Tarsonemus fraxini, Magowski, Wojciech L. & Khaustov, Alexandr A., 2006
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.174647 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6494060 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B8767E-4F58-FFE6-FEC4-FC13AE1CFC0B |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Tarsonemus fraxini |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Tarsonemus fraxini n. sp.
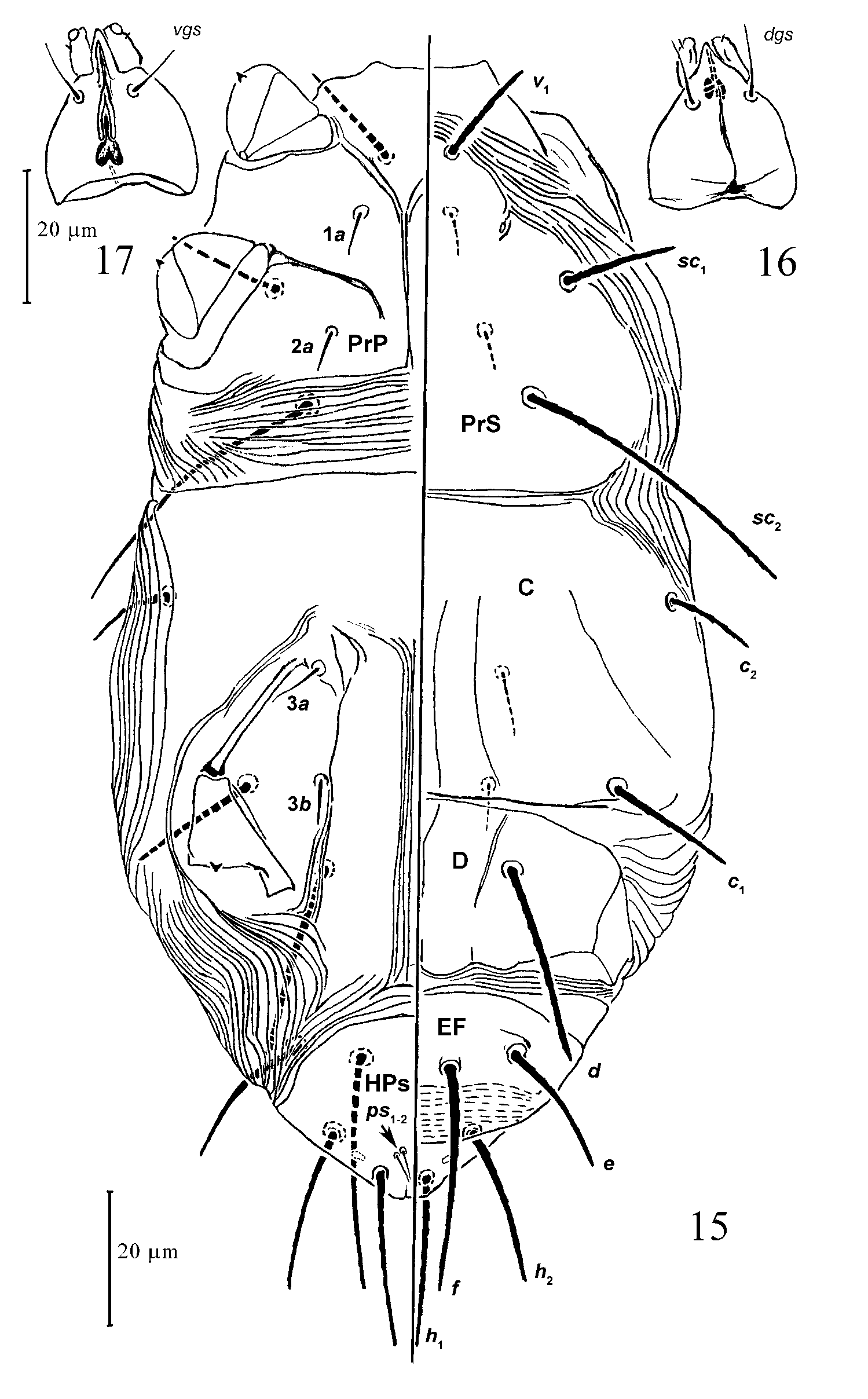
( Figs. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 3 –20)
Diagnosis
All instars: pharyngeal glandular bodies half as long as the length of the external part of the pharynx. Tarsi of leg I–III lacking one attenuate seta, femora I with 3 setae. Female: dorsal opisthosomal setae f stronger and longer than others on opisthosomal dorsum, esp. c2; tegula slightly wider than long, dorsal and ventral shields with varying ornamentation: dimples being larger towards margins of shields. Male: dorsal setae (except for sc2 and c2) strong, roughly serrate. Dorsal ornamentation made up of smaller and larger distinct dimples (as in female), ventral ornamentation with small, scattered dimples. Solenidion Φ located slightly proximally of transverse midline of constricted tibia IV. Larva: all dorsal setae strong, roughly serrate, stiff, weakly tapering, c2 shorter than c1.
Females of the T. fraxini can be distinguished from the similar species, T. naegelei Suski , by: (1) setae v1 half as long as the distance between their bases (exceeding the distance between their bases in T. naegelei ); (2) differentiated ornamentation of the metapodosomal plate, including smaller and larger dimples (uniform in T. naegelei ). Males can be differentiated by: (1) dorsal setae d subequal in length to f (setae d longer than f in T. naegelei ); (2) ornamentation of shield CD restricted to dimples (with lines and dimples in T. naegelei ). Larvae can be differentiated from T. spatulaphorus Magowski & Khaustov by having setae sc2 longer than the distance between their bases and all dorsal setae stout and robust (setae sc2 much shorter that the distance between their bases and dorsal setae shorter, more slender and attenuate in T. spatulaphorus ).
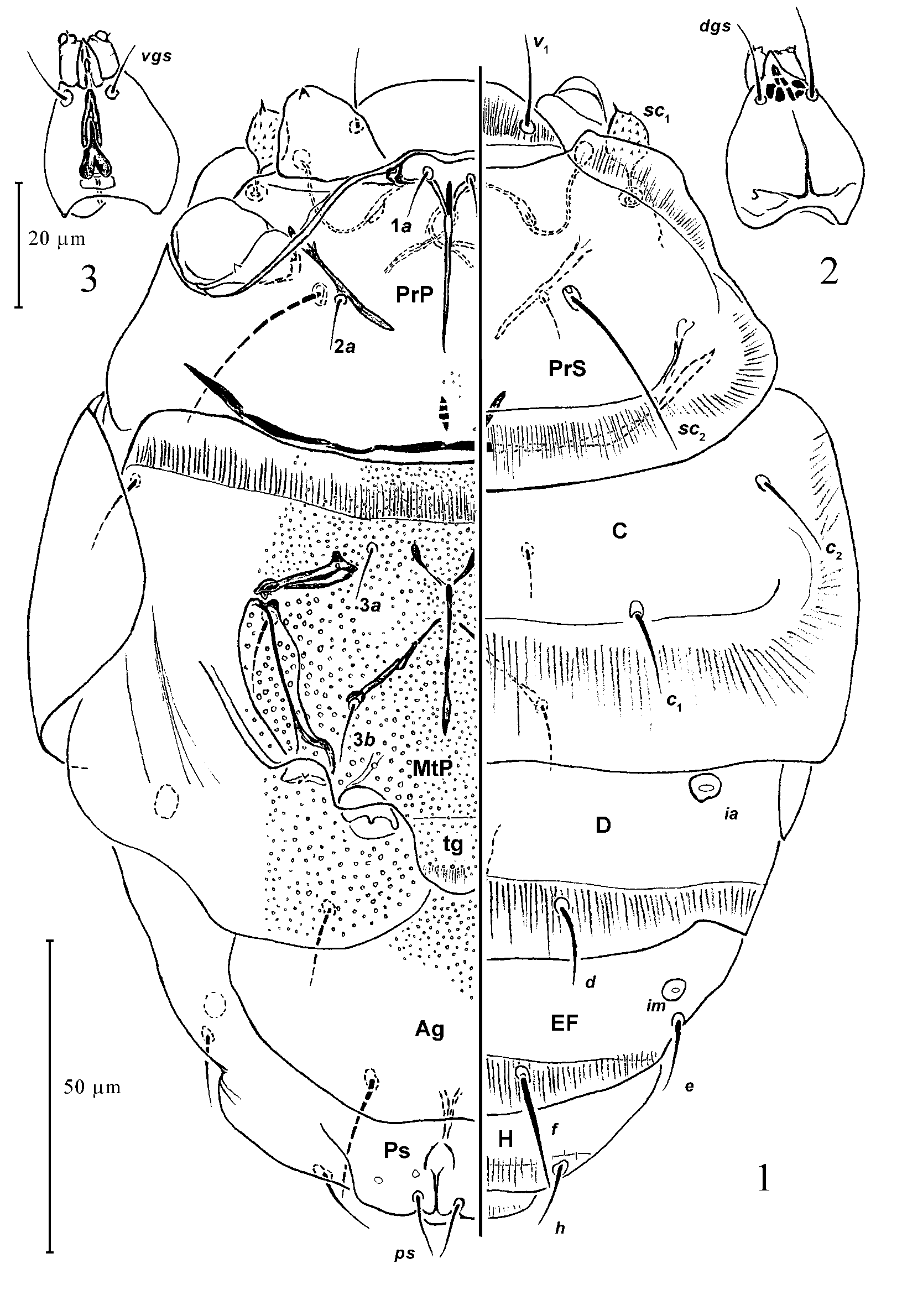
Description: Female ( Figs. 1–7 View FIGURES 1 – 3 View FIGURES 4 – 7 )
Gnathosoma: ovoid-conical in shape; pharynx width less than 0.2x the basal width of gnathosoma, with a pair of large glandular bodies posteriorly. Chelicerae small, short. Palpi over twice as long as their basal width, each with small palptarsal process and two minute setae. Palptibial claw almost indiscernible. Setae dgs only slightly longer than vgs, setae pp indiscernible.
Idiosomal dorsum (length = 1.7x width): relative length of setae ( v1: sc1: sc2: c2: c1: d: e: f: h): 1: 0.8: 1.7: 0.7: 0.7: 0.9: 0.6: 1.1: 0.6. Rostral shieldlet over 3x wider than long. Prodorsal shield about 1.6x as wide as long. Tracheae with visible atria; no postatrial sacs or other structures present. Distance between setae v1 ca. 1.7x of their length. Pits v2 indiscernible. Setae sc2 located nearly at midline of prodorsal shield, their tips extending to the posterior edge of prodorsal shield; the distance between their bases about 1.5x their length. Setae c2 extending halfway to the bases of c1. Tips of setae c1 extending halfway to the posterior edge of tergite C. Setae d reaching well beyond the posterior edge of tergite D; the distance between their bases being about 2.6x their length. Setae f spaced by a distance of about 1.7x their length. The distance between bases of setae h slightly over 4x their length. All dorsal setae slender, sharply pointed; d and f weakly barbed, remaining ones smooth. Tergites covered with dimpled sculpture, dimples being bigger and more sparsely arranged towards the margins of shields and of the idiosoma in general.
Idiosomal venter: apodemes 1 pronounced, sclerotized, fused to anteromedian apodeme; that well defined up to the level of posteromedian ends of apodemes 2, diffuse further posteriorly. Sejugal apodeme well defined, tripartite, almost continuous, with lateral parts weakly bent anterolatelally. Setae 1a located on apodemes 1, separated by a distance of 1–1.3x their length. Setae 2a located on apodemes 2; the distance between their bases being almost 5x their length. Ventral propodosomal plate concave anteriorly, its lateral edges without apparent bent between proximal corners of trochanters I and II. Apodemes 3 not extending beyond condyli of trochanters III, apodemes 4 reaching to bases of setae 3b; posteromedian apodeme with pronounced anterial bifurcation. Setae 3a located at a distance of over 3x their length from the bases of setae 3b, and separated from each other by a distance shorter than that between 3b. Setae 3b longer than 3a, separated by a distance of over 3x their length. Ventral metapodosomal plate concave anteriorly, with angularity between trochanters III and IV. Trochanters IV divided by an interval of ca. 2.5x their diameters. Tegula slightly wider than long. The distance between bases of setae ps about 0.7x their length. Venter with ornament consisting of smaller and larger dimples, the latter particularly expressed in the distal areas of the metapodosomal, laterogenital, and aggenital plates.
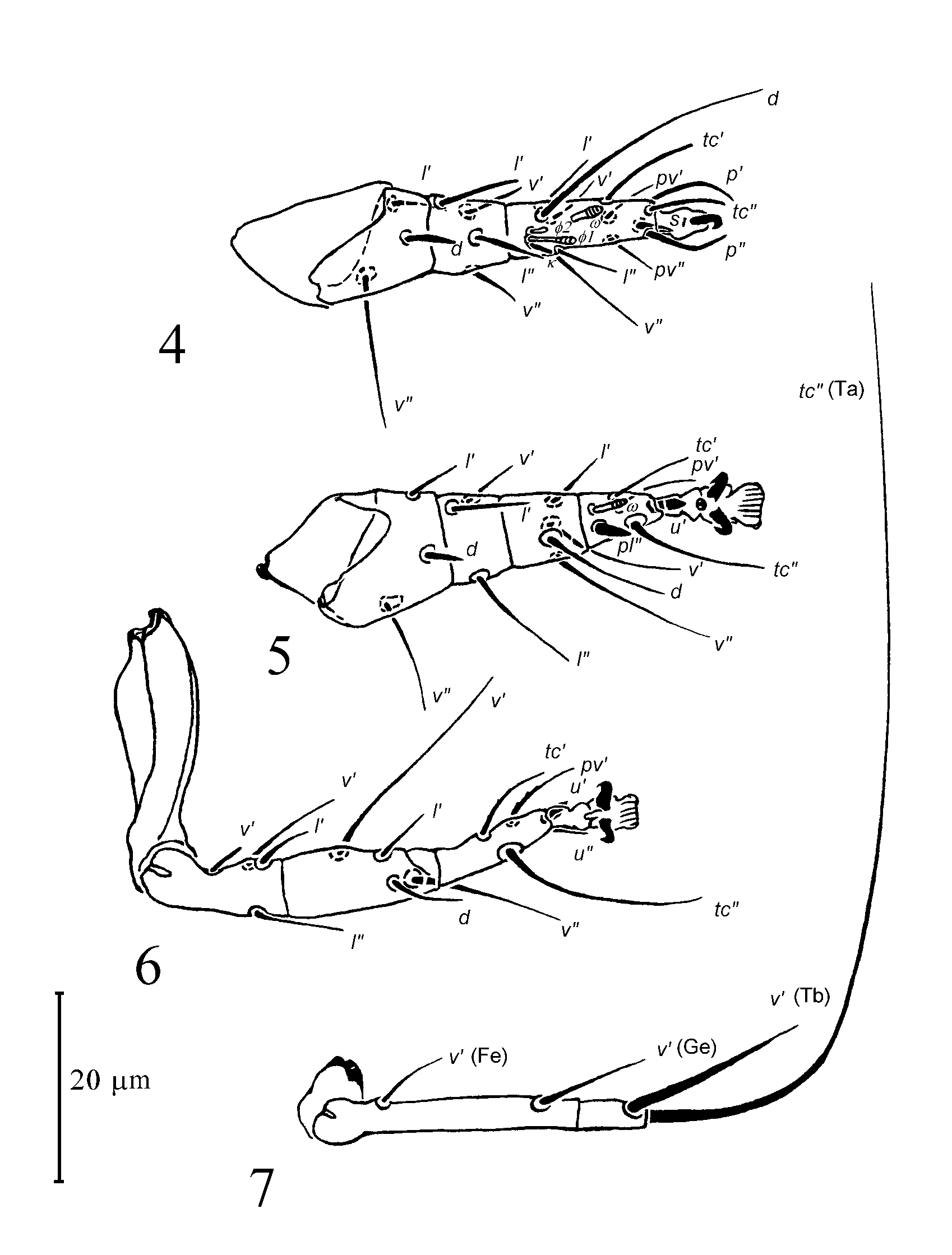
Legs: Proportions of free segments of legs: (I: II: III: IV): 1: 1: 1.2: 0.9. Leg chaetotaxy (for Fe, Ge, Tb and Ta): leg I: 3-4-6(2Φ)+7(1ω); leg II: 3-3-4-5(1ω); leg III: 1+3-4-4. Leg I: claw smaller than those of tarsi II and III. Spine-like seta s small, acute, slightly smaller than seta u' on leg II and as large as that on III. Setae u’ and u” indiscernible. Tibiotarsus ca. 2.6x as long as wide at base. Three subequal eupathidia inserted apically on tibiotarsus I ( p', p" and tc"); tc' longer, inserted in distal part of segment. Seta pl' missing from tarsal part of a segment. Solenidion ω with striated head, slightly longer than Ta ω II. Tibial solenidion Φ 2 smaller, Φ 1 nearly twice larger; only Φ 2 with striation; famulus k subequal to Φ2; located at the same level. Seta l' on genu stiff, blunt-ended. Femur I without ventral lobe. Femoral seta l" missing, l' weak, d stouter. Leg II: claws typically sized, hooked; empodium medium-sized, striated. Tarsal spine-like seta pl" as large as solenidion Ta IIω, located at nearly same level. Tarsal seta tc" the longest on a segment; pv" missing. Tibia cylindrical, with v" the longest, and l' the shortest; seta Ge l' stiffer than remaining ones on the segment. Femur with seta d stout, spine-like. Leg III: claws smaller than those on leg II. Seta tc" ca. 2x as long as other setae of segment; pv" missing from tarsus. Leg IV: free segments of leg apparently longer than femurogenu and tibia III. Femurogenu 4x longer than tibiotarsus. Tarsal seta tc" over 2.6x as long as whole leg IV. Seta Tb v' shorter than length of femurogenu. Genual seta v' ca. 1.6x longer than femoral v'; located in a distance nearing the distal width of Fege from the end of segment.
Measurements ( holotype, followed by four paratypes from the type locality in parentheses): Body and tagmata: Length of body: 188 (203–215); length of idiosoma: 161 (171–191); width of idiosoma: 100 (105–113); length of gnathosoma: 30 (30–33); width of gnathosoma: 23 (20–25); length of pharynx: 9 (9–10); width of pharynx: 4 (4); dgs: 10 (8–11); vgs: 9 (8–9). Dorsum: length of PrS: 67 (63–68); width of PrS: 102 (103–110). Length of setae: v1: 17 (15–18); sc1: 12 (13–14); sc2: 28 (27–30); c2: 13 (11–13); c1: 12 (11–13); d: 13 (13–15); e: 10 (10–12); f: 17 (16–22); h: 7 (8–11). Distances between setae and stigmae: v1–v1: 28 (27–28); sti–sti 45 (45–47); sc1–sc1: 57 (50–80); sc2–sc2: 41 (40–43); c2–c2: 96 (95–100); c1–c1: 55 (54–60); c1–c2: 28 (29–30); d–d: 34 (34–38); e–e: 71 (72–77); f–f: 21 (20–25); e–f: 26 (25–29); h–h: 36 (39–40). Venter: length of setae: 1a: 5 (4–6); 2a: 7 (6–7); 3a: 6 (6–8); 3b: 7 (7–10); ps: 8 (8–10). Distances between setae: 1a–1a: 6 (6–7); 2a–2a: 31 (33–35); 3a–3a: 27 (25–26); 3b–3b: 30 (27–32); ps–ps: 5 (6–6). Length of PrP: 49 (46–49); width of PrP: 99 (98–108); ap. 1–1: 16 (16–17); ap. 2–2: 46 (44–48); length of tegula 11 (10–11); width of tegula 13 (12–13). Leg segments and leg setae (length): Tbt I: 16 (15–17); Ta I ω: 4 (4–5); Τb Ι Φ 2: 2 (2–3); Τb Ι Φ 1: 5 (5–5); Tb I k: 3 (3–4); Ta II ω: 3 (3–4); Ta II pl": 4 (4–4); Tbt IV: 8 (8–8); Ta IV tc": 100 (95–110); Tb IV v': 23 (25–28); Fege IV: 32 (29–34); Ge IV v': 13 (13–15); Fe IV v': 9 (7–10).
Male ( Figs. 8–14 View FIGURES 8 – 10 View FIGURES 11 – 14 )
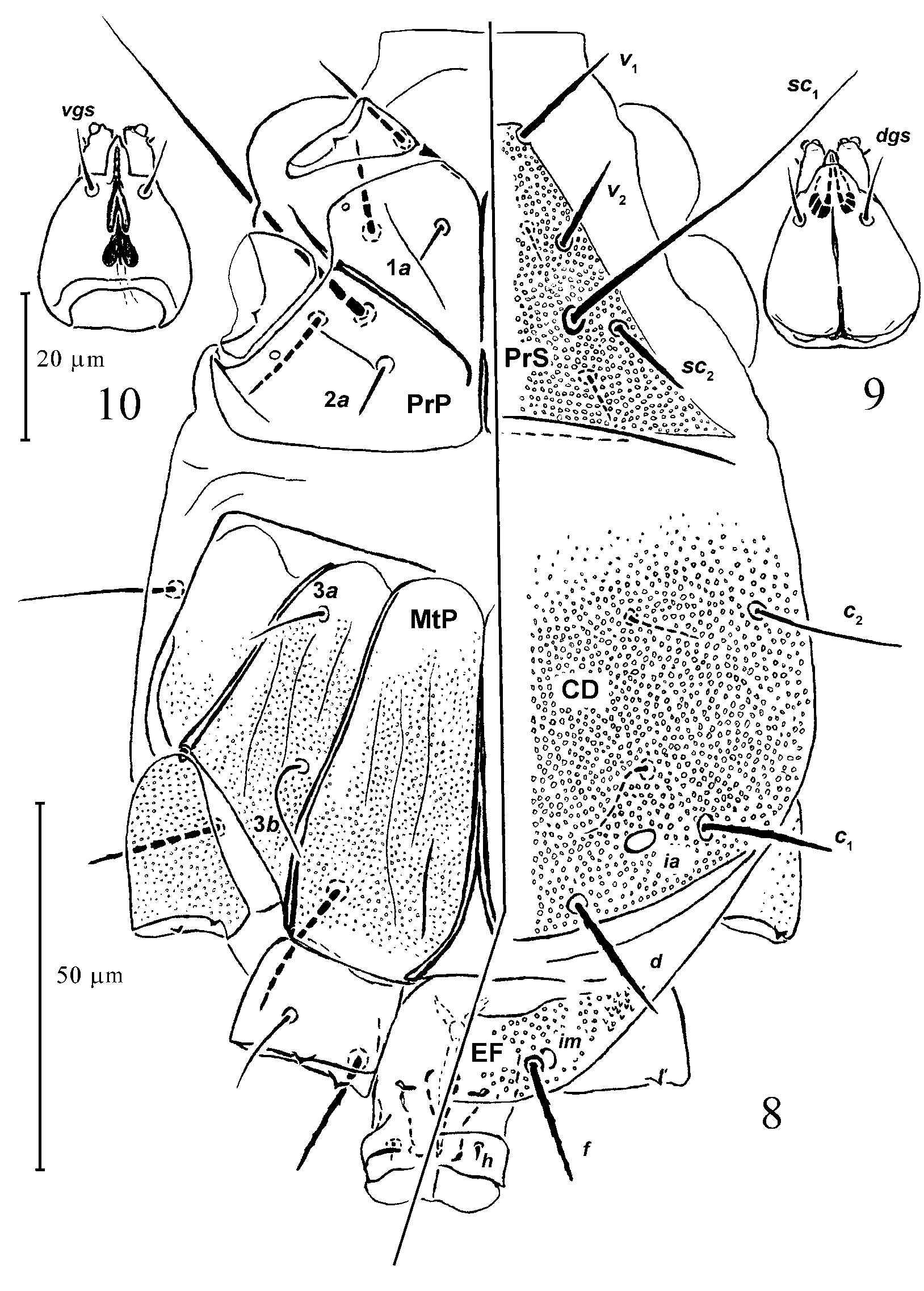
Gnathosoma: similar to that of a female but shorter. Pharynx less wide than 0.2x of basal width of gnathosoma, as long as half of ventral length of capsule; with a pair of large glandular bodies posteriorly (sclerotization defined as in female). Idiosomal dorsum (length=1.7x width): relative length of setae ( v1: v2: sc1: sc2: c2: c1: d: f): 1: 0.8: 3.1: 0.8: 1.2: 1.2: 1.3: 1.1. Prodorsal shield (PrS) about 1.7x as wide as long. Setae v1 separated by a distance of 0.9x their length. Setae sc2 located just behind the level of sc1. Setae sc1 located posterior of two-thirds of the length of prodorsal shield, reaching beyond the level of setae c2, placed in a distance of 0.5x their length each to another. Setae c2 reaching no further than 0.7x of the distance to the bases of c1. Setae c1 located by a distance to bases of d slightly shorter than their length. Setae d reaching far beyond the posterior edge of shield CD; separated by a distance of almost 1.4x their length. Setae f located by a distance of ca.
1.3x their length each to another. Setae sc1 and c2 slender, pointed; v1, v2, sc2, c1, d and f stiff and blunt or pointed; all barbed. Cupuli im contiguous with bases of f. Genital capsule with hyaline flange from small to moderate in size. Accessory stylets weak, located in distal part of genital capsule. Dorsum shields covered with coarse, uniform dimpled sculpture.
Idiosomal venter: anteromedian apodeme connecting anteriorly with apodemes 1, interrupted anteriad of bases of 2a. Apodemes 2 not visibly joining with anteromedian one. Sejugal apodeme mostly obscured except medial and lateral parts. Coxal setae la separated by a distance of about 2x their length; setae 2a ca. 2x longer, bases separated by less than their 3x their length. Setae 3a shorter than 3b. Setae 3a separated by a distance of almost 4x their length, setae 3b separated by a distance of almost 3.5x their length. Distance between bases of setae 3a apparently shorter than that between 3b.. Setae 1a and 2a stiffer, 3a and 3b more slender; all smooth. Apodemes 4 and 3 joined with each other and with posteromedian apodeme by diffused areas. Ventral propodosomal plate not clearly ornamented, coxal fields III and IV very indistinctly dimpled (nearly smooth), each with several weak parallel lines; lateral fields of ventral metapodosomal plate poorly dimpled posteriorly.
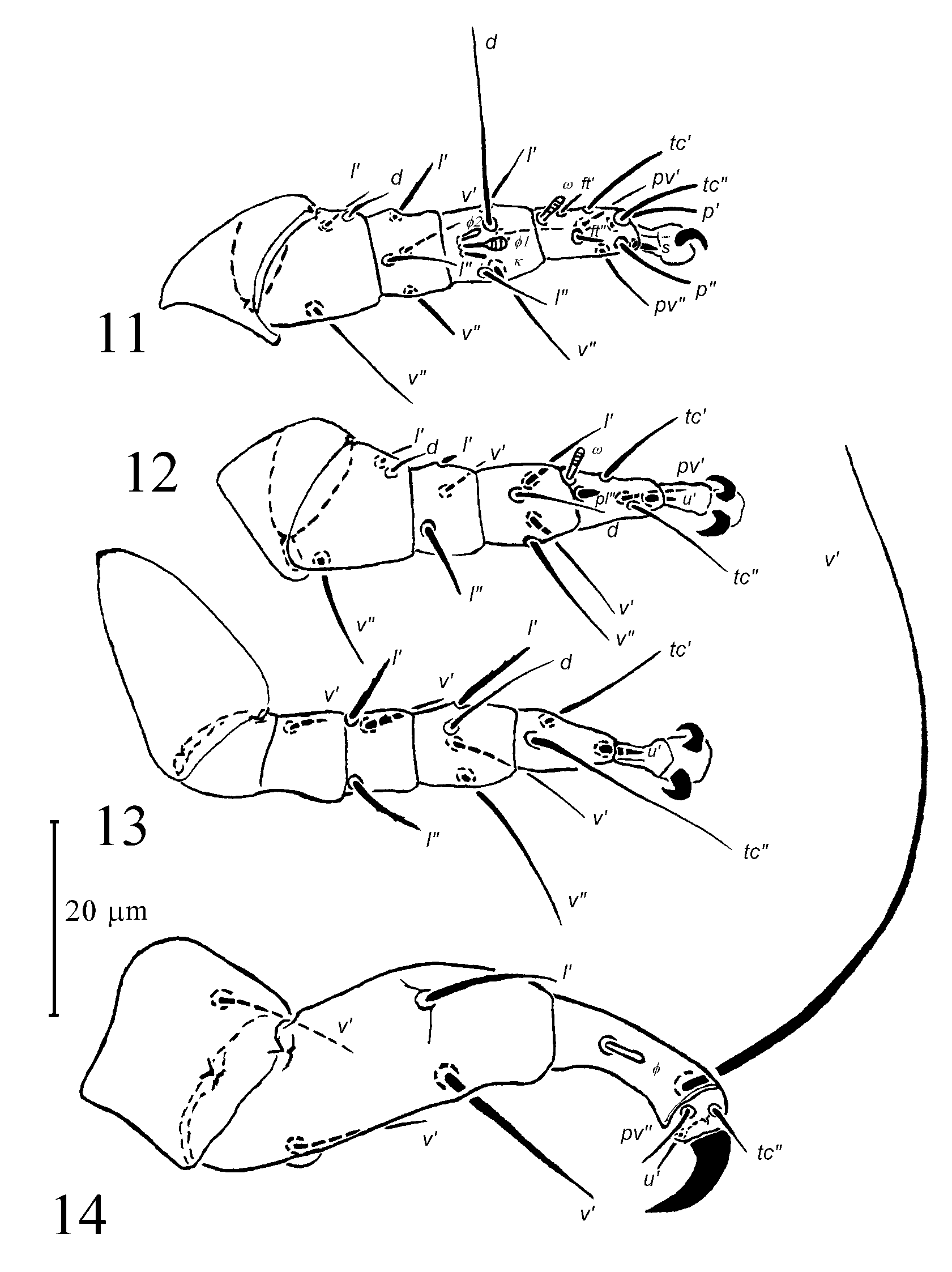
Legs: Proportions of free segments of legs (I: II: III: IV): 1: 1: 1.1: 1.5. Leg chaetotaxy: leg I: 3-4-6(2Φ)-9(1ω); leg II: 3-3-4-5(1ω); leg III: 1-3-4-3. Leg I: claw apparently weaker than those of tarsi II and esp. III. Seta s weakly spine-like, smaller than setae u' of Ta II and III. Tarsus slightly less than 2x as long as wide at the base. Three subequal eupathidia ( tc", p' and p") inserted apically on tarsus, one ( tc') at midline of the tarsus. Solenidion ω inserted almost at the base of segment, with small, striated head, smaller than Ta II ω. Both fastigial eupathidia ft' and ft" present, similar in length to ω. Tibial solenidion Φ 2 small, Φ 1 almost twice larger; eupathidion k rod-like, as long as Φ 2, located in row with solenidia. Setae genual l' and femoral d not stronger than other setae of segments. Femoral l" missing. Leg II: claws strong, hooked; empodium moderate. Spine pl" subequal to solenidion ω; both located at the base of segment. Seta tc" longer than other setae of segment, reaching to the tip of empodium. Seta Ge l' very short, stout. Femoral setae d and l' slender, both short. Leg III: claws and empodium slightly larger than those on leg II. Setae flanking pretarsus, p' and u' hardly discernible. Seta tc" reaching beyond the empodial pad, both with tarsal tc' attenuate; pv" missing. Tibial seta v" nearly as long as tarsal tc". Tibial l', genual l', v' and l" stout, barbed. Leg IV: Free segments of leg IV longer as those of leg III. Tarsal claw curved, blade like, 3x as long as wide at the base. Tarsus separate from tibia, with three small setae (all subequal in length). Tibia nearly 4x longer than tarsus, 2.5x longer (adaxial face) than its basal width, constricted at midlength. Tibial solenidion Φ slightly larger than tarsal solenidia of legs I and II, with slightly expanded head, smooth. Seta Tb v' attenuate, whip like, smooth, about 1.5x longer than free segments of leg IV. Femurogenu IV ca. 2.3x as long as wide at the base, with very small posterior protrusion at the base of the seta Fe v'. Setae Ge v' and l” strong, tapering, pointed, Fe v' as long as Ge l" but weaker. Seta v' on trochanter subequal to Ge l' and Fe v'.
Measurements (three male paratypes): Body and tagmata: Length of body: 176–190; length of idiosoma: 148–162; width of idiosoma: 86–96; length of gnathosoma: 25–29; width of gnathosoma: 21–23; length of pharynx: 6–7; width of pharynx: 3–3; dgs: 7–8; vgs: 7–7. Dorsum: length of PrS: 41–42; width of PrS: 68–70. Length of setae: v1: 15–19; v2: 13–16; sc1: 50–57; sc2: 12–15; c2: 18–24; c1: 19–22; d: 20–26; f: 17–19; h: 1,5–2. Distances between setae: v1–v1: 14–17; v2–v2: 25–27; sc1–sc1: 26–30; sc2–sc2: 41–45; c2–c2: 76–80; c1–c1: 63–65; c1–c2: 30–34; d–d: 30–32; f–f: 23–23; h–h: 11–11. Venter: length of setae: 1a: 4–5; 2a: 9–10; 3a: 10–11; 3b: 12–14. Distances between setae: 1a–1a: 10–10; 2a–2a: 24–27; 3a–3a: 37–42; 3b–3b: 41–48. Length of PrP: 38–39; width of PrP: 61–73; ap. 1–1: 17–22; ap. 2–2: 35–40. Length of genital capsule 22–26; width of genital capsule 22–23. Leg segments and leg setae (length): Ta I: 10–11; Ta I ω: 3–4; Τb Ι Φ 2: 2–3; Τb Ι Φ 1: 4–5; Tb II k: 3; Ta II ω: 3–4; Ta II pl": 3–4; claw IV length: 9–13; claw IV width: 3–4; Tb+Ta IV: 16–23; Tb IV v': 87–92; Tb IV Φ: 4–5; Fege IV: 28–40; Ge IV v': 20–24; Ge IV l" 12–16; Fe IV v': 11–15.
Larva ( Figs. 15 View FIGURES 15 – 17 –20)
Gnathosoma: slightly smaller than in adults, otherwise similar. Pharynx width approximately 0.16x basal width of gnathosoma, and shorter than its ventral length. Setae dgs slightly longer than vgs. Chelicerae slightly weaker than those in adults. Palpi pronounced; palptibial claw indiscernible.
Idiosomal dorsum (length= 2x width); relative length of setae ( v1: sc1: sc2: c2: c1: d: e: f: h2: h1): 1: 0.9: 2.8: 1.2: 1.2: 1.8: 1.4: 2.2: 1.5: 1.7. Prodorsal shield approximately 1.3x as wide as long. Setae v1 separated by a distance of 0.7x their length. Setae sc2 located at 0.7x of the length of prodorsal shield, extending beyond the posterior edge of the prodorsal shield by approximately 0.7x of their length, and separated by a distance of about 0.8x their length. Setae c2 reaching halfway to the bases of c1, separated from each other by a distance of approximately 3x their length. Setae d extending beyond the posterior edge of tergite D by about half their length; setae separated by about one setal length. Setae e separated by a distance of 1.5x their length. Distance between setae e and f less than 0.5x length of e, between bases setae f approximately 0.4x the length of f. Setae h2 separated by a distance of 0.9x their length; h1 by a distance by about 0.3x their length. Cupuli ia and im indiscernible. Cupuli ih located half way between bases of h1 and h2. All dorsal setae stiff, blunt, barbed. Dorsal shields smooth.
Idiosomal venter: apodemes 1 and 2 and anteromedian apodeme distinct; the latter weakening posteriad of apodemes 2. Setae 1a the shortest, separated by a distance of ca. 2.5x their length, setae 2a by a distance of almost 3,6x their length. Setae 3a longer than 2a, bases of 3a and 3b separated by a distance of almost twice their length. Setae 1a, 2a and 3b stiff, blunt-ended, setae 3a slender, sharp; all smooth. Two pairs of minute setae ps symmetrically arranged between and anteriad of bases of h1. Ventral shields smooth; ventral coxal plates divided by a large area of densely striated cuticle.
Legs: Proportions of free segments of legs (I: II: III): 1: 0.9: 0.9. Leg chaetotaxy: leg I: 3-4-6(1Φ)-5(1ω); leg II: 3-3-4-4(1ω); leg III: 1-3-4-3. Leg I: Claws weak, smaller, than those of legs II and III. Seta s spine-like, slightly smaller than u' on tarsi II and III. Tarsus ca. 1.7x as long as wide at its base. Eupathidia tc' and tc" subequal in length, both located subapically. Solenidion ω approximately as large as Ta II ω. Solenidion Φ 1 with smooth head, apparently longer than famulus k. Seta Ge l" stiffer than others, pointed. Setae l' and d on femur minute, pointed, l" missing. Leg II: Claws and empodium pronounced. Spine pl" short, blunt, located at nearly same level as solenidion ω. Seta tc" longer than tc', reaching beyond the distal edge of the empodium. Seta Ge l' very short, stout, blunt. Setae d and l' on femur tiny, stiff, short. Leg III: Claws weaker than those on tarsus II. Seta tc" nearly twice as long as tc', reaching far beyond the edge of the empodium. Tibial setae d, l' and genual l' stiff.
FIGURES Tarsonemus fraxini , larva paratype. 18,leg I; 19, leg II; 20, leg III.
Measurements (five larval paratypes): body and tagmata: length of body: 180–200; length of idiosoma: 152–172; width of idiosoma: 76–91; length of gnathosoma: 23–29; width of gnathosoma: 19–23; length of pharynx: 7–9; width of pharynx: 3–4; dgs: 8–10; vgs: 8–9. Dorsum: length of PrS: 45–55; width of PrS: 62–70. Length of setae: v1: 12–17; sc1: 13–16; sc2: 31–49; c2: 16–22; c1: 16–22; d: 20–33; e: 15–23; f: 22–41; h2: 15–26; h1: 22–29. Distances between setae: v1–v1: 10–12; sc1–sc1: 40–45; sc2–sc2: 31–35; c2–c2: 65–78; c1–c1: 55–63; c1–c2: 26–29; d–d: 25–30; e–e: 31–34; f–f: 13–16; e–f: 9–10; h2–h2: 19–21; h1–h1: 7–8. Venter: length of setae: 1a: 5–6; 2a: 6–7; 3a: 9–10; 3b: 6–7; ps: 4.5–5. Distances between setae: 1a–1a: 11–15; 2a–2a: 21–25; 3a–3b: 15–19; ps–ps: 2.5–4. Length of PrP: 25–32; width of PrP: 62–74; ap. 1–1: 21–22; ap. 2–2: 41–42; length of HPs: 26–29; width of HPs: 32–39. Leg segments and leg setae (length): Tbt I: 8–10; Ta I ω: 3–4; Τb Ι Φ 1: 5; Tb I k: 3; Ta II ω: 3; Ta II pl": 2–3.
Material
Female holotype, 4 female paratypes, 3 male paratypes, 5 larvae paratypes, all in the galleries of Hylesinus fraxini (Panzer, 1779) under bark of Fraxinus oxycarpa, Yalta , Crimea, Ukraine, 03. 11. 1996, leg. A.A. Khaustov.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |