Muntiacus gongshanensis, Ma, 1990
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6514377 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6514423 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A087C4-FFC6-FFC7-FA74-FEBAE152FA2C |
|
treatment provided by |
Conny |
|
scientific name |
Muntiacus gongshanensis |
| status |
|
Gongshan Muntjac
Muntiacus gongshanensis View in CoL
French: Muntjac de Gongshan / German: Gongshan-Muntjak / Spanish: Muntiaco de Gongshan
Taxonomy. Muntiacus gongshanensis Ma, 1990 View in CoL ,
Mijio, Gongshan county ( Yunnan, China).
Closely related to M. erinifrons, the divergence of these two species is a relatively recent event. Monotypic.
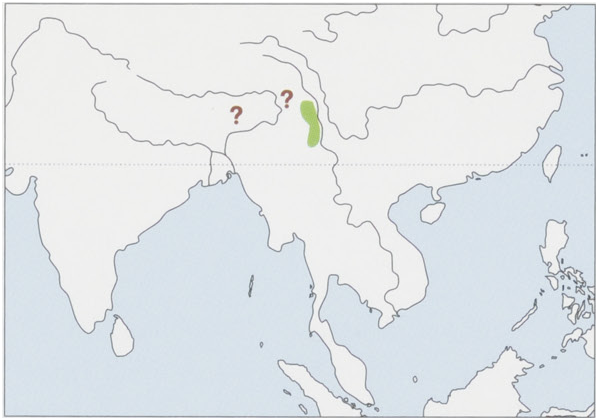
Distribution. S China ( Yunnan) and N Myanmar; possibly SE Xizang, NE India, and Bhutan. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 90-110 cm, tail 20 cm, shoulder height 55 cm; weight 20-25 kg. Medium-sized; similar to the Black Muntjac (M. c¢rinifrons) but with males lacking the frontal tuft; females have a crown tuft more prominentlaterally than centrally. The coat is brown, with back and tail dark brown, the head pale brown with dark lines on pedicles. Antlers relatively short. The diploid number of chromosomesis 2 n =9 (males) and 8 (females).
Habitat. The Gongshan Muntjac prefers evergreen, lowland forests.
Food and Feeding. Nothing is known, but likely a partially omnivorous browser.
Breeding. No information for this species, but most other tropical muntjacs bear a single young, aseasonally.
Activity patterns. Nothing is known forthis species; other muntjacs range from diurnal through crespucular to nocturnal.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. No data for this species, but likely solitary, as in other species of muntjacs.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Data Deficient on The IUCN Red List, probably decreasing. Hunting appears to be the major threat.
Bibliography. Amato et al. (2000), Huang Ling et al. (2006), Ma Shilai et al. (1990), Timmins, Duckworth & Zaw (2008a), Wang Wen & Lan Hong (2000).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.