Rhynchocalamus barani, Olgun, Kurtuluş, Avci, Aziz, Ilgaz, Çetin, Üzüm, Nazan & Yilmaz, Can, 2007
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.175393 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5627404 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038E87E9-FFB1-C741-9BE3-39DEFAB11CC9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Rhynchocalamus barani |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Rhynchocalamus barani n. sp.
Holotype: ZDEU 122/2006: 1, Ψ, collected at Amanos Mountain (36°50’N, 36°25’E; altitude 1310 m a.s.l.), 34 km E of Dörtyol, Hatay Province, Turkey, 0 1.05.2006, leg. A. Avcı, C. Yılmaz.
Paratype: ZDEU 122/2006: 2, ɗ, same data as for holotype.
Material used for comparison:
R. m. melanocephalus : ZDEU 123/2006. 1–2ɗ, Sofular Village, Harbiye, Hatay, 29.04.2006, leg. A. Avcı, C. Yılmaz; ZDEU 124/2006. 1 Ψ, Kuruyer Village, Hatay, 30.04.2006, leg. A. Avcı, C. Yılmaz.
R. m. satunini: ZDEU 125/2006. 1ɗ, Nurdaġı, Gaziantep, 0 3.05.2006, leg. A. Avcı, C. Yılmaz.
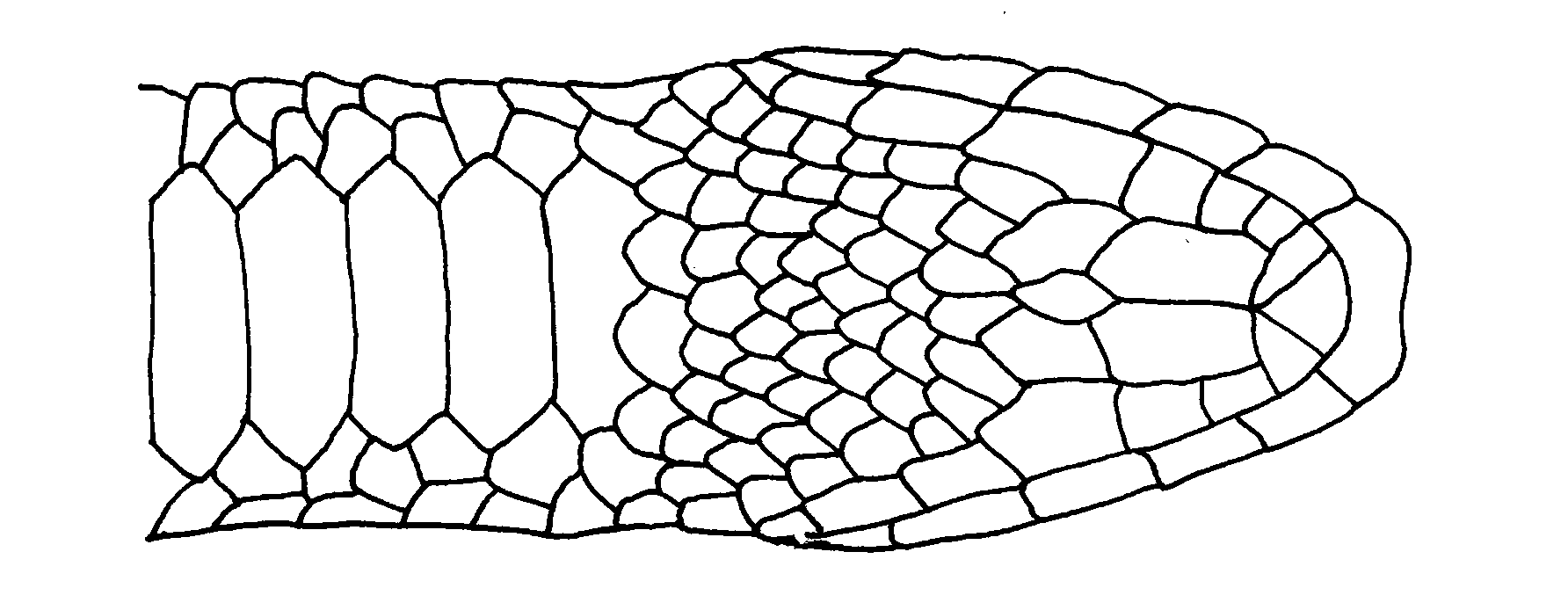
Description of holotype ( Figures 1–5 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 ). Eight maxillary teeth, the posterior teeth long and welldeveloped, broad at the base with an impression; palatine teeth absent; mandibular teeth slightly longer anteriorly than posteriorly. Head small, not distinct from the neck, with oblique shape at anterior side. Head scales between rostral and posterior margin of parietal area not keeled. Temporals not keeled. Rostrum with height of 2.06 mm and width of 2.66 mm, bordered by two upper labials, two nasals and two internasals. Rostrum curved towards top of the head and intruding between the internasals. Internasals of trapezoid shape, with a suture length approximately equal to length of the prefrontal suture. Nostrils situated on one nasal at either side. Distance between nostrils 3.16 mm. Loreal at either side in contact with 1st and 2nd upper labials. One preocular and two postoculars on each side. Eyes small with circular pupil of 1.78 mm diameter. Length of narrow frontal 3.10 mm; width 2.60 mm. Five upper labials, 3rd in contact with eyes. Seven lower labials on left side and eight on right side. Three and four pairs of lower labials in contact with anterior chin shields at the left and right side, respectively. Parietal length shorter than the distance from posterior tip of the rostral to the posterior tip of frontal (3.54 mm versus 4.64 mm). One temporal and two posttemporals on each side. The number of dorsal plus temporal scales surrounding the posterior margin of the parietals 13. Seventeen dorsal scale rows at midbody, 17 on neck one headlength behind head, 17 dorsal scale rows on one headlength anterior to anal and two anal plates. One gular scale in contact with anterior inframaxillar. One hundred and seventy three ventrals and 65/65+1 subcaudals. Pileus length 9.00 mm, pileus width 4.48 mm and head height 4.04 mm. Snoutvent length 312.98 mm and tail length 89.60 mm.
Basic color of the head (from tip of the rostral to posterior margin of the parietals) ashgray. This basic color extends to the first upper labial plate at the flanks of the head. A narrow black blotch present from the lower part of eyes up to the contact of the 3rd and 4th upper labials. The 2nd, 3/4 part of 3rd, 4/5 part of 4th and 2/ 3 part of 5th upper labials of white color. Other lower labials also white except last lower labial that is black. Narrow black neck band present at the upper part of the head, from margin of the parietals to top of the posterior margin of the temporals, in the gular region of the head in contact with dorsals over a width of six scales. No contact with ventrals at the lower part of the head. Length of head patterns (from tip of rostrum), proportional to snoutvent length 4.1 mm. Temporals white (ca. 75%) or otherwise black. The basic color of the dorsum reddish brown without spots. Lower part of the head and ventral separated by black head band, otherwise white without spots. Lower part of the tail white including tail tip.
Description of paratype ( Figure 6 View FIGURE 6 ). Dentition features of the paratype similar to that of holotype (in having eight maxillary teeth; comparatively strong subequal in size; posterior broad at the base, with an impression, but without longitudinal groove; palatine teeth absent and the mandibular teeth slightly longer anteriorly than posteriorly). Paratype similar to holotype in most morphological characters, except for loreal plate absent. Colorpattern very similar to that of holotype. Counts of gular scales in a row between posterior inframaxillars higher and counts of ventrals and dorsal plus temporal scales surrounding the posterior margin of the parietals lower than in holotype (see Table 1 View TABLE 1 ).
Differential diagnosis: Rhynchocalamus barani n. sp. differs from congeneric species ( R. melanocephalus melanocephalus , R. m. satunini and R. arabicus ) in having higher number of dorsals (17 instead of 15) and lower number of ventrals (163–173 instead of 180–240) and upper labials in contact with eye (1 instead of 2) and by an oblique shape of the head at the anterior side. It also differs by a characteristic colorpattern of the body and the basic color of the head, by the presence of a black blotch under the eye running into a narrow stripe, all as described above. In contrast to other species of the genus the ground color of the dorsum is reddish brown with no spotting.
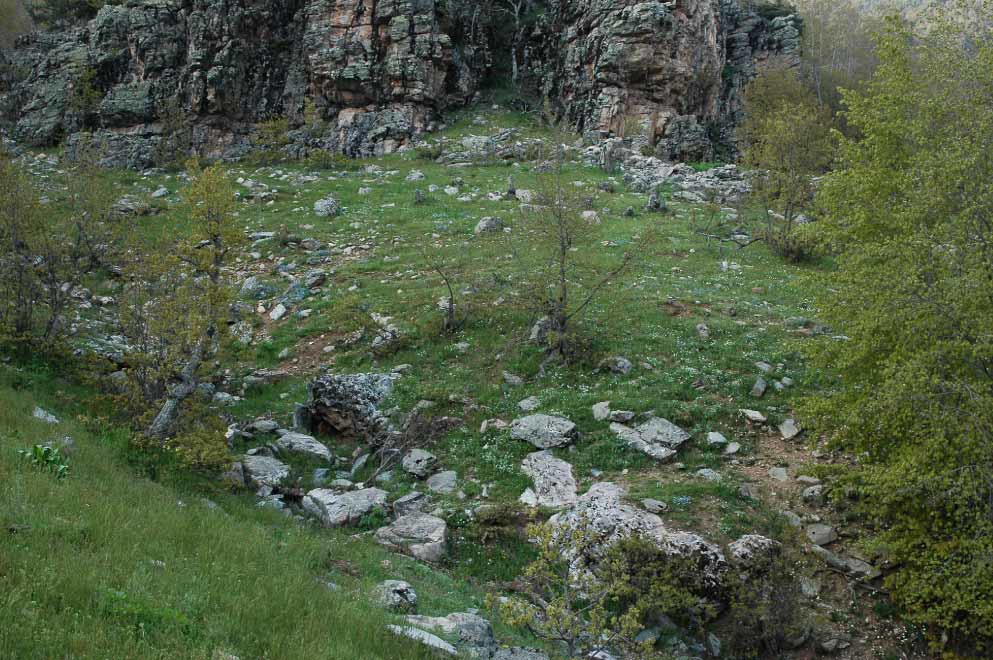
Habitat and ecology. Two specimens of R. barani n. sp. were captured between 16.30 and 18.30 hours, under stones along a stream ( Figure 7 View FIGURE 7 ). The altitude where the sampling was carried out was 1310 m a.s.l. The specimens were collected during sunny conditions and a temperature of 15ºC. Other amphibian and reptile species observed are Salamandra infraimmaculata , Ablepharus budaki , Laudakia stellio , Lacerta laevis , Lacerta cappadocica , Lacerta media , Ophisops elegans and Eirenis barani .
The maximum altitude of the research area ranges from 50 m a.s.l. in the west to 2240 m in the east ( Türkmen & Düzenli 1998). It is composed of Mesozoic and Cretaceous limestone, Upper Cretaceous ultrabasic Gabro and Serpentine rock and Tertiary marl and Quaternary alluvial deposits in the plains. Common soil formations are ‘Brown Calcarousless, ‘Brown Forest', ‘Terrarosa’, ‘Reddish Brown Mediterranean’, ‘Colluvial’ and mixed soils ( Akman 1973). The climate is Mediterranean, characterized by dry summers and rainy winters ( Türkmen & Düzenli 1998 and Table 2 View TABLE 2 ). The study area lies within the Mediterranean Phytogeographical Region ( Türkmen & Düzenli 1998). Three main vegetation types in the study area are the ‘Macchie’ vegetation from 50 to 600 m, the ‘Forest’ vegetation from 350 to 1900 m and the ‘Steppe’ vegetation at 1900 m and over. According to Türkmen & Düzenli (1998) common species include Quercus coccifera , Erica manipuliflora , Rhamnus punctatus var. angustifolius , Pistacia terebinthus subsp. palaestina , Cotinus coggyrea , Myrtus communis (Macchie) , Fagus orientalis , Pinus brutia , Quercus cerris var. cerris , Pinus nigra subsp. pallasiana , Carpinus orientalis , Cedrus libani and Abies cilicica (Forest) and Acantholimon libanoticum , Marrubium globosum subsp. glubosum, Astragalus macrourus, Ferula elaeochytris, Rosa pulverulenta , Cotoneaster nummularia , Vincetoxicum tmoleum , Asperula stricta subsp. monticola , Thymus kotschyanus var. glabrescens , Verbascum amanum , Asphodelina damascena subsp. damascena Echinops ritro and Eremurus spectabilis (Steppe) .
Distribution. Rhynchocalamus barani n. sp. is at present only known from the type locality ( Figure 8 View FIGURE 8 ). Etymology. The new species is in dedication to Prof. Dr. İ brahim BARAN of the University of Dokuz Eylül, İzmir, to acknowledge his prolific and uninterrupted contribution to the herpetology of the Turkey.
TABLE 1. Pholidotic characters and morphological measuremenst of Rhynchocalamus barani n. sp. (1. Sex, 2. Preocular, 3. Loreals, 4. Postoculars, 5. Temporals, 6. Postemporals, 7. Upper labials, 8. Lower labials, 9. Gular scales in a row between posterior inframaxillars, 10. Dorsals plus temporals scales surrounding the posterior margin of the parietals, 11. Ventrals, 12. Dorsal scale rows at midbody, on neck one headlength behind head, one headlength anterior to anal. 13. Subcaudals, 14. Rostral height, 15. Rostral width, 16. Internostril distance, 17. Diameter of eyes, 18. Supraoculars width, 19. Frontal width, 20. Frontal length, 21. Anterior inframaxillar length, 22. Posterior inframaxillar length, 23. Internasal triangular (d) or trapezoid shaped (t), 24. Suture length of internasal much shorter (), shorter (), equal (=) or longer (+) than prefrontal suture, 25. Parietals shorter (), equal (=) or longer (+) than the distance from posterior tip of rostral to the posterior tip of frontal, 26. Pairs of lower labials in contact with anterior chin shields, 27. Length of black head patterns (from tip of rostral scale), proportional to snoutvent length, 28. Pileus length, 29. Pileus width, 30. Head height, 31. Snoutvent length, 32. Tail length. (All measurements are in mm).
| 1 Ψ, | ɗ, | 17 1.78 | 1.84 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 11 | 11 | 18 1.50 | 1.20 |
| 3 1 / 2 | Absent | 19 2.60 | 2.52 |
| 4 2 / 2 | 2 / 2 | 20 3.10 | 3.10 |
| 5 1 / 1 | 1 / 1 | 21 2.42 | 2.64 |
| 6 2 / 2 | 2 / 2 | 22 1.54 | 2.02 |
| 7 5 / 5 | 5 / 5 | 23 Trapezoid | Trapezoid |
| 8 7 / 8 | 7 / 7 | 24 + | = |
| 9 1 | 2 | 25 (3.544.64) | (3.604.42) |
| 10 13 | 11 | 26 3 / 4 | 3 / 3 |
| 11 173 | 163 | 27 4.1 / 12.82 | 4.9 / 12.26 |
| 12 17 17 17 | 17 17 17 | 28 9.00 | 8.22 |
| 13 65/65+1 | 74/74+1 | 29 4.48 | 4.30 |
| 14 2.06 | 1.64 | 30 4.04 | 3.70 |
| 15 2.66 | 2.48 | 31 312.98 | 252.20 |
| 16 3.16 | 3.04 | 32 89.60 | 90.04 |
| ZDEU |
Zoology Department, Ege University |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.