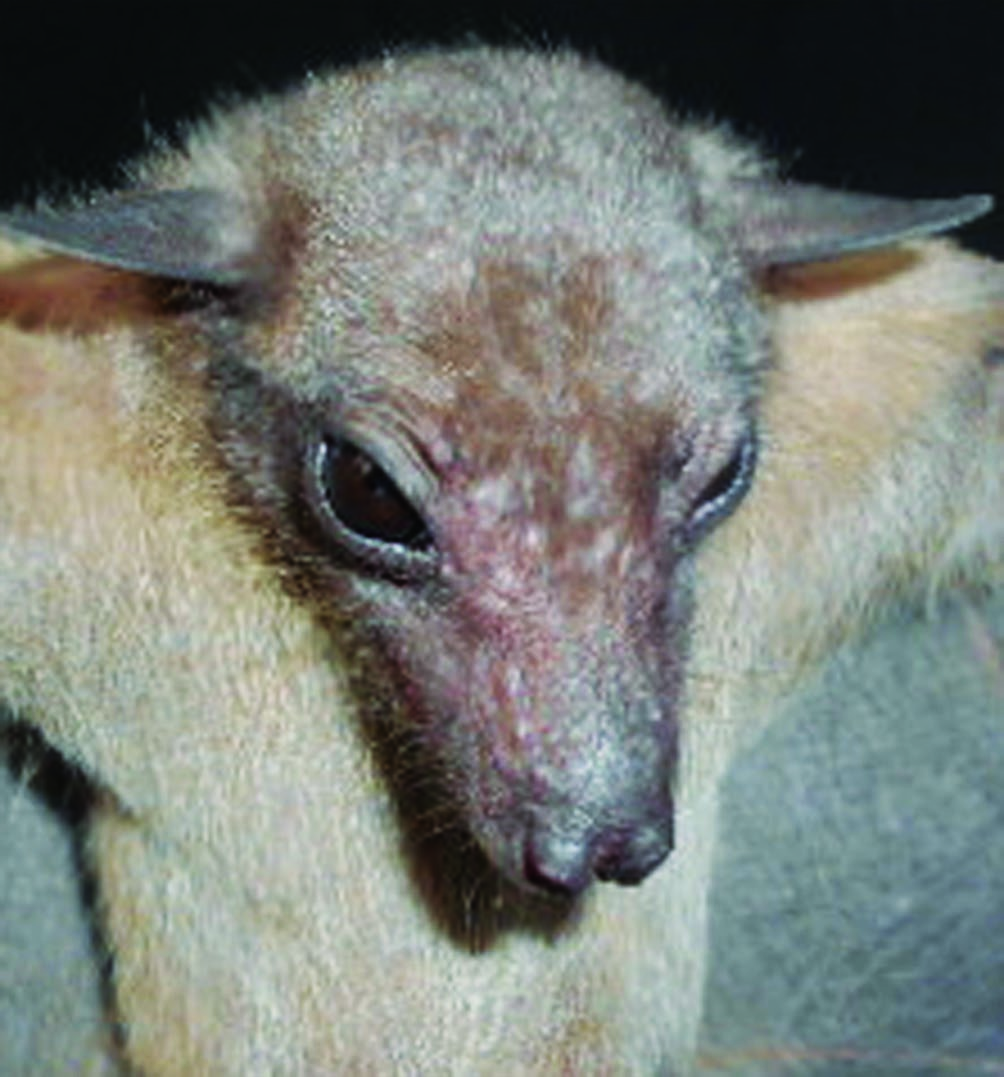
Rousettus aegyptiacus (E. Geoffroy, 1810)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5252/zoosystema2020v42a24 |
|
publication LSID |
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:4369E104-E14C-4436-9B57-6C38A6AEBE65 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4338041 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039A87C3-D54F-394A-1F46-FE14FA544680 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Rousettus aegyptiacus |
| status |
|
Rousettus aegyptiacus View in CoL (E. Geoffroy St.-Hilaire, 1810)
( Fig. 10 View FIG , Table 3 View TABLE )
Pteropus egyptiacus E.Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1810: 96 View in CoL .
COMMON NAMES. — English: Egyptian Fruit Bat. French: Roussette d’Egypte.
MATERIAL EXAMINED. — 230 specimens (including original data). Mount Cameroon area • 29 specimens; Isobi ; 4°07’15”N, 8°59’33”E; 56 m; Martin Eisentraut leg.; SMNS 6687 to 6694, ZFMK 1961.0577, 0580, 0581, 0583, 0587 to 0591, 0594, 0598, 0599; ZFMK 1963.0208a to 0208e, 0218c; ZFMK 1969.0417, 0419, 0489a GoogleMaps • 27 specimens; Mueli ; 4°23’00”N, 9°07’00”E; 600 m; 8.II-23. II.1958; Martin Eisentraut leg; SMNS 6672 to 6686; ZFMK 1959.0450; ZFMK 1961.0576, 0578, 0582, 0584 to 0586, 0595 to 0597, 0600, 0602 GoogleMaps • 8 specimens; Koto-Barombi ; 4°27’57”N, 9°16’01”E; 457 m; 17.I-26.I.1958; Martin Eisentraut leg.; SMNS 6667 to 6671; ZFMK 1961.0575, 0579, 0601 GoogleMaps • 24 specimens; Above Buea ; 4°09’34”N, 9°14’12”E; 1850 m; 23.XI-26.XI.1957, 04.I.1958; Martin Eisentraut leg.; SMNS 6658 to 6666, 6828 to 6832, 8155, 8156; ZFMK 1961.0592, 0593; ZFMK 1963.0209a to 0209f GoogleMaps • 1 ♀; Victoria ; 4°00’46”N, 9°13’13”E; 136 m; Strunk leg.; ZMB 54700 GoogleMaps • 2 specimens; Musake ; 4°12’00”N, 9°12’00”E; 2000 m; Martin Eisentraut leg.; ZFMK 1969.0418, 0489b GoogleMaps .
Other localities of Cameroon. Yaoundé, ZMB 10239 • 2 specimens; Bipindi ; 3°05’00”N, 10°25’00”E; 184 m; Zenker Georg August leg.; ZMB 54691, 54699 GoogleMaps .
ORIGINAL DATA. — With 137 individuals (131 males and 6 females) the echolocating and cave-dependent Egyptian Rousette was the second most abundant bat species captured during our field surveys ( Table 1 View TABLE ). The species was trapped in both primary montane forest and lowland secondary and cultivated forest at a wide range of altitudes from 470 m up to 2280 m a.s.l. ( Table 1 View TABLE ). The species has previously been sampled in large caves on the lower slopes and in montane grassland of Mount Cameroon ( Eisentraut 1963; Fedden & MacLeod 1986).
HABITATS AND DISTRIBUTION. — Rousettus aegyptiacus is widespread in sub-Saharan Africa, North Africa, Middle East, the Arabian Peninsula right across to Iran and Pakistan ( Korine 2016). This species has broad habitat preference and has been recorded in arid to moist tropical and subtropical habitats where large colonies roost in caves and artificial structures such as mosques, tombs and mines ( Happold 2013c). Happold (1987) noted that the local distribution of this species is influenced more by the availability of suitable roost sites than by vegetation type. The species is threatened in parts of its range by bushmeat trade, cave disturbance and persecution ( Korine 2016).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Rousettus aegyptiacus
| Mongombe, Aaron Manga, Fils, Eric Moise Bakwo & Tamesse, Joseph Lebel 2020 |
Pteropus egyptiacus E.Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1810: 96
| Pteropus egyptiacus E.Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1810: 96 |