Bifidocoelotes obscurus, Zhou, Yan-Chen, Yuen, Yan Ling & Zhang, Zhi-Sheng, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4232.3.11 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:0B41000B-7BDE-46BC-8364-E131DD9C5664 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6002118 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C38781-FFE1-FF87-FF7F-8A35FCD4CBE1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bifidocoelotes obscurus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Bifidocoelotes obscurus sp. nov. (ŔǠDZĦ)
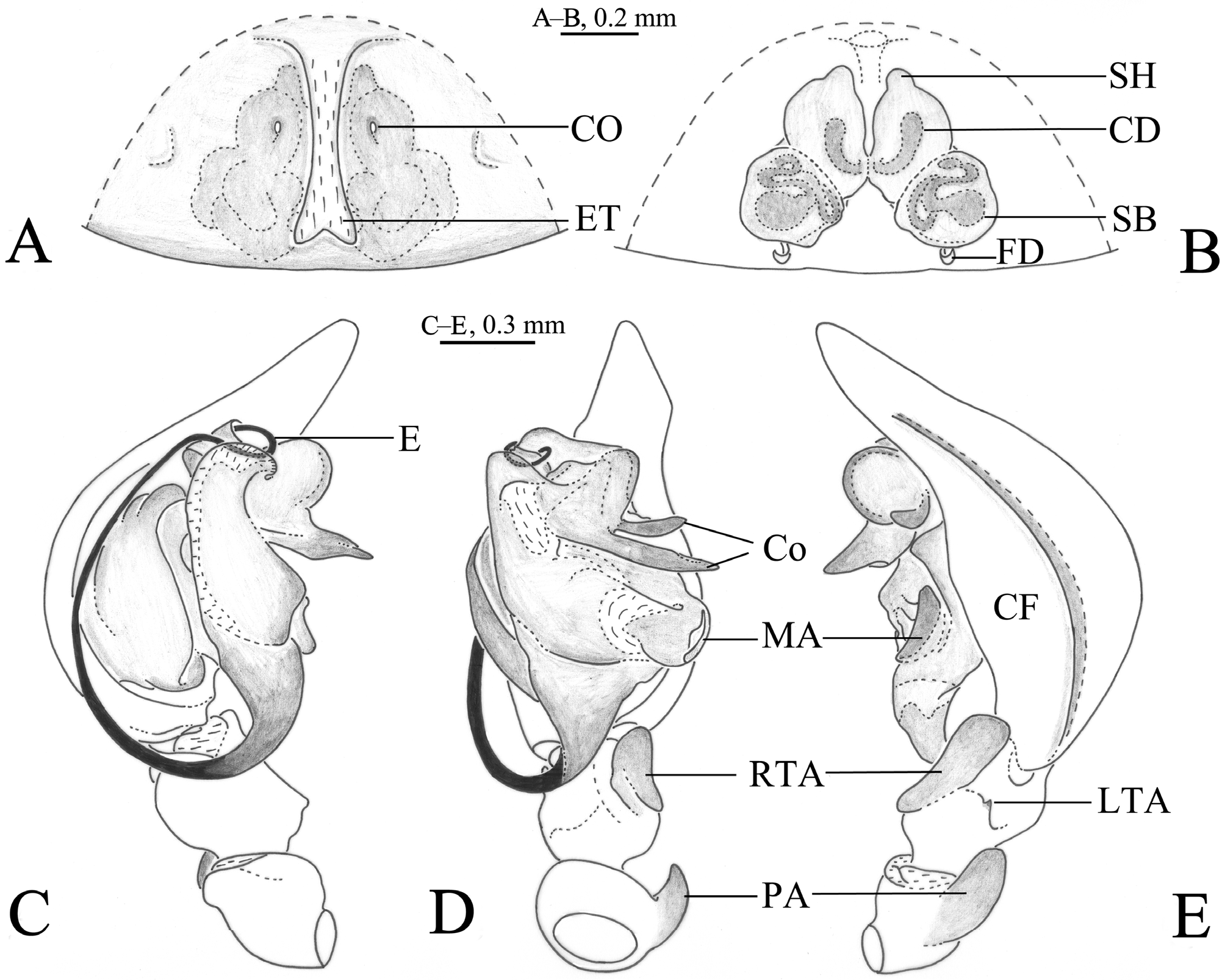
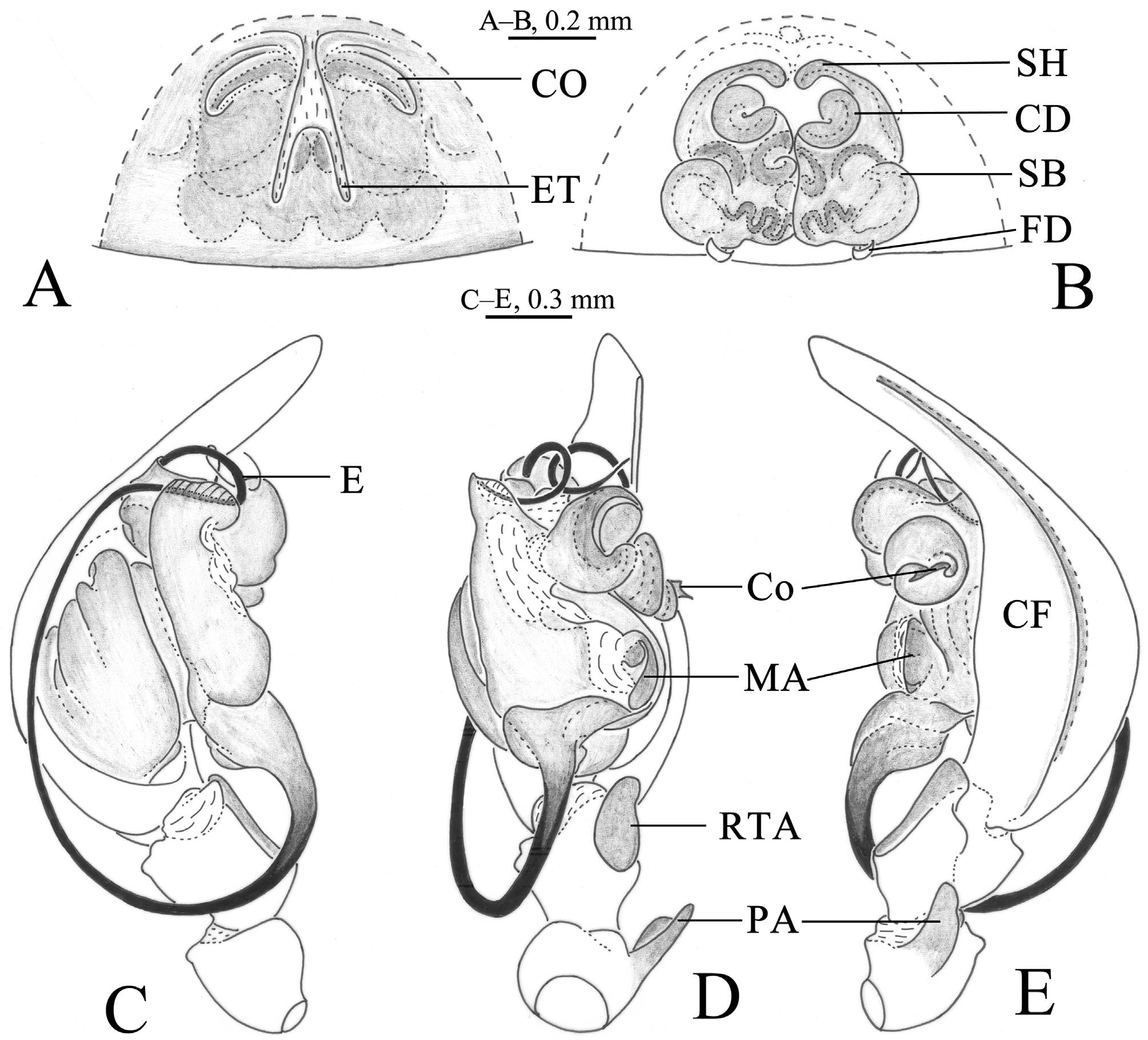
Figures 1 View FIGURE 1 A–E, 2A–G
Type material. Holotype male, China, Hong Kong, Tai Po Kau Forest Stream , 22°25′24′′N, 114°10′48′′E, 9 January 2014, Y.L. Yuen leg. Paratypes (9 males and 10 females) GoogleMaps : 3 males and 1 female, with same data as holotype GoogleMaps ; 2 males and 2 females, Hong Kong, Lead Mine Pass Stream , 22°23′51′′N, 114°09′05′′E, 5 December 2013, Y.L. Yuen leg. GoogleMaps ; 1 female, Hong Kong, Lead Mine Pass Stream. 22°23′51′′N, 114°09′05′′E, 18 December 2013, Y.L. Yuen leg. GoogleMaps ; 1 male and 2 females, Hong Kong, Lead Mine Pass Stream. 22°23′51′′N, 114°09′05′′E, 10 January 2014, Y.L. Yuen leg. GoogleMaps ; 1 male and 3 females, Hong Kong, Tai Po Kau Forest Stream , 22°25′24′′N, 114°10′48′′E, 12 December 2013, Y.L. Yuen leg. GoogleMaps ; 1 female, Hong Kong, Tai Po Kau Forest Stream , 22°25′24′′N, 114°10′48′′E, 24 January 2014, Y.L. Yuen leg. GoogleMaps ; 2 males, Hong Kong, 2014, Y.L. Yuen leg.
Etymology. The specific epithet comes from the Latin word obscurus , meaning “dark”, referring to the dark habitus; adjective.
Diagnosis. The new species can be distinguished from the type species, B. bifidus ( Wang 2002: 38, figs 86–91) by the large and strongly bifid conductor and relatively large median apophysis of the male pedipalp ( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 C–E, 2E–G) (conductor shorter and less bifid, with shorter branches and median apophysis smaller in B. bifidus (Wang 2002: figs 88–89)), the long and shallowly bifurcated epigynal tooth, the strongly coiled and well-sclerotized copulatory ducts and the ball-like spermathecae of the female epigyne ( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 A–B, 2C–D) (tooth long and deeply bifurcated, copulatory ducts elongate and weakly sclerotized and spermathecae elongate in B. bifidus (Wang 2002: figs 86–87)). The new species differs from B. primus by the tiny pointed lateral tibial apophysis and relatively straight conductor of the male pedipalp ( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 D–E, 2F–G) (lateral tibial apophysis rounded and conductor spiraled in B. primus ( Figs 3 View FIGURE 3 D–E, 4F–G)) and the shallowly bifurcated tooth and small copulatory openings of the epigyne ( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 A, 2C) (tooth very deeply bifurcated and copulatory openings elongate in B. primus ( Figs 3 View FIGURE 3 A, 4C)).
Description. Male. Total length 6.83–7.37. Holotype ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A) total length 6.83. Prosoma 3.46 long, 2.25 wide; opisthosoma 3.20 long, 2.26 wide. Eye region and dorsum of prosoma dark. Cervical groove and radial furrows distinct. Eye sizes and interdistances: AME 0.09, ALE 0.15, PME 0.19, PLE 0.18; AME–AME 0.06, AME–ALE 0.03, PME–PME 0.08, PME–PLE 0.11, ALE–PLE 0.05. MOA 0.42 long, front width 0.28, back width 0.42. Clypeus height 0.16. Chelicerae robust, brown, with three promarginal and two retromarginal teeth. Gnathocoxae yellow brown, longer than wide. Labium yellow brown, longer than wide. Sternum brown and scutiform, with sparse brown hairs. Legs yellow brown, with black ring-like stripe in femora, patella and tibia. Leg measurements: I 11.02 (3.02, 3.48, 2.58, 1.94); II 9.02 (2.45, 2.76, 2.22, 1.59); III 8.20 (2.22, 2.49, 2.30, 1.19); IV 11.76 (3.04, 3.73, 3.38, 1.61). Leg formula: 4123. Opisthosoma oval. Dorsum yellowish brown, with dark markings and some light chevron-like markings. Venter yellow brown, with some dark markings.
Male pedipalp ( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 C–E, 2E–G). Patellar apophysis strong, finger-like in retrolateral view. RTA wide, with a somewhat rounded distal end, extending beyond distal end of tibia. Lateral tibial apophysis small and pointed. Embolus very long and slender, proximally originated. Conductor strong, relatively straight and deeply bifurcated with distal arm shorter and slightly curved distally and proximal arm longer. Median apophysis relatively large and spoon-like.
Female. Measurements from a single paratype ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 B). Total length 6.65. Prosoma 3.27 long, 2.15 wide; opisthosoma 3.58 long, 2.47 wide. Eye sizes and interdistances: AME 0.09, ALE 0.16, PME 0.16, PLE 0.20; AME–AME 0.08, AME–ALE 0.04, PME–PME 0.07, PME–PLE 0.08, ALE–PLE 0.06. MOA 0.38 long, front width 0.25, back width 0.41. Clypeus height 0.16. Leg measurements: I 8.46 (2.34, 2.78, 2.00, 1.34); II 7.26 (2.06, 2.32, 1.72, 1.16); III 6.59 (1.84, 2.12, 1.66, 0.97); IV 9.41 (2.59, 3.12, 2.48, 1.21). Leg formula: 4123. Dorsum yellowish brown, with dark markings and some light chevron-like markings. Venter yellow brown, with some dark markings.
Epigyne ( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 A–B, 2C–D) with a shallowly bifurcated epigynal tooth (slightly variable among individuals). Copulatory openings small, located on the lateral side of epigynal tooth. Copulatory ducts and spermathecae difficult to differentiate from each other, strong convoluted and sclerotized. Spermathecal heads located anteriorly. Bases of spermathecae well separated. Fertilization ducts originating ventrally on spermathecae.
Distribution. Known only from Hong Kong ( China).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |