Trachystolodes huangjianbini, Huang & Guo & Liu, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4759.1.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:EEABD0EB-4DC7-4EF9-90BE-F7A8CA1A55FD |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3811923 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C5878E-9B5A-8975-FF0D-FF11FE2A56E2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Trachystolodes huangjianbini |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Trachystolodes huangjianbini View in CoL sp. nov. ªḦṆḆX+
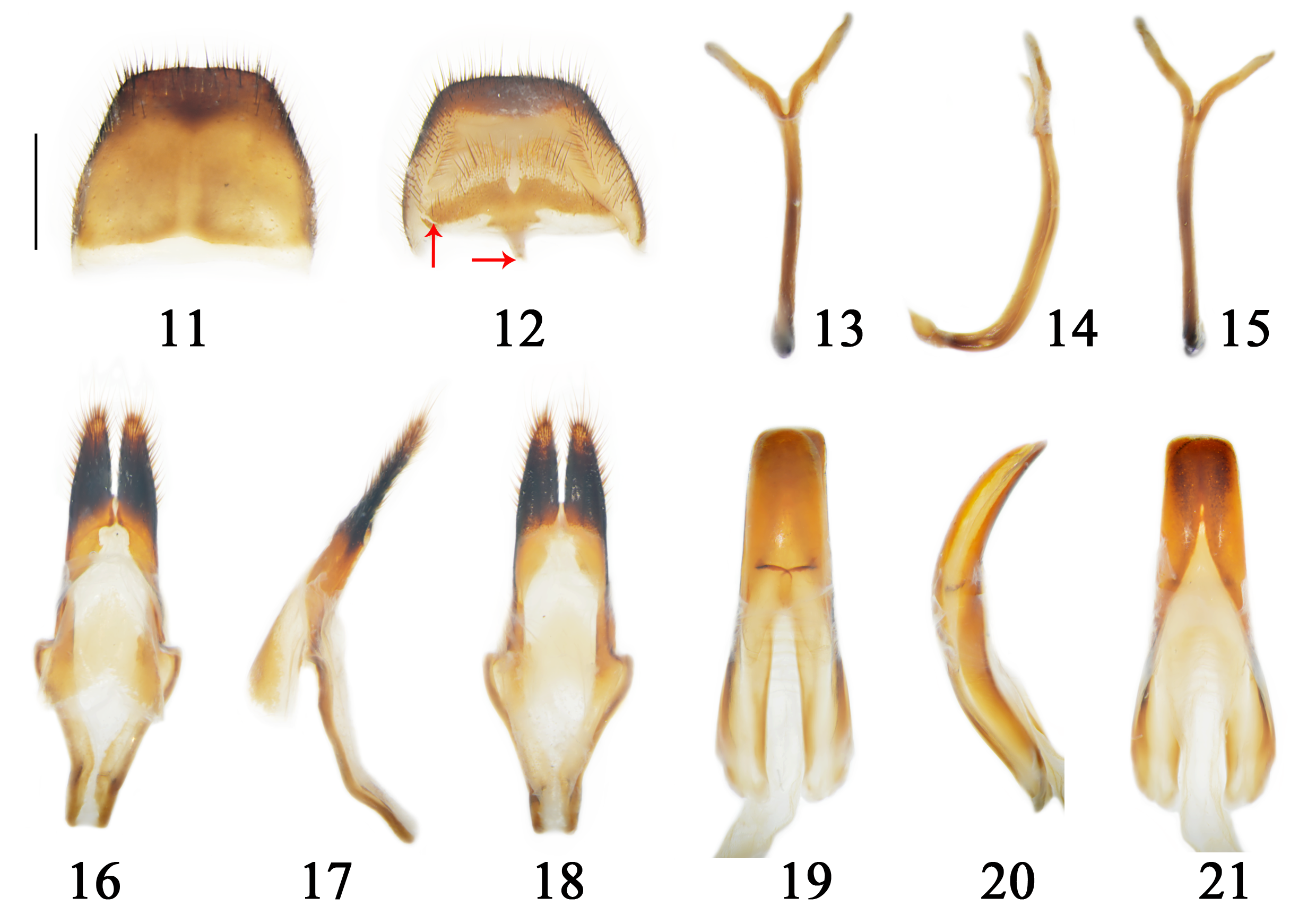
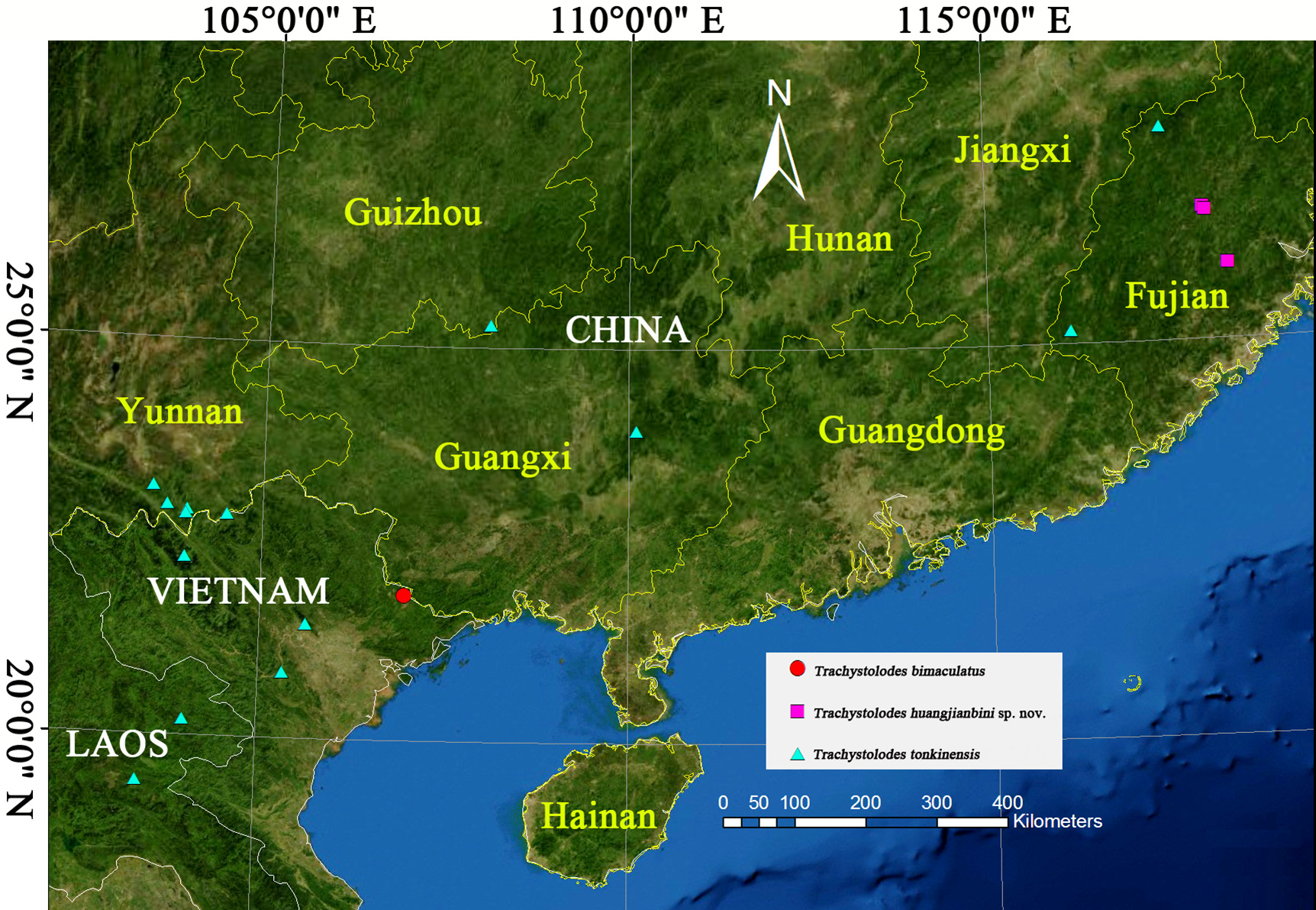
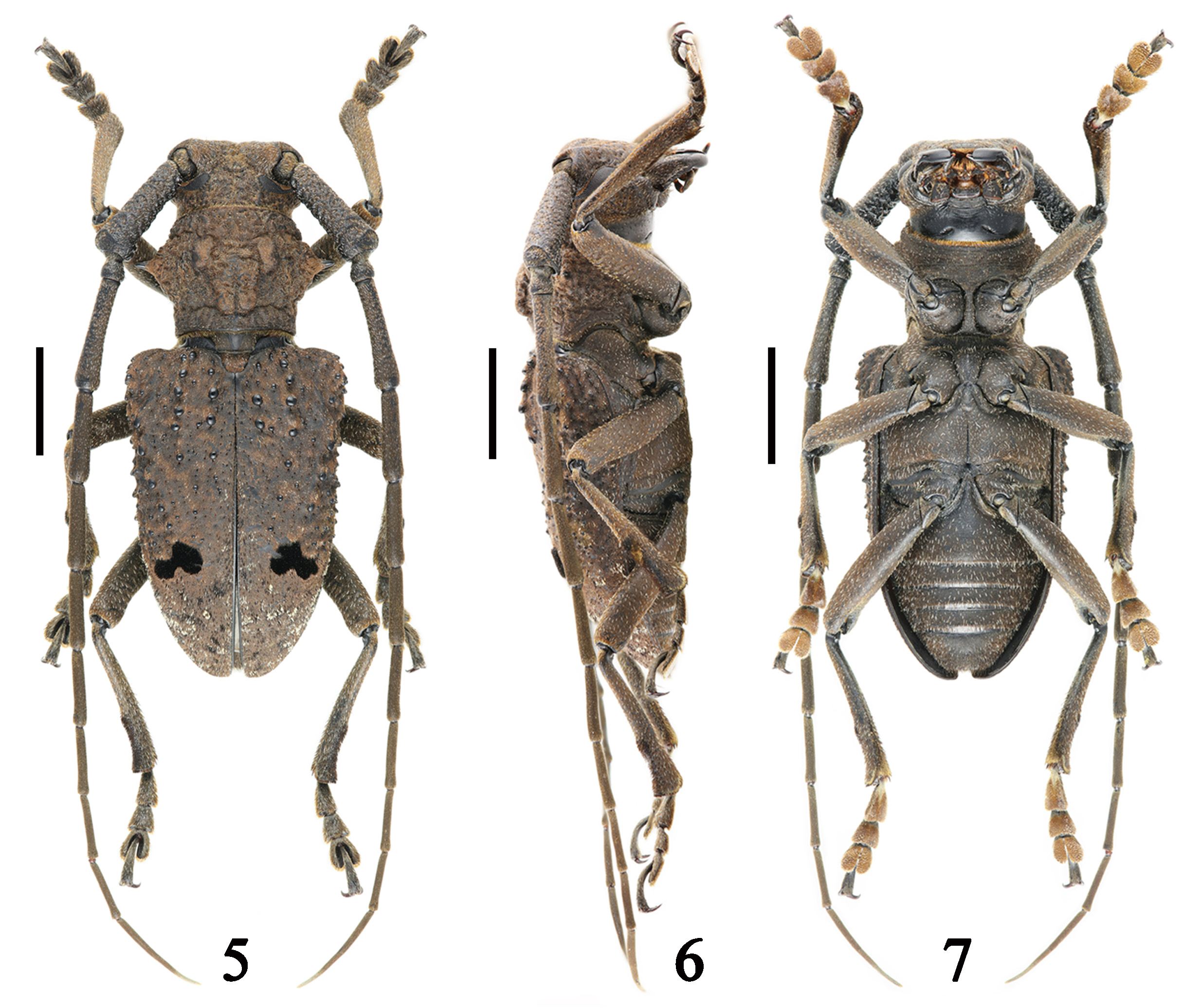
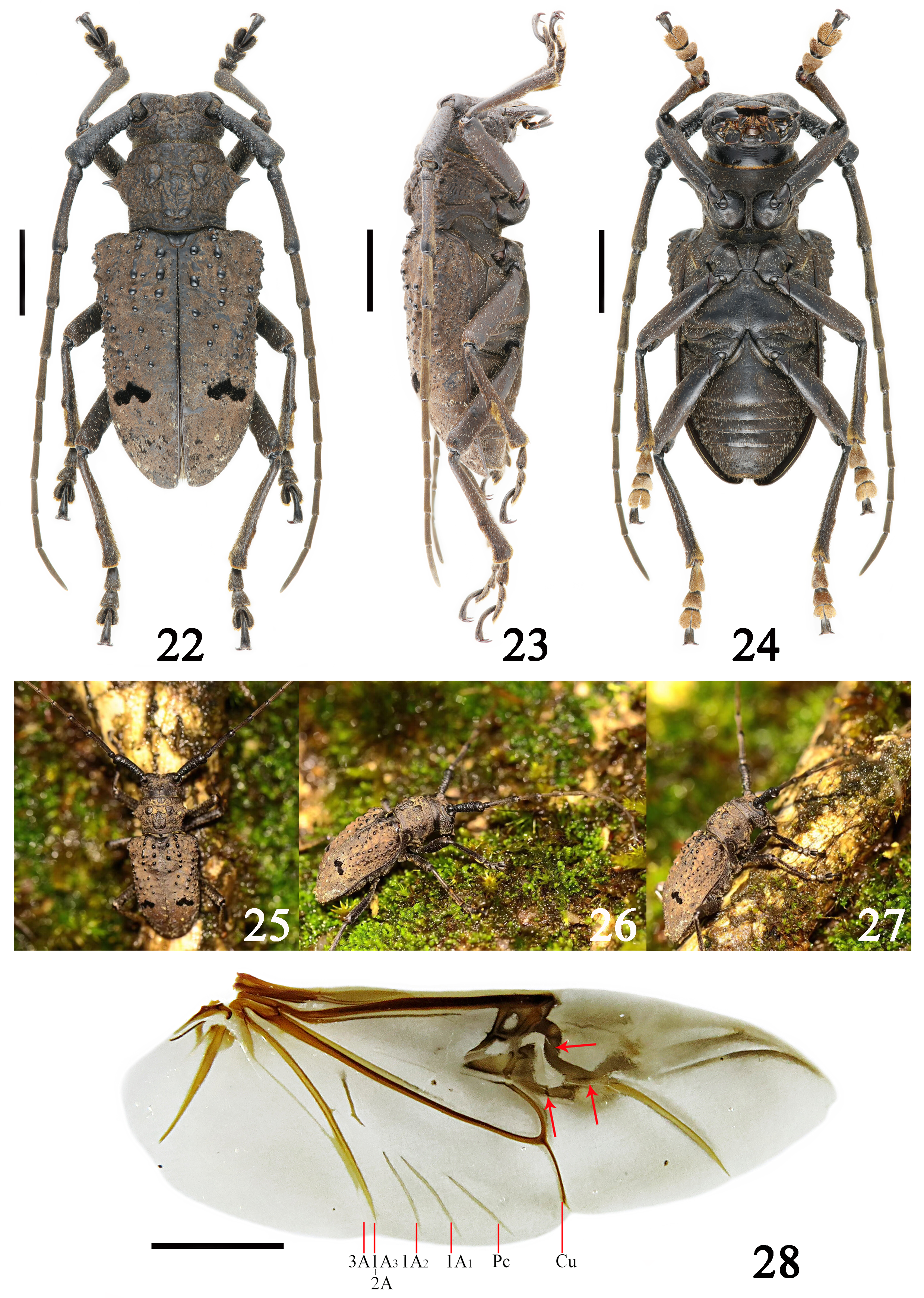
Figures 5–7 View FIGURES 5–7 , 8–10 View FIGURES 8–10 , 11–21 View FIGURES 11–21 , 22–28 View FIGURES 22–28 , 52 View FIGURE 52
Description. Male. Body length: 24.0 mm, humeral width: 10.0 mm (2 individuals); holotype ( Figs. 5–10 View FIGURES 5–7 View FIGURES 8–10 , 11–21 View FIGURES 11–21 ), body length: 24.0 mm, humeral width: 10.0 mm. Anteclypeus brown ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 8–10 ). Mandibles sparsely covered with short white setae and short brown setae on outside of dorso-basal 3/5 and latero-basal 3/5, with several long brown hairs on latero-basal 3/5 ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 8–10 ). Labrum sparsely covered with long brown hairs (mainly concentrated at sides), short white setae and short brown setae, with a row of extremely dense golden setae at apex ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 8–10 ). Frons sparsely covered with long brown hairs at basal margin ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 8–10 ), vertex with several long dark brown pubescence at posterior of upper lobe of eyes. Antennomeres covered with short grayish-brown hairs (hairs gradually dense from basal segments to apical segments, but densest at antennomeres 9 th– 11 th), antennomere 11 th densely with short light grayish-brown hairs at apical 1/3; scape, pedicle, inner sides of antennomere 3 rd sparsely with short dark brown setae; antennomeres 3 rd– 10 th sparsely covered with slightly long and thick brown hairs apically. Pronotum and sides of prothorax sparsely covered with short dark brown setae located in rounded punctuations, pronotum with several long dark brown pubescence near sides of large callus and near base of lateral spines. Black setal spots near elytral middle mushroom-shaped ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 5–7 ). Abdomen sparsely covered with semi-erected light brown and dark brown setae, abdominal 5 th segment sparsely with long and thick dark brown hairs at apical 1/3 (slightly dense at apical margin). Apex (except venter) of femora and basal dorsum of tibiae densely covered with short brown setae.
Mandibles wide and thickened, nearly as long as frons, nearly smooth at dorso-apical 2/5, wrinkled on outsides of dorso-basal 3/5 and latero-basal 3/5, depressed on latero-basal 3/5. Labrum transversally raised in middle. Frons with a transverse furrow at base and a pair of oblique short furrows at basal sides. Antennae 1.65 times as long as body, relative length of each antennomere as follows: 4.5: 1.0: 4.0: 3.2: 2.9: 2.6: 2.5: 2.0: 1.8: 1.6: 3.0. Pronotum and sides of prothorax sparsely covered with rounded punctuations; posterior of both small calluses closed to anterior of large callus on pronotum, both small calluses sub-rectangular with oblique depression on inner side of dorsum, large callus sub-rectangular, wrinkled and with a mesial longitudinal furrow dorsally, notched apically. Elytra 1.38 times as long as wide at base. Hind wing with Cu vein weak apically, Pc vein reduced into basal and apical parts, basal part short, not connecting with Cu vein and without a cross vein connecting with 1A 3 +2A; 1A 1 and 1A 2 veins dissociative and weak apically, 1A 3 +2A and 3A veins well developed (weak apically) and fused at most of parts of apical 1/2 ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 8–10 ). Abdominal 5 th segment sub-truncated apically. Profemora, sides of mid femora and inner sides of hind femora wrinkled.
Male terminalia. Dorsum of tergite VIII ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 11–21 ) sparsely covered with long and short brown setae (most of setae located at sides and apex), sparsely with long thick dark brown setae at apex and near apical sides, with a piece of longitudinally glabrous section in center of basal 2/3; venter of tergite VIII ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 11–21 ) sparsely covered with short brown setae at apical 1/3 (setae mainly concentrated on dark brown section), sparsely with slightly long brown setae at apical 3/4 of sides, sparsely with short dark brown setae at apex, sparsely with long dark brown setae at apex (setae mainly concentrated at apex) and apical 3/4 of sides; disc slightly wider than long, sub-trapezoidal and truncated apically. Venter of sternite VIII ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 11–21 ) sparsely covered with long and short brown setae (setae mainly concentrated at apical 1/3), sparsely with long dark brown setae at sides; most of parts of disc membranous, with a piece of longitudinally glabrous section in center, sclerotic section with a triangular notch at apical center. Spiculum gastrale ( Figs. 13–15 View FIGURES 11–21 ) nearly 2.0 times as long as tergite VIII, stem of spiculum gastrale slightly curved at apical 1/4, strongly curved at basal 1/4, base drop-shaped in profile ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 11–21 ), branches of spiculum gastrale less than 0.5 time as long as stem. Tegmen ( Figs. 16–18 View FIGURES 11–21 ) slightly longer than penis, dorsum of parameres nearly glabrous at basal 1/3, sparsely covered with short brown setae (setae mainly concentrated at apical 1/3) and long thick brown setae (setae mainly concentrated at apical 1/4, longest setae nearly 0.5 time as long as parameres) at apical 2/3 ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 11–21 ); venter of parameres sparsely with short fine brown setae at basal 2/3 (setae mainly concentrated at base), sparsely with long thick brown setae on apical 1/3, each lobe rounded apically and longitudinally depressed at outer half of ventro-basal 1/2 ( Fig. 18 View FIGURES 11–21 ); phallobase nearly 2.6 times as long as parameres, expanded at apical 2/5 and gradually constricted to base, then curved near basal 1/5 ( Fig. 17 View FIGURES 11–21 ), both struts of anterior tegminal strut separated and only connected through membrane ( Figs. 16 & 18 View FIGURES 11–21 ). Penis abruptly curved at basal 2/5 ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 11–21 ), dorsal plate shorter than ventral plate and rounded apically ( Fig. 19 View FIGURES 11–21 ), ventral plate wider than dorsal plate near apex ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 11–21 ), sub-truncated apically ( Fig. 21 View FIGURES 11–21 ); dorsal struts about 0.5 time as long as entire penis and rounded apically, apex of dorsal struts slightly expanded towards inner sides ( Fig. 19 View FIGURES 11–21 ), outer side of apical margin of dorsal struts slightly folded towards dorsum ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 11–21 ).
Variation. The black setal spots near elytral middle securiform in male paratype.
Female. Paratype ( Figs. 22–28 View FIGURES 22–28 ), similar to male, but body length: 23.5 mm, humeral width: 10.0 mm. The black setal spots near elytral middle converse “V” shaped ( Figs. 22 & 25 View FIGURES 22–28 ).
Antennae 1.33 times as long as body, relative length of each antennomere as follows: 3.4: 0.6: 2.6: 2.0: 1.7: 1.4:
1.3: 1.2: 1.1: 1.1: 1.6. Elytra 1.46 times as long as wide at base. Hind wing with 1A 3 +2A vein connecting with a very short cross vein near middle ( Fig. 28 View FIGURES 22–28 ). Abdominal 5 th segment notched apically.
tographs by Peng-Yu Liu on 2 July 2019); 28. right hind wing (A: anal, C u: cubitus, P c: post cubitus; red arrows indicate broken sections); 22, 25 & 28. dorsal view, 23, 26 & 27. lateral view, 24. ventral view. Scale bars: 5 mm.
Diagnosis. This new species can be distinctly distinguished from T. bimaculatus and T. tonkinensis by the black setal spots near elytral middle mushroom-shaped or securiform (drop-shaped in T. bimaculatus , sub-rectangular and bordered with short light yellowish brown setae in T. tonkinensis ) in males and converse “V” shaped (sub-rectangular and bordered with short light yellowish brown hairs in T. tonkinensis ) in females, apex (except venter) of femora and basal dorsum of tibiae densely covered with short brown hairs (with short golden yellow hairs in T. bimaculatus and T. tonkinensis ), the three calluses on pronotum large (compare with pronotum, small in T. bimaculatus and T. tonkinensis ); tergite VIII truncated apically (rounded apically in T. tonkinensis ), stem of spiculum gastrale strongly curved at basal 1/4, drop-shaped basally in profile [stem of spiculum gastrale curved (not strongly) at basal 1/4 and hook-like basally in profile in T. tonkinensis ], parameres long (compare with width, short in T. tonkinensis ) and apical 1/2 narrow (compare with basal width, wide in T. tonkinensis ), the interval between both parameres gradually expanded from base to apex (sub-paralleled in T. tonkinensis ), both struts of the anterior tegminal strut separated (combined in T. tonkinensis ) in males.
Type material examined. CHINA: Fujian. Holotype: male ( LPSNU ex CJBH), Mountain temple, Gaoping village, Mangdang mountain , Nanping city, 118°5’24” E, 26°37’43” N, alt. 923 m, 21.V.2019, Jian-Bin Huang leg. GoogleMaps
Paratypes: 1 female ( LPSNU ex CPYL), Daopaiyan , Zhongxian town , Youxi county, Sanming city, 2.VII.2019, Chao-Ming Chen leg. ; 1 male ( YZU), Yichao village , Mangdang town , Yanping district, Nanping city, 14. VI.1983, Bing-Rong Chen leg.
Etymology. This new species is dedicated to Mr. Jian-Bin Huang (ª Ḧ «), who collected the holotype and is a good friend of the authors.
Distribution. Only known from type locality Fujian, China.
Remarks. Figures 5, 7 View FIGURES 5–7 , 22 and 24 View FIGURES 22–28 show the elytra of this new species separated from each other at apex, which was caused by the senior author dissecting the hind wings, the elytra actually are not separated from each other at apex in natural condition; photographs used in Figs. 25–27 View FIGURES 22–28 were taken by the third author outdoors after collecting the specimen instead of in situ.
| YZU |
Yuzhou University |
| VI |
Mykotektet, National Veterinary Institute |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |