Schendylops Cook, 1899
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4691.4.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:05E8776E-5339-47F0-90F8-A8D828E03838 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5624589 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B07544-FFB3-FFF5-FF5F-FCB8E64A72EB |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Schendylops Cook, 1899 |
| status |
|
Genus Schendylops Cook, 1899 View in CoL View at ENA
Type species: Scolopendra grandidieri Saussure & Zehntner,1902
Other taxa included: 68 species ( Bonato et al. 2016)
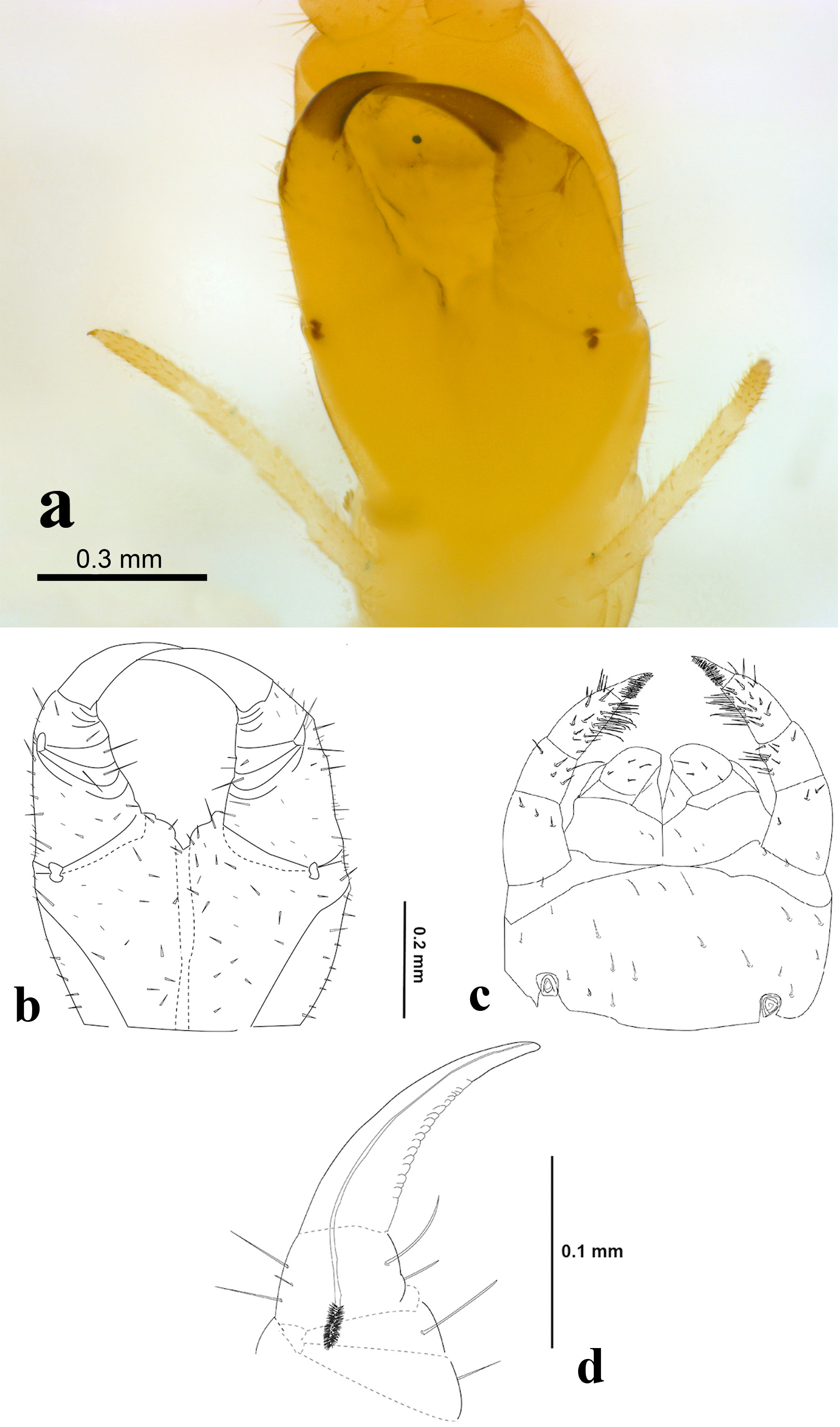
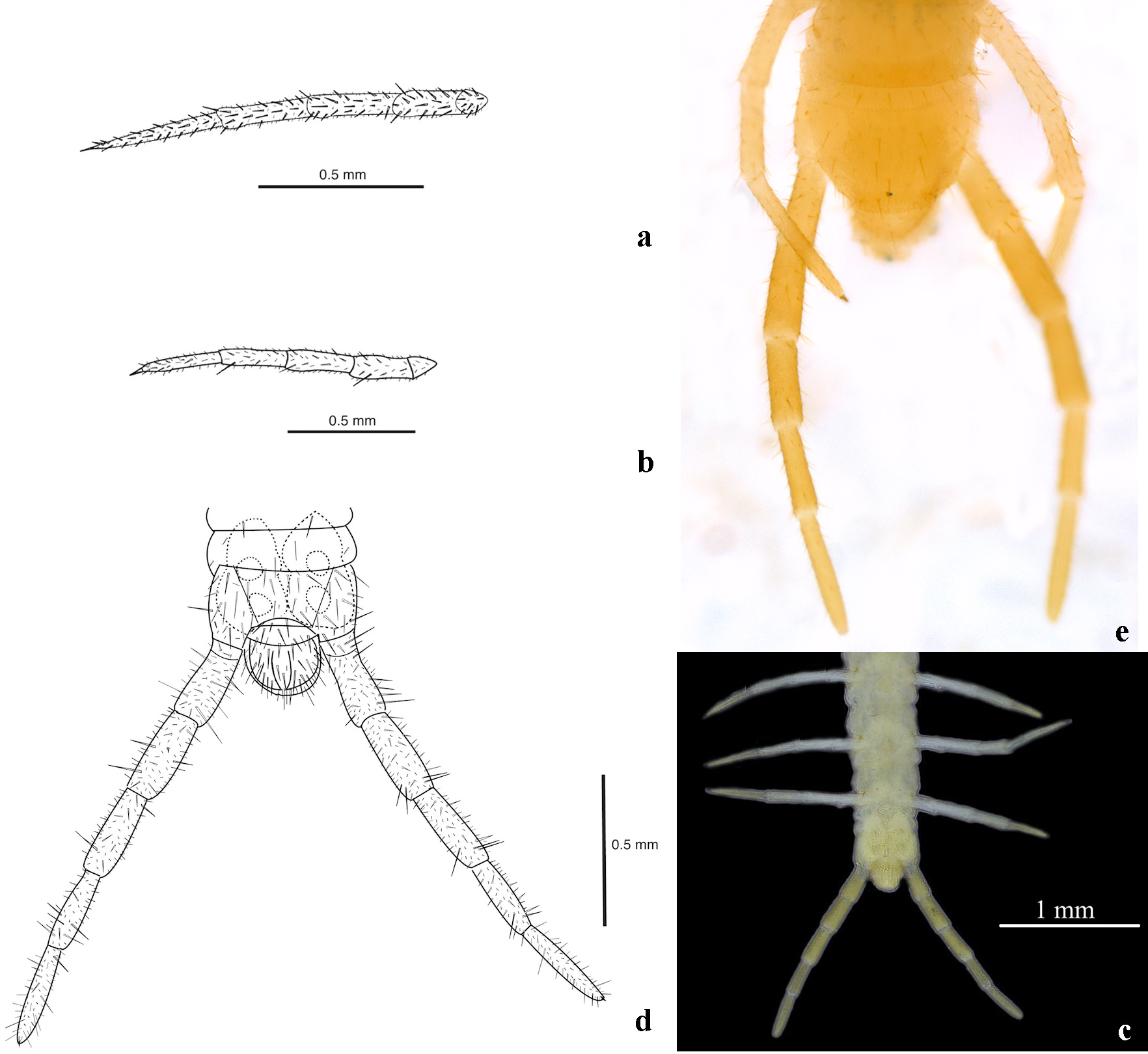
Diagnosis. Pleurites of second maxillae not fused with coxosternum ( Figure 5C View FIGURE 5 ). Apical claw of second maxillae pectinate on both dorsal and ventral edges. Sterna with pore fields ( Figure 7 View FIGURE 7 A–E). Last pair of legs with seven podomeres ( Figure 7 View FIGURE 7 A–E). Praetarsus in form of a small pilose tubercle or replaced by a small spine or altogether absent. Coxopleura of the ultimate leg-bearing segment each with two internal coxal organs of simple structure (“homogeneous coxal glands” sensu Brölemann & Ribaut 1912) ( Figure 7 View FIGURE 7 A–E).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |