Enochrus (Methydrus) vulgaris (Steinheil, 1869)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.188528 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5630374 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03CB0A3E-FF97-FFED-60C5-D806A75C0EF3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Enochrus (Methydrus) vulgaris (Steinheil, 1869) |
| status |
|
Enochrus (Methydrus) vulgaris (Steinheil, 1869) View in CoL
( Figs. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 2 , 7–10 View FIGURES 7 – 10 , 18–21 View FIGURES 18 – 21 , 24–25 View FIGURES 22 – 25 , 28–29 View FIGURES 26 – 29 , 31 View FIGURES 30 – 31 )
Material examined. ARGENTINA: Buenos Aires City: “Golf Club Lagos de Palermo”, 3 breeding adults collected on 02.xi.2006 by B. Byttebier. Buenos Aires City: Ecological Reserve “Costanera Sur”; 6 breeding adults collected on 02.xi.2006 by B. Byttebier (10 egg cases, 17 instar I, 5 instar II and 7 instar III larvae, 3 pupae, 5 emerged adults).
Diagnosis. Larvae. Coronal sulcus short (instar I) or very short (instar III); left mandible with one inner tooth; AN10 and AN11 subapically on the second antennomere; stipes with MX 4–6 distally on outer margin, located on a longitudinal row; PA26 closer to PA27 than to PA17; sterna III–VII with a pair of prolegs, each one bearing a group of cuticular spine strongly curved as hooks.
Egg case ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 2 ). Total length = 4.34–6.75 mm, width = 1.91–2.36 mm; length without mast = 2.48–3.47; mast length = 1.86–4.09 mm.
Eggs, laid out without specific order pattern inside the egg case. (length = 0.52–0.67 mm, width = 0.27–0.35 mm). Number of eggs variable in each egg case, between 14 and 17 (N = 6).
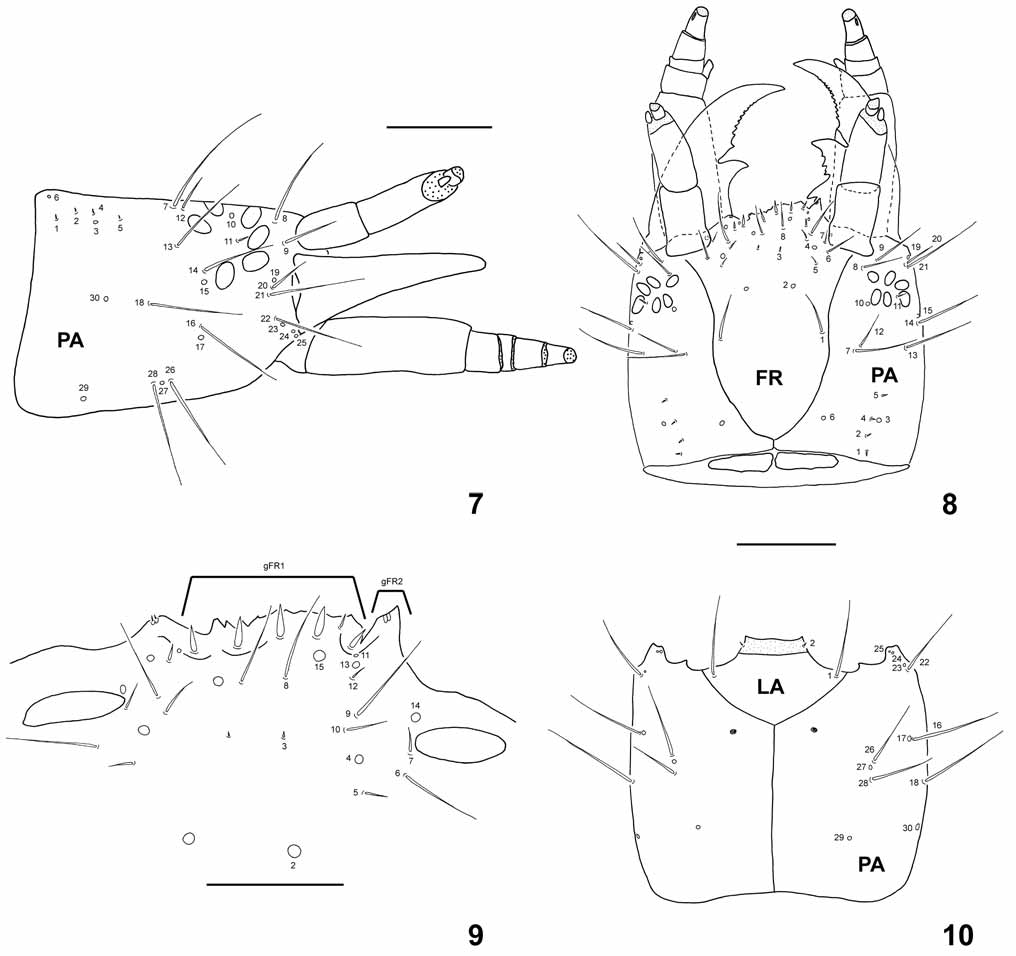
First-instar larva ( Figs. 7–10 View FIGURES 7 – 10 , 18 View FIGURES 18 – 21 ). Morphometric measures detailed in Table 2 View TABLE 2 .
Color. Head capsule dark brown. Antenna, mandible and labium light brown. Maxilla light brown with maxillary palpomere darker in some specimens. Thoracic tergites dark brown, thoracic appendages light brown; membranous areas of the thorax grayish brown. Abdominal sclerites, urogomphi and lateral appendages of abdominal segment VIII dark brown; membranous areas of the abdomen grayish brown.
Head capsule ( Figs. 7–10 View FIGURES 7 – 10 ). Coronal sulcus short. Mandible. Left mandible with one inner tooth.
Thorax. Prosternum composed by one undivided plate with a basal notch.
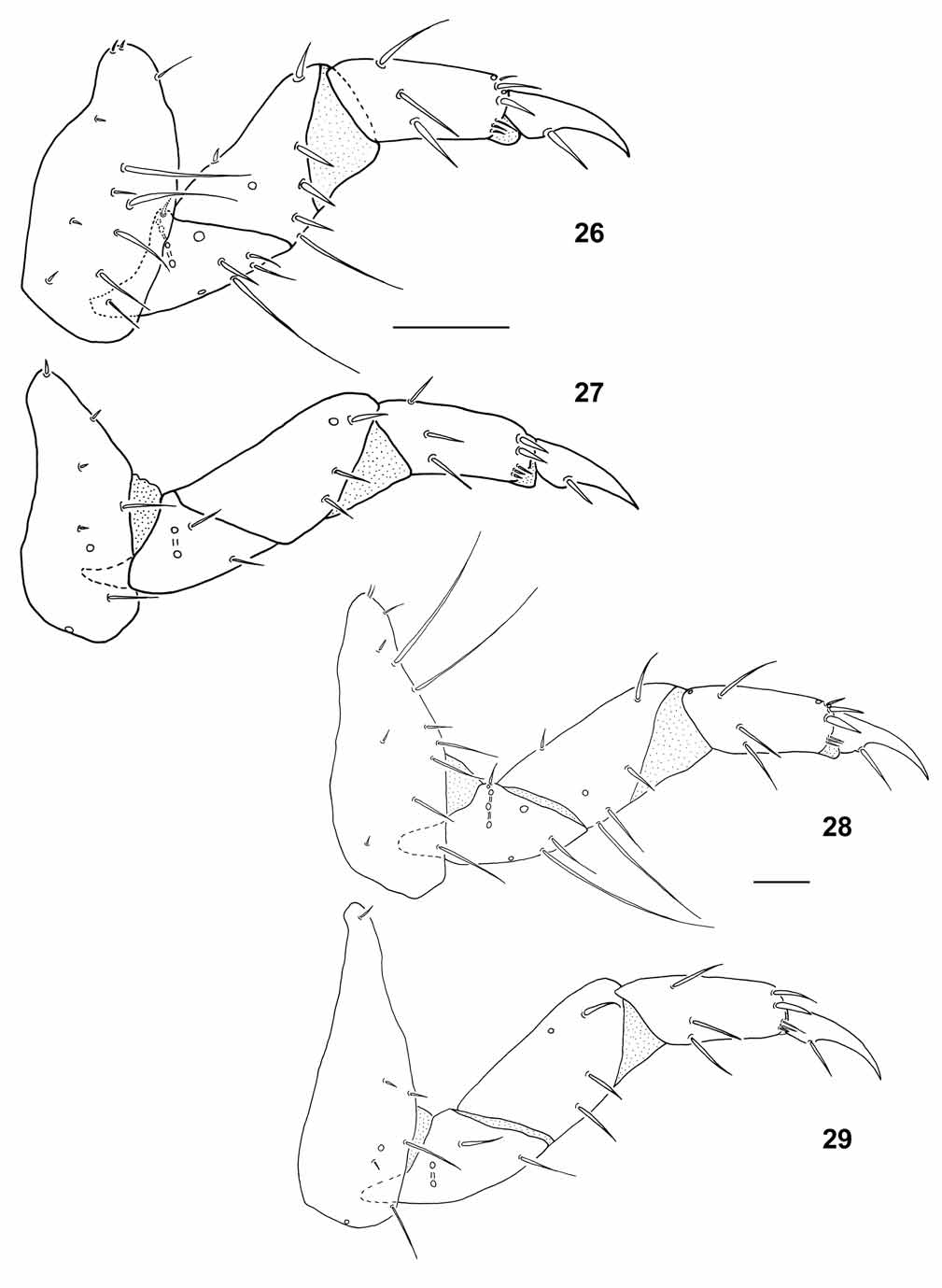
Abdomen. Sterna III–VII with a pair of prolegs, each proleg bearing a group of cuticular spine strongly curved as hooks ( Fig. 31 View FIGURES 30 – 31 ).
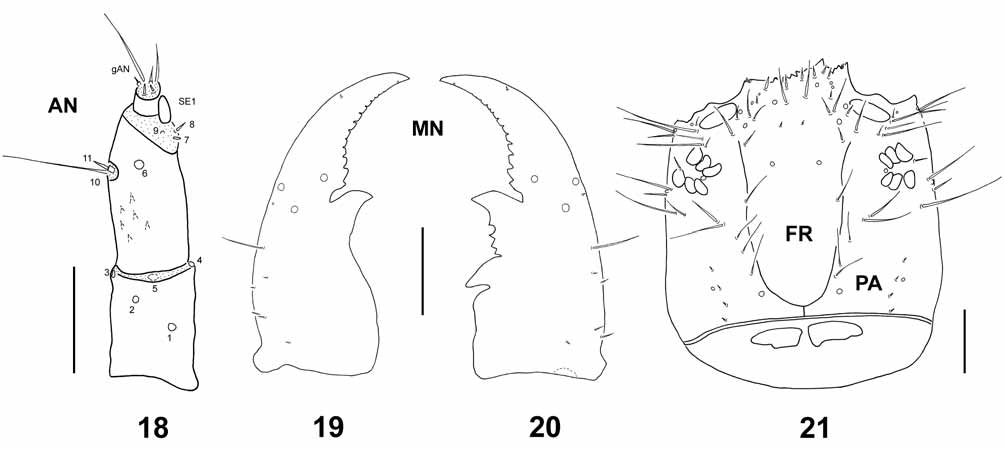
Chaetotaxy ( Figs. 7–10 View FIGURES 7 – 10 , 18 View FIGURES 18 – 21 ). Head capsule ( Figs. 7–10 View FIGURES 7 – 10 ). Ventral surface ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 7 – 10 ) of each parietale, with sensilla PA26–PA28 located on a longitudinal row, very close to each other (PA26 closer to PA27 than to PA17). Antenna ( Fig. 18 View FIGURES 18 – 21 ). AN10 and AN11 situated subapically on outer margin of second antennomere.
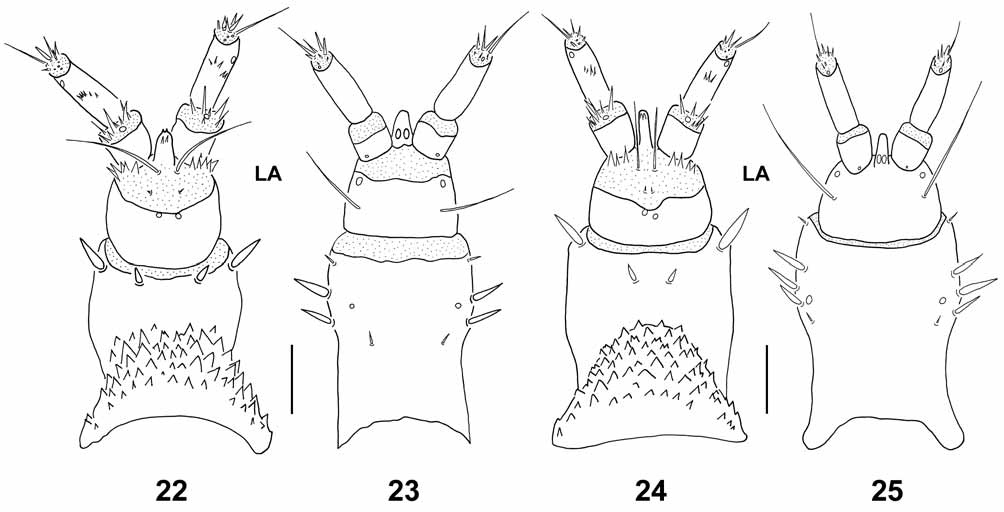
Maxilla. Stipes with MX 4–6 located distally on outer margin, on a longitudinal row. Labium. LA2 located on the membranous area between submentum and mentum ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 7 – 10 ); LA6 very long (1/3 longer than in E. variegatus ). Legs. Ligula without apical processes. Chaetotaxy of legs summarized in Table 3.
Second-instar larva. Similar to first-instar larva except for the following features.
Morphometric measures detailed in Table 2 View TABLE 2 .
Chaetotaxy. Head capsule. Parietale with 10–12 secondary sensilla: 3 setae and 1 pore close to PA8–PA9; 4–5 setae on the lateral margin; a row of 2–3 setae between PA6 and PA7. Mandible. With 5–7 secondary sensilla. Labium. Ligula without minute process apically ( Fig. 24 View FIGURES 22 – 25 ). Legs. Chaetotaxy summarized in Table 3.
Third-instar larva ( Figs. 19–21 View FIGURES 18 – 21 , 24–25 View FIGURES 22 – 25 , 28–29 View FIGURES 26 – 29 , 31 View FIGURES 30 – 31 )
Similar to second-instar larva except for the following features.
Morphometric measures detailed in Table 2 View TABLE 2 .
Head capsule ( Fig. 21 View FIGURES 18 – 21 ). Coronal sulcus short or very short, in general difficult to distinguish.
Thorax. Prosternum composed by one subdivided plate with an incomplete sagittal line on more than the basal third.
Chaetotaxy ( Figs. 19–21 View FIGURES 18 – 21 , 24–25 View FIGURES 22 – 25 , 28–29 View FIGURES 26 – 29 ). Head capsule. Each parietale with 9–11 secondary sensilla: 3 setae and 1 pore close to PA8–PA9; 4–5 setae on the lateral margin; a row of 1–3 setae between PA6 and PA7. Mandible ( Figs. 19–20 View FIGURES 18 – 21 ). With 7–8 secondary sensilla. Labium ( Figs. 24–25 View FIGURES 22 – 25 ). Each lateral margin of mentum with 4 stout secondary setae. Legs ( Figs. 28–29 View FIGURES 26 – 29 ). Chaetotaxy summarized in Table 3.
Pupa. Body. TL (excluding pronotal styli and cerci) = 3.25–4.40 mm; MW = 1.14–1.59 mm.
Head. Maxillary palpi extending to first abdominal segment.
Abdomen. Segment I with 2 pairs of styli situated on a transversal row.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.