Aphropsylla conversa ( Jordan & Rothschild, 1913 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.8.82 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:D7B7C104-B1A4-414F-8356-779145C4E794 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3792414 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03949A3B-2F3C-FFEC-FF02-FAED0B2E284C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Aphropsylla conversa ( Jordan & Rothschild, 1913 ) |
| status |
|
Aphropsylla conversa ( Jordan & Rothschild, 1913) View in CoL
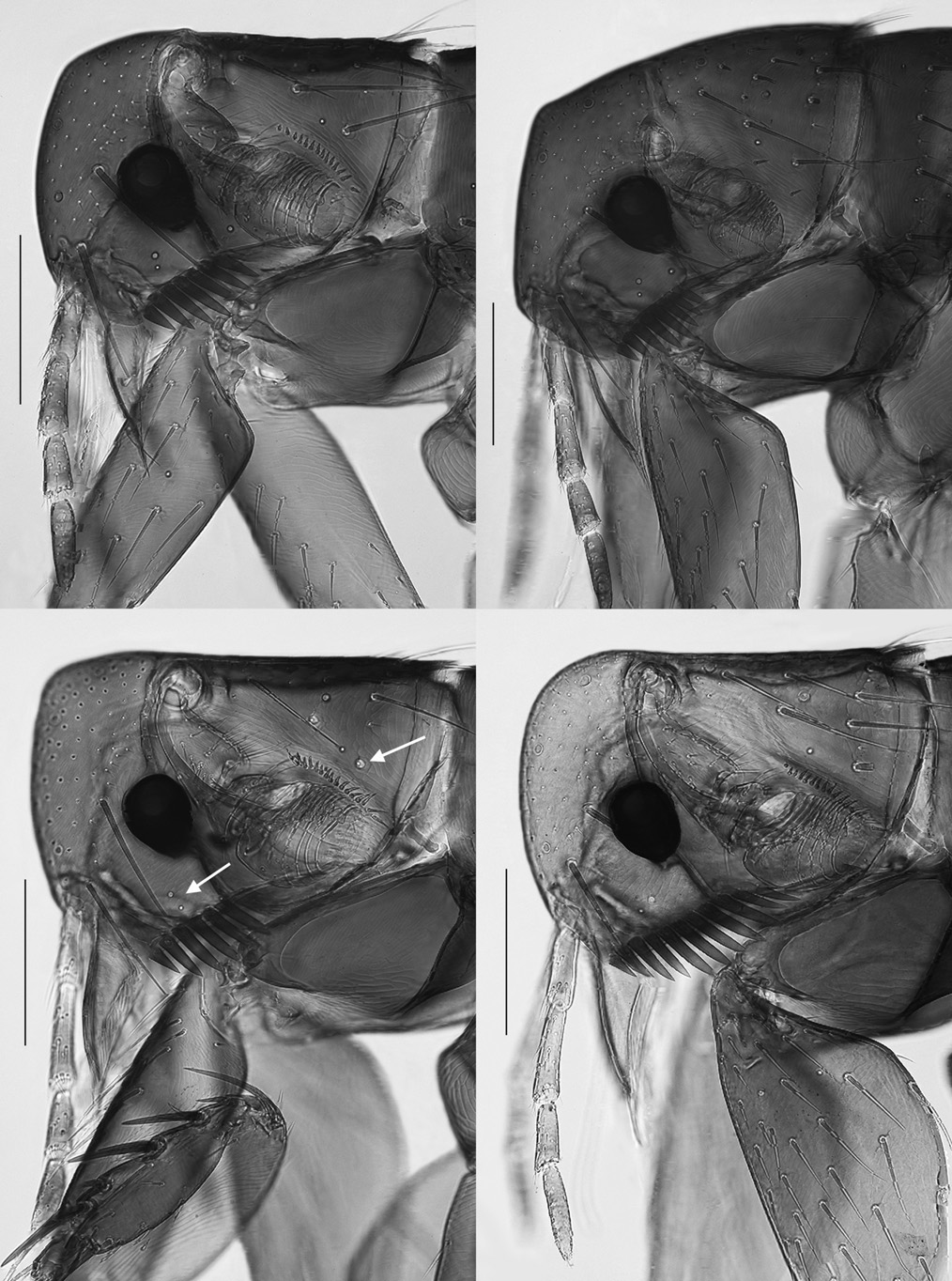
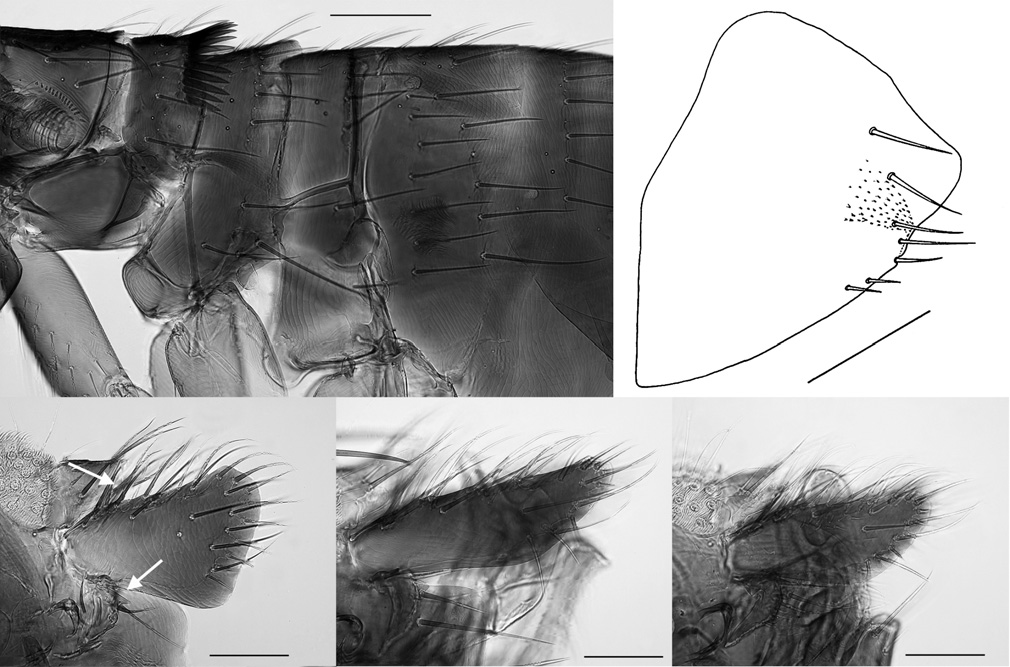
( Figs. 3 View Figures 1-4 , 8 View Figures 5-9 , 11, 13 View Figures 10-13 , 17 View Figure 14-18 )
Ctenocephalus conversus View in CoL Jordan & Rothschild. 1913. Novitates Zoologicae, 20:231-232.
Aphropsylla conversus Jordan. 1932:292-293 ; Hopkins. 1947:152.
Aphropsylla conversa Hopkins & Rothschild. 1953:133 View in CoL ; Cheetham. 1988:35; Beaucournu. 2004:190.
Material Examined. Holotype ♁, Kenya: Mutaragwa , Aberdare Range, [̴ 0°08’S, 36°07’E], ex. Lophuromys testudo = Lophiomys imhausi Milne-Edwards , 15 III 1910, GoogleMaps
Robin Kemp (BMNH); “neallotype” ♀, same data as holotype except ex. Dendrohyrax crawshayi = Dendrohyrax arboreus (A. Smith) , 17 III 1910 ( BMNH); paratype ♁, same data as holotype except Genetta stuhlmanni Mataschie = Genetta maculata (Gray) , 23 III 1910, Robin Kemp ( BMNH); 5 ♁, 4♀, Uganda: Bumagabula , foot of Butandiga [̴ 1°10’N, 34°22’E], west side of Mt. Elgon, 2135 m elev., ex. “on man (acc.)”, 22 II 1961, A.W. R. McCrae ( BMNH) GoogleMaps .
New Records. Uganda: nr Bumagabula , foot of Butandiga [̴ 1°10’N, 34°22’E], west side of Mt. Elgon, 2135 m elev., ex. “on man (acc.)”, 20 II 1961, A.W. R. McCrae ( British Museum Reg. No. 1961-684), 5 ♁, 4♀ ( BMNH) GoogleMaps .
Remarks. When Jordan and Rothschild described this species, they erroneously labeled one female (same data as holotype) as a “neallotype”. It is presumed they ment “ allotype ” and not “neallotype” or neoallotype. Host preferences for this species of Aphropsylla are virtually unknown since only a single specimen had been collected from each of the three known host species (other than man). Genetta maculata , a small agile
and scansorial carnivore, is certainly an accidental host, likely infested with one specimen correlated with the host’s carnivorous habits. Lophiomys imhausi and D. arboreus are both herbivores. Although the latter is arboreal, the single specimen recorded from it is also likely accidental. Th e label data for the nine specimens reported here, all indicate that the host was “on man” and it is presumed that the collector (or labeler) assumed man was an “acc. =?accidental” host. Unfortunately, the circumstances are not known surrounding the collection of no less than nine specimens from a human. There was surely some intimate contact with a bird or mammal nest by the “human host”. Th e fact that a sizable series of the new species described below was collected from bird nests (and not from a mammal per se) might suggest that the genus has close evolutionary affi nities to avian hosts.
| R |
Departamento de Geologia, Universidad de Chile |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Aphropsylla conversa ( Jordan & Rothschild, 1913 )
| Hastriter, Michael 2009 |
Ctenocephalus conversus
| Ctenocephalus conversus Jordan & Rothschild. 1913. Novitates Zoologicae, 20:231-232. |
Aphropsylla conversus Jordan . 1932:292-293
| Aphropsylla conversus Jordan . 1932:292-293 |
| Hopkins. 1947:152 |
Aphropsylla conversa
| Aphropsylla conversa Hopkins & Rothschild. 1953:133 |
| Cheetham. 1988:35 |
| Beaucournu. 2004:190 |