Hygrobatidae Koch, 1842
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.204868 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6183765 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B987B5-FF96-284E-14B7-8C46FDB9FB9D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Hygrobatidae Koch, 1842 |
| status |
|
Family Hygrobatidae Koch, 1842 View in CoL View at ENA
Iranobates Peši ć, Smit & Asadi gen. nov.
Diagnosis. Characters of the subfamily Hygrobatidae ; integument striated; muscle attachments plates unsclerotized; excretory pore smooth; genital field with three pairs of acetabula; anterior coxal plates fused medially and with posterior margin of the gnathosoma; caudal margin of Cx-IV with a protruding muscle attachment apodeme; glandularia of Cx-IV located a considerable distance from the posterior margin of Cx-IV. Palp: P-2 distoventrally protruding in a relatively long and slender, bluntly-pointed projection, bearing a few small dents at the tip, rarely smooth, P-3 with a strong lamellar protrusion, denticulated at the tip, distinctly set up from the ventral segment margin. Legs: weak sexual dimorphism; in the male sixth segment of I-, II-, III-L with one long and relatively thickened seta inserted in its proximal part; in the both sexes: I-L-5 at the distal margin anteriorly with a fine, whiplike seta and ventrodistally one strong, apically rounded seta; II-, III- and IV-L-5 at the distal margin anteriorly with one fine and long hair; claws with ventral clawlet.
Type species. Iranobates hesabii sp. nov.
Etymology. Named after the country where the type species was collected.
Remarks. The new genus resembles Mixobates Thor, 1905 due to the position of the glandular opening on the surface of Cx-IV and the broad fusion of the gnathosoma with the anterior coxae (similarly in Hygrobates ). According to Tuzovskij & Gerecke (2003), Mixobate s should be considered as a member of the Atractides -like genera characterized by the modified shape and setation of I-L (I-L-5 with an anterodistal, whip-like seta, and a pair of modified ventrodistal setae, and I-L-6 with numerous ventral setae). The new genus is rather similar to Mixobates in some details of the morphology of I-L-5 and -6, but differs in I-L-5 bearing ventrodistally only one stout, apically rounded seta instead of two setae found in other Atractides -like genera (see: Gerecke 2000). Furthermore, the new genus is characterized and differs from Mixobates in the following characters combinations: 1) sixth segment of I-, II-, III-L of male with sexual dimorphism (as showed in Fig. 2E View FIGURE 2 A – G ), 2) P-3 with a strong lamellar protrusion, distinctly set up from the ventral margin.
Iranobates hesabii Peši ć, Smit & Asadi sp. nov. ( Figs. 1–2 View FIGURE 1 A – E View FIGURE 2 A – G )
Type material. Holotype female, dissected and slide mounted; Iran, Kerman Province, Aseminon near Manoojan city, pool in stream, 30° 34' 2" N, 53° 49' 01" E, 674 m a.s.l. ( ZMAN). Paratypes: 2/14/0, same data as holotype, two males and one females dissected and slide mounted.
Further records. Iran, Kerman Province: Tiab near Manoojan city, stream, 30° 18' 4.6" N, 56° 26' 4.6" E, 462 m a.s.l. 10/8/0; Roodan stream near Manoojan city, 30° 38' 5.7" N, 52° 49' 5.9" E, 341 m a.s.l. 18/9/0.
Diagnosis. As for genus.
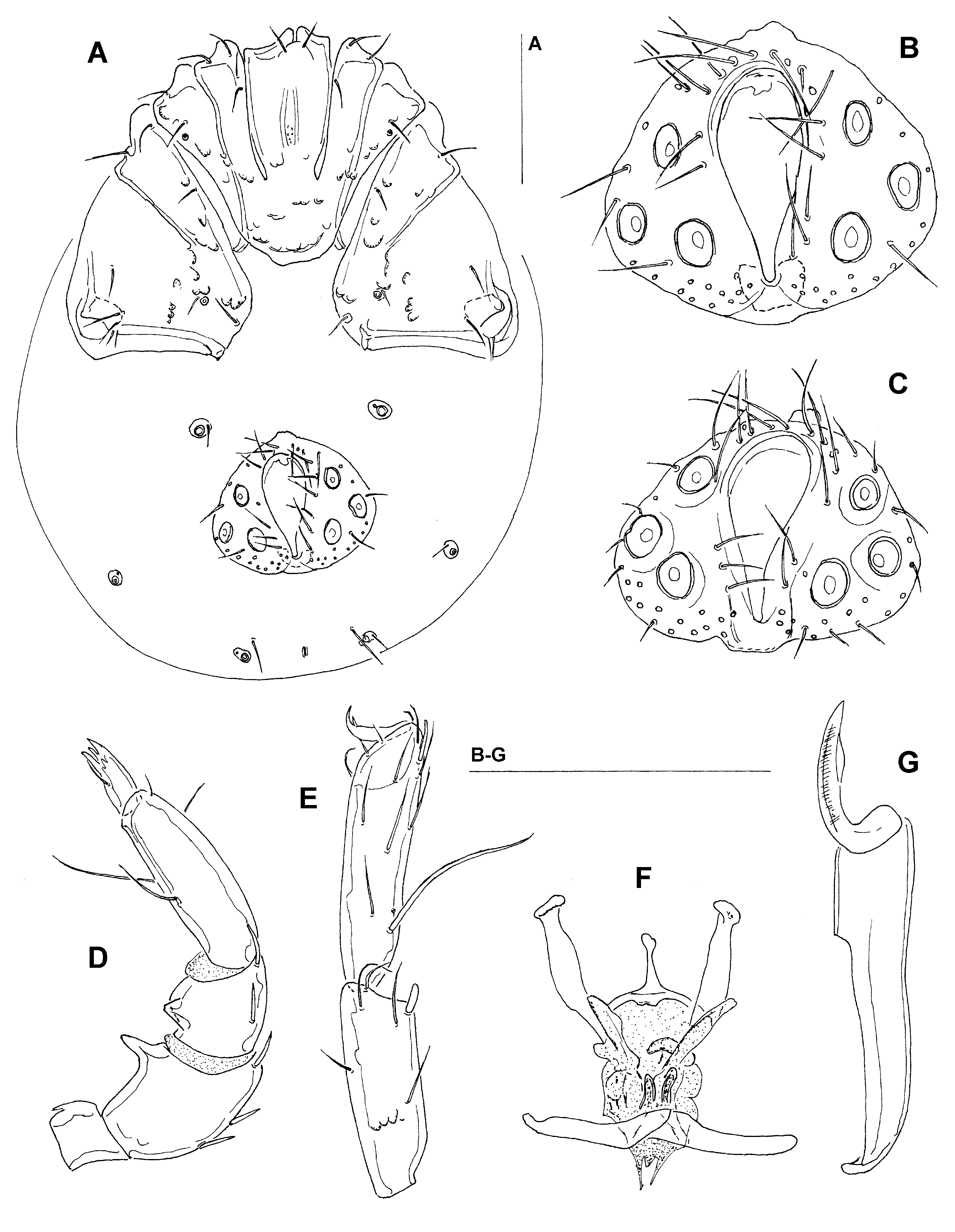
Description. Female (holotype, some measurements of paratypes are given in parentheses): Idiosoma L/W 462–500/306–356; setae Dgl-1 3 times longer than their insertion sclerite; integument striated, without dorsal and ventral plates. Coxal field ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 A – E ) L 223 (226); Cx-3 W 252 (277); Cx-I fused medially without any trace of a suture line; posterior apodemes of Cx-I short; suture line between Cx-III and – IV incomplete, not extending to medial margin; glandularia of Cx-IV located a considerable distance from the posterior margin of Cx-IV. Genital field ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 A – E ): L/W 129/122, pregenitale W 68 (70); genital plate L 58–60 (57); maximum diameter of Ac-1-3: 14 (12), 15 (15), 19 (13); 5–7 hairs on each plate; egg maximum diameter 131. Palp ( Fig. 1D–E View FIGURE 1 A – E ) total L 225–227, dL: P-1, 22 (25); P-2, 62 (63); P-3, 37 (38); P-4, 75 (74); P-5, 29 (27); L P-2/P-4 ratio 0.83–0.85; P-2 distoventrally protruding in a relatively long and slender, bluntly-pointed projection, denticulated at tip, P-3 with a strong lamellar protrusion, denticulated at tip, distinctly set up from the ventral segment margin; chelicera total L (163); L of I- L-4-6: 65 (66), 68 (72), 88 (91); I-L-5 at the distal margin anteriorly with a fine, whip-like seta and ventrodistally with one strong, apically rounded seta ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 A – E ); II-, III- and IV-L-5 at the distal margin anteriorly with one long and fine seta; claws with slightly developed claw blade, internal clawlet about 50 % L of external clawlet.
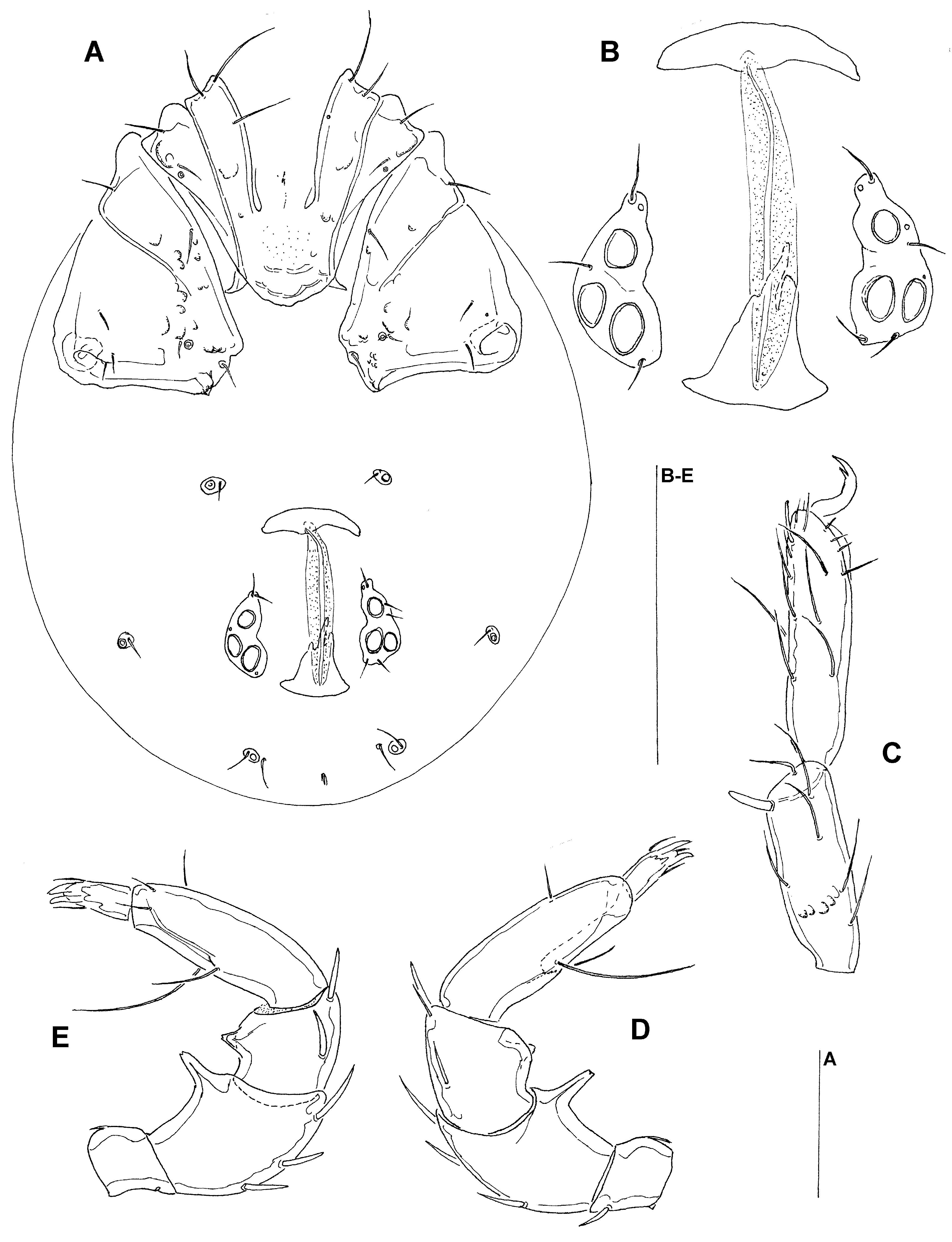
Male (n =2): Idiosoma L/W 447/325; coxal field L 206–212; Cx-3 W 237–249; coxae ( Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2 A – G ) as described for female. Genital field ( Fig. 2B–C View FIGURE 2 A – G ): L/W 80–90/102–112; gonopore L 63–69; 24–29 setae on each side of the gonopore; maximum diameter of Ac-1-3: 13–15, 13–16, 15–18; ejaculatory complex ( Fig. 2F View FIGURE 2 A – G ) L 84–95. Palp ( Fig. 2D View FIGURE 2 A – G ) total L 206, dL: P-1, 21–22; P-2, 57; P-3, 34–35; P-4, 66–69; P-5, 27; L P-2/P-4 ratio 0.83–0.86; shape and chaetotaxy of palp as in female; chelicera total L 155–162; L of I-L-4-6: 65–66, 71–75, 88–91; I-L-5 as in the female; I-, II-, III-L-6 with one long and thickened seta inserted in the proximal part of the segment ( Fig. 2E View FIGURE 2 A – G ); II-, III- and IV-L-5 at the distal margin anteriorly with one fine and long seta; claws as in female.
Etymology. Named after Prof. Mahmood Hesabi, the founder of University of Tehran.
Distribution. Iran (Kerman province).
| ZMAN |
Instituut voor Taxonomische Zoologie, Zoologisch Museum |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.