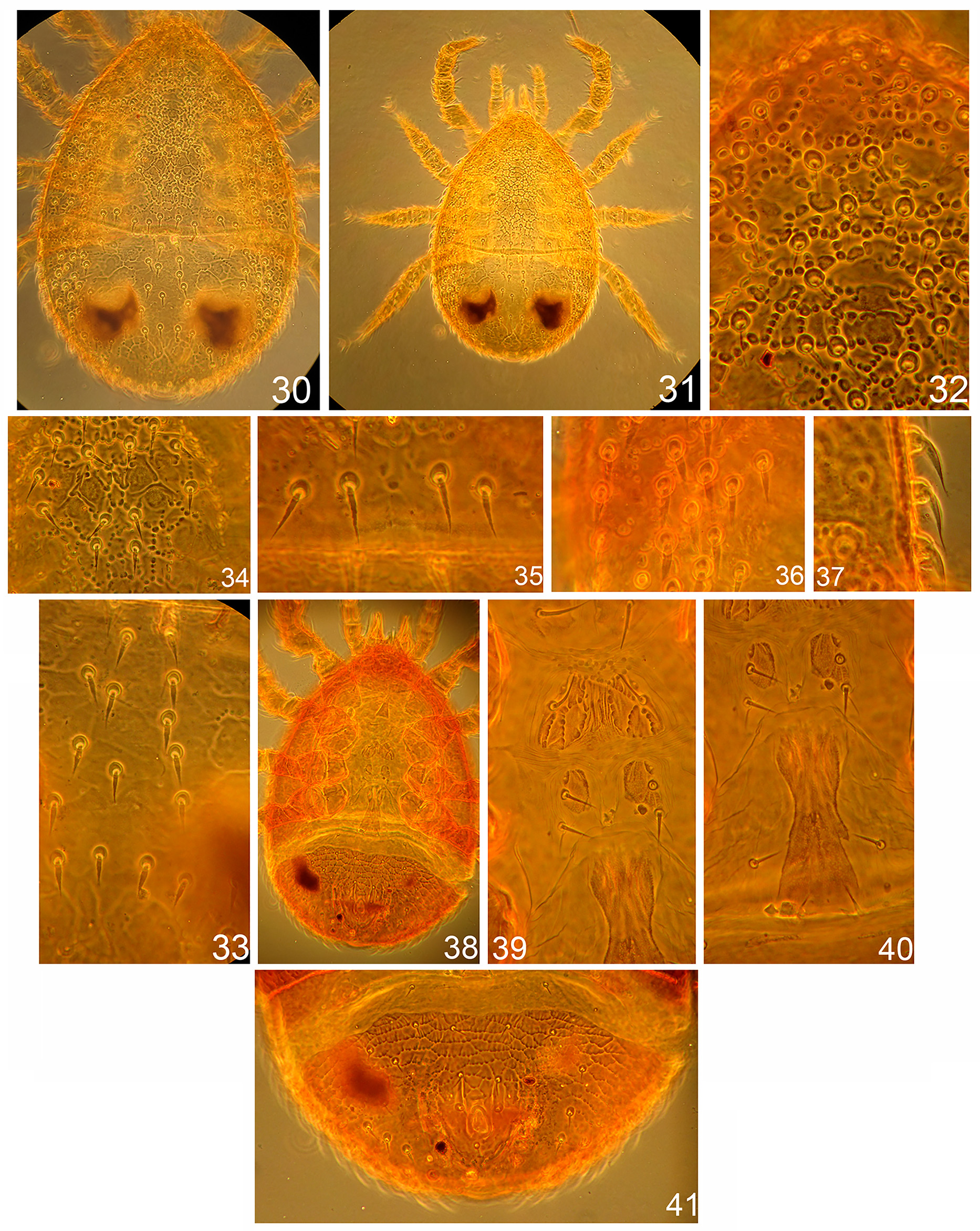
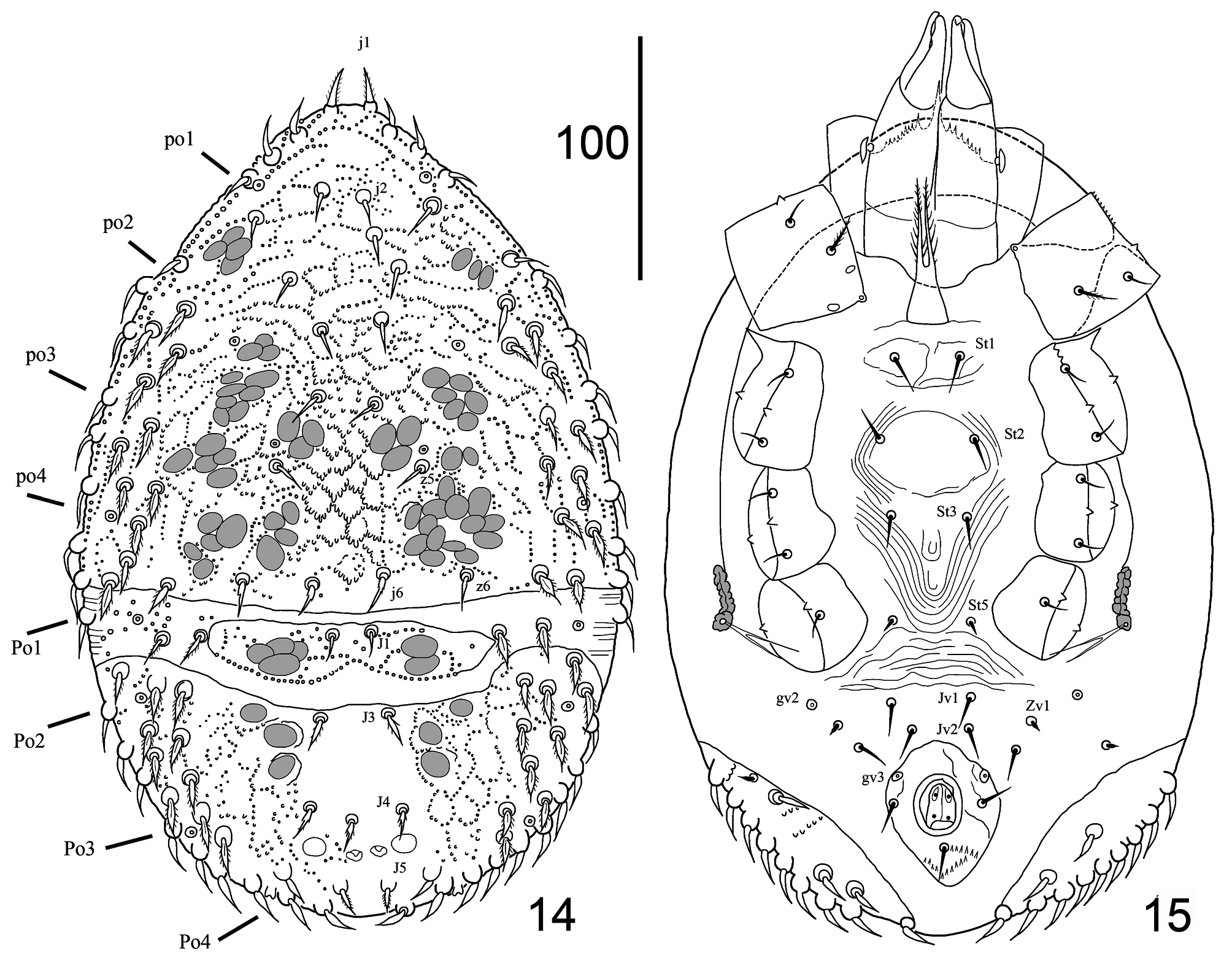
Dorsal idiosoma ( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 , 18, 19 View FIGURES 18–23 , 30–37 View FIGURES 30–41 ). Idiosoma suboval, 490–525 long and 315–350 wide ( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 , 18 View FIGURES 18–23 , 30– 31 View FIGURES 30–41 ). Anterior margin of the podonotum curved ventrally to form a vertex; two setae inserted on the ventral side of idiosoma: seta j1 (17–20) stout, slightly pilose and seta z1 smooth (8–12), pore-like structures ip1 absent. Podonotal shield strongly neotrichous ( Figs 30–36 View FIGURES 30–41 ), with about 69–72 setae on each side, including marginal r setae ( Fig. 37 View FIGURES 30–41 ). Podonotum ornamented with small tubercles and festoon reticulation over the entire surface of the shield ( Figs 32–34 View FIGURES 30–41 ). Setae in central region smooth, slightly lanceolate, 15–20 long ( Figs 32–34 View FIGURES 30–41 ); lateral setae leafshaped or lanceolate, pilose or smooth, 15–20 long ( Figs 19 View FIGURES 18–23 , 36 View FIGURES 30–41 ), the most posterior row of setae lanceoate and slightly pilose ( Fig. 35 View FIGURES 30–41 ). Four pairs of pore-like structures (glands) po1–po4 located in podonotum, glands po3 the smallest. Opisthonotum with 63–71 setae on each side, including marginal R setae. Median region neotrichous, with 17–22 setae of J series, arrangement asymmetrical, lanceolate, slightly serrated, 17–20 long ( Figs 30–31, 33 View FIGURES 30–41 ). Setae of Z, S series inserted