Sonotetranychus madinahensis, Alatawi & Kamran, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2018.1434251 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C41BB3ED-99D5-4DCF-B557-09526FA7D56B |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03980147-210D-4F05-FE12-6BDA025C3C3A |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Sonotetranychus madinahensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Sonotetranychus madinahensis sp. nov.
(Figures 1 – 12)
Diagnosis
Female. Dorsal body setae setiform, serrate, set on small tubercles, longer than longitudinal intervals between their bases; striations between setae f 1 transverse; tarsus I with one solenidion proximal to most proximal set of duplex setae; chaetotaxy of genua I – IV 5 – 5 – 4 – 4; tibiae I – IV 9(1) – 5 – 5 – 5; tarsus IV with solenidion; empodial claws without dorsal hair.
Male. Aedeagus bent dorsad, lightly sigmoid, head without anterior projection, posterior projection 1.4 long, axis of head forming 35° angle with the main shaft.
Description
Female (n = 14). Measurement of holotype followed by 13 paratype females (in parentheses).
Dorsum (Figure 1). Length of body 441 (433 – 447) including gnathosoma, 315 (310 – 321) excluding gnathosoma, maximum width (at the level of setae c) 220 (213 – 226). Prodorsum entirely with longitudinal striations; striations on hysterosoma widely V shaped between setae d 1 and e 1, transverse between setae f 1 and posteriad up to caudal end, longitudinal on lateral edges. All dorsal striations dotted with rounded lobes (sometime suboval or subtriangular). All dorsal setae setiform, serrate, set on small tubercles (Figure 1(a)); length of dorsal setae: v 2 50 (47 – 53), sc 1 47 (44 – 49), sc 2 51 (48 – 55), c 1 32 (30 – 34), c 2 51 (49 – 52), c 3 55 (52 – 56), d 1 43 (40 – 45), d 2 51 (49 – 53), e 1 54 (51 – 56), e 2 62 (59 – 64), f 1 59 (56 – 61), f 2 57 (56 – 58), h 1 53 (51 – 55). Distances between dorsal setae: v 2 –v 2 56 (53 – 57), v 2 –sc 1 21 (20 – 22), sc 1 –sc 2 42(38 – 44), sc 1 –sc 1 77 (73 – 80), sc 2 – sc 2 150 (145 – 160), c 1 –c 1 77 (74 – 80), c 1 –c 2 31 (29 – 35), c 2 –c 3 42 (39 – 45), c 2 –c 2 139 (133 – 140), c 3 –c 3 210 (210 – 215), d 1 –d 1 63 (57 – 66), d 1 –d 2 43 (39 – 46), c 1 –d 1 43 (39 – 45), c 3 –d 2 45 (40 – 47), d 2 –d 2 145 (140 – 150), e 1 –e 1 36 (33 – 37), e 1 –e 2 46 (42 – 47), e 2 –d 2 57 (53 – 59), e 2 –e 2 125 (125 – 130), f 1 –f 1 23 (21 – 25), f 1 –f 2 34 (30 – 36), f 2 –f 2 78 (74 – 79), f 1 –d 1 44 (41 – 46), h 1 –h 1 22 (21 – 24), f 1 –h 1 50 (46 – 53), h 1 –f 2 36 (34 – 39).
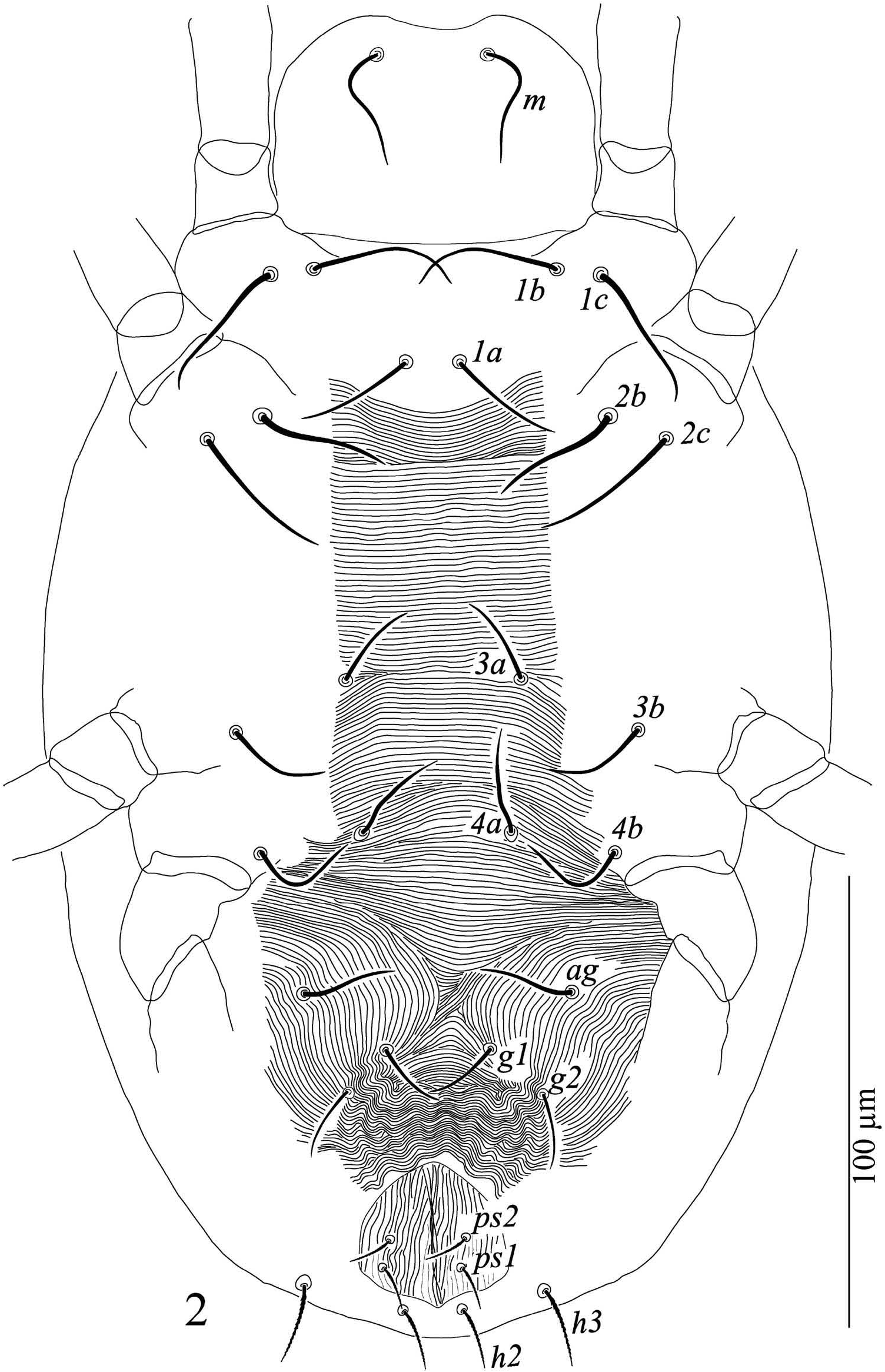
Venter ( Figure 2 View Figure 2 ). Striations on ventral idiosoma from setae 1a to 4a transverse, oblique or longitudinal in pre-genital area; striations on venter without lobes. Length and distances between intercoxal setae: 1a 34 (32 – 35), 1a–1a 13(13 – 14), 3a 29 (29 – 31), 3a–3a 52 (49 – 54), 4a 31 (30 – 33), 4a–4a 43 (40 – 43); length of coxal setae: 1b 43 (42 – 44), 1c 45 (42 – 45), 2b 40 (38 – 41), 2c 44 (42 – 46), 3b 40 (41 – 43), 4b 38 (38 – 40), distances 1b–1c 15 (15 – 17), 2b–2b 17 (17 – 18). Aggenital setae ( ag) 26 (25 – 27), ag–ag 77 (75 – 78), genital setae 2 pairs, g 2 22 (21 – 23), g 1 23 (21 – 23), g 1 –g 1 29 (28 – 31), g 2 –g 2 57 (55 – 58), g 1 –g 2 21 (20 – 22), anal setae two pairs ps 1 13 (12 – 13), ps 2 12 (11 – 12), ps 1 – ps 1 22 (21 – 23), ps 2 –ps 2 23, ps 1 –ps 2 8, para-anal setae two pairs h 2 20 (21 – 22), h 3 20 (21 – 23), h 2 –h 2 16 (16 – 17), h 3 – h 3 73 (71 – 75), h 2 –h 3 28 (27 – 29).
Gnathosoma. Stylophore rounded anteriorly with longitudinal striations dorsally. Peritremes terminating in simple bulb (Figure 3). Subcapitular setae m 36 (34 – 38), m–m 32 ( Figure 2 View Figure 2 ). Palpfemur with one seta, dPFe 33 (30 – 34); palpgenu with one seta, l’’PGe 20 (19 – 21); palptibia with three setae, dPTi 18 (18 – 19), l’’PTi 16 (16 – 17), l’ PTi 12 (11 – 12); palptarsus with three setae a 9 (8 – 9), b 9, c 12 (12 – 13), a spinneret suζ 5.5 long, 3.5 wide, two eupathidia ul’’ζ 5, ul’ ζ 5, a solenidion ω, 3.5 long; palptarsus slightly longer than its diameter, 11 long, 9 wide. Palptibial claw strongly curved with divided tip (Figure 4).
Legs (Figures 5–8). Length of legs I – IV 220 (215 – 223), 205 (201 – 210), 182 (176 – 186), 214 (209 – 220), respectively. Number of tactile setae and solenidia (in parentheses) on legs I – IV: coxae 2 – 2 – 1 – 1; trochanters 1 – 1 – 1 – 1; femora 8 – 7 – 3 – 2; genua 5 – 5 – 4 – 4; tibiae 9 (1) – 5 – 5 – 5; tarsus I with 10 tactile setae, two sets of duplex setae, three eupathidia, and one solenidion; tarsus II with nine tactile setae, one set of duplex setae, three eupathidia and a solenidion, tarsus III 10 tactile setae and a solenidion; tarsus IV 10 tactile setae and a solenidion. Tarsus I with four tactile setae well proximal to proximal duplex setae, sloenidion and one tactile seta slightly proximal to proximal set of duplex setae; tarsus II with two tactile setae and solenidion proximal to duplex setae, while two tactile setae almost in line with the duplex setae; empodium without proximoventral hairs, empodial claw longer than pads of the true claws (Figure 5(a)).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.