Cotithene
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.182350 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6231082 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B2C225-FFBD-FFFE-FF52-6614ACA5FD5F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Cotithene |
| status |
|
Key to the species of Cotithene
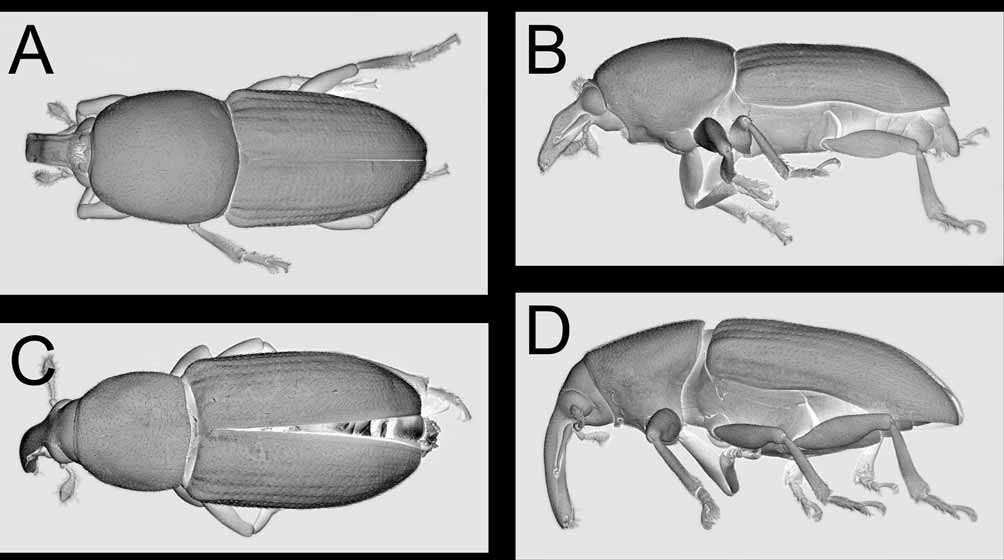
1. Length 2.7–3.4 mm; rostrum of male in lateral view widest near basal 2/5 (e.g., Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 A), pronotum slightly convex (e.g., Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 B); procoxal cavities in female narrowly separated by narrow septum.......2
1'. Length 4.4–6.1 mm; rostrum of male in lateral view widest near apical 2/5 (e.g., Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 A), pronotum strongly expanded (e.g., Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B); procoxal cavities in female separated by about width of antennal club..................................................................................................................................................................3
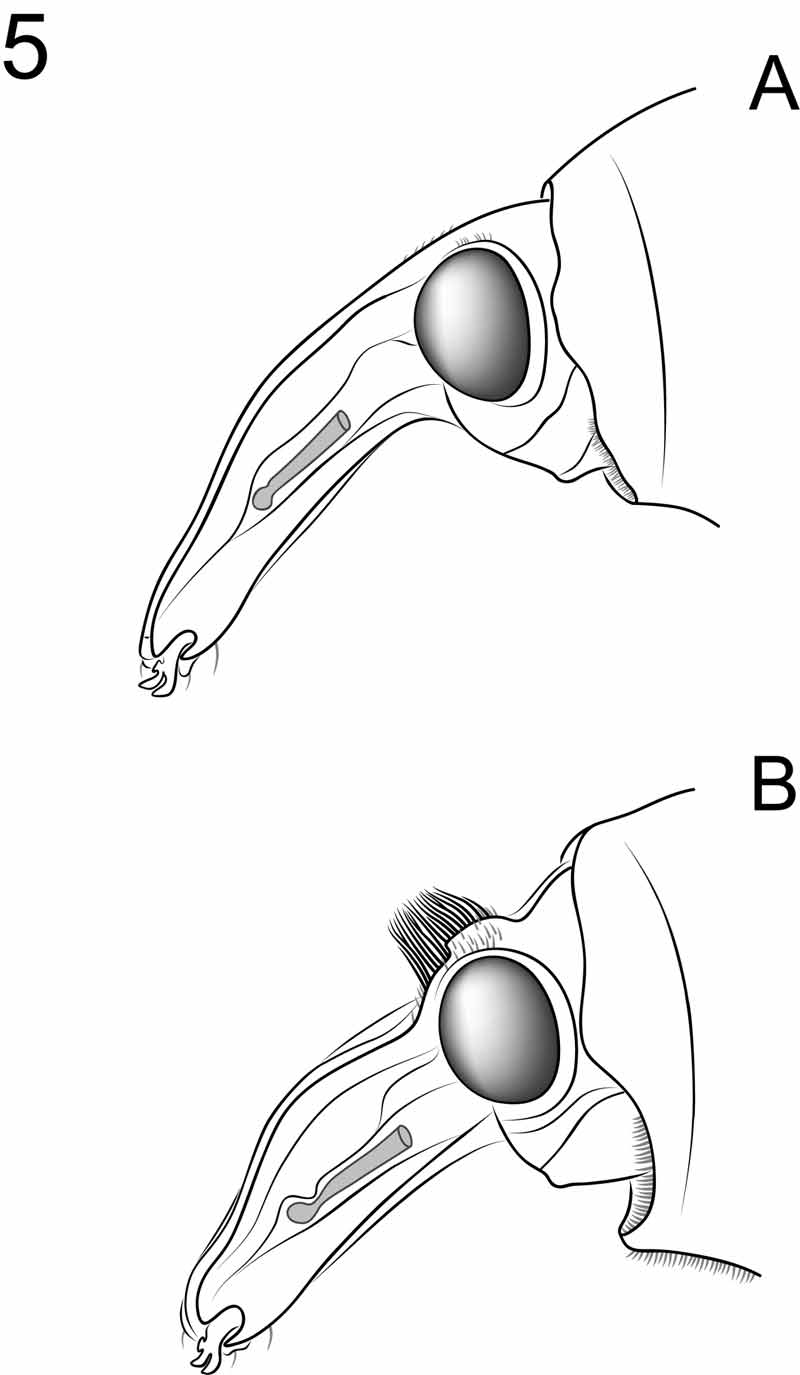
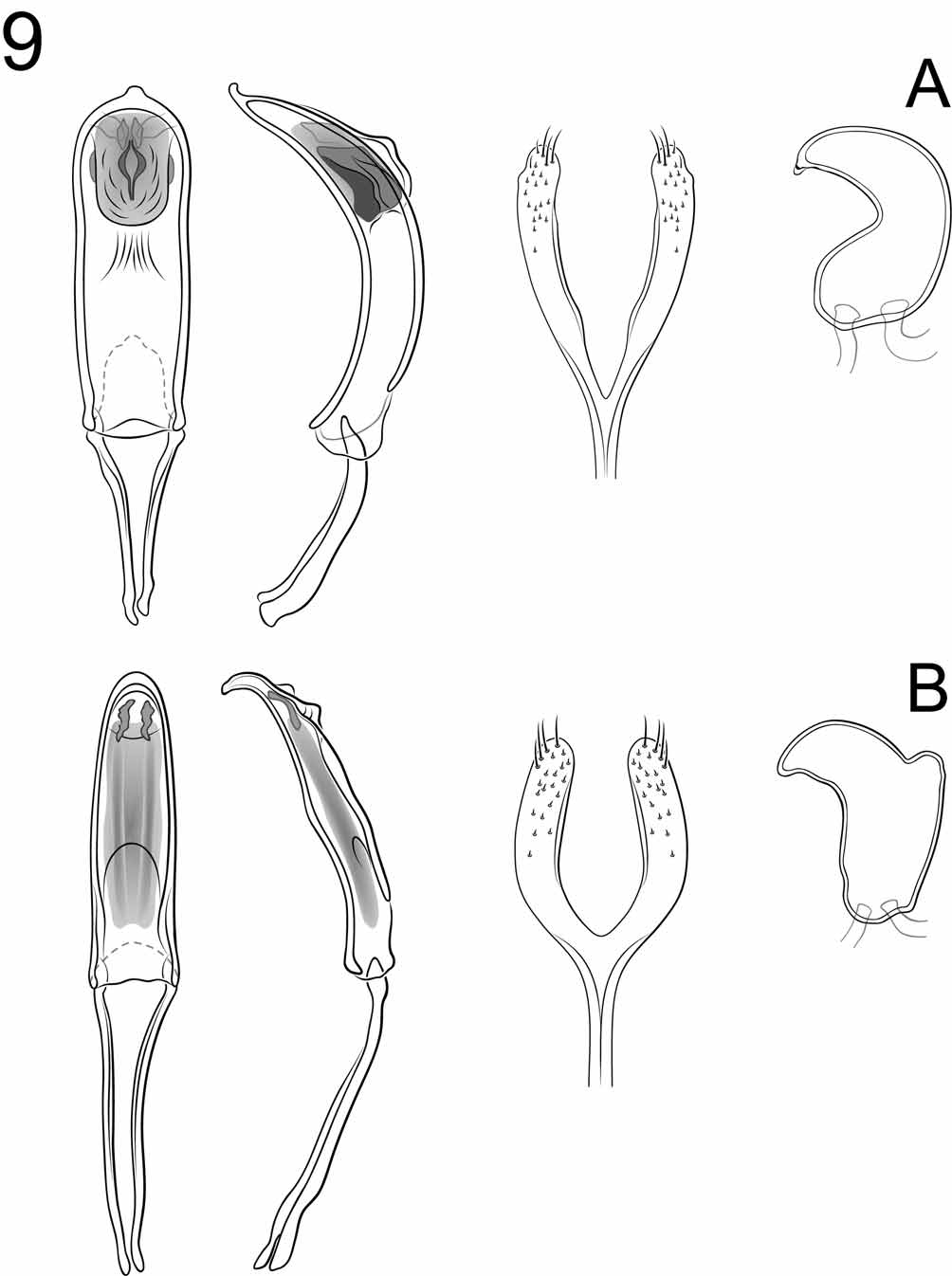
2(1). Head of male dorsally without any projections or long, suberect setae ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 A); spermatheca C-shaped, without projection on outer margin at point of deflection ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 A) ..................... C. dicranopygia sp. n.
2'. Head of male dorsally with convex elevation, three triangular projections and long, suberect setae ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 B); spermatheca J-shaped, with small, narrowly convex projection on outer margin near point of deflection ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 B) .................................................................................................. C. stratiotricha sp. n.
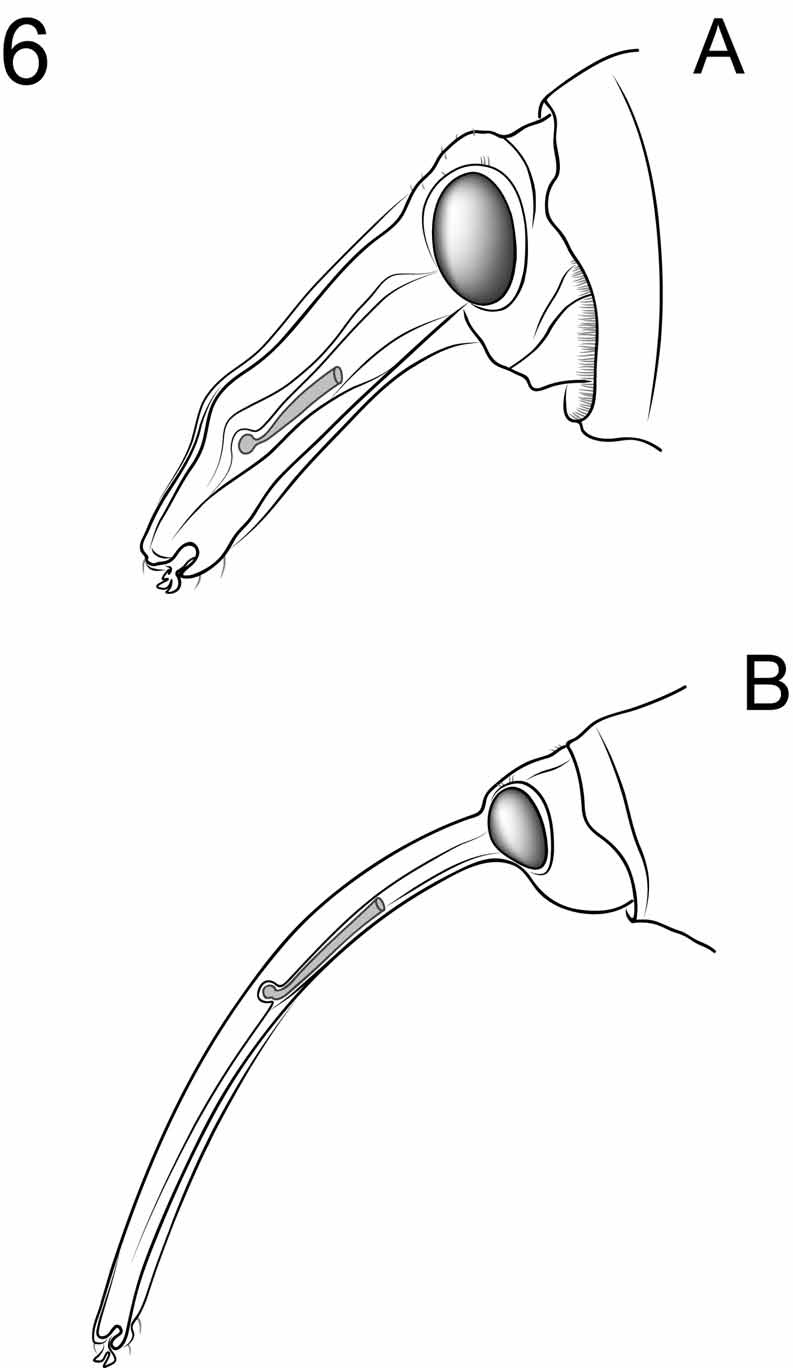
3(1'). Head of male dorsally without projections or longer setae, anterodorsal region rugulose, prosternum without small obtuse elevation anteriorly of each procoxal cavity, aedeagus with subapical constriction ( Figs. 10 View FIGURE 10 A,B); rostrum of female 1.7–2.1x longer than pronotum, (very) narrow, arcuate, scape not reaching eye, rostrum-head transition in lateral view slightly concave ( Figs. 6 View FIGURE 6 B, 7B)...........................4
3'. Head of male with small, posterior, triangular projection and longer, suberect setae, anterodorsal region slightly convex, prosternum with small obtuse elevation anteriorly of each procoxal cavity, aedeagus apically continuously narrowed (e.g., Figs. 11 View FIGURE 11 , 12 View FIGURE 12 ); rostrum of female 0.9–1.1 x as long as pronotum, narrow, slightly arcuate, scape reaching anterior margin of eye, rostrum-head transition in lateral view evenly convex ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 B)...........................................................................................................................5
4(3). Pronotum light reddish-brown, elytra darker reddish-brown, sclerites of aedeagus ventrally expanded at apex, irregular, undulate ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 A); rostrum of female 2.0–2.1x as long as pronotum, very narrow ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 B) ......................................................................................................................... C. leptorhamphis sp. n.
4'. Pronotum yellowish-brown, elytra dark brown, apex of aedeagal sclerites ventrally narrowed, acute
( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 B); rostrum of female 1.7x as long as pronotum, narrow ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 B) .................... C. trigaea sp. n. 5(3'). Pronotum light reddish-brown, elytra dark reddish-brown; internal sac of aedeagus without ventral, subquadrate to annulate structure ( Fig. 11 View FIGURE 11 ); spermatheca slightly constricted near apical 3/5 ( Fig. 11 View FIGURE 11 ) ... .................................................................................................................................. C. globulicollis Vo s s
5'. Pronotum nearly orange, elytra dark reddish-brown to black; internal sac of aedeagus with ventral, subquadrate to annulate structure ( Figs. 12 View FIGURE 12 A, 12B); spermatheca apically gradually narrowed ( Figs. 12 View FIGURE 12 A, 12B)...........................................................................................................................................................6
6(5'). Rostrum of male without basal impression, head dorsally with sparse, long, recurvate setation, internal sac of aedeagus ventrally with complex, annulate structure ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 A); female with posterior margins of furcal arms of sternum VIII obliquely truncate, spermatheca J-shaped ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 A); Costa Rica............... ................................................................................................................................ C. anaphalanta sp. n.
6'. Rostrum of male with slight, basal impression, head dorsally with dense, long, recurvate, anteromedially directed setation, internal sac of aedeagus ventrally with irregular, subquadrate structure ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 B); female with posterior margins of furcal arms of sternum VIII evenly rounded, spermatheca Cshaped ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 B); Venezuela.................................................................................. C. melanoptera sp. n.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.