Daptonema donghaiensis, Wang & An & Huang, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4514.4.11 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:6F45E6CF-705E-420C-A633-78E26B8B37F5 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5978344 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B487B2-FFAC-FFCF-FF73-6A951CA3783C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Daptonema donghaiensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Daptonema donghaiensis View in CoL sp. nov.
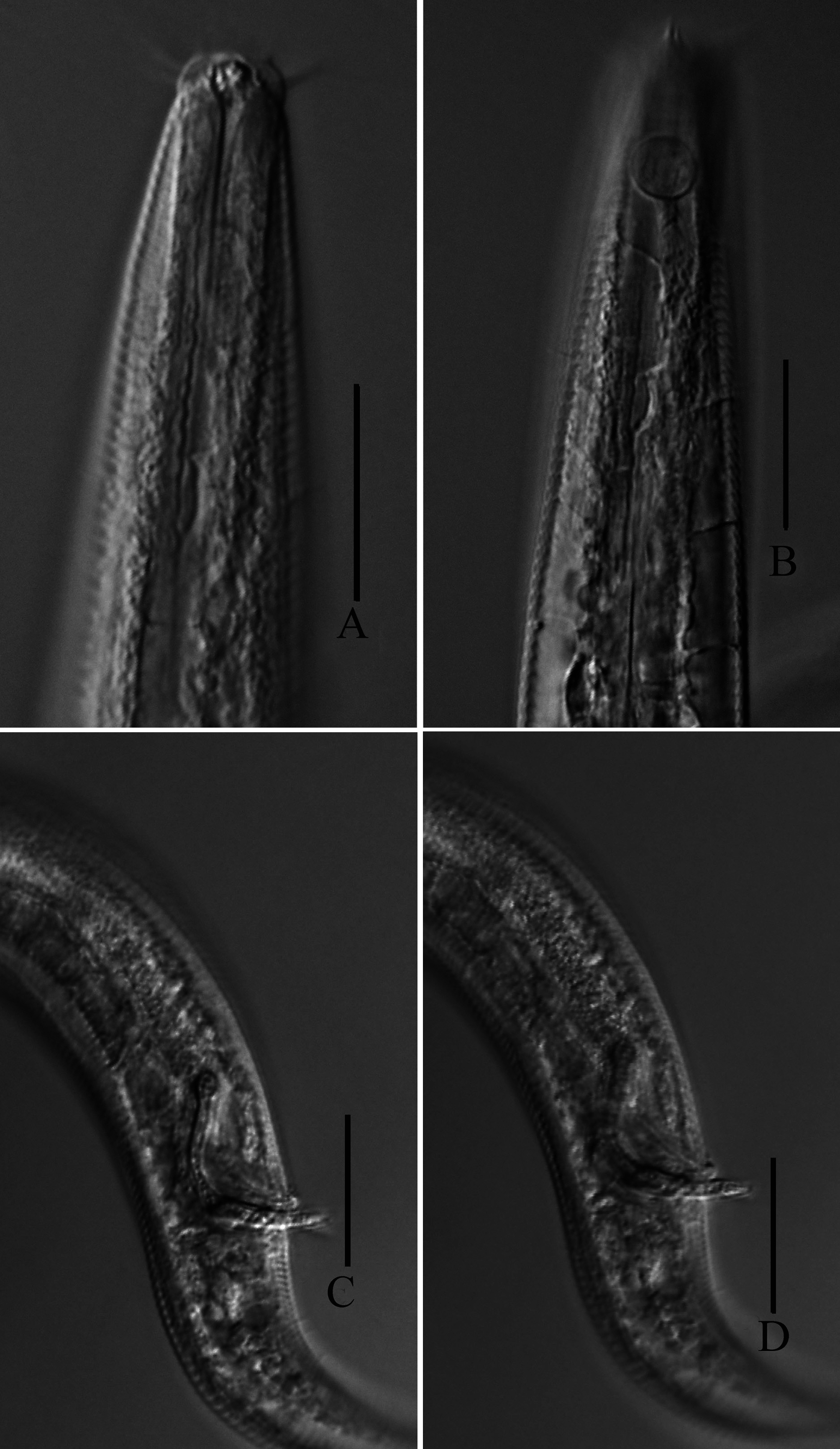
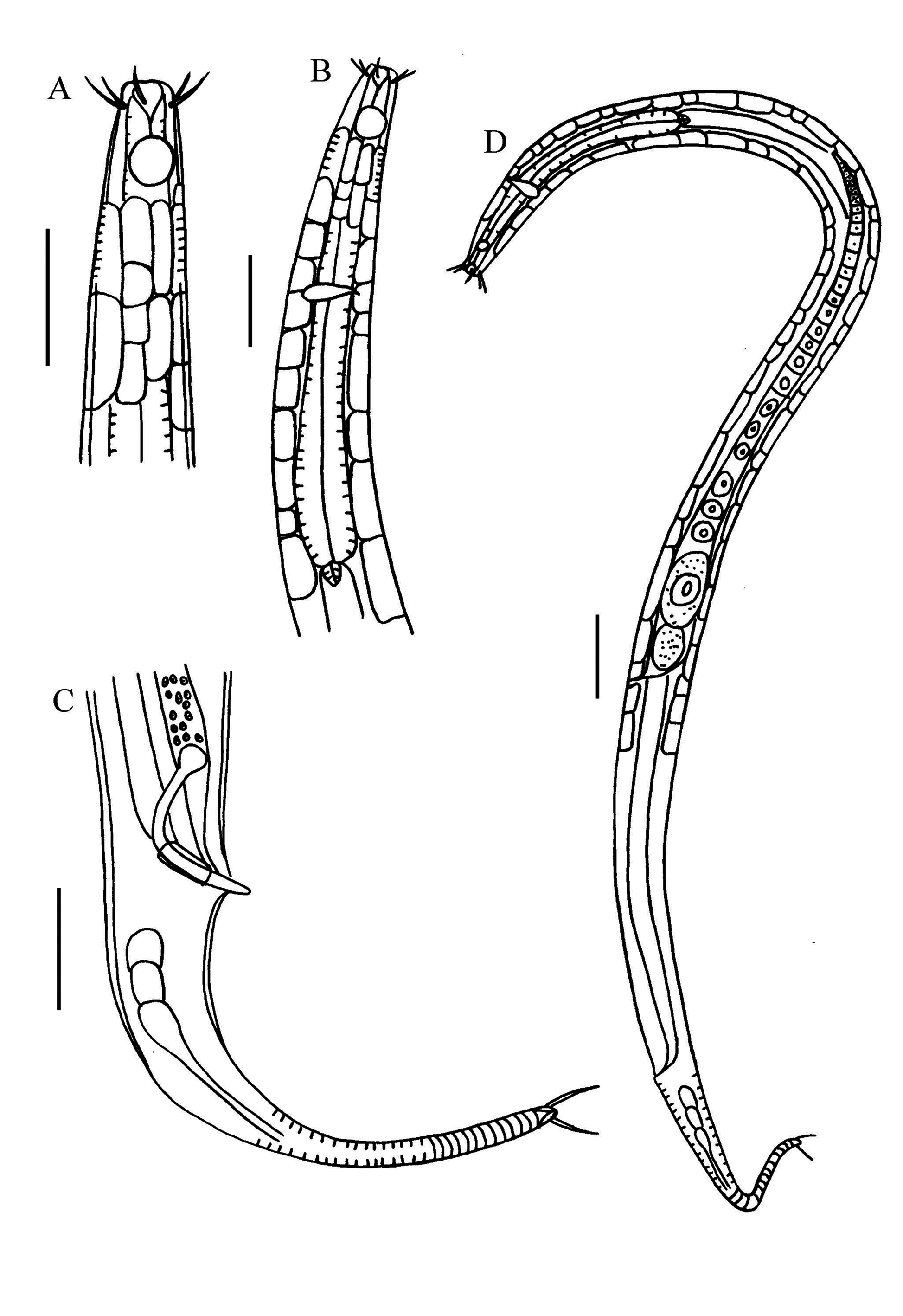
( Figs 1-2 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 )
Type material. Five males and two females were measured and studied. Holotype male and paratype male on slide DH12-422-13; paratype females on slides DH12-422-8, DH12-422-11; additional males on slides DH12-413-2, DH12-418-4, DH12-418-5.
Type locality and habitat. Sublittoral in the East China Sea. Holotype and paratype specimens comes from Station DH4-2: 29°18´N, 123° 22´E, water depth 70 m. Muddy with a little sand sediment fraction.
Additional specimens come from station DH4-1: 29° 28´N, 123° 6´E, water depth 61 m. Muddy with a little sand sediment fraction.
Etymology. This name refers to the East China Sea, where the species was collected. ‘Donghai’ means ‘East China Sea’ in Chinese.
Measurements. Table 1.
Description. Male. Body short, 836–972 µm long. Maximum diameter 27–34 µm. Cuticle finely striated. Epidermal chords consisting of transparent cells present in dorsal, ventral and lateral sides of anterior and middle body parts, especially in pharyngeal region. Buccal cavity funnel-shaped, 5.2–5.7 µm wide and 4.1–4.5 µm deep. Six inner labial papilliform sensilla. Six outer labial setae (9 µm) and four cephalic setae (6.4–7.2 µm) arranged in one circle. Somatic setae absent. Amphids circular, 6.6–6.9 µm in diameter (43.5–47.1% of corresponding body diameter) and 13–15.8 µm (1.7–2.2 times the head diameter) from the anterior body end. Pharynx muscular and cylindrical, 144–172 µm long, 16–20% of body length. Nerve ring 66–94 µm from the anterior body end. Cardia conical, 5.8–6 µm long. Tail conico-cylindrical, 113–136 µm long (5–6.5 times the anal body diameter), cylindrical part long (46-54% of tail length). Three caudal glands in line. Two terminal setae, 6.5–7.5 µm long.
Gonads diorchic and opposed. Anterior testis to the left of the intestine. Posterior testis to the right of the intestine. Spicules L-shaped, 26–31 µm along arc (1.33–1.48 times the anal body diameter), cephalated at proximal end. Gubernaculums tubular, parallel to the distal part of spicules, 9.5 µm long.
Female. Similar to males in most respects. Reproductive system monodelphic, prodelphic. Ovary outstretched, situated to the right of the intestine. Spermatheca oval in shape (43 µm long, 22 µm wide). Vagina short, bending anteriorly. Vulva a transverse slit-like structure, located slightly posterior to midbody, 544 µm (63.6%) from anterior end.
Differentiation diagnosis and discussion. Daptonema donghaiensis sp. nov. is characterized by a short body, finely striated cuticle, six outer labial setae and four cephalic setae in one circle, absence of somatic setae, epidermal chords of transparent cells in anterior and middle body parts, spicules L-shaped and cephalated at proximal end, gubernaculums tubular, tail conico-cylindrical with a long cylindrical part.
Daptonema View in CoL possesses the highest number of valid species in Xyalidae View in CoL and is taxonomically one of the most difficult genera. The presence of transparent cells in epidermal chords is considered one of the diagnostic features by Aryuthaka & Kito (2012). To date, four species of Daptonema View in CoL possessing transparent cells have been reported: D. trabeculosum G. Schneider, 1906 View in CoL ; D. conicum Filipjev, 1922 View in CoL ; D. hyalocella Aryuthaka & Kito, 2012 View in CoL and D. setihyalocella Aryuthaka & Kito, 2012 View in CoL ( Aryuthaka & Kito 2012).
D. donghaiensis View in CoL sp. nov. mostly resembles D. hyalocella View in CoL in its similar body length, finely striated cuticle, tail with a long cylindrical part and two terminal setae. However, it differs in its slender body (maximum diameter 27– 35 µm vs. 36–48 µm), anterior sensilla configuration (6+10 vs. 6+12), narrower head diameter (6.5–9.5 µm vs. 13.5–15.3 µm), larger amphids (35–47% of corresponding body diameter vs. 25–33% of corresponding body diameter), position of amphids (1.7–2.2 times the head diameter vs. 0.5–0.9 times the head diameter, from anterior end), shape of spicules (L-shaped with cephalated proximal end vs. loosely S-shaped without proximal cephalation) and distinct tubular gubernaculums (indistinct in D. hyalocella View in CoL ) ( Aryuthaka & Kito 2012).
D. donghaiensis sp. nov. differs from D. setihyalocella in its body length (786–972 µm vs. 1124–1347 µm), absence of somatic setae, anterior sensilla configuration (6+10 vs. 6+12), position of amphids (1.7–2.2 times the head diameter vs. 0.6–0.9 times the head diameter, from anterior end), tail length (5–6.5 times the anal body diameter vs. 3.6–4.1 times the anal body diameter), length of spicules (26–31 µm vs. 48–57 µm), and gubernaculums without apophysis ( Aryuthaka & Kito 2012).
D. donghaiensis sp. nov. differs from D. trabeculosum in its shorter body (786–972 µm vs. 880–1100 µm), anterior sensilla configuration (6+10 vs. 6+12), position of amphids (1.7–2.2 times the head diameter vs. 0.9 times the head diameter), shorter spicules (26–31 µm vs. 34–36 µm), gubernaculum shape (tubular vs. gubernaculum with lateral piece) and absence of somatic setae.
D. donghaiensis sp. nov. resembles D. conicum in its similar body length, cephalic setae configuration and similar values of de Man’s c ratios. However, it differs in its slender body (maximum diameter 27–35 µm vs. 36–43 µm), longer cephalic setae (6.4 µm vs. 2 µm), larger amphids (6–7.7 µm vs. 4 µm), position of amphids (1.7–2.2 times head diameter vs. 1.4 times the head diameter, from anterior end) and shorter gubernaculums (9.5 µm vs. 17 µm) ( Lorenzen 1977).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Daptonema donghaiensis
| Wang, Chunming, An, Liguo & Huang, Yong 2018 |
D. donghaiensis
| Wang & An & Huang 2018 |
D. hyalocella
| Aryuthaka & Kito 2012 |
D. setihyalocella
| Aryuthaka & Kito 2012 |
D. hyalocella
| Aryuthaka & Kito 2012 |
D. hyalocella
| Aryuthaka & Kito 2012 |
Xyalidae
| Chitwood 1951 |
D. conicum
| Filipjev 1922 |
Daptonema
| Cobb 1920 |
Daptonema
| Cobb 1920 |
D. trabeculosum
| G. Schneider 1906 |