Lactarius kamengensis, Bera & Das, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5252/cryptogamie-mycologie2023v44a11 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10372475 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B89C63-3C28-FFB4-9382-F96CBF68FC72 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Lactarius kamengensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
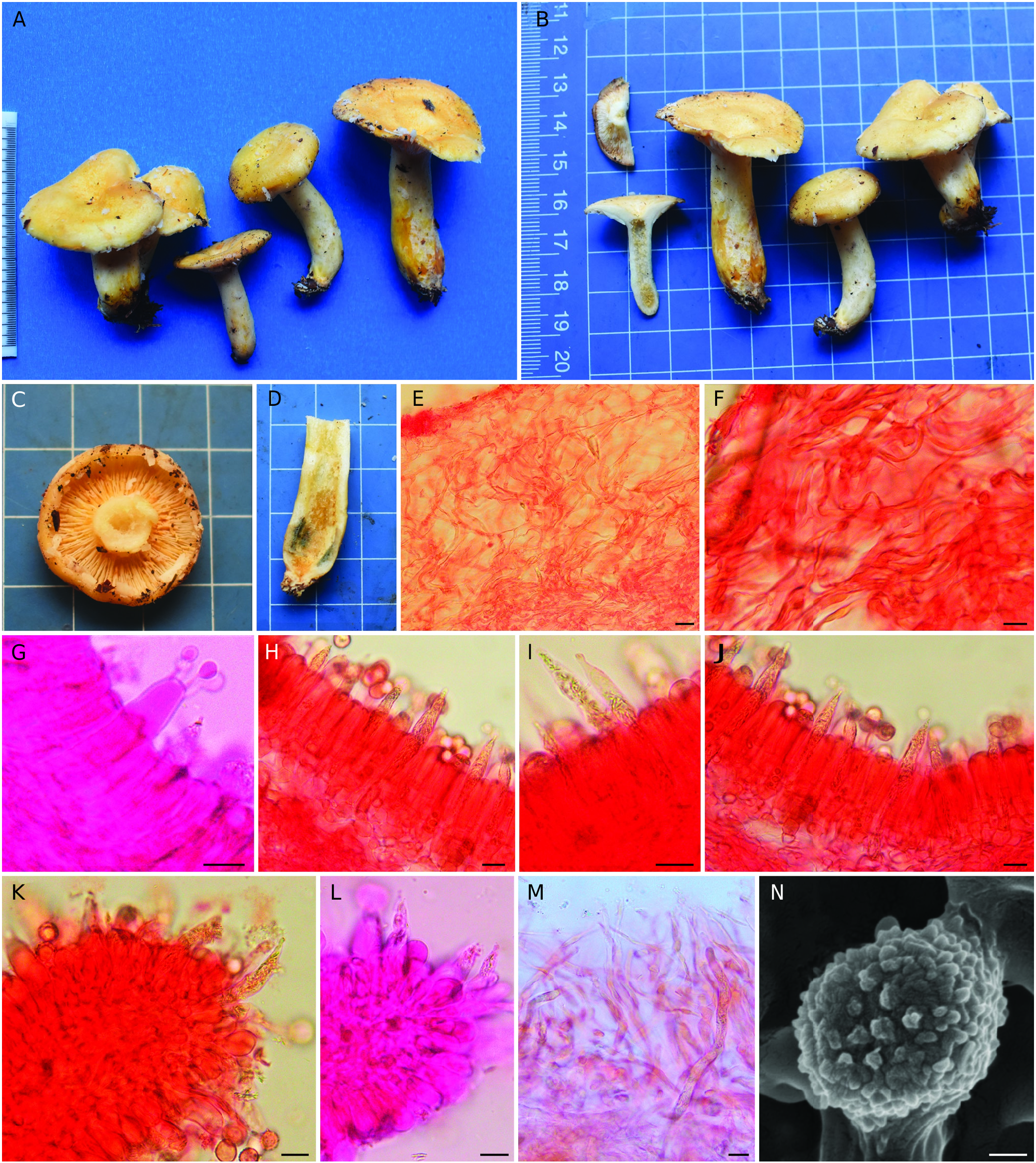
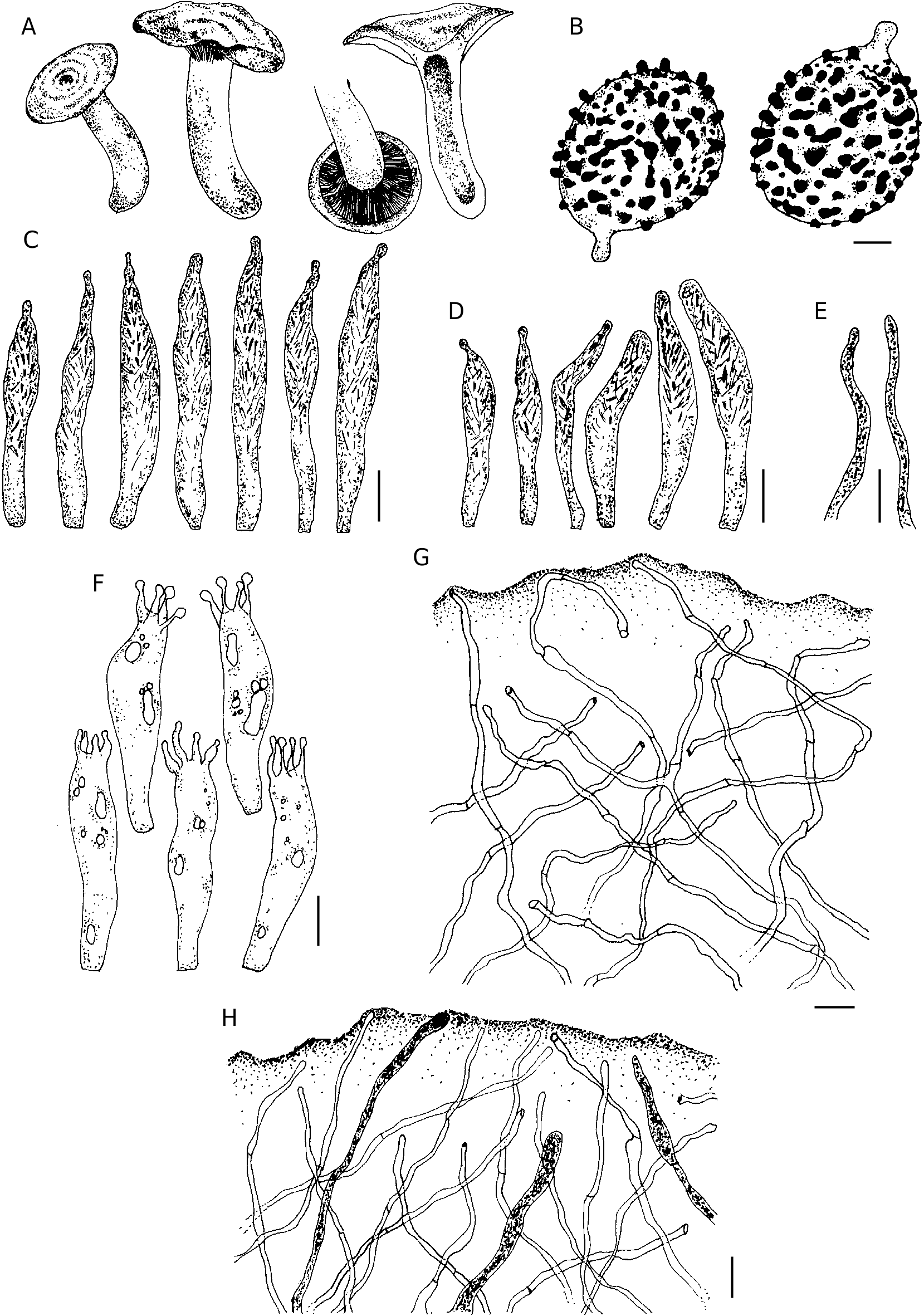
Lactarius kamengensis sp. nov.