closely in lateral regions, asymmetrical, neotrichous, lanceolate or leaf-shaped, smooth or serrated, 17–22 long ( Figs 18, 19 View FIGURES 18–23 ). Reticulation indistinct in median region between setae of J series and lateral setae, ornamented small tubercles in lateral regions. Four pairs of pore-like structures (glands) Po1–Po4 inserted in opisthonotum. All dorsal setae surrounded by enlarged basal rings. Marginal dorsal setae of r–R series neotrichous, inserted on high tubercles, elongated, 17–25 long, slightly curved and usually smooth ( Fig. 37 View FIGURES 30–41 ).
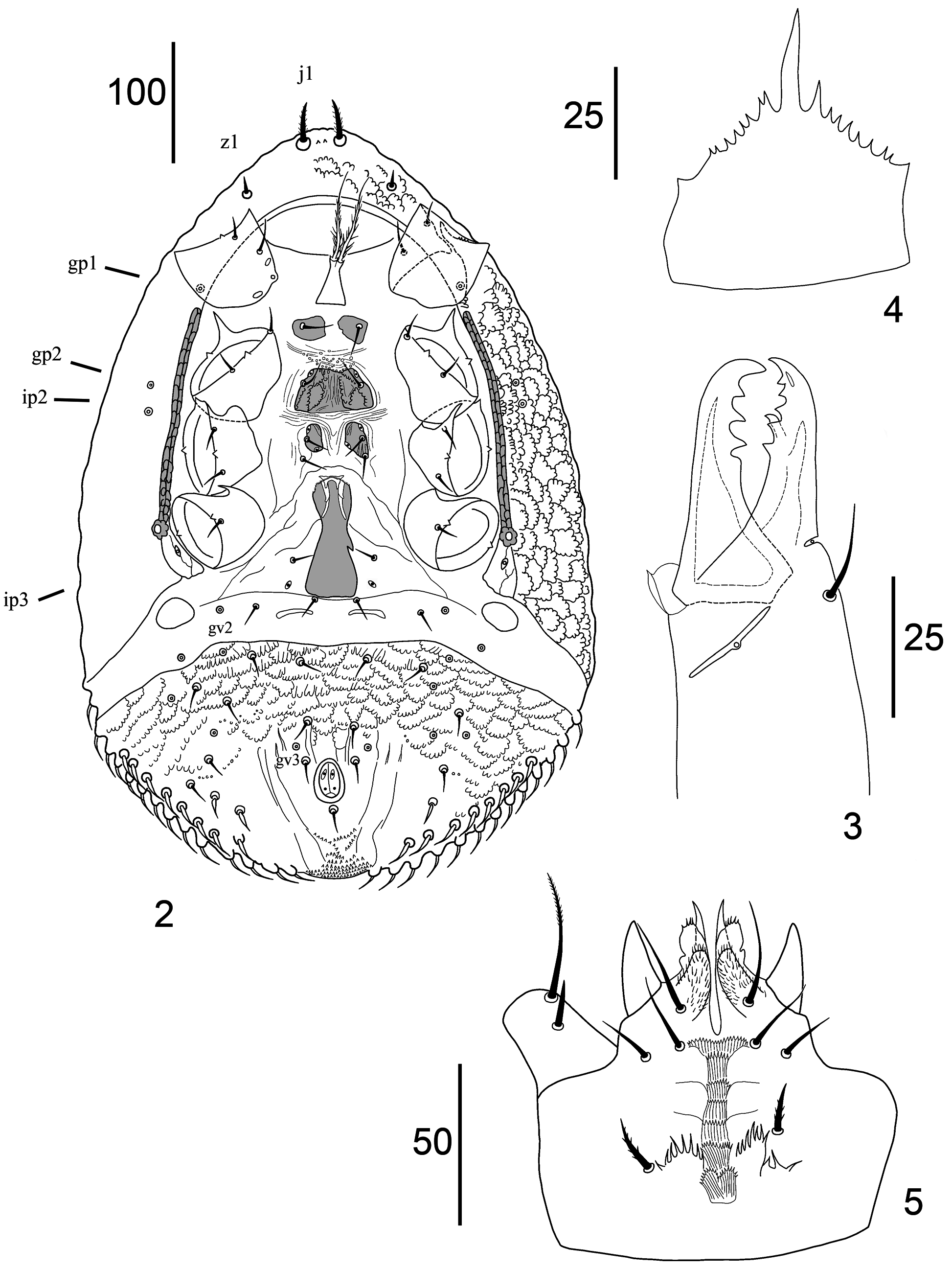
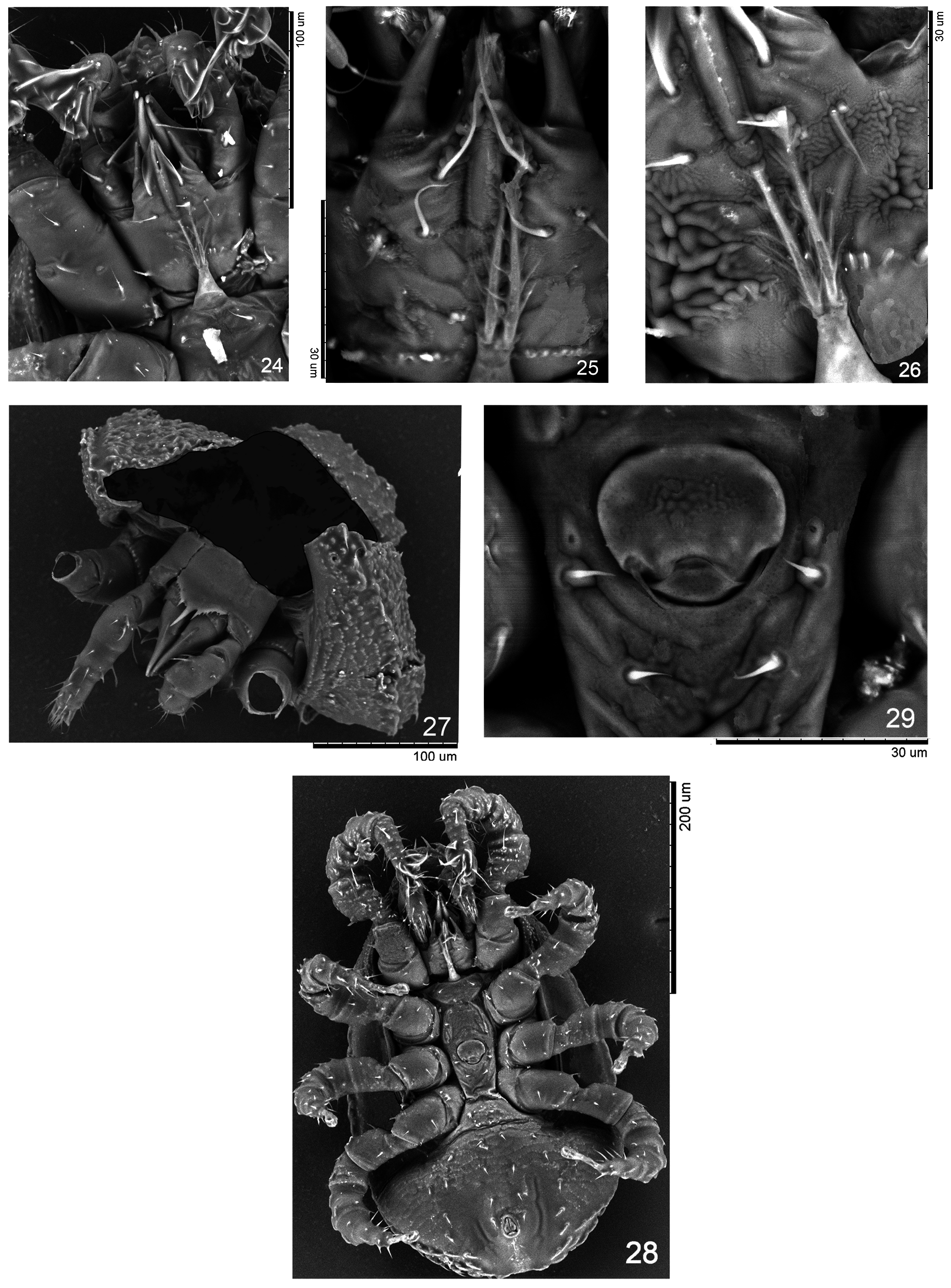
Ventral idiosoma. ( Figs 2 View FIGURES 2–5 , 20–23 View FIGURES 18–23 and 38–41 View FIGURES 30–41 ). Base of tritosternum 25–30 long and 18–20 wide, paired pilose laciniae free from each other along entire length, 47–55 long ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 2–5 ). Presternal (jugular) platelets irregular shape, weakly sclerotised, with pair of St1 (23–25) setae ( Figs 20–23 View FIGURES 18–23 ). First sternal platelet entire, 33–38 long and 50–63 wide; with pair of St2 setae (18–20) and pair of lyrifissures iv2 ( Figs 23 View FIGURES 18–23 , 40 View FIGURES 30–41 ). Second pair of sternal platelets suboval, with two pairs of setae St3, St4 (15–17) or in some specimens St4 seta from one side is inserted in soft cuticle; with two pairs of lyrifissures iv3, iv4 ( Figs 22, 23 View FIGURES 18–23 ). Genital shield elongated, 77–80 long, 35–42 wide, irregularly-shaped, with individual shape in each specimen; expanded anteriorly and posteriorly; anterior margin with fine folding; with genital setae St5 (13–15) and lyrifissures iv5 on soft cuticle laterad of shield ( Figs 38–41 View FIGURES 30–41 ). Subtriangular membrane ( Figs 20–22 View FIGURES 18–23 ) surrounds the genital shield. Genital shield with complex formation, including one median unpaired cap and two pairs of fine sclerites, a short anterior pair and elongate posterior pair. Endo- and exopodal shields absent. Metapodal shields large, suboval, located between posterior margins of periterematal and ventri-anal shields. Adgenital gland pores gv2 are multiple, dispersed over the surface: two gland openings located in soft cuticle posterolaterad of genital shield, another three to four openings located in ventri-anal shield. Soft cuticle between genital and ventri-anal shields with two pairs of setae Jv1, Zv1 and two slightly sclerotised plates. Peritrematal shields fused anteriorly forming a vertex and fused with dorsal shield laterally; strongly sclerotised, postero-lateral ends are drawn back in an oblique angle; ornamented with festoon reticulation along entire length. Four pairs of pore-like structures inserted in peritrematal shield: gp1, gp2 and ip2, ip3. Peritremes straight, 150–163 long, reaching level of spine top of coxae II anteriorly; with internal cell structure. Ventri-anal shield entire, broad, 130–173 long and 290–320 wide, fused to opisthonotal shield around the outer edge; with festoon reticulation, with 7–8 pairs of smooth opisthogastric setae inserted asymmetrically (10–12), and about 8–12 pairs of opisthonotal leaf-shaped smooth setae inserted posteriorly (18–20). The most posterior marginal row with elongated smooth setae (20–25) on raised tubercles duplicates opisthonotal rows of setae as in Fig. 37 View FIGURES 30–41 . Anal area with smooth para-anal and post-anal setae (12–15); anal opening 30–33 long; with two lyrifissure on each valve; cribrum located posteriorly of post-anal seta. Pair of glands gv3 located antero-laterad of para-anal setae.
Gnathosoma . ( Figs 3–5 View FIGURES 2–5 and 27 View FIGURES 24–29 ). Fixed digit of chelicera 42–45 long, with five teeth in addition to apical hook and leaf-shaped pilus dentilis ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 2–5 ); movable digit the same length with three teeth in additional to apical hook. Chelicera with long dorsal seta (20), lateral (antiaxial) and dorsal (paraxial) lyrifissures; with arthrodial corona. Epistome subtriangular, with irregularly serrated edges and smooth pointed median projection ( Figs 4 View FIGURES 2–5 , 27 View FIGURES 24–29 ). Corniculi 27–30 long and 15–17 wide. Internal malae slightly longer than corniculi, with complex three-layer structure as in Fig. 5 View FIGURES 2–5 . Deutosternal groove with 7–8 transverse denticulate rows, usually with three paired smooth lateral transverse lines. The posterior fourth pair of lateral transverse lines arch-shaped, with large denticles, located at the level of pc setae. Setae h1–h3 smooth: h1 (33–35) longest, seta h2 (11–13) shorter than h3 (15–19); pc (15–17) serrated. Dorsal side of gnathosoma with the pair of protruding wedge-shaped structures between palpal coxa and trochanter, lateral to epistome. Palpal chaetotaxy 2–5–6–12 –15, palp with five free segments; trochanter with seta al1 long and pilose in the distal third; with seta al2 short and smooth; palp genu with setae al1 and al2 pilose in distal third, palp apotele two-tined.
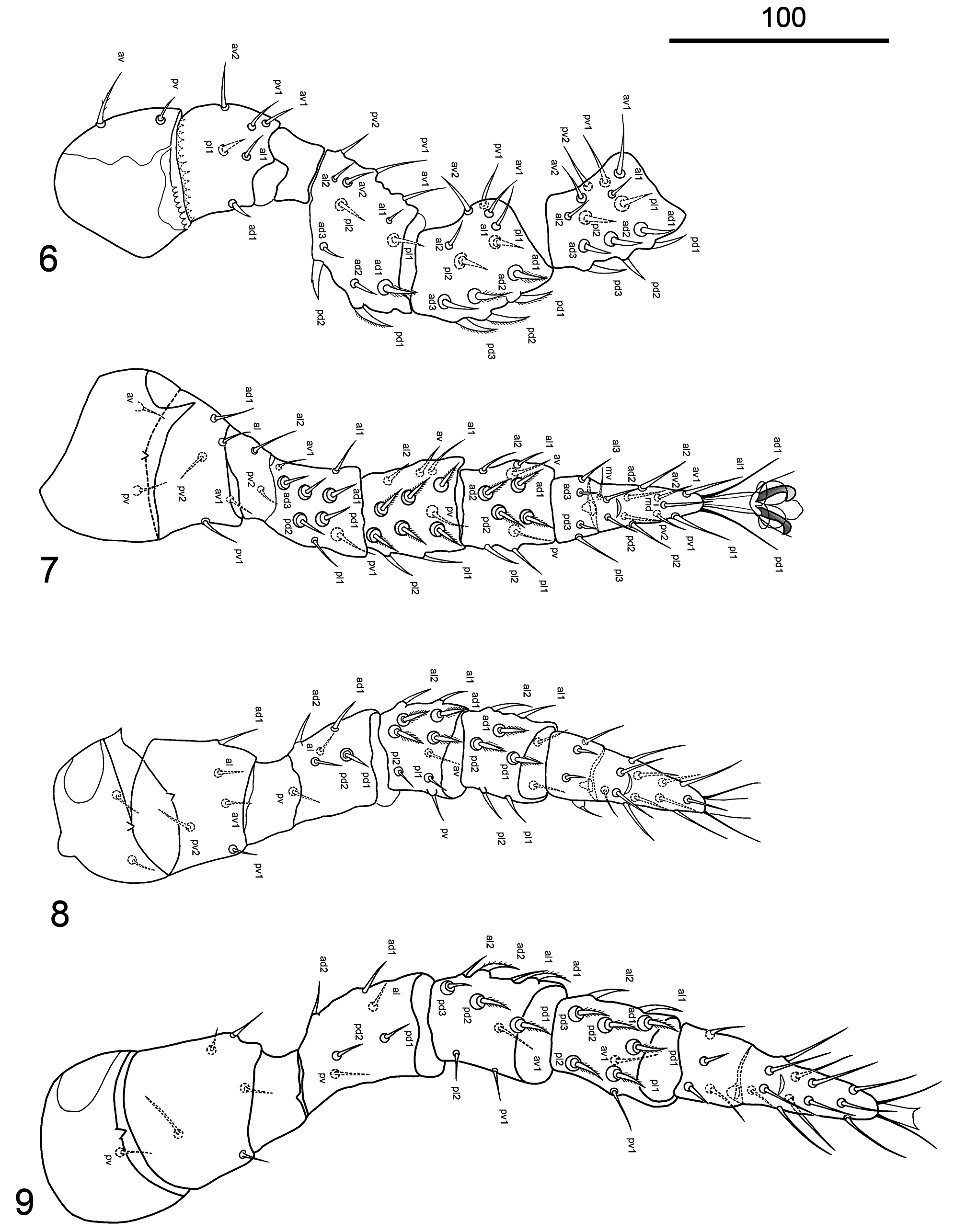
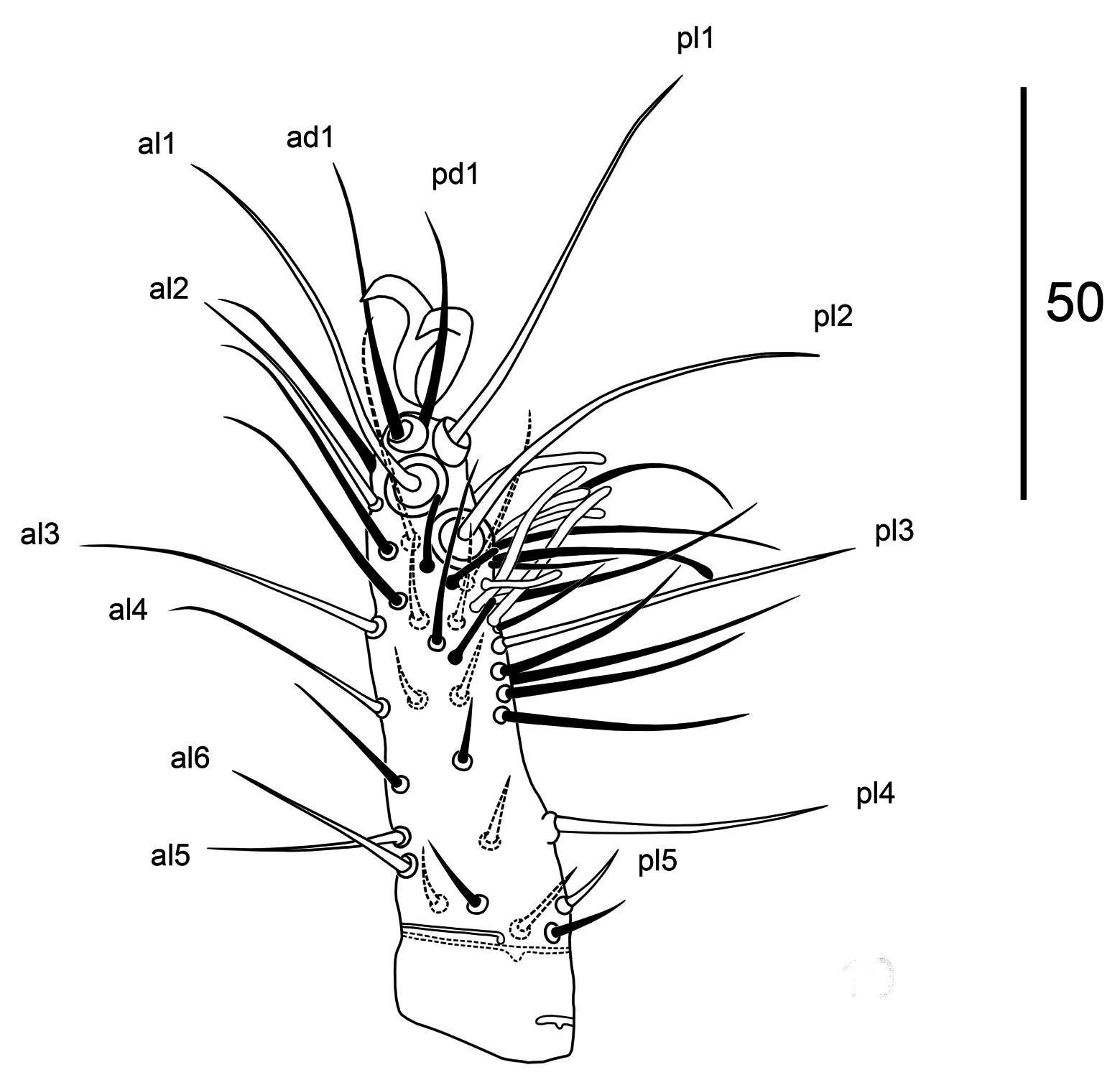
Legs. ( Figs 6–10 View FIGURES 6–9 View FIGURE 10 ). Lengths: I 337–350, II 270–280, III 265–275, IV 325–350 µm. Chaetotaxy of legs I–IV: coxae 2, 2, 2, 1; trochanters 6 (1 1/3 1), 5 (1 1/3 0), 5 (1 1/3 0), 5 (1 1/3 0), femora 13 (2 5/4 2), 11 (2 5/3 1), 6 (1 4/1 0), 6 (1 4/1 0); genua 13 (2 6/3 2), 12 (2 6/2 2), 10 (2 4/2 2), 10 (2 5/2 1); tibiae 14 (2 6/4 2), 10 (2 4/2 2), 9 (2 3/2 2), 10 (2 4/ 2 2); tarsi 49, 18 (3 7/5 3), 18 (3 7/5 3), 18 (3 7/5 3). Tarsi of leg I with 49 setae, including 6 antero-lateral, 5 posterolateral, 9 ventral and 29 dorsal setae ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 ). All legs with pair of sclerotised claws and pulvillus with five lobes. Pretarsus of legs II–IV with ambulacral stalk, legs I with sessile claws. Coxae I–IV are grouped closely together vertically; coxae I split on dorsal side ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 6–9 ), coxae III–IV with recesses on anterolateral side ( Figs 8, 9 View FIGURES 6–9 ). Coxae II– III with antero-dorsal spines: coxae II with large sharp spine, coxae III with small one ( Figs 7, 8 View FIGURES 6–9 ).
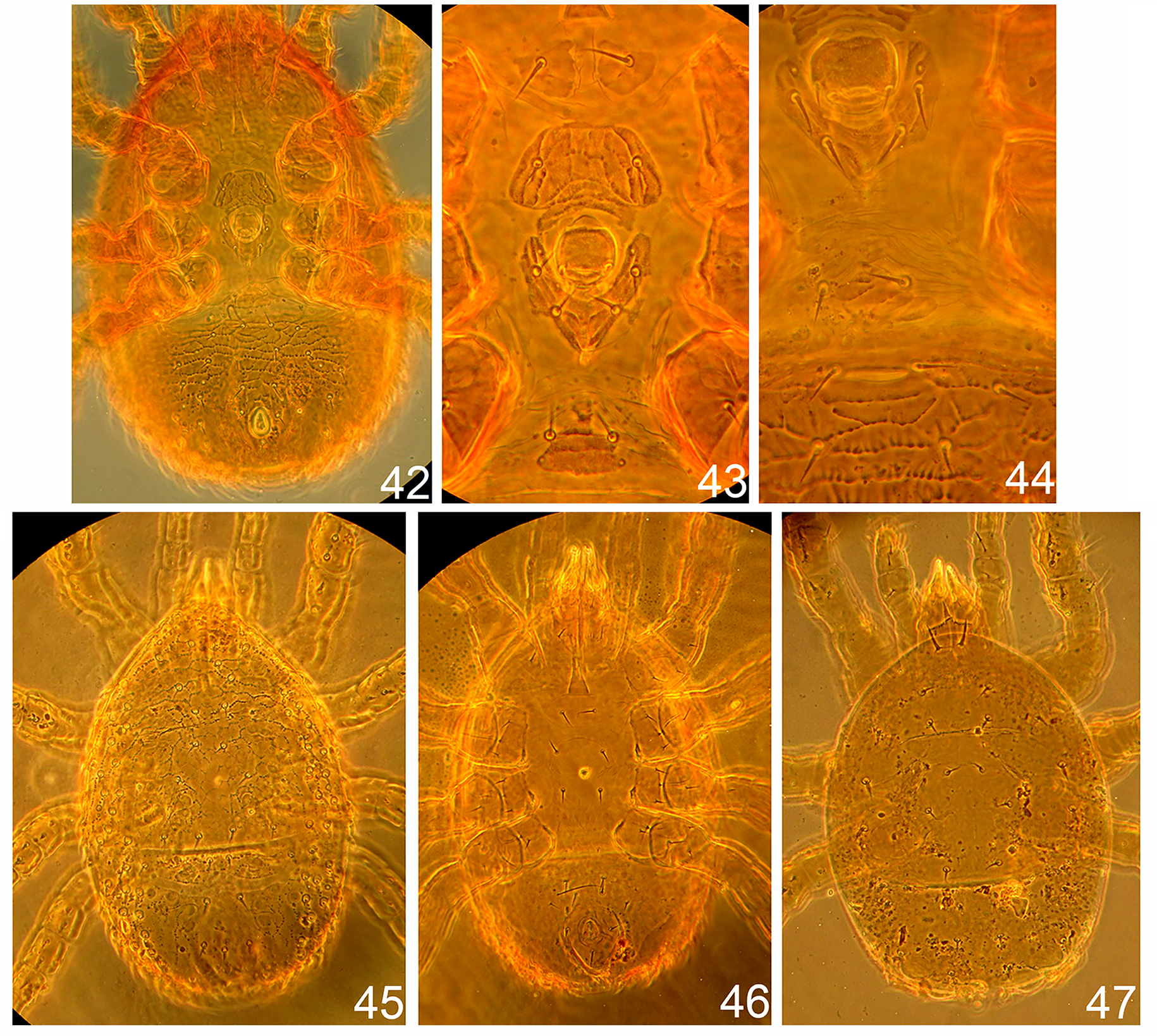
Male. ( Figs 11–12 View FIGURES 11–12 , 28–29 View FIGURES 24–29 and 42–44 View FIGURES 42–47 , n=10).
Dorsal idiosoma. Dorsal shield suboval shape, 435–460 long and 265–285 wide. Ornamentation and chaetotaxy similar to that of female.
Ventral idiosoma ( Figs 11 View FIGURES 11–12 , 28–29 View FIGURES 24–29 and 42–44 View FIGURES 42–47 ). Base of tritosternum 25–27 long and 15–17 wide, laciniae pilose, 37–45 long. Pair weakly sclerotised presternal (jugular) platelets with pair of St1 setae ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 11–12 ). First sternal platelet entire, with pair of St2 setae, with festoon ornamentation, 30–32 long and 52–62 wide. Second sternal platelet entire, subcordate shape, slightly ornamented by lines and folds; with two pairs of setae St3, St4 and two pairs of lyrifissures iv3, iv 4 in antero-lateral margins; 25–27 long on median line and 47–50 wide at level of St3 setae; surrounds the genital opening. Genital opening located at level of coxae III; with a pair of eugenital setae, covering by two platelets ( Figs 11 View FIGURES 11–12 , 28–29 View FIGURES 24–29 , 43–44 View FIGURES 42–47 ). Third sternal platelet entire, triangular, 15–30 long and 30–45 wide, with pair of St5 setae and pair of iv5 lyrifissures. Measurements of St1–St5 setae: 19–20, 18–19, 15–17, 15– 17, 11–13 µm respectively. Endo- and exopodal shields absent. Metapodal shields fused with ventri-anal shield and not distinct. Peritrematal shields similar to that female, with four pairs of pore-like structures: gp1, gp2, i2, ip3. Peritremes similar to those of female. Arch of vertex with two dorsal setae: pilose j1 (17–19) and smooth thornshaped z1 (10–12). Ventri-anal shield broad, 145–160 long and 255–265 wide, fused to opisthonotal shield around the outer edge; with festoon reticulation; 6–10 pairs of opisthogastric smooth setae inserted asymmetrically (12– 15) with 7–9 dorsal leaf-shaped smooth setae (12–15) inserted posteriorly. Adgenital gland pores gv2 are multiple, dispersed over the surface: one pair of glands located on soft cuticle posteriorly of coxae IV, other 3–4 openings located in ventri-anal shield. The most posterior marginal row with elongated smooth setae (17–20) on raised tubercles duplicates opisthonotal rows of setae as in female. Anal area with pre-anal and post-anal setae 10–12 long, anal opening 25–27 long; with two lyrifissure on each valve; cribrum present. Pair of glands gv3 located antero-laterad of para-anal setae.
Gnathosoma . Fixed digit of chelicera with five teeth in addition to apical hook and leaf-shaped pilus dentilis ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 11–12 ). Movable digit of chelicera the same length as fixed digit (38–40), tridentate in addition to apical hook, with arthrodial corona at base of digit. Chelicera with long dorsal seta, lateral (antiaxial) and dorsal (paraxial) lyrifissures. Male chelicera lacking spermatodactyl, without sexual dimorphism. Epistome, corniculi, internal malae, hypostomal and palpal structures as in female.
Legs. Lengths: I 300–330, II 250–275, III 250–275, IV 300–330 µm. Chaetotaxy and morphology of legs as in female. Leg II without sexual dimorphism ( Fig. 28 View FIGURES 24–29 ).
Deutonymph ( Fig. 13, n=10).
Dorsal idiosoma. Dorsal shield suboval shape, 415–430 long and 260–290 wide. Anterior margin of the podonotum curved ventrally to form a vertex, with setae j1 and z1. Podonotal and opisthonotal shields neotrichous as in adults.
Ventral idiosoma ( Fig. 13). Presternal (jugular) and first sternal platelets slightly distinct with pair of St1 and St2 setae accordingly; other setae St3–St5 of sternal region inserted in soft cuticle. Peritrematal shields narrow, fused with dorsal shield laterally, with festoon reticulation along entire length. Four pairs of pore-like structures present, three of them inserted in soft cuticle: gp1, gp2 and ip2; ip 3 in small platelet posterior to stigmata. Lyrifissures iv5 located laterad of St5 setae. Peritremes straight, 100–112 long, shorter than in adults, reaching level of middle of coxae II anteriorly; with internal cell structure. Three pairs of adgenital gland pores gv2 located on soft cuticle posteriorly to coxae IV. Opisthogastric area with 6–7 pairs of simple setae inserted in soft cuticle asymmetrically. Anal shield with folded ornamentation, 75–120 long and 70–75 wide, with pair of Jv3, para-anal and post-anal setae; with cribrum and pair of gv3 glands located antero-laterad to para-anal setae. Dorsal shield is curved on the ventral side posteriorly, does not connect with anal shield, with 6–7 pairs of smooth leaf-shaped setae inserted asymetrically.
Gnathosoma . As in adults.
Legs. Lengths: I 265–290, II 210–240, III 210–240, IV 250–290. Chaetotaxy of legs as in adults.
Protonymph ( Figs 14–15 View FIGURES 14–15 , 45–46 View FIGURES 42–47 , n=10).
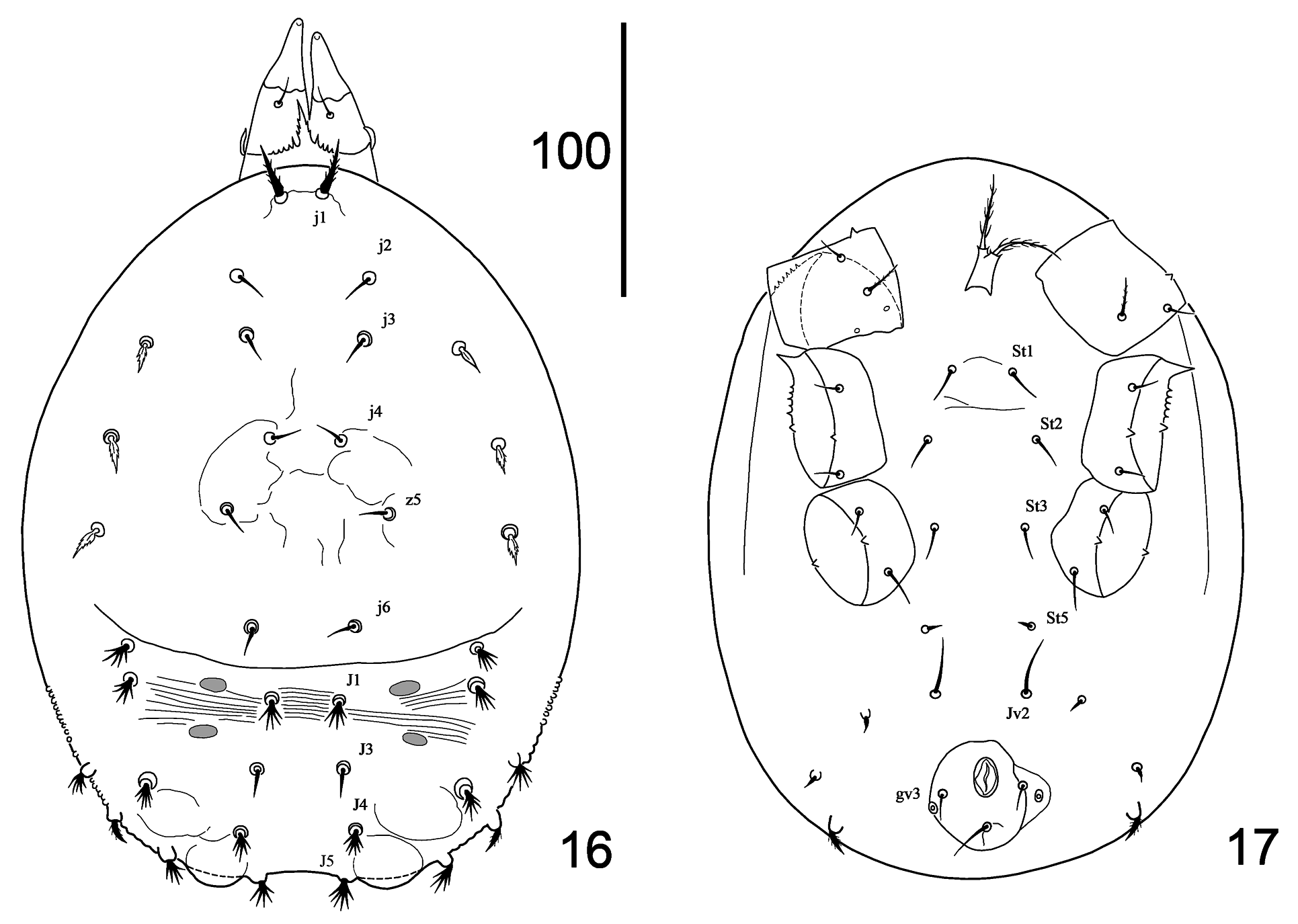
Dorsal idiosoma ( Figs 14, 15 View FIGURES 14–15 ). Dorsal idiosoma 335–345 long and 230–235 wide, with weakly sclerotised podonotal and opisthonotal shields. Anterior margin of podonotum curved ventrally to form a vertex, with setae j1. Podonotum with about 31–32 setae on each side (including marginal) and four pairs of pores. Row j with six setae j1–j6 and one additional asymmetrical seta in some specimens, z —row with recognisable z5 and z6 setae, homologies of other dorsal setae are obscure. Pygidial region with about 27–28 setae on each side and four pairs of pores; divided on two shields. Row J with four pairs of setae: J1, J3–J5. Other opisthonotal setae multiple.
Ventral idiosoma ( Figs 15 View FIGURES 14–15 , 46 View FIGURES 42–47 ). Presternal and sternal platelets not distinct. Setae St1–St3 and St5 inserted in soft cuticle; St5 minute seta, 4–5 long. Peritrematal shields and pore-like structuresof periteremaral regions not distinct. Peritremes short (23–25), with internal cell structure; with thin ducts leading from stigmata. One pair of adgenital gland pores gv2 located in soft cuticle posteriorly to coxae IV. Opisthogastric area with 4–5 pairs of simple setae inserted in soft cuticle: Zv1 as long as St5 setae. Anal shield with folded ornamentation and cribrum, 57–63 long and 50–57 wide, with para-anal and post-anal setae; pair of glands gv3 located laterad to para-anal setae. Dorsal shield is curved on the ventral side, does not connect with anal shield; with 2–4 pairs of asymmetrical setae, with posterior row of smooth marginal setae.
Gnathosoma . As in adults.
Legs. Lengths: I 265–280, II 200–210, III 210–215, IV 235–250.Chaetotaxy of legs I–IV: coxae 2, 2, 2, 1; trochanters 4, 4,4, 4; femora 10, 8, 5, 4; genua 8, 6, 6, 5; tibiae 8, 6, 7, 7; tarsi II–IV: 17, 17, 17. Structures of pretarsus and coxae I–IV as in adults and deutonymph, coxae III without distinct spine.
Larva ( Figs 16–17 View FIGURES 16–17 , 47 View FIGURES 42–47 , n=1).
Dorsal idiosoma ( Figs 16 View FIGURES 16–17 , 47 View FIGURES 42–47 ). Dorsal idiosoma 270 long and 260 wide with podonotal, pygidial shields and two pairs of mesonotal sclerites in pygidium region. Posterior surface of pygidium with two pairs of bubbles. Podonotal shield with nine pairs of setae, including five pairs of j row setae; setae j1 the longest (20) located on anterior margin of shield; stout, pilose, inserted on tubercles. Pygidium with ten pairs of setae: simple and brushform. J -row with three pairs of setae.
Ventral idiosoma ( Fig. 17 View FIGURES 16–17 ). Tritosternum as in adults. Sternal setae St1–St3 inserted in soft cuticle. Periremes and stigmas are absent. Pore-like structures not visible. Opisthogastric area with five pairs of setae inserted in soft cuticle, of which seta Jv2 the longest; most posterior pair of setae pilose. Anal shield 50 long and 40 wide with pair of para-anal and post-anal setae, simple form.
Gnathosoma . Gnathosoma in forward position not curved in ventral side of idiosoma.
Legs. Lengths: I 237, II 188, III 200 µm. Structures of pretarsus and coxae of leg I–III as in protonymphs. Material examined. Holotype female, Russia, Altaiskii krai, North-Western Altai Mountains, Tigeretskii Range, Tigerekskii Nature Reserve, 1300 m a.s.l., 51 ̊04ʹ N, 83 ̊02ʹ E, Betula tortuosa forest, in litter, 18 June 2017, leg. I.I. Marchenko. Paratypes: 29 females, 19 males, 5 deutonymphs, 6 protonymphs, 1 larva, same data as holotype. Other material: 42 females, 15 males, 4 deutonymphs, geographical and locality data as paratypes, 7 August 2013, leg. I.I. Marchenko; 68 females, 53 males, 9 deutonymphs, same geographical region, Picea obovata - Abies sibirica - Pinus sibirica forest, 1000 m a.s.l., in litter, 7 August 2013, leg. I.I. Marchenko; 12 females, 7 males, 11 protonymphs, 5 larvae, same geographical region, 1700 m a.s.l., highland woodland with Pinus sibirica - Picea obovata - Juniperus sabina , 5 June 2017, leg. T.M. Krugova.
Etymology. The species is named after Tigerek village and Tigeretskii Range in the Altai Mountains, where this species inhabits.
Remarks. Adults of H. tigerek most similar to H. barguzin Marchenko, 2018 , but differ from those having podonotal shield ornamented with small tubercles and festoon reticulation over the entire surface; median region of opisthonotal shield neotrichous, with 17–22 setae of J series. Female of H. tigerek with first sternal shield entire in all specimens, ornamented by folds, with pair of iv2 lyrifissures; soft cuticle between genital and ventri-anal shields with two slightly sclerotised plates. Adults of H. barguzin have podonotal shield ornamented only in anterior and lateral regions; median region of opisthonotum usually with 12–13 setae of J series. Female of H barguzin with first sternal shield entire or divided into two, ornamented by folds and lines of tubercles, without lyrifissures; soft cuticle between genital and ventri-anal shields without sclerites. In adult and deutonymph of H. barguzin , the peritremes are of equal length, while deutonymph of H. tigerek have peritremes shorter than adults. Deutonymph periteremes of H. tigerek reaching the level of middle of coxae II anteriorly; versus H. barguzin with periteremes reaching level of spine top of coxae II anteriorly.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.