Lophophaena hispida ( Ehrenberg, 1862 ) Petrushevskaya, 1971
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5160.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A9179C79-EE43-44E4-8723-919505500049 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10551535 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C96F50-FFAA-FFC2-75DF-E7BFFD11C2D1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Lophophaena hispida ( Ehrenberg, 1862 ) Petrushevskaya, 1971 |
| status |
|
Lophophaena hispida ( Ehrenberg, 1862) Petrushevskaya, 1971 View in CoL
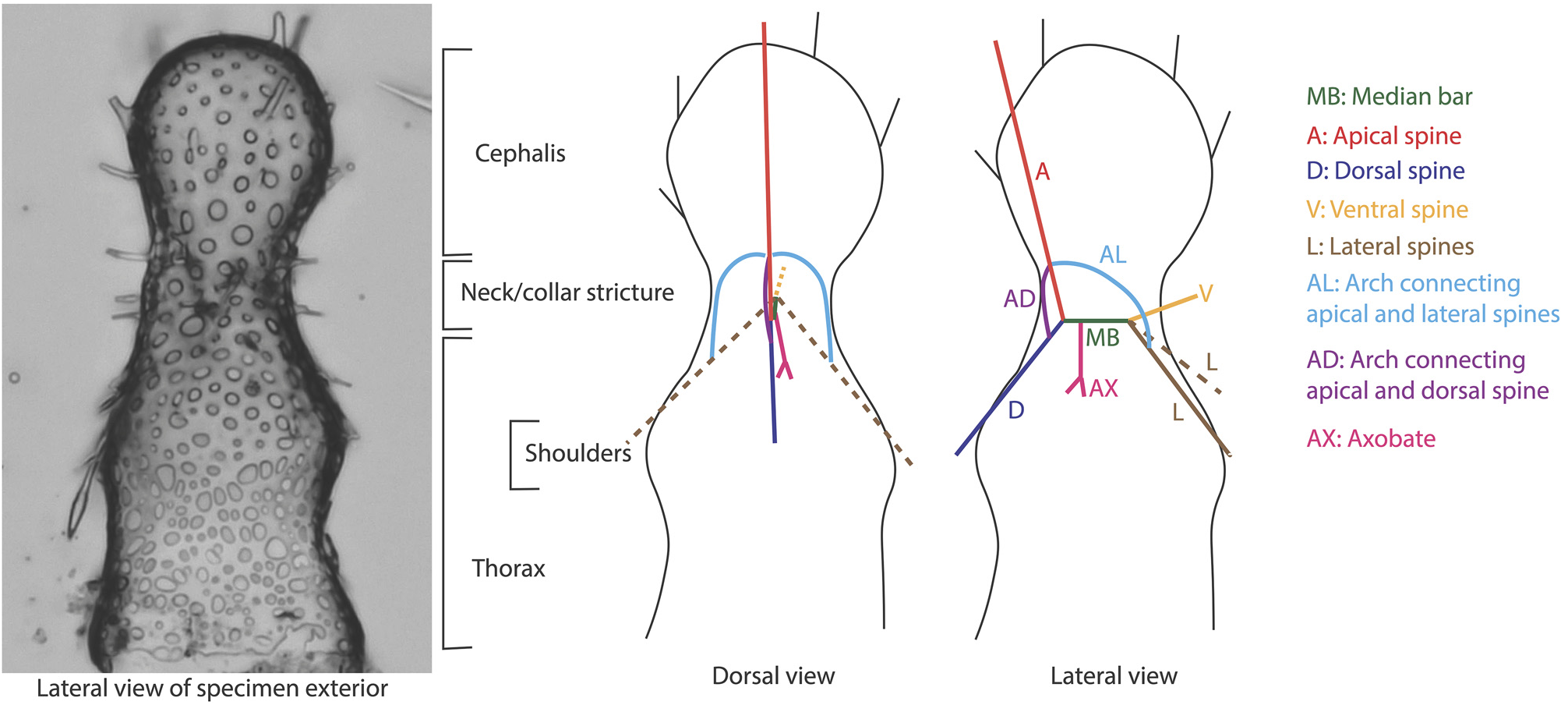
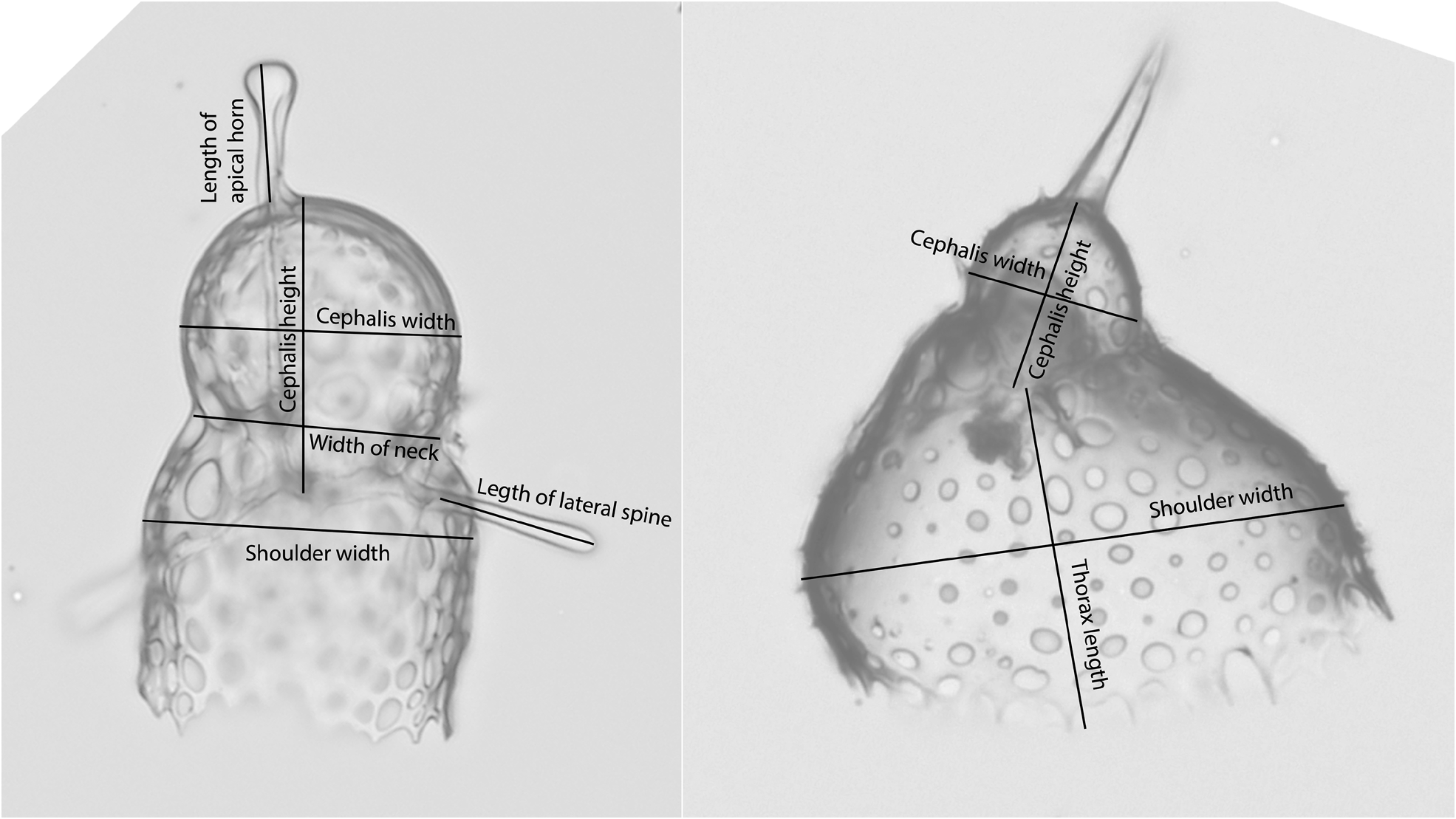
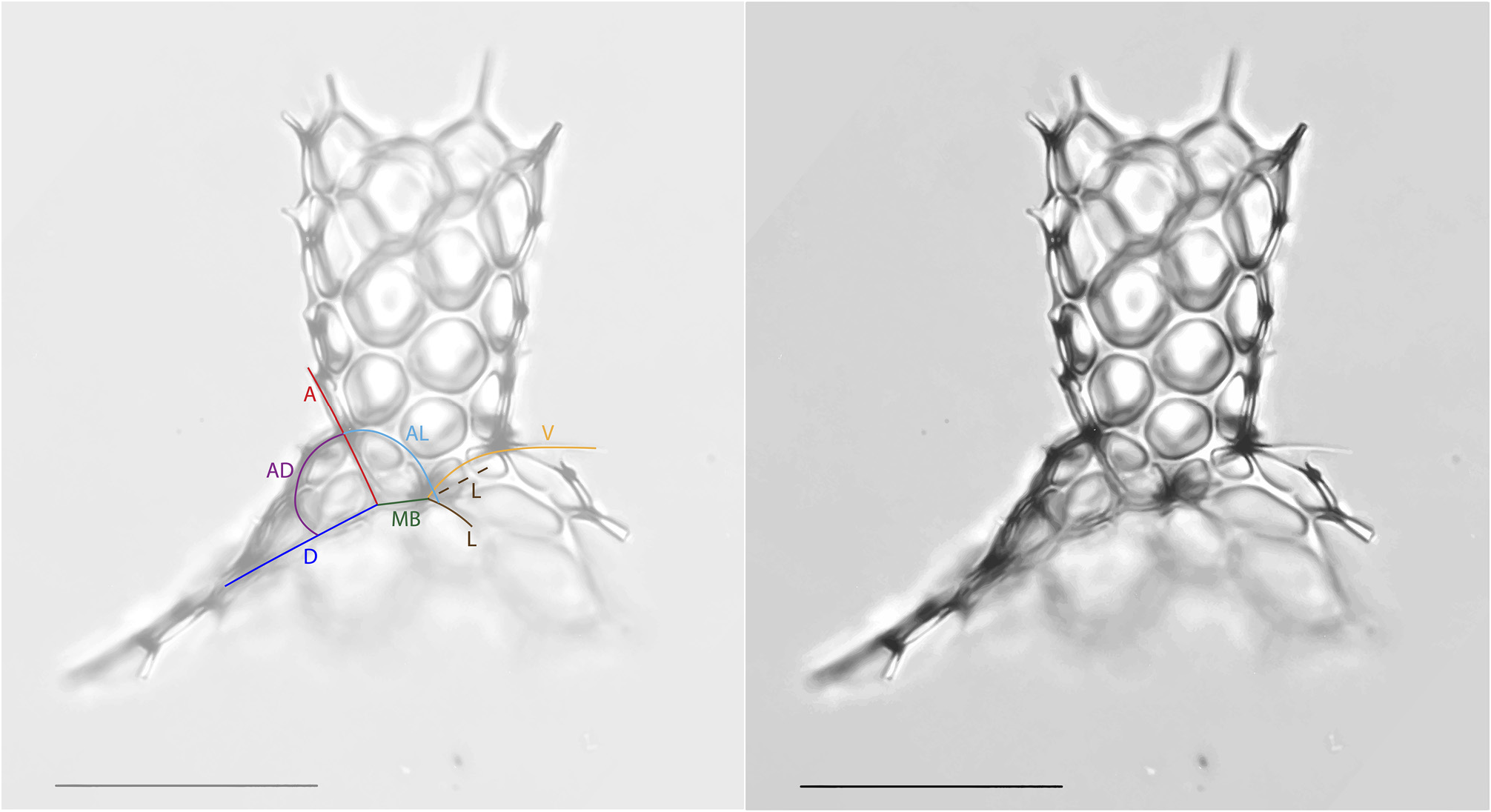
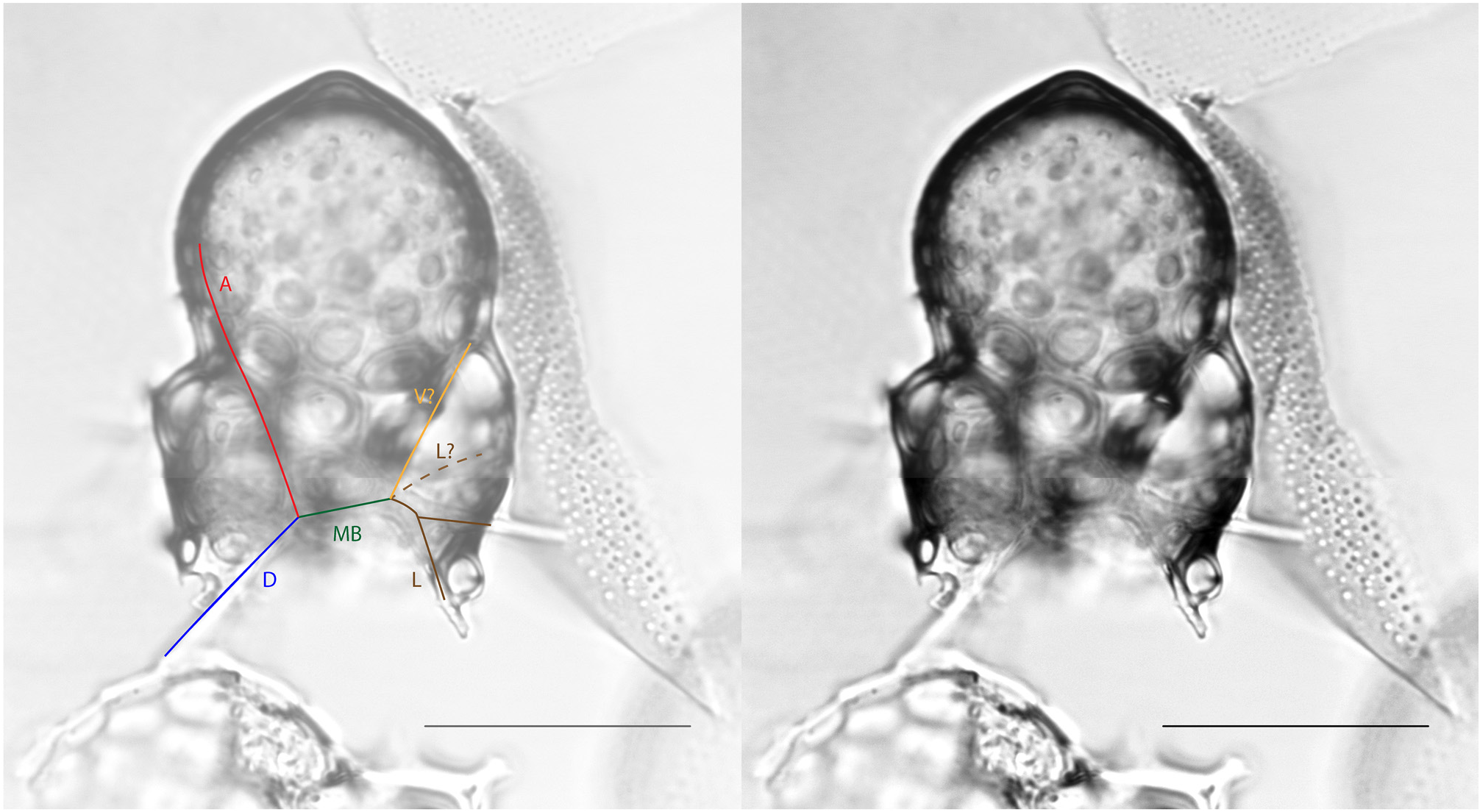
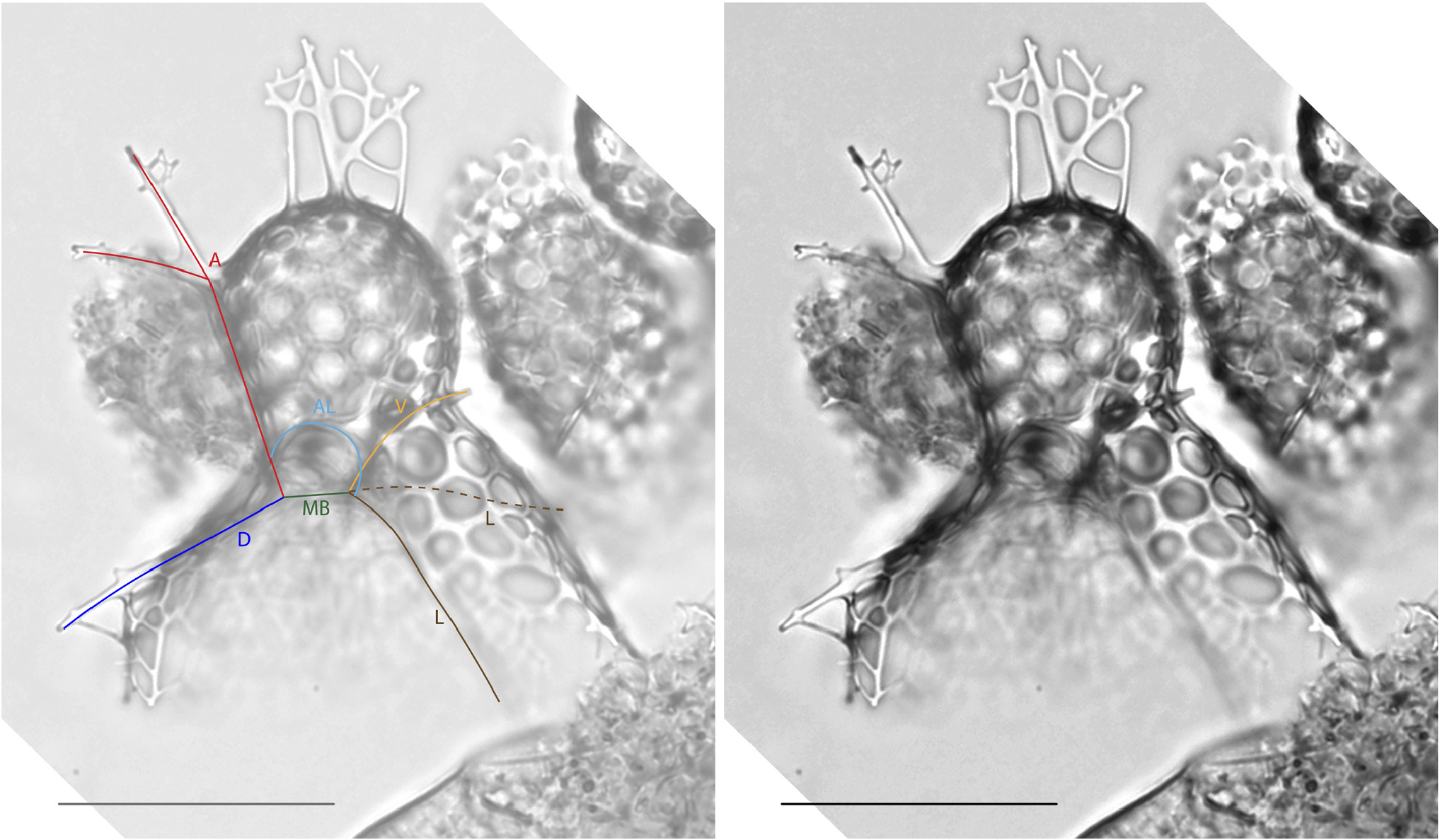
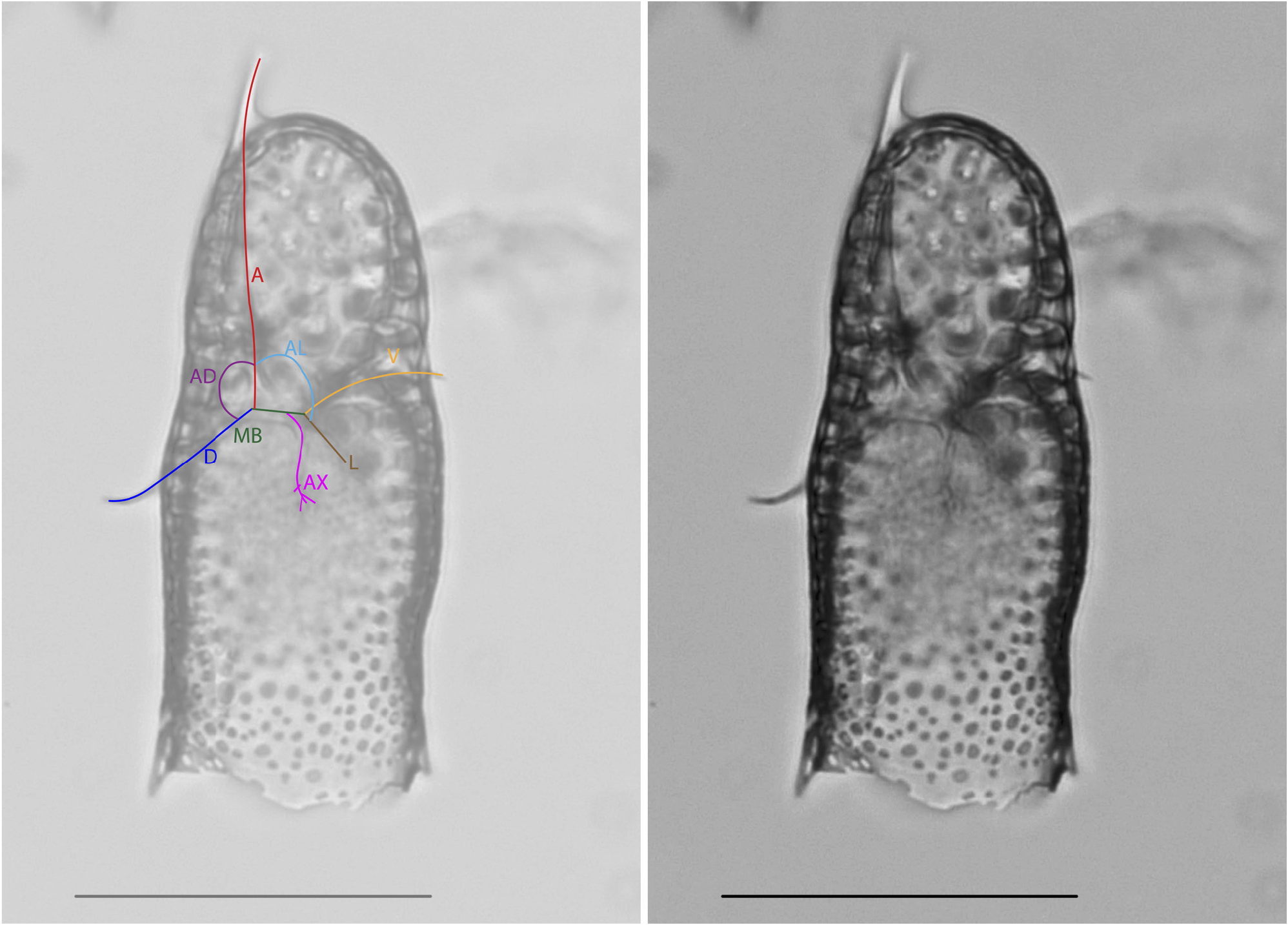
Plate 22, Figs. 5–8B View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7 View FIGURE 8 .
Dictyocephalus hispidus n. sp., Ehrenberg, 1862, p. 298 [not figured].
Dictyocephalus hispidus Ehrenberg, Ehrenberg, 1873b , pl. 5, fig. 18.
Dictyocephalus (Dictyocryphalus) hispidus Ehrenberg, Haeckel, 1887, p. 1309 [not figured].
? Theocapsa democriti n. sp., Haeckel, 1887, p. 1427, pl. 66, fig. 8.
Sethoconus crinitus n. sp., Cleve, 1900, p. 11, pl. 3, fig. 13.
Acanthocorys variabilis n. sp. Popofsky, 1913, p. 360 –364, text-figs. 74–77,?73; non text-figs. 71–72, 78–81.
Lophophaena hispida (Ehrenberg) View in CoL , Petrushevskaya, 1971, p. 115, 117, pl. 61, figs. 1–3.
? Lophophaena hispida Ehrenberg View in CoL , atyp., Petrushevskaya, 1971, pl. 57, fig. 4.
Theocapsa democriti Haeckel, Tan and Tchang, 1976 , fig. 69a–c.
Lophophaena cylindrica Cleve, Renz, 1976 View in CoL , pl. 6, fig. 21.
Lophophaena hispida Ehrenberg, Kruglikova, 1978 View in CoL , pl. 22, fig. 7.
Lophophaena hispida Ehrenberg, Nishimura and Yamauchi, 1984 View in CoL , pl. 32, figs. 6–7.
Lophophaena hispida Ehrenberg, Boltovskoy and Jankilevich, 1985 View in CoL , pl. 4, fig. 6.
Lophophaena hispida Ehrenberg, Nishimura, 1990, p. 93 View in CoL –95, figs. 17.1a–17.3b.
Lophophaena cylindrica Cleve, Takahashi, 1991 View in CoL , pl. 25, figs. 4–5 (non fig. 3).
Lophophaena hispida Ehrenberg View in CoL forma hispida, Van de Paverd, 1995 View in CoL , pl. 65, figs. 1–2.
Lophophaena hispida Ehrenberg, Itaki et al., 2010 View in CoL , pl. 6, figs. 11–12.
Lophophaena hispida Ehrenberg, Matsuzaki et al., 2016 View in CoL , figs. 9.17–9.18.
Lophophaena hispida Ehrenberg, Matsuoka 2017 View in CoL , fig. 22.1–22.8.
Lophophaena hispida Ehrenberg, Trubovitz et al., 2020 View in CoL , supplementary data 7.
Remarks. The basionym of this species is Dictyocephalus hispidus Ehrenberg, 1862 . The species was emended and transferred to the genus Lophophaena by Petrushevskaya (1971). Since then, the species has occasionally been confused with Lophophaena cylindrica (Cleve) Petrushevskaya, 1971 in the literature. Beyond the difference in pore sizes on the cephalis and thorax, L. hispida differs from L. cylindrica (Pl. 22, Figs. 1A View FIGURE 1 – 4 View FIGURE 4 ) in that cephalic spines are directly related to the nodes of the pores. Van de Paverd (1995) split Lophophaena hispida into two forms, L. hispida hispida and L. hispida cylindrica , which are largely consistent with the species designations Lophophaena hispida and Lophophaena cylindrica . Here we maintain that these are two separate species, following the usage most common in the literature, and it is our opinion that the differences between the two justify separate species. Popofsky (1913) illustrated a wide variety of forms within Acanthocorys variabilis , which we herein divide into four species, including L. hispida , as well as L. buetschlii , L. leshii n. sp., and L. variabilis , partially following the designations of previous authors as well as one new species. The specimens of L. hispida in our material varied considerably in their degree of silicification. Some specimens exhibited a closed base of the thorax. Haeckel designated specimens with the enclosed base and more elongated cephalis as a separate species, Theocapsa democriti Haeckel 1887 . We observed a few L. hispida specimens with semi-enclosed and fully-enclosed thorax bases, suggesting this may be an ontogenetic character. However, the specimen Haeckel (1887) figured as Theocapsa democriti also appears to have a more elongated, thumb-shaped cephalis than is typical for L. hispida , so these may indeed be separate species.
Range. Late Pliocene—Recent, EEP ( Table 1 View TABLE 1 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Lophophaena hispida ( Ehrenberg, 1862 ) Petrushevskaya, 1971
| Trubovitz, Sarah, Renaudie, Johan, Lazarus, David & Noble, Paula 2022 |
Lophophaena hispida Ehrenberg, Nishimura, 1990 , p. 93
| Nishimura, H. 1990: 93 |
Lophophaena hispida (Ehrenberg)
| Petrushevskaya, M. G. 1971: 115 |
Acanthocorys variabilis
| Popofsky, A. 1913: 360 |
Sethoconus crinitus
| Cleve, P. T. 1900: 11 |
Dictyocephalus (Dictyocryphalus) hispidus Ehrenberg, Haeckel, 1887 , p. 1309
| Haeckel, E. 1887: 1309 |
Theocapsa democriti
| Haeckel, E. 1887: 1427 |
Dictyocephalus hispidus
| Ehrenberg, C. G. 1862: 298 |