Bambusicola autumnalis R.R. Liang, S.N. Zhang and Jian K. Liu, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.601.3.1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8141740 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03CDC56B-FFBA-FFB4-FF17-D597FC41FB0C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bambusicola autumnalis R.R. Liang, S.N. Zhang and Jian K. Liu |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Bambusicola autumnalis R.R. Liang, S.N. Zhang and Jian K. Liu , sp. nov.
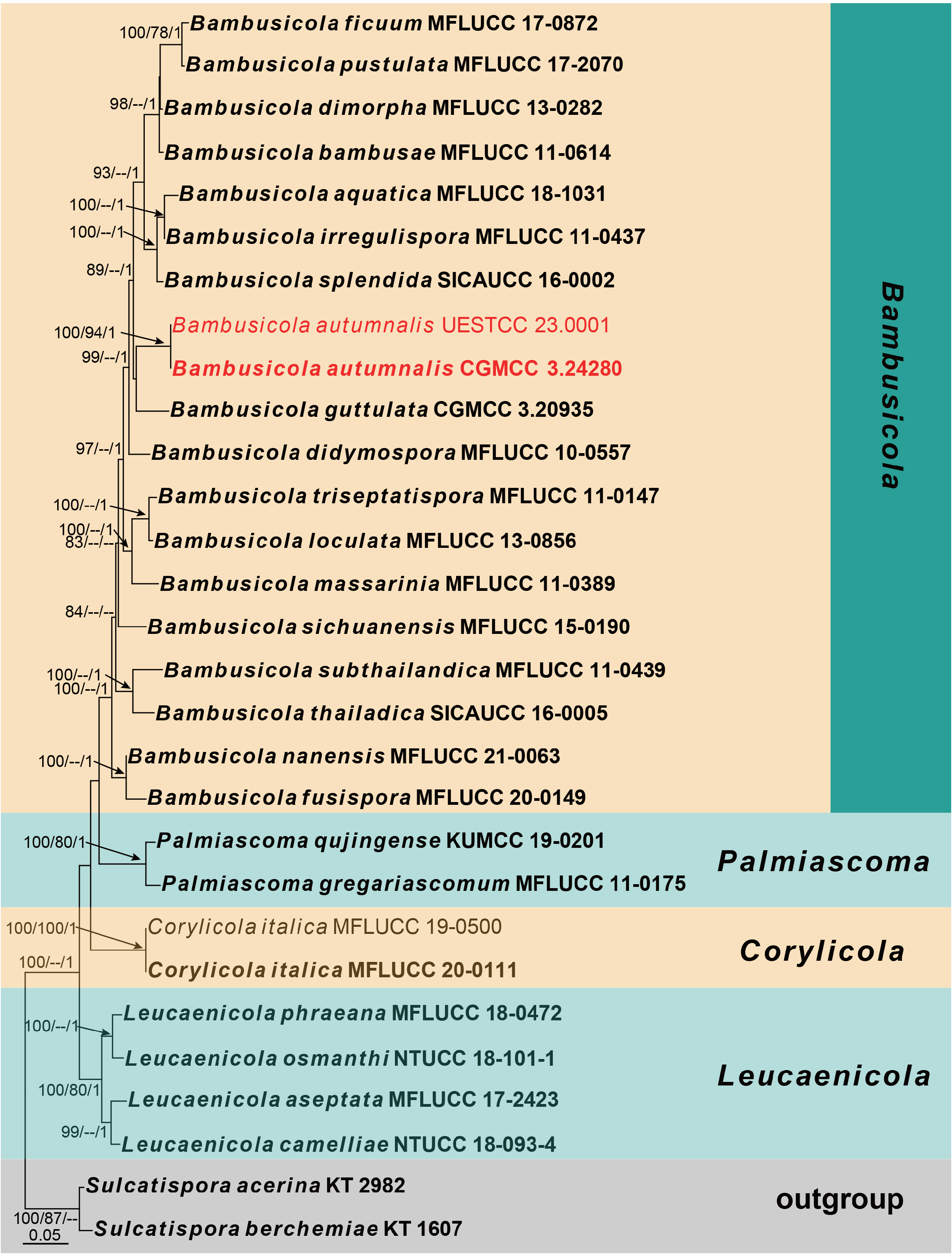
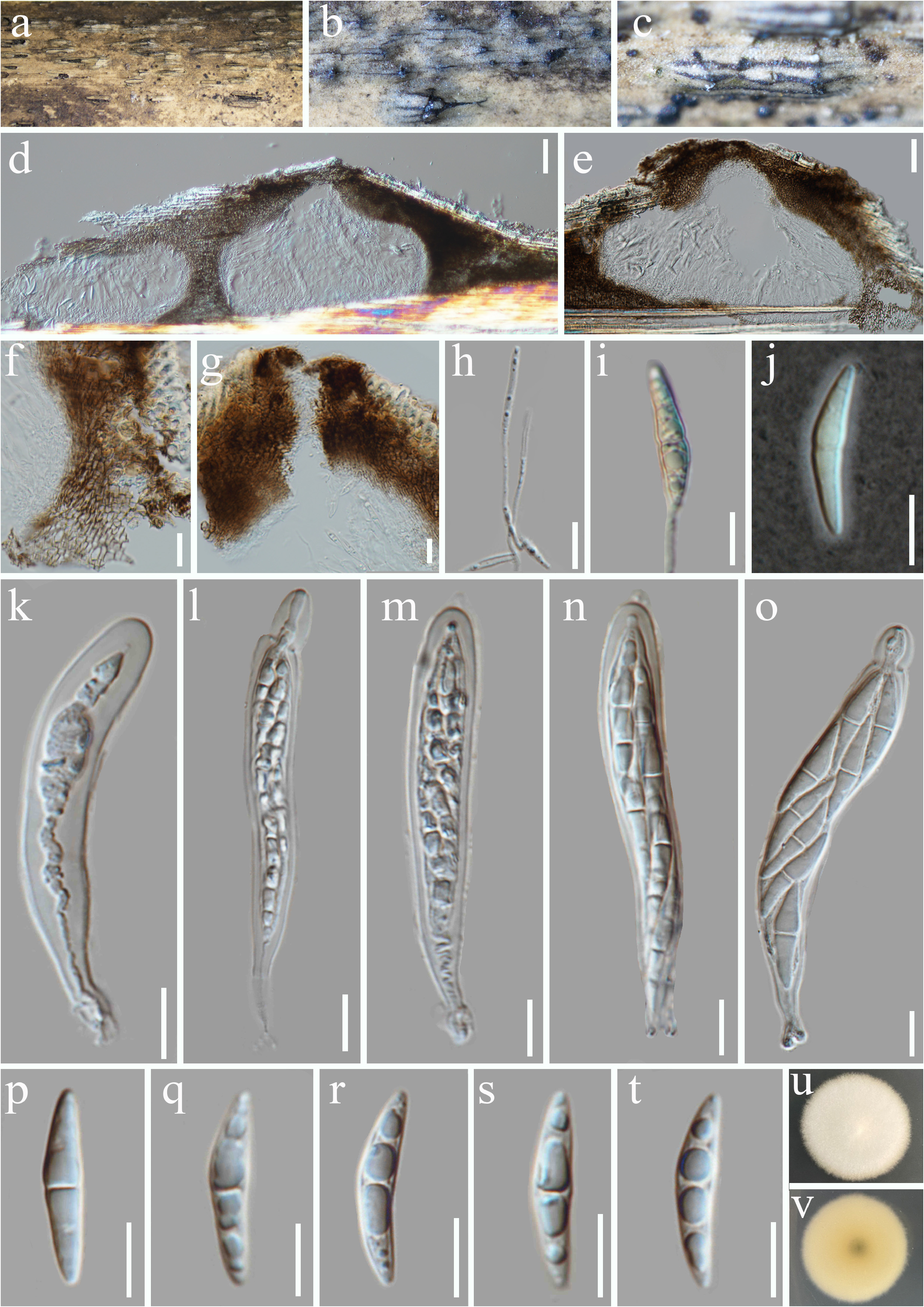
MycoBank: 847551; FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 2 .
Etymology: —The epithet “ autumnalis ” refers to the season “autumn” when the fungus was collected.
Holotype:—HKAS 126508
Saprobic on dead bamboo branches. Sexual morph: Ascostromata solitary to gregarious, rarely scattered, immersed to erumpent, pseudostromatic, visible as bumped areas with cracks and a central black minute papilla, in vertical section conical to subglobose, ostiolate, periphysate, individual locules 190–325 μm high, 215–295 μm diam ( x = 280 × 250 µm, n = 10). Peridium 19–43 μm, composed of several layers of thick-walled, brown cells of textura angularis. Hamathecium 1–1.9 μm wide, trabecular pseudoparaphyses, anastomosing, hyaline, remotely septate. Asci 52–102 × 8–17 µm ( x = 71 × 12 µm, n = 20), 8-spored, bitunicate, fissitunicate, long cylindric-clavate, shortly pedicellate, apically rounded with a minute ocular chamber. Ascospores 22–30 × 4.5–7 µm ( x = 27 × 5 µm, n = 30), overlapping bi-seriate or multi-seriate, fusiform, 1-septate, constricted at the septum, guttulate, smooth-walled, surrounded by a thin, inconspicuous mucilaginous sheath. Asexual morph: Undetermined.
Culture characteristics:—Colonies on PDA reaching 28–32 mm after 4 weeks incubated at 25 °C in dark, circular, dry, mycelium velvety, milky white to pale yellow, reverse yellow to light brown.
Material examined:— CHINA, Sichuan province, Chengdu city, Chengdu Botanical Garden , 30°76.48’ N, 104°13.03’ E, 516 m elevation, on dead branches of bamboo in a terrestrial environment, 21 Nov. 2022, R.R. Liang, (HKAS 126508, holotype), ex-holotype living culture CGMCC 3.24280 ; ibid., HUEST 23.0001, isotype, ex-isotype living culture UESTCC 23.0001 .
Notes:—Multi-gene phylogenetic analysis showed that our isolates belong to Bambusicola and are closely related to B. guttulata ( FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 1 ). However, it is not able to compare their morphology as the latter species only represented by a coelomycetous asexual morph. Nevertheless, Bambusicola autumnalis differs from B. guttulata in their nucleotide sequences, viz. SSU (6/950), ITS (44/450), LSU (17/800), RPB2 (73/993) and TEF1-α (49/959), respectively. Morphologically, Bambusicola autumnalis resembles B. loculata in having stromatic ascomata, 8-spored, cylindric asci, and narrowly fusiform, 1-septate ascospores surrounded by an inconspicuous sheath ( Dai et al. 2015). However, they have different dimensions of asci (52–102 × 8–17 μm vs. 80–105 × 8–13 μm) and ascospores (22–30 × 4.5–7 µm vs. 22–26.5 × 5–6), and the bumped ascostromata with cracks of B. autumnalis also differs from B. loculata . Moreover, the two species are phylogenetically distinct ( FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 1 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |