Leptanillinae Emery, 1910
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2015.120 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:54714320-5726-44CB-8FF5-60E0B984873D |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3795073 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038E878C-FFB4-B145-FDEA-FBBCFB3019EB |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Leptanillinae Emery, 1910 |
| status |
|
Subfamily Leptanillinae Emery, 1910 View in CoL
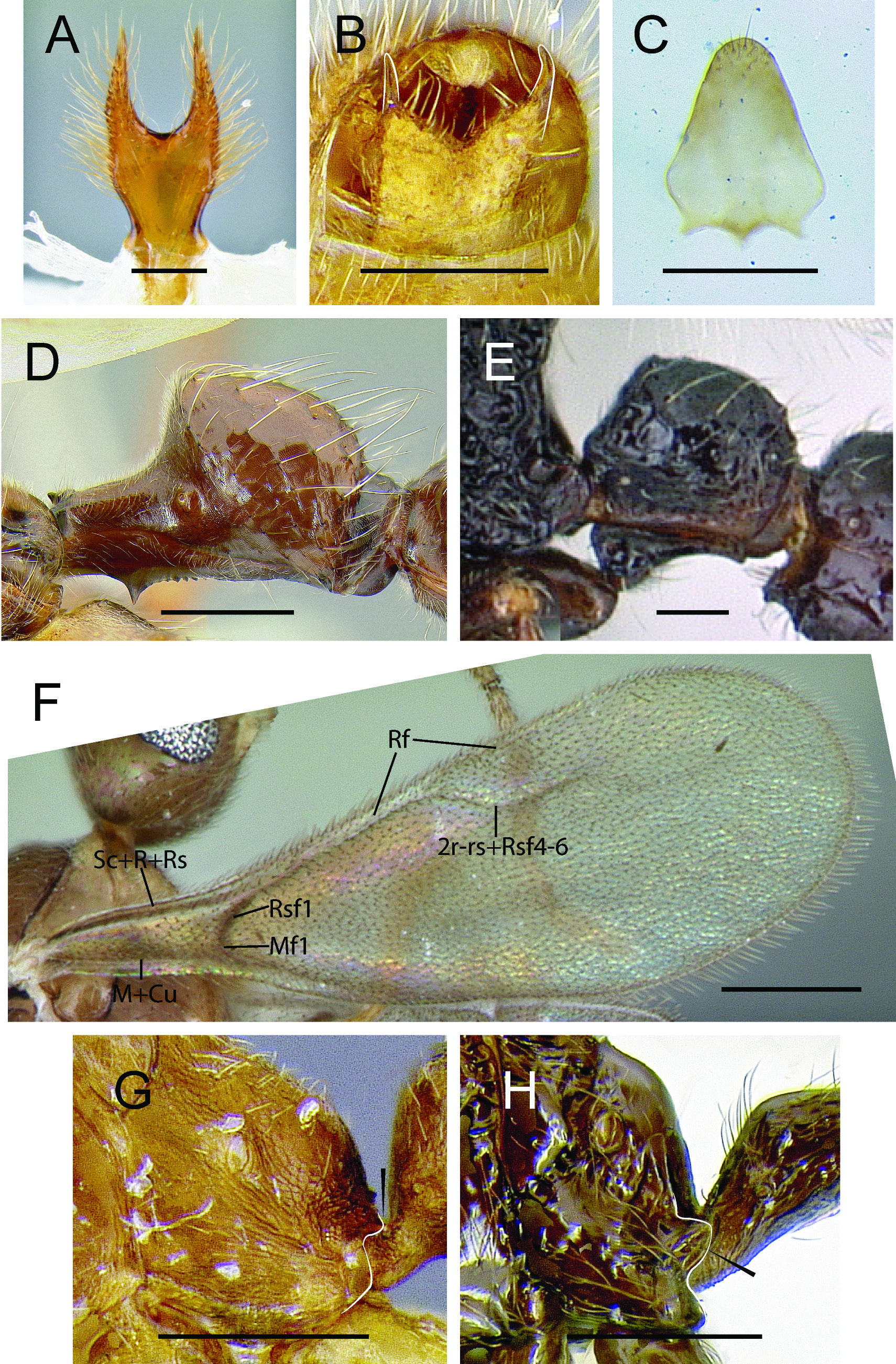
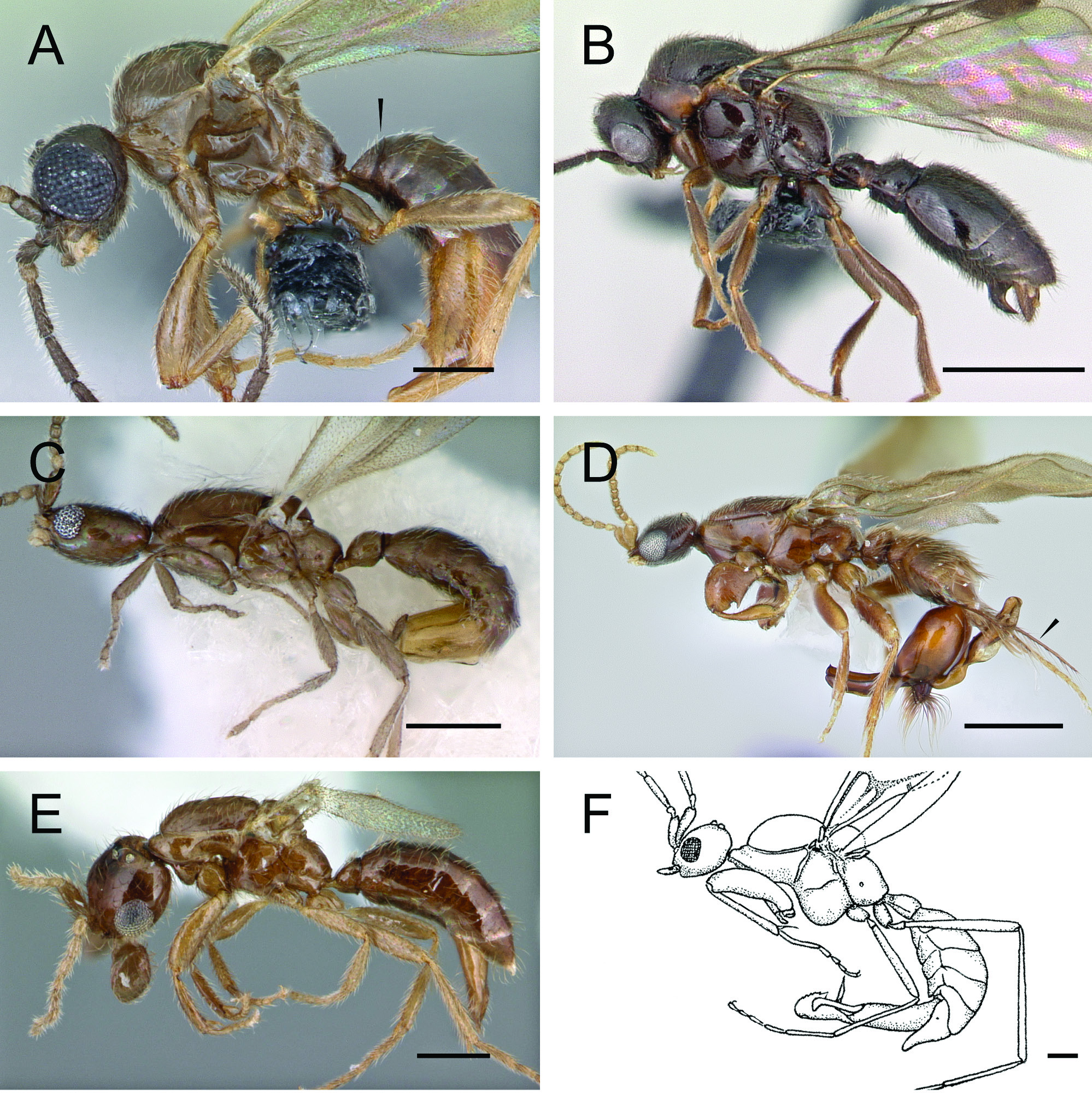
Figs 4F View Fig , 6F View Fig , 10 View Fig
Leptanillini Emery, 1910: 32 View in CoL . Type-genus: Leptanilla View in CoL .
Note
All diagnoses in the references below pertain to the tribe Leptanillini ; males of Anomalomyrmini undescribed.
Male references for subfamily
Wheeler 1910: 138 (diagnosis [ Leptanilla ]); Wheeler & Wheeler 1930: 193 (diagnosis [ Leptanilla , Phaulomyrma ]); Morley 1939: 114 (morphology comments); Kutter 1948: 293 (diagnosis); Bernard 1967: 90 (diagnosis [ Leptanilla ]); Petersen 1968: 577 (generic diagnoses, discussion); Gotwald 1969: 97 (mouthparts morphology); Wheeler & Wheeler 1972: 37 (diagnosis); Baroni Urbani 1977: 430 (diagnosis, generic diagnoses); Bolton 1990b: 269 (diagnosis); Baroni Urbani et al. 1992: 316 (morphology); Ogata et al. 1995: 32 (diagnosis, genitalia); Bolton 2003: 39, 151 (diagnosis); Borowiec et al. 2011: 11 (venation comments [ Anomalomyrmini ]).
Male diagnosis
Male Leptanillinae are recognizable by the combination of nub-like mandibles, extremely reduced wing venation (three cells enclosed by tubular abscissae at most development: costal, basal, and subbasal cells; no cells enclosed by tubular abscissae at least development), and absence or inconspicuousness of propodeal lobes. Otherwise, male leptanillines are highly variable, often resembling “normal” poneroids, although some males are so derived as to be difficult to intuitively ascribe to the Formicidae ; this modification includes even loss of abdominal segment II petiolation.
1. Mandibles strongly reduced, nub-like not meeting at head midline, or spatulate and hypertrophied
( Scyphodon ) (note 1).
2. Palpal formula 4,1 or 1,1 (note 2).
3. Clypeus usually strongly reduced such that antennal toruli situated anteriorly, separated from anterior clypeal margin by much less than one torulus diameter; occasionally ( Yavnella , Protanilla , Noonilla ) antennal toruli situated about one torulus diameter from anterior clypeal margin (note 3).
4. Anterior clypeal margin without pegs.
5. Anterior tentorial pits usually situated lateral to lateral torular arch; occasionally ( Yavnella ) situated anterolaterad torular arch.
6. Frontal carinae and lobes absent.
7. Antenna 13-merous; funiculus filiform to submoniliform.
8. Occipital carina absent.
9. Oblique mesopleural sulcus present, anterior terminus contacting posterolateral pronotal corner or situated well ventral to pronotal corner.
10. Metapleural spiracular plate absent.
11. Propodeal lobes absent or very inconspicuous.
12. Metacoxal cavities closed.
13. Tibial spur formula 2s,2s; 1s,2(1s,1p); 1s,2s; 1s,1s; 0,1p.
14. Metatarsus lacking posterolateral line of dense differentiated setae.
15. Pretarsal claws edentate.
16. Pterostigma usually strongly reduced, but may be enlarged ( Anomalomyrma , some Protanilla ) (note 4).
17. Ogata wing venation type IVb ( Fig. 4F View Fig ), but would be type IIIb should the maximum complement of spectral veins be hypothetically tubular; at most 3 closed cells present (costal, basal, subbasal); at the most extreme reduction only Sc+R+Rs and Rf present along anterior wing margin, with narrow stretch of membrane present anterobasally (notes 5, 6).
18. Hindwing venation reduced: all abscissae absent, or R+Rs tubular and short, or R+Rs and 1A tubular and short.
19. Jugal lobe absent.
20. Petiolar laterotergite absent; tergum fused with sternum, suture visible.
21. Petiolar tergum not forming anteroventral collar around sternum.
22. Helcium axial or infraaxial.
23. Helcial sternite overlapped laterally by tergite, thus not visible in lateral view.
24. Abdominal segment III undifferentiated to somewhat constricted posteriorly to strongly differentiated with posterior constriction, forming postpetiole.
25. Abdominal segment IV as long as or infrequently distinctly longer than following abdominal segments; not vaulted.
26. Abdominal spiracles IV–VIII obscured by preceding tergites.
27. Pygostyles absent or present as extremely elongate rods.
28. Genitalia partially exserted; subject to extreme modification.
29. Basimere separated from telomere ventrally by corium or basimere and telomere fused.
30. Telomere highly variable; least modified telomeres are digitate to wedge-shaped; sometimes telomere laminar.
31. Basivolsella lateromedially narrow in ventral view, occasionally extremely elongated.
32. Cuspis present or absent; when present usually lobate and otherwise unmodified.
33. Digitus highly variable; least modified digiti are elongate and arched.
34. Valviceps highly variable; almost always with lateral apodeme produced laterally (note 7).
Notes on diagnosis
1. Mandibles also reduced and nub-like in Ponerini (Ponerinae) , Apomyrma (Amblyoponinae) , and some Myrmicinae (e.g., Acanthognathus , Daceton , the Adelomyrmex genus group, Myrmecina ).
2. Some unidentified Protanilla males have higher palp counts, similar to workers. Future work should
establish the extent of palpomere count variation inter- and intragenerically.
3. Anteroposteriorly broad clypeus is pleisiomorphic for Leptanillinae , and is present in Protanilla and Yavnella .
4. The polarity of pterostigmal reduction is unclear, as Anomalomyrma and some Protanilla have an enlarged pterostigma; it seems likely though that this is a secondary development.
5. Wing venation also reduced to the Ogata type IVb pattern convergently in other groups, including some Myrmicinae ( Strumigenys , the Adelomyrmex genus group, and the inquiline Pheidole acutidens ) and some Proceratiinae (Probolomyrmex) . These taxa may be distinguished from leptanillines by a suite of characters, including presence of the propodeal lobe. Contrary to the sentiment of Ogata et al. (1995) the reduced wing venation of the Leptanillinae is eminently valuable for diagnosis of the subfamily. While certainly this reduction in venation may be driven by functional constraints, the particular pattern occurring in the Leptanillinae is nearly globally unique. Although it has been indicated that the forewing venation of Leptanilla is completely absent ( Wheeler 1910; Bernard 1968; Wheeler & Wheeler 1972), no specimens were observed which had this state; at the least one compound abscissa was present along the leading wing margin.
6. Detailed forewing abscissal development description: Costal vein present or absent, when absent Sc+R+Rs very close to anterior wing margin (costal cell closed or open). Rsf1+Mf1 tubular or nebulous, indistinguishable from one another, or both abscissae absent (basal cell distally closed or open). Rs+M usually absent, infrequently spectral; Rsf2+3 absent (submarginal cell 1 open). Rsf4+ tubular, continuous with 2r-rs which is directed posteroapically, ending before wing apex, or Rsf4+ and 2r-rs absent (marginal cell 1 open). Mf2+ absent or spectral and 2rs-m absent (submarginal cell 2 absent). 1m-cu absent (discal cell 1 open). M+Cu nebulous or absent (basal cell closed posteriorly or open). Cuf tubular to nebulous, short, or absent (subdiscal cell 1 absent). 1A tubular, partially nebulous, or absent (subbasal cell closed or open).
7. One morphogroup of South East Asian male Leptanillinae has lateromedially compressed valviceps, other morphogroups and genera have the lateral apodeme consistently laterally produced, and often modified.
Taxa examined (♀ = queen, ♂ = male)
Anomalomyrma indet. [♀: Indonesia]; Leptanilla africana Baroni Urbani [♂: Nigeria]; L. bifurcata Kugler [♂: Israel]; L. islamica Baroni Urbani [♂: Yemen]; L. israelis Kugler [♂: Israel]; L. miniscula Santschi [♂: Tunisia]; L. swani Wheeler [♂: Australia: Queensland, W. Australia]; L. tanit Santschi [♂: Tunisia]; L. tenuis Santschi [♂: Tunisia]; L. GR01 [♂: Greece]; L. GR02 [♂: Greece]; L. GR03 [♂: Greece]; L. IL01 [♂: Israel]; L. TH01 [♂: Thailand]; L. TH02 [♂: Thailand]; L. TH03 [♂: Thailand]; L. TH04 [♂: Thailand]; L. TH05 [♂: Thailand]; L. TH06 [♂: Thailand]; L. TH08 [♂: Thailand]; L. TH10 [♂: Thailand]; L. ZA01 [♂: South Africa]; L. indet. [♂: Australia]; Noonilla BMNH01 [♂: Ivory Coast]; Noonilla indet. [♂: Malaysia]; Phaulomyrma MM01 [♂: Myanmar]; Ph. TH01 [♂: Thailand]; Ph. indet. [♂: Myanmar]; Protanilla TH01 [♂: Thailand]; Pr. TH02 [♂: Thailand]; Pr. TH03 [♂: Thailand]; Pr. indet. [♂: Indonesia]; Scyphodon cf. bruesi [♂: Indonesia]; Yavnella argamani Kugler [♂: Israel]; Y. indica Kugler [♂: India]; Yavnella BEB001 [♂: Sri Lanka]; Leptanillinae ? Protanilla [♂: Indonesia, Malaysia]; Leptanillinae indet. [♂: Borneo, Democratic Republic of Congo, Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, Thailand].
Distribution
Old World: Palearctic (Europe, Southern Asia, and Northern Africa), Afrotropical, Australasian, and Australian regions.
Discussion
The Leptanillinae , based on males, is defined by the apomorphies presented in the diagnosis above (in italics). At present the subfamily is comprised of eight genera with the re-inclusion of the male-
based taxa Noonilla Petersen, 1968 (stat. rev.) and Scyphodon Brues, 1925 (stat. rev.). Both N. copiosa Petersen, 1968 and S. anomalum Brues, 1925 are transferred to the Leptanillinae .
The Leptanillinae was first delimited as a tribe of Dorylinae by Emery (1910), but has consistently been considered a distinct subfamily since Wheeler (1923), except for Bernard’s (1951) treatment of the “ Formicoidea ”, in which the leptanillines were treated as a family. Opamyrma was described by Yamane et al. (2008) who assigned the genus to the Amblyoponinae using the concept of Saux et al. (2004) for
the subfamily, although they concomitantly referred to the genus as belonging to the Apomyrminae . Discovery of the male of Opamyrma and the larvae and gynes of Opamyrma and Martialis are anticipated to contribute to the resolution of the “basal ant problem”.
As noted by prior authors (e.g., Baroni Urbani 1977; Bolton 1990b; Ogata et al. 1995), the Leptanillinae is unfortunately subject to parallel taxonomies, with two genera known only from workers ( Anomalomyrma , Furcotanilla ), four genera known only from males ( Noonilla , Phaulomyrma , Scyphodon , Yavnella ), and two genera known from both castes ( Leptanilla , Protanilla ). The Leptanillinae is in need of generic revision, especially given the highly variable morphologies of the males. As this is beyond the scope of the present paper, the male of Protanilla , although recently identified by the Ant Tree of Life Team (P.S. Ward et al., unpubl. data; AntWeb 2014), is not described. Moreover, there is a spectacular and perplexing diversity of leptanilline males from Southeast Asia, which await classification and association with workers ( Fig. 10 View Fig ).
Except for the mandibles of Scyphodon and the sexual characteristics of Noonilla , these two are “typical” leptanillines (compare specimens in Fig. 10 View Fig ). They exhibit proposed formicid synapomorphies: the prodisticoxal cavity is closed, the propodeal spiracle is situated low on the propodeum, and the metasoma is petiolate. Placement of these genera in the Leptanillinae is supported by the presence of the following apomorphies: mandibles nub-like to spatulate (secondarily hypertrophied in Scyphodon ); buccal cavity reduced; medial hypostoma vestigial; clypeus strongly reduced; and Ogata venation type IVb. The following characteristics support the placement: palpal formula 1,1; meso-segment of mesosoma elongated anteriorly; and abdominal tergum VIII enlarged (not present in all material attributed to Scyphodon ). Of the formicid pleisiomorphies present in these genera, the most diagnostically valuable is absence of propodeal lobes.
Ogata et al. (1995) indicated several characters which were dubiously diagnostic for the Leptanillinae , specifically including: reduced palp formula; elongated pronotum; fore femora shape; reduced venation; metapleural gland absence; terminal abdominal segment reduction; cupula (= basal ring) absence; and cuspis absent. It is agreed that palpal formula may be reduced in other Formicidae , but reduction to 1,1 occurs in the Dorylinae (Aenictogiton) , the Myrmicinae (e.g., Eurhopalothrix , Pheidole and Tetramorium -clade inquilines, Strumigenys , Rhopalomastix ), and the Ponerinae (e.g., Hypoponera and Simopelta ). It is evident that Scyphodon and Noonilla are not closely related to the genera indicated above. The elongate mesoscutum with concomitant posterior elongation of the pronotum is not present in all Leptanillinae and also occurs in Apomyrma (Amblyoponinae) , but is otherwise unique among the Formicidae . The fore femoral modifications of Noonilla are autapomorphic, and are certainly sexual characters.As discussed in note 5 of the Leptanillinae diagnosis, the reduced venation of the Leptanillinae is highly diagnostic of the group. Certainly, of any of the dubious characters Ogata et al. indicated, the metapleural gland absence is the least valuable and in no way supports contentions about relationships in male ants. It is difficult to assess development of the cupula without dissecting the few specimens of Noonilla and Scyphodon available, so evaluation of these characters is set aside for future studies. Cuspides are present at least in some Protanilla males, and thus are not diagnostic for the Leptanillinae on the whole, but absence may be apomorphic for the remainder of the subfamily.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.