Pudu puda (Molina, 1782)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6514377 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6514579 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A087C4-FFDA-FFDB-FA73-FBAEEE34F3BB |
|
treatment provided by |
Conny |
|
scientific name |
Pudu puda |
| status |
|
Southern Pudu
French: Poudou austral / German: Siidpudu / Spanish: Pudu
Other common names: Chilean Pudu
Taxonomy. Capra puda Molina, 1782 ,
Chiloé Province ( Chile).
This species is monotypic.
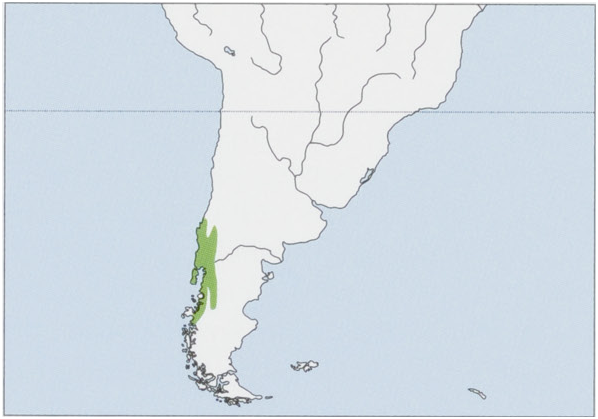
Distribution. It is found in S Chile between 35° S (Mataquito River) and 47° S (Lake Buenos Aires, Peninsula Esmeralda & Laguna San Rafael) and in adjacent W Argentina from SW Neuquén Province, southward along the foothills of the Andes to Los Alerces National Park in Chubut Province. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head—body 80 cm, tail 4 cm, shoulder height 30-40 cm; weight 9-10 kg (up to 14 kg). Small-sized deer,slightly larger than the Northern Pudu. The coat is rufous in summer, dark brown in winter; the legs are paler. Fawns are spotted until they are three months of age. A large preorbital gland and a small interdigital gland are present. Permanent dentition of 32 teeth. Antlers of adults are spikes 5-9 cm long (up to 10 cm). Thefirst true set of antlers develops at 9-12 months of age. Antler cycle is synchronized: antler casting is in June—July, velvet cleaning in October. Hooves are short.
Habitat. It lives in temperate pristine rain forests, from sea level to 1700 m above sea level, more frequently at high elevations. It also occurs in secondary forests. It feeds along forest edges.
Food and Feeding. As a browser,it eats young leaves, sprouts of trees and shrubs, forbs, and fruits.
Breeding. Females attain puberty at 12-18 months of age, sometimes at 5—6 months. Males are able to reproduce at two or three years of age. Breeding is markedly seasonal, with a rut mainly in March-April and a fawning season in November-December. In the courtship approach males lower their body in an exaggerated crouched posture with belly almost touching the ground. Females have an estrous cycle of eleven days. The length of pregnancy is about 195 days. Females give birth to a single fawn weighing about 0.7-0. 9 kg. The first solid food is eaten at twelve days of age. Weaning occurs very early, possibly at two months of age. Maximum longevity in captivity is 17-18 years. Main predators are Pumas (Puma concolor), Kodkods (Leopardus guigna), foxes and Magellanic horned owls (Bubo magellanicus). On Chiloé Island, pudus comprise 3-7% of the diet of Darwin’s Fox (Pseudalopexfulvipes).
Activity patterns. It is mainly crepuscular, but can be active both day and night as well.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. Its small and compact body enables it to move in the thick understory of the forest. It occupies home ranges of 15-25 ha, sometimes larger, which it defends actively. Fighting includes jumping at the rival, biting, and thrashing him with the front legs. Marking includes depositing feces in latrines. It lives solitarily or in temporary pairs.
Status and Conservation. CITES Appendix I. Classified as Vulnerable on The IUCN Red List and decreasing. Total population is thought to be less than 10,000 animals. Poaching and habitat loss and fragmentation have caused a rapid decline in recent decades. Over 90% ofits former habitat in Chile has been lost. Predation by domestic dogs and competition with domestic livestock and exotic wildlife are important additional threats.
Bibliography. Blainvillain et al. (1997), Eldridge et al. (1987), Feer (1984), Hershkovitz (1982), Jimenez (2010), MacNamara & Eldridge (1987), Meier & Merino (2007).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.