Ilyocypris ramirezi Cusminsky & Whatley, 1996
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3957.1.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:9D6024F9-A826-4EF2-9C51-DEDB6943EB61 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6122088 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C21336-FFFA-FF96-5789-390FFC3BFE79 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Ilyocypris ramirezi Cusminsky & Whatley, 1996 |
| status |
|
Ilyocypris ramirezi Cusminsky & Whatley, 1996
Material examined. 17 of a total of 818 ♀♀ adults and juveniles; 3 ♀♀ adults deposited in the Invertebrate collection of the Museo de La Plata, Argentina ( MLP 26900).
Diagnosis. Ilyocypris species with dorsal margin inclined and rather sinuous. Ornamented regularly with small pits, mainly concentrically arranged as a sieve. Marginal spines present in posterior margin, arranged in a conspiscuous row of six to eight spines situated at little distance from it. Natatory setae of A2 short. Endopodite of T1 small and with only one segment with a small constriction on one side. Protopodite of T2 with only one seta d1. Terminal segment cylindrical with three terminal setae. Males unknown.
Measurements of adults.
RV (n=11), L = 728–901 µm (816 ± 46 Μm); H = 358–506 µm (426 ± 38 Μm);
LV (n=11), L = 765–876 µm (845 ± 34 Μm); H = 407–494 µm (444 ± 25 Μm);
Cp (n= 6), W = 259–370 µm (321 ± 44 Μm); LV, L = 728–900 µm (820 ± 75 Μm), H = 370–494 µm (422 ± 49 Μm); RV, L = 728–901 µm (832 ± 73 Μm) 898 µm, H = 395–506 µm (434 ± 44 Μm)
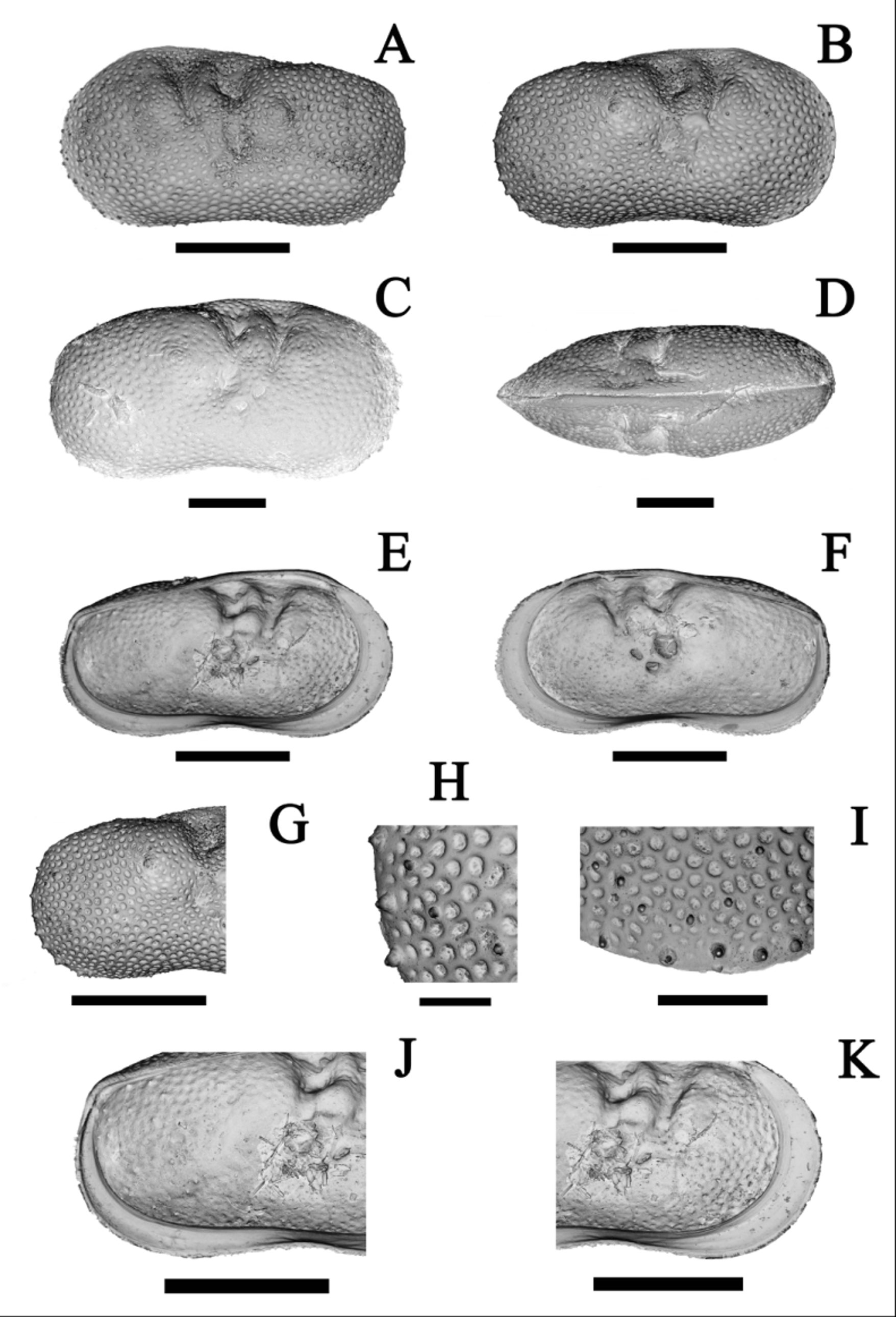
Anatomy of valves (after Cusminsky & Whatley 1996) ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A–K):
Medium sized. Valves subrectangular in lateral view ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A–C). Anterior margin rounded. Posterior margin rounded in ventral part and straighter dorsally. Dorsal margin inclined and rather sinuous. Ventral margin concave. Maximum height situated approximately at anterior third of maximum length. Carapace elongated in dorsal view ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 D). Regularly ornamented with small pits, mainly concentrically arranged as a sieve. Three lateral tubercles present, low, rounded and ornamented, the posterior one well developed. Two medio-dorsal transverse sulci. Marginal spines present and pointed, numerous in anterior margin and in posterior margin bigger and arranged in a conspicuous row of six to eight spines situated at a little distance from it ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 G–I). Normal pore canal with few, perforated small conuli. Internal features as for genus. Inner lamella relatively narrow ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 E–F, J–K) but well developed. Adductor scars a tightly compact group of seven scars in two rows. LV overlapping RV on all sides, except in postero-dorsal margin.
In juveniles, the dorsal margin of the carapace is straight, and the ornamentation, tubercles and sulci are more prominent.
Anatomy of soft parts (Fig. 3A–I). A1 (Fig. 3A) with seven segments. First segment with one short ventral and two long dorsal setae, all of them plumose. Second segment with one ventral seta. Third segment with one short aesthetasc and one short seta ventrally, same segment with one short dorsal seta. Fourth segment with two long subequal setae ventrally, and with one aesthetasc and one long seta dorsally inserted. Fifth segment with two long sub-equal ventral setae and two unequal dorsal setae. Sixth segment with four long apical natatory setae. Terminal segment with one long aesthetasc y a, one long seta and two claws.
A2 (Fig. 3B) second segment of protopodite with one ventral seta. Exopodite with one long and two short setae. First segment of endopodite with a ventral aesthetasc Y, five sub-equally short natatory setae and one long seta inserted on the anteroventral corner of the segment. Second segment of endopodite with one dorsal and one ventral setae, one mid-ventral aesthetasc y1 and one apical aesthetasc y2; same segment with three medium-sized apical claws G1, G2, G3. Terminal segment with two strong claws GM and Gm and aesthetasc y3 fused with a short seta.
Md (Fig. 3C) Md-coxa slender with 6–7 cuspate teeth. Mandibular palp with four segments. First segment with two plumose and one serrate seta S1. Second segment with four long setae, one short ventral β-setae, and one long dorsal seta. Third segment with two sub-equal ventral setae and three dorsal setae. Terminal segment with three apical claw-like setae. Branchial plate (exopodite) with three setae that arise dorsally from the palp.
Mx (Fig. 3D) with terminal segment of palp sub-quadrate. Second segment of palp cylindrical, c. twice as long as basal width, with two dorso-apical setae. Terminal segment with three apical claw-like setae and two setae. Zahnborsten on third endite smooth. Branchial plate with c. 20 rays.
T1 (Fig. 4E) with masticatory process bearing 12 mostly smooth setae of unequal length, d and b setae plumose. Branchial plate (exopodite) with 5 plumose setae. Endopodite small with only one segment with a small constriction on one side. Three smooth setae present.
T2 (Fig. 3F) a walking leg, with one seta d1. First segment of endopodite with one short apical e seta, second segment with one apical d seta, third segment with one apical f seta. Terminal segment with one long apical claw and two smooth short setae.
T3 (Fig. 3G) a cleaning limb; first segment of endopodite with one apical seta. Second segment with one ventral and one dorsal setae. Terminal segment cylindrical with three terminal setae.
FIGURE 3. Ilyocypris ramirezi ♀: A. A1(MLP26900); B. A2 (MLP26900); C. Md (MLP26900); D. Mx (MLP26900); E. T1 (MLP26900); F. T2 (MLP26900); G. T3 (MLP26900); H. CR (MLP26900); I. CRa (MLP26900). y a, Y, y1, y2, y3: aesthetascs, G1, G2, G3, GM, Gm, Gp, Ga: claws, S1, d, b, d1, d2, Sp, Sa: setae, db: dorsal branch, vb: ventral branch. Scale bar: 100 µm.
CR (Fig. 3H) of normal structure, posterior seta long and plumose. Anterior and posterior claws smooth. Posterior seta (Sp) longer than anterior seta (Sa).
CRa (Fig. 3I) robust but short, with simple triangular structure at basis. Dorsal branch (db) long and ventral branch (vb) short.
Ecology. Ilyocypris ramirezi has been found in freshwater to sub-saline (salinity range: 0.2–2.7 g /L) environments. The species was most abundant in Malargüe Delta River in summer and in Los Menucos rheocrene spring in autumn and spring, but the specimens were found in all seasons. In creeks and La Porteña limnocrene spring specimens of I. ramirezi were less abundant, but present in all seasons. The environments were characterized by alkaline pH values, temperature from 0.1 to 29.5 °C, conductivity from 0.8 to 5.1 mS/cm. Dissolved oxygen saturation varied between 20 and 170 % (Table 1).
| MLP |
Museo de La Plata |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |