Acromis, Chevrolat. Se, 1837
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1649/0010-065X(2001)055[0075:RAPAOA]2.0.CO;2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:DEB11AA7-D0F0-46F3-9D94-D54841095BEC |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039787F8-FFA3-FFD6-FD42-FB5B9BD9D6B6 |
|
treatment provided by |
Tatiana |
|
scientific name |
Acromis |
| status |
|
Redescription of Acromis View in CoL
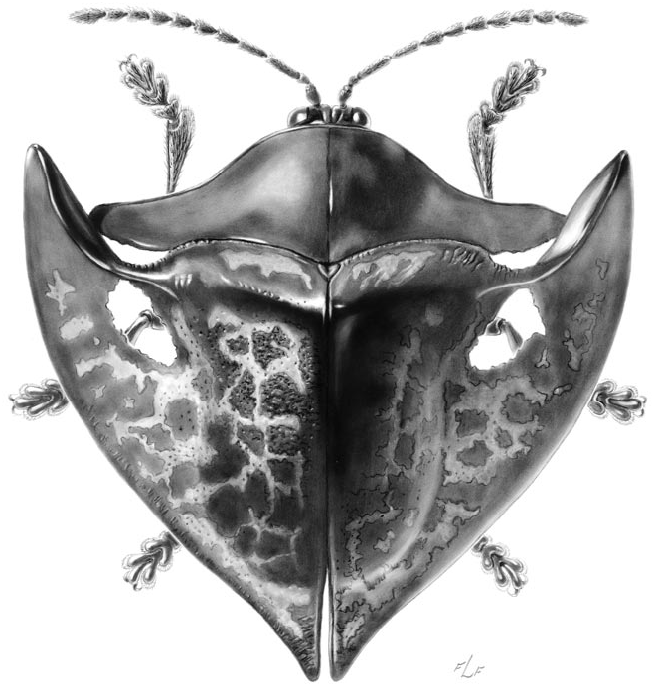
Adult (Figs. 1–7): Length 8.6–13.4 mm, width 9.2–11.1 mm. Body ( Fig. 12 View Fig ) outline discontinuous, elytral outline generally triangular to rounded in dorsal view. Body (Fig. 11) profile rounded to angular, highest behind scutellum and sloping ventrad anteriorly and posteriorly. Dorsal and ventral color ranging from yellowtan to reddish black, with some maculation on pronotum and elytra.
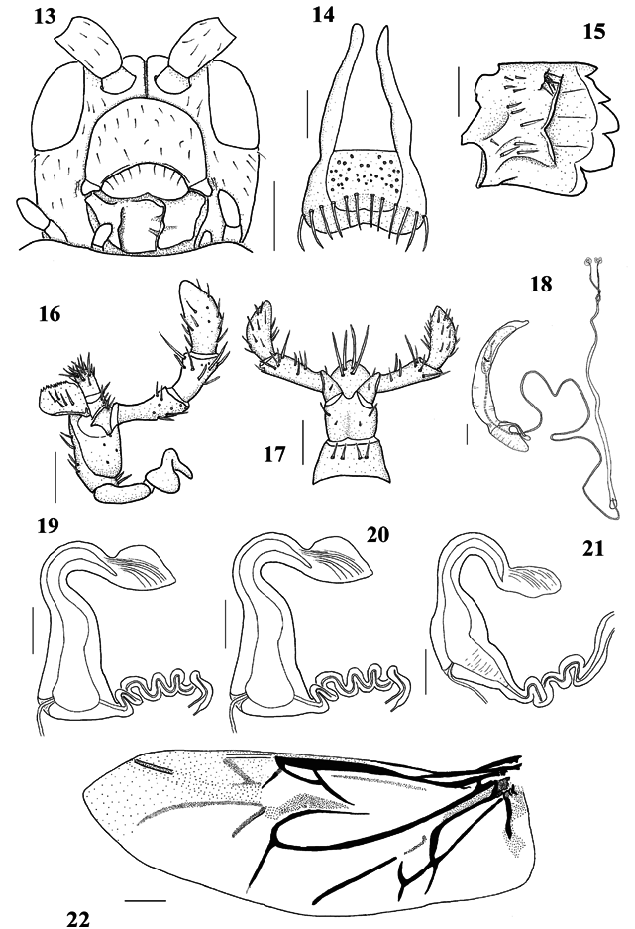
Head ( Fig. 13 View Figs ): Shape quadrate, margins more or less parallel. Eyes protuberant, separate from antennal socket; ventral margin anteriad of labral insertion; inner margin entire, not elevated. Gular region wider than long, gular sutures almost reaching posterior margin of buccal cavity. Coronal sulcus present, extending from clypeus to beyond dorsal margin of eye. Dorsal surface and genae with irregular striations, sparse punctures and setation. Supraorbital puncture with single seta present, positioned dorsally and midway between eye orbit and coronal sulcus. Antenna: 11segmented; antennomeres I–IV cylindrical, light to dark brown; antennomeres V–XI dorsoventrally compressed and expanded apically, increasingly dark brown to black and pubescent distally; III and IV longest; antennal sockets separate. Mouthparts: Clypeus quadrate to hemispherical; clypeus with sparse punctures and setation; lateral margins well defined and slightly to strongly protuberant; posterior margin with row of macrosetae. Labrum ( Fig. 14 View Figs ) more or less trapezoidal, distally emarginate; exterior surface with single row of macrosetae overlapping distal margin; dorsal and ventral surfaces without microsetae. Mandible ( Fig. 15 View Figs )
Figs. 1–11. Acromis spp. 1 –7) Habitus, scale bar = 1 mm. 1–3) A. sparsa ; 4–5) A. spinifix ; 6–7) A. venosa . Figs. 8–10) elytral apex, scale bar = 1 mm; 8) A. sparsa ; 9) A. spinifix ; 10) A. venosa . Fig. 11) A. venosa , lateral profile, scale bar = 2 mm.
palmate; exterior bristles present; mesal margin differentiated into five teeth, fifth smallest. Maxilla ( Fig. 16 View Figs ) with foursegmented palpus; galea twosegmented, soft rounded lobe, with apical hairs; lacinia onesegmented, with finelytoothed anterior margin. Labium ( Fig. 17 View Figs ): Mentum and prementum quadrate, with sparse setae; palpus threesegmented, with long hairs; ligula undivided, pointed, with few long hairs. Thorax: Pronotum extended laterally, especially posterolaterally, 1.9–3.7 times wider than long; surface with fine isodiametric meshes; lateral edges thickened slightly; hind margin smooth; lateral angles of explanate margin hidden in dorsal view by overlap of elytra in males; disc slightly convex, well defined from explanate margin anteriorly, poorly defined from explanate margin posteriorly, with fine median impressed line extending from posterior angle but not reaching anterior edge of disc. Prosternal collar elevated from prosternum; defined posteriorly by paired grooves; medial depression present or absent. Prosternal process expanded posteriorly, canaliculate; extended posteriad to procoxae. Mesosternum Yshaped, approximately 1/3 length of prosternum; anterior margin concave and locking with prosternal process. Metasternum convex. Scutellum: triangular, smooth, concave, receiving posterior median apex of prothorax; anterior margin hidden under pronotum. Elytra: explanate margin, ventrolaterally directed, wider than disc in anterior portion; explanate margin welldefined from disc, narrowing distally; anterior edge crenulate along its contact with pronotal margin, terminating near posterolateral angles of pronotum in females and tapering along humeral ridge in males. Hind wings ( Fig. 22 View Figs ): Cu, Sc, RA, RP, MP, CuA, AA and AP3 + 4 present. Radial cell developed, triangular; veins RA3 + 4, RP1 and RP2 appear as dusky lines; r4 absent; cubital anal cell 1 present, closed; cubital anal cell 2 present, open; CuA1 + 2 and CuA2 dusky, not always connected. Legs: Pro, meso, and metalegs similar; trochanter and tibia with ventral surface sparsely setose; femur dorsal and ventral surfaces sparsely setose proximally; densely setose on inner apex; tarsomeres with sparse setation dorsally; claws paired, smooth and divaricate, with single basal tooth; tooth smooth and quadrate. Abdomen: 5segmented; segments I–II connate, with faint groove indicating line of fusion; segments I–IV with sparse fine posterolateral hairs. Male genitalia ( Fig. 18 View Figs ): Median lobe with basal piece and apex curved abruptly in same direction, internal sac weakly sclerotized, surface with spines; ejaculatory guides present; tegmen with manubrium (= basal piece) as long as arms (lateral lobes); ejaculatory duct with sclerotized knob at junction of upper and lower portions of duct. Female genitalia: Ovipositor: spiculum lightly sclerotized, with emarginate apex, and widened distally; coxites shorter than T8. Spermatheca ( Figs. 18–20 View Figs ) elongate, deflexed 90 °, Cshaped; wellsclerotized; apically narrowed, pump with diameter smaller than receptacle; pump and receptacle broadly joined; receptacle more or less flaskshaped; appendix present, flattened along long axis, distal margin slightly to strongly concave, proximal margin evenly curved or sinuous; gland present, elongate and basally positioned; duct and gland opening separately and directly into receptacle; duct, proximal section with few (four to seven) coils, distal section without coils.
Sexual dimorphism. Males (Figs. 1, 4, 6) with humeral angles extended anteriorly, but not beyond head; humeral angle complexly folded, anterior margin upturned and overlapping lateral corner of pronotum; explanate margin behind humeral ridge with thin, lightcolored cuticle, frequently perforated in mature males. Females (Figs. 3, 5, 7) without humeral extension; anterolateral margin of explanate margin rounded.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |