Premicrodispus gorganiensis Rahiminejad & Seyedein, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.24349/acarologia/20204388 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:7FD7D3DB-1488-4C29-9519-AD8B6262D005 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/686F49BC-B7F0-409F-A406-96217D5A4CCA |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:686F49BC-B7F0-409F-A406-96217D5A4CCA |
|
treatment provided by |
Marcus |
|
scientific name |
Premicrodispus gorganiensis Rahiminejad & Seyedein |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Premicrodispus gorganiensis Rahiminejad & Seyedein sp. nov.
Zoobank: 686F49BC-B7F0-409F-A406-96217D5A4CCA
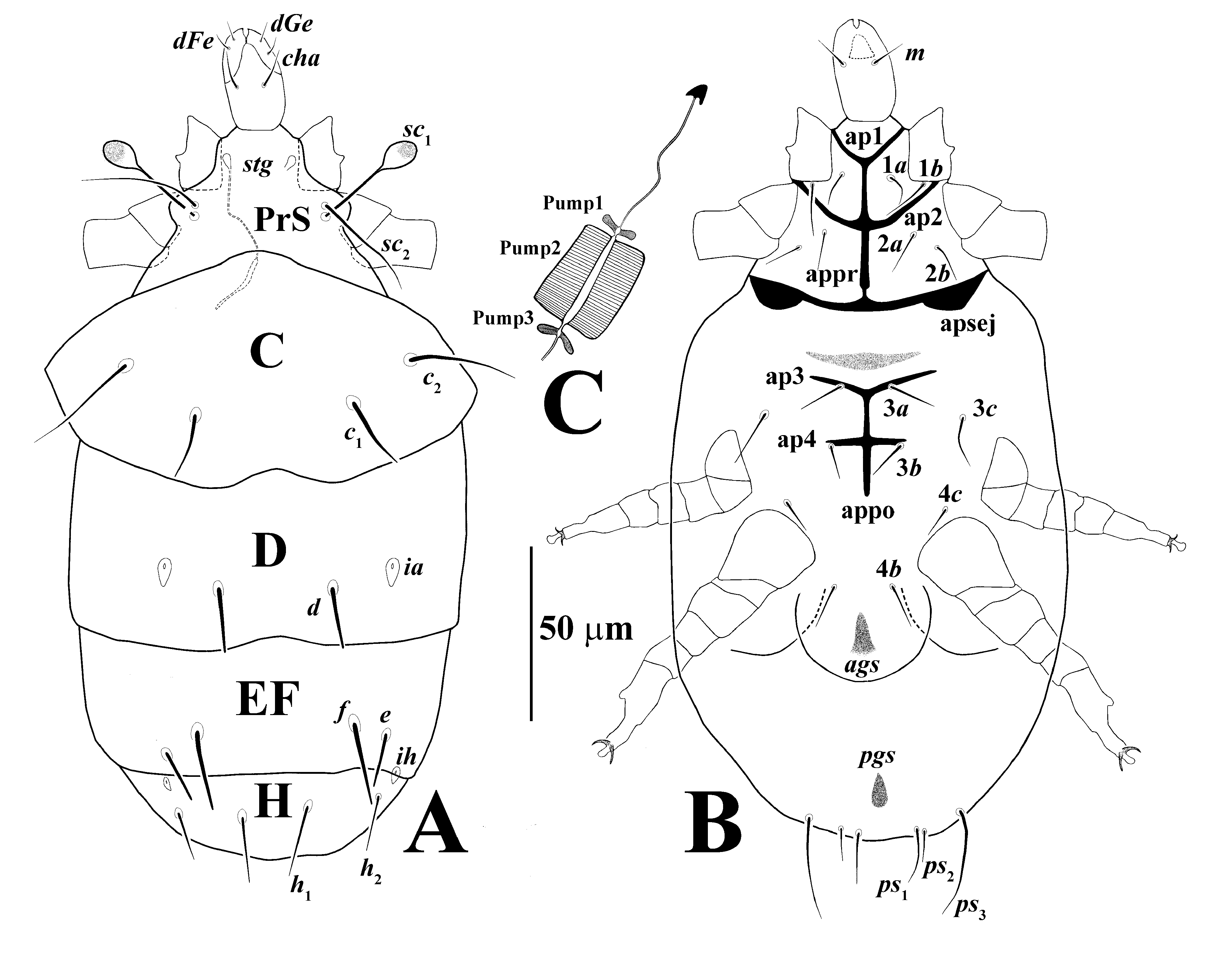
