Bathyuroconger cf. vicinus, Vaillant, 1888
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4454.1.13 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:71994727-A446-4D66-B7DB-87F9272A5930 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5986580 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C587E2-FFA7-D20C-FF44-FBC8F196F819 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bathyuroconger cf. vicinus |
| status |
|
Bathyuroconger cf. vicinus View in CoL
Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4 , 5C View FIGURE 5 ; Tables 2, 3
Bathyuroconger vicinuS View in CoL : Smith, 1989a:541.
Material examined. USNM 135270 View Materials (2, 444‒475), Indonesia, off NE Borneo, 4°07’00”N, 118°49’54”E, 871 m, Albatross sta. 5585, 28 Sep. 1909 GoogleMaps . ASIZP 73853 View Materials (1, 250+), ASIZP 73804 View Materials (1, 276+), ASIZP 73877 View Materials (1, 200+), 2°37’48.7”N, 150°2’54.2”E, off Papua New Guinea, 840‒865 m, 27 Aug. 2010 GoogleMaps .
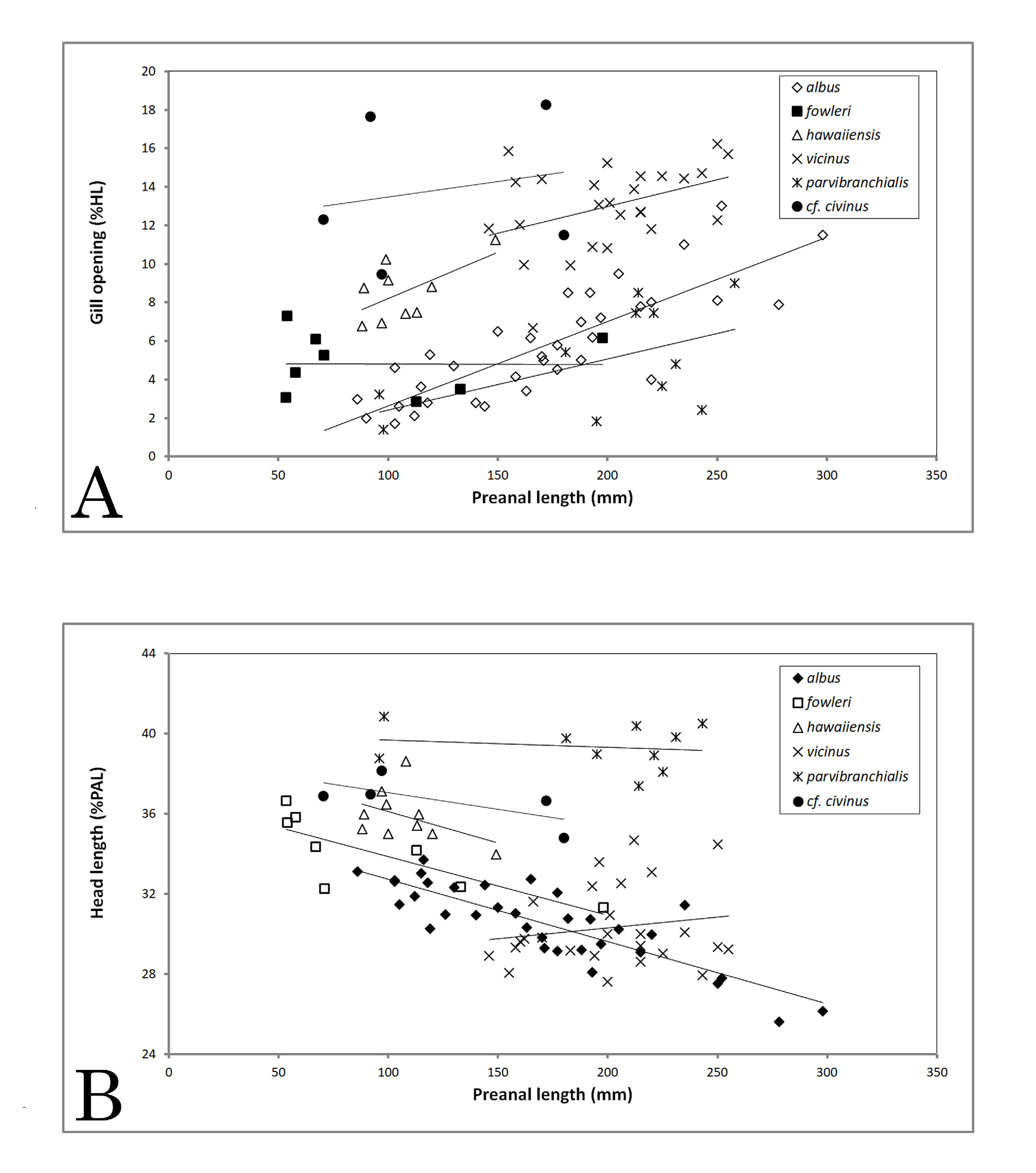
Diagnosis. A species of Bathyuroconger with an unreduced gill opening and 196‒202 total vertebrae.
Description. Measurements in %TL: PAL 34.7‒37.8, PDL 14.6‒15.5, HL 13.3‒14.6, TR 23.2‒24.4, DA 3.8‒4.1. In % PAL: PDL 38.7‒41.1, HL 35.2‒38.6, TR 61.4‒64.8, DA 10.2‒10.8. In % HL: S 27.0‒28.1, E 12.7‒14.4, IOW 12.8‒14.3, UJ 35.2‒35.7, GO 8.1‒15.1, IB 19.4‒25.0, PL 14.9‒16.8. Pores: PALL 47‒48, PDLL 7‒9, PPLL 6‒7; SO 3, IO 5, POM 10, ST 1. Vertebrae: PDV 12‒13, PAV 49‒53, PCV 61‒62, TV 196‒202.
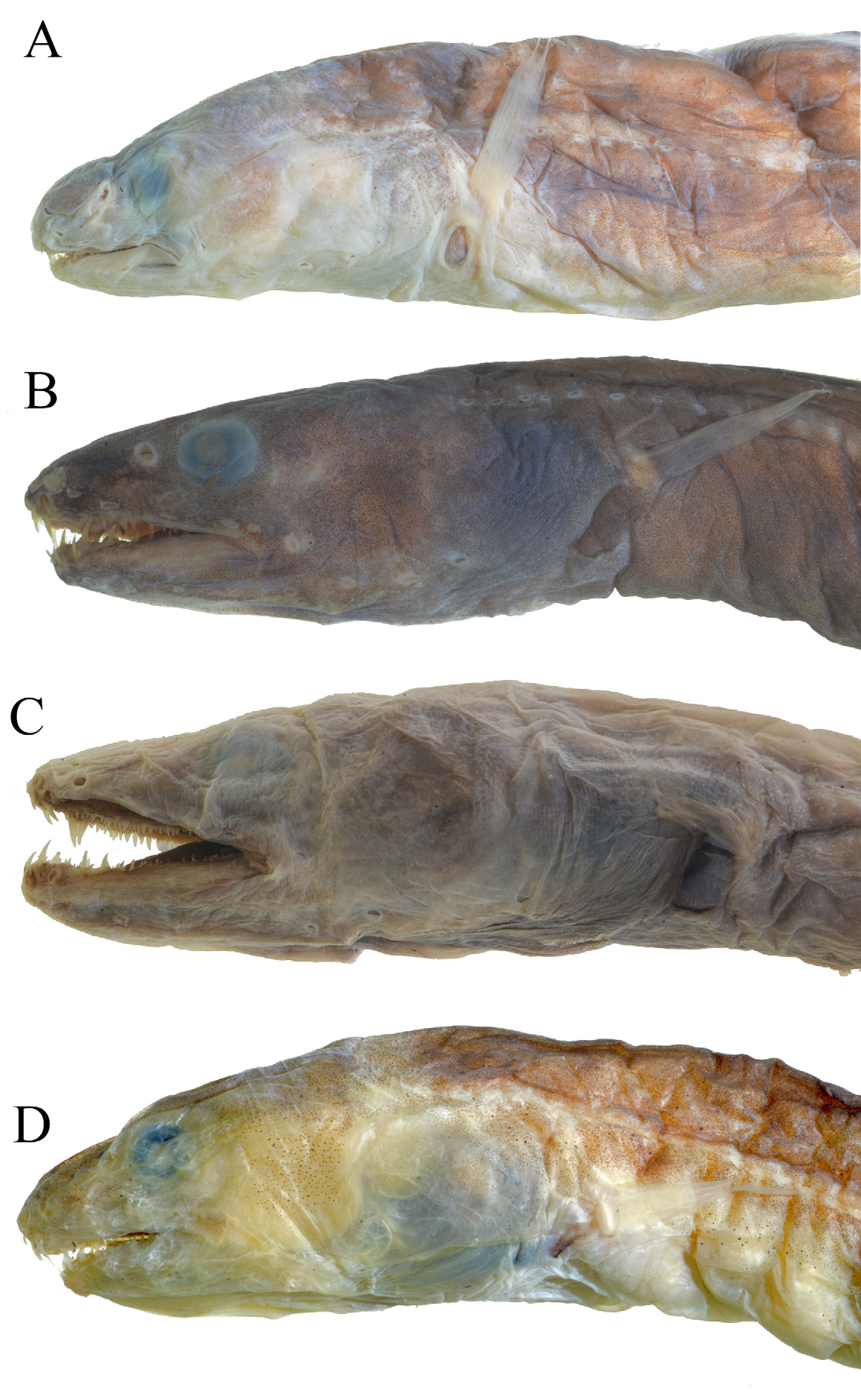
Body slender, cylindrical anteriorly, gradually tapering and compressed posteriorly, trunk moderately long, truck length 1.6‒1.9 times head length. Tail thin, anus anterior to mid-body at slightly more than one-third total length. Dorsal and anal fins confluent with caudal, dorsal fin begins behind base of pectoral fin, anal fin begins immediately behind anus. Head stout, rounded, deeper than body; jaws nearly equal. Snout short and blunt, rounded in dorsal view, about 1.9‒2.2 times eye diameter. Eye moderate, over posterior third of upper jaw, posterior margin at level of rictus; interorbital space about equal to eye diameter. Anterior nostril short and tubular, at front of snout; posterior nostril in front of mid-eye, a simple pore. Gill opening unreduced, its upper margin contacting base of pectoral fin near lower end of fin base.
Head pores moderately enlarged, not elongate and slit-like. Supraorbital pores 3; first pore small, at tip of snout on edge of upper lip, opening ventrally; second pore larger, at level of and anterior to anterior nostril; third pore slightly larger and above posterior margin of anterior nostril; no pores on interorbital space. Infraorbital pores 5; first immediately behind anterior nostril; second between anterior and posterior nostrils; third below posterior nostril; fourth below middle of eye; fifth behind rictus; no pores behind eye. Preoperculomandibular pores 10; 7 on mandibular section, 3 on preopercular section, progressively larger posteriorly, the last one at about level of first lateral-line pore. One median supratemporal pore, anterior to first lateral-line pore. Lateral line complete, lateralline pores large; predorsal 7‒9; prepectoral 6‒7; preanal 42‒47. Vertebrae: predorsal 12‒13, preanal 49‒53, precaudal 61‒62, total 196‒202.
Teeth pointed, variable in size. Intermaxillary teeth in 2 transverse rows of about 4‒6 teeth each, enlarged and fang-like, exposed when mouth closed. Vomer with 1 or 2 enlarged median teeth, with a few smaller teeth around and behind, the row relatively short. Maxillary teeth in 3 rows anteriorly and 2 posteriorly, the outer teeth larger. Dentary teeth in about 3‒4 irregular rows anteriorly, narrowing to 2 rows posteriorly, the outer teeth larger; the anteriormost teeth enlarged and fang-like, exposed when mouth closed.
Color in preservative medium to dark brown; interior of mouth, gill cavity, digestive tract, and peritoneum black.
Remarks. These specimens were included by Smith (1989a) in his account of Bathyuroconger vicinus , provisionally treated as a single world-wide species. He did not mention their unusually high vertebral counts, which would have grouped them with the Hawaiian specimens and separated them from the Atlantic and Indian Ocean specimens. Karmovskaya (2004:S20) reported six specimens from the South Pacific ( Norfolk Island Ridge, Loyalty Ridge, Marquesas Islands) with vertebral counts of ca. 200‒205, which are close to the values of the specimens reported here but also to B. hawaiiensis . She did not mention the condition of the gill opening. Specimens from the Indian and Pacific Oceans need to be examined and compared in more details in order to determine what species are present and where they occur. In the meantime, we refer to the present specimens as Bathyuroconger cf. vicinus .
The third infraorbital pore is somewhat more anterior in this species than in the others, under the posterior nostril and distinctly before the eye.
The three specimens collected from Papua New Guinea have the same coloration and the same gill size as the two Indonesian specimens, but their tails are damaged and the total vertebral counts are unavailable. They are provisionally treated as the same species herein.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Bathyuroconger cf. vicinus
| Smith, David G., Ho, Hsuan-Ching & Tashiro, Fumihito 2018 |
Bathyuroconger vicinuS
| Smith, 1989a :541 |