( Figs 3 View FIG ; 4 View FIG )
A medium-sized bitter to acrid tasting Lactarius with pale yellowish, vaguely zonate pileus, scrobiculate stipe, white latex turning pale yellowish and occurring under Castanopsis (D.Don) Spach.
HOLOTYPE. — India. Arunachal Pradesh, West Kameng district, Shergaon , 27°09.216’N, 92°16.174’E, alt. 2369 m a.s.l., scattered 0.01 on soil under Castanopsis in temperate broadleaf forest, 28.VII.2019, I. Bera, IB 19-016 (holo-, CAL [ CAL 1878 ]!) GoogleMaps .
ADDITIONAL SPECIMEN EXAMINED. — India. Arunachal Pradesh, West Kameng district, Shergaon , 27°07.810’N, 92°15.116’E, alt. 2243 m a.s.l., scattered on soil under Castanopsis in temperate broadleaf forest, 30.VIII.2019, I. Bera, IB 19-054 ( CAL [ CAL 1879 ]) GoogleMaps .
ETYMOLOGY. — Referring to the type locality, West “Kameng” district of Arunachal Pradesh.
GENBANK. — OP806537 (nrITS, holotype) and OP806830 (nrITS, IB 19-054), OP811192 (nrLSU, holotype) andOP811193 (nrLSU, IB 19-054).
MYCOBANK. — MB 848906.
DESCRIPTION
Pileus 40-60 mm diam., convex when young, gradually becoming planoconvex on maturity; surface moist, smooth, slightly viscid; surface zonate, with combination of pale yellow, greyish yellow to greyish dull yellow (2-4B3), a little darker on maturity but fading towards margin, mostly with whitish concentric, rather vague zones; margin entire, rarely lobed, incurved. Lamellae subdecurrent, yellowish white, crowded (20 L+l/cm at pilear margin); lamellulae present in 4-5 series; concolorous; edge entire. Stipe 40-70 × 18-20 mm, central, cylindrical; surface viscid, yellowish white (1A2) with distinct greyish yellow (4B4) scrobicules at base. Context in pileus thick, pithy in stipe, yellowish white (1-2A2), unchanging in 3% KOH and FeSO4 but immediately turning greenish blue in guaiac. Latex white, turning pale yellow to light yellow within 10 seconds, very bitter. Taste quite bitter at first, then acrid. Odor mild. Spore print could not be obtained.
Basidiospores 7.4-8.5-9.8(10) × 6.2-7-7.89 µm, (n = 30, Q =1.08-1.2-1.39), usually subglobose to ellipsoid; ornamentation amyloid, up to 1.1-1.7 µm high, composed of isolated warts, sometimes fused into short ridges but never forming any reticulum; suprahilar spot inamyloid. Basidia 35.4-46.9× 7.8- 10.4 µm, subclavate, 4-spored; sterigmata 3-6 × 1-2.5 µm. Pleuromacrocystidia abundant, 47-70×4.5-8 µm, emergent up to 26 µm, subcylindric with fusoid, subfusoid to mucronate apices, thin-walled; content dense, granular to fibrous. Pleuropseudocystidia abundant, 1.2-1.4 µm wide, mostly non-emergent, cylindrical to slightly tortuous, with rounded apex. Lamellae edge heteromorphous with basidia, basidioles and cystidia. Cheilomacrocystidia rare, 37-55× 5-7.5 µm, emergent up to 20 µm, subcylindric with subfusoid to appendiculated apices, thin-walled; content dense, granular to fibrous. Subhymenium up to 29 µm thick, cellular. Lamellar trama composed of lactifers, sphaerocytes, and connecting hyphae. Pileipellis up to 215 µm thick, an ixotrichoderm; suprapellis composed of interwoven, septate, mostly ascending hyphae. Stipitipellis up to 114 µm thick, an ixotrichoderm; suprapellis composed of interwoven, septate, mostly ascending hyphae intermixed with lactifers.
NOTES
The presence of viscid, zonate, pale yellowish pileus with scrobiculate stipe clearly indicates that the described species is a member of section Zonarii ( Heilmann-Clausen et al. 1998) . Moreover, bitter to acrid tasting medium-sized basidiomata with slightly viscid, zonate, greyish yellow to pale yellow pileus, scrobiculate (towards the base) stipe, white latex turning the cut lamellae light yellowish and the positive macrochemical reaction of the context with guaiac make the studied Lactarius sp. quite distinct in the field. Further, the micromorphological characters such as the basidiospore ornamentation of isolated warts sometimes connected with ridges and ixotrichoderm nature of the pileipellis and stipitipellis make it a recognizable species amongst its other relatives. The similar stature of the basidiocarp, its zonate yellowish pileus and the occurrence with broad-leaved trees remind of the European L. zonarius (Bull.) Fr. Yet striking dissimilarities in characters such as the pale pinkish buff pileus with ochraceous zones, tomentose margin, smaller spore ornamentations (only up to 0.75-1.0 µm high) and ixocutis pileipellis of L. zonarius segregate it from the currently studied specimens of Lactarius ( Heilmann-Clausen et al. 1998) . The zonate pileus character has been shared with some of the closest Asian species belonging to the subsect. Zonarii and associated with broad-leaved forest trees, L. austrotorminosus H.T.Le & A.Verbeken ( Thailand), L. austrozonarius H.T.Le & A.Verbeken ( Thailand), L. sinozonarius X.H.Wang ( China), and L. indozonarius Uniyal, K.Das & Nuytinck ( India). Despite that, pale orange to pinkish basidiomata with infundibuliform, papillate, hairy pileus with hairy margin and absence of cheilomacrocystidia in L. austrotorminosus and robust basidiomata (pileus 50-135 mm diam., stipe 25-115 × 15-35 mm) with reddish brownish scaly pileus, subdistant (6 L+l/cm) lamellae, larger basidiospores (7.2- 8.9 -12.2 ×7- 8.4 -10.2 µm) with higher ornamentations (2.5-3.5 µm high), the complete absence of cheilomacrocystidia and ixocutis nature of stipitipellis in L. austrozonarius evidently distinguish these Thai species from the present species ( Le et al. 2007). On the other hand, the ochraceus brown hygrophanous pileus with forked lamellae, low ornamentations (0.5-1.0 µm high) of basidiospores, absence of cheilomacrocystidia and ixocutis nature of pileipellis in L. sinozonarius separate it out ( Wang 2017). The Indian L. indozonarius has a larger pileus ( 60-122 mm diam.) with hairy margin and ixocutis pileipellis which are absent in the studied specimens ( Uniyal et al. 2018).
Lactarius yazooensis (originally described from North America) might be confused with the described Lactarius due to its viscid, smooth, zonate pileus, whitish latex, similar-sized and ornamented basidiospores, and occurrences under the broad-leaved trees ( Hesler & Smith 1979). But with the striking dissimilarities like the orange ochraceous to rusty orange basidiomata with larger pileus ( 50-150 mm broad), absence of cheilomacrocystidia, ixocutis nature of pileipellis and presence of caulocystidia, L. yazooensis is quite morphologically distinguishable from the current studied species of Lactarius ( Hesler & Smith 1979) . Yet, many look-alikes have been misnamed as L. yazooensis after the North American representatives clearly doubted their conspecificity. The phylogenetic analysis (depicted inFigure 1) states that the North American collections of L. yazooensis are distantly related to the Chinese misnamed L. yazooensis specimens that have formed the clade with L. kamengensis sp. nov.
| CAL |
Botanical Survey of India |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |