Bolbolaimus major, Wen & Huixin & Yanwei & Chunming, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5353.2.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:CE56D56F-B347-46B9-BFB5-8FF8A51C235F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8427208 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03CB879E-FFC4-FFA3-A7E2-F96DA6B8F885 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bolbolaimus major |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Bolbolaimus major sp. nov.
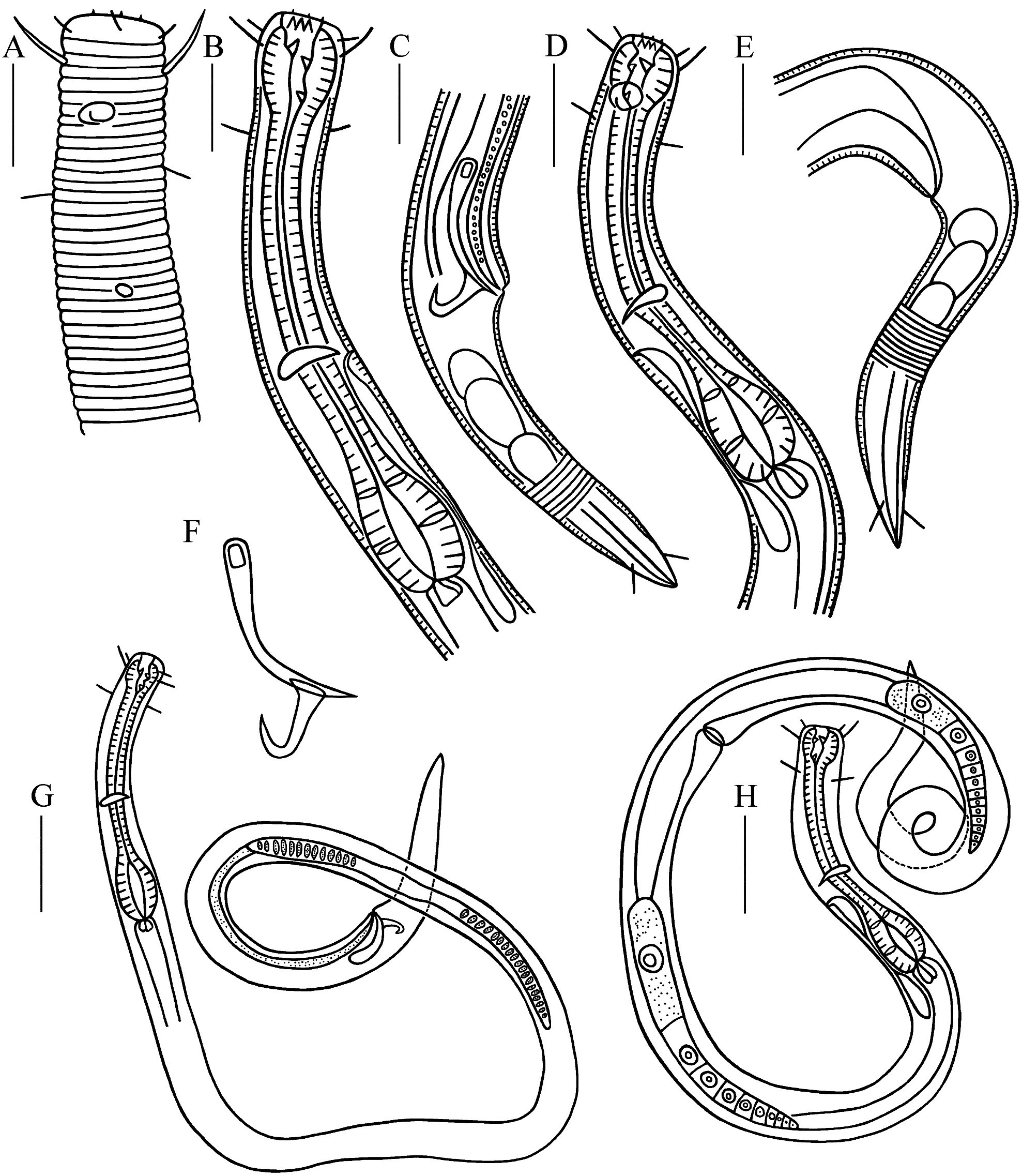
( Figures 1–2 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 , Table 1 View TABLE 1 )
Type material. Five males and three females were measured and studied. Holotype: ♁1 on slide 22 JSDN 1–2 – 54 ; paratypes: ♁2 on 22 JSDN 1–3 – 46 , ♁3 on 22 JSDN 1–2 – 41 , ♁4 on 22 JSDN 1–1 – 70 , ♁5 on 22 JSDN 1–2 – 63 , ♀ 1 on 22 JSDN 1–2 – 69 , ♀ 2 on 22 JSDN 1–2 – 41 , and ♀ 3 on 22 JSDN 1–2 – 68 .
Type locality and habitat. Rizhao coast, Shandong Province, China, 35°14′N, 119°24′E GoogleMaps .
Etymology. major refers to the large body size.
Measurements. All measurement data are given in Table 1 View TABLE 1 .
Description. Males. Body relatively large and cylindrical, with faint golden colour. Cuticle strongly annulated from immediately posterior to cephalic setae to near tail tip. Six inner labial sensilla papilliform and six outer labial sensilla setiform, 4–5 μm in length (0.17–0.25 head diameter long) in two separate circles. Four cephalic setae, 0.48– 0.65 head diameter long, situated at the level of dorsal tooth. Somatic setae (6–7 μm long) only present in pharynx region and at the posterior end of the tail. Head blunt, slightly set off from the rest of the body. Amphidial fovea situated 0.57–0.70 head diameter from anterior end, unispiral and oval shaped, 7 µm in width and 4 µm in length, small (31.8–35.0% c.b.d.—corresponding body diameter) and completely surrounded by cuticle annulations. Buccal cavity large, 22–24 µm in depth, obviously cuticularized. Cheilostoma short with 12 cuticularized longitudinal folds. Pharyngostoma with one large dorsal tooth and two subventral teeth, one tooth opposite the dorsal one and one tooth lies at the base of posterior part of pharyngostoma. Pharynx cylindrical, anterior region surrounding buccal cavity swollen into a prominent bulb, posterior region muscular and swollen into an oval-shaped bulb (21.5– 23.5% of pharynx length). Nerve ring slightly posterior to middle pharynx region (52.1–56.8% of pharynx length). Secretory–excretory system present; renette cell situated slightly posterior to pharynx bulb, excretory pore located posterior to the nerve ring. Cardia elongated triangular.
Reproductive system diorchic, testes opposed and outstretched. Sperm cells large, maximum dimensions 13×11 µm. Two equal spicules, curved, 1.58–1.78 cloacal body diameters long, with slightly swollen proximal end and pointed distal end. Gubernaculum short, apophysis dorso–caudally directed with anterior pointed hook. Precloacal supplement not observed. Tail conical, 3.9–4.4 cloacal body diameters long. Three caudal glands and spinneret very short.
Females. Similar to males in most characteristics. Amphidial fovea unispiral and circular shaped, occupying 29.2–30.4% of the body width, 7 µm in width and 7 µm in length. Reproductive system didelphic, with opposed and outstretched ovaries. Anterior ovary to left of intestine and posterior ovary to right of intestine. Vulva at the middle of the total body. Vagina short and surrounded by constrictor muscles.
Differential diagnosis and discussion. Bolbolaimus major sp. nov. is characterized by large body size, cuticle strongly annulated, head slightly set off from rest of the body, buccal cavity large with one large dorsal tooth and two small subventral teeth, six outer labial sensilla setiform and four cephalic setae long, amphidial fovea in the level of posterior part of buccal cavity, pharynx with anterior and posterior bulb, spicules curved with proximal end slightly swollen, gubernaculum with anterior–hooked dorso–caudal apophysis and tail conical with short spinneret.
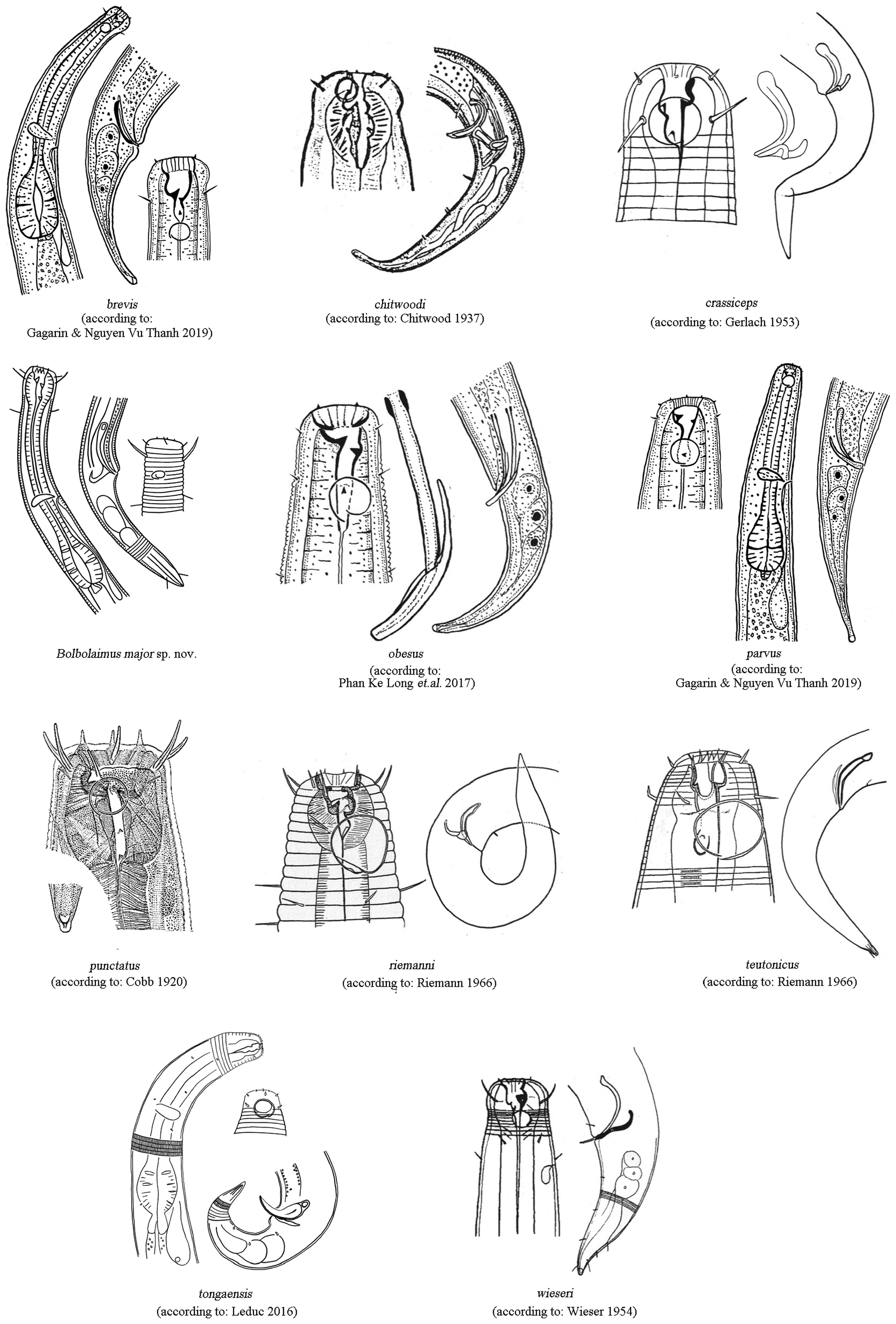
The new species belongs to the group of head slightly set off and with prominent anterior pharynx bulb ( Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 ) and morphometric characters of valid species of Bolbolaimus are given in Table 2 View TABLE 2 . Bolbolaimus major sp. nov. differs from all other species of the genus Bolbolaimus by amphidial fovea oval shaped in males and circular shaped in females and gubernaculum apophysis with anteriorly pointed hook. B. major sp. nov. is similar to B. chitwoodi , B. riemanni ( Riemann, 1966) Jensen, 1978 and B. wieseri in body length and gubernaculum shape but it differs from B. chitwoodi in amphidial fovea position (0.57–0.70 head diameter from anterior end vs. at anterior body end), cephalic setae length (11–13 μm vs. 2.5 μm), and tail shape and length (conical, c=10.5–11.3 vs. conical and cylindrical, c=6.3–6.6) (Phan Ke Long et al. 2017); differs from B. riemanni in amphidial fovea size (32–35% c.b.d. vs. 50% c.b.d.), cephalic setae length (11–13 μm vs. 6.3 μm) and spicules shape and length (slightly swollen in proximal end, 41–42 μm vs. even in length, 20.5 μm); differs from B. wieseri in outer labial setae length (setiform, 4–5 μm in length vs. papilliform), and tail length (3.9–5.1 cloacal body diameter vs. 2.2–2.3 cloacal body diameter).
By now, B. major sp. nov. is the only species of Bolbolaimus deposited in Genbank. It shows a close relationship with Microlaimus korari Leduc, 2016 in phylogenetic trees based on SSU and LSU D2–D3 fragment sequences, but it differs by 8% (109 in 1451 bp, including 16 gaps) in SSU and 18% (102 in 564 bp, including 18 gaps) in LSU D2–D3 fragment. Although Bolbolaimus and Microlaimus show high morphological similarities, M. korari can be easily differentiated by short cephalic setae (2 μm), anterior pharynx bulb only slightly swollen, long spicules (84 μm) and gubernaculum without dorso-caudally apophysis ( Leduc 2016).
The SSU interspecific p-distance among family Microlaimidae (identified to species level) is 0.1221±0.0067, and intrageneric p-distance among genus Microlaimus is 0.0957±0.0069. The mean SSU p-distance of B. major sp. nov. to other species is 0.2361±0.0173. The LSU D2–D3 fragment interspecific p-distance among family Microlaimidae (only Aponema pseudotorosum Fu & Leduc, 2019 and Microlaimus korari identified to species level) is 0.3644±0.0188, and the mean p-distance of B. major sp. nov. to other species is 0.3131±0.02607. Intraspecific and intrageneric p-distances based on SSU and LSU D2-D3 fragment confirm B. major sp. nov. as a new species.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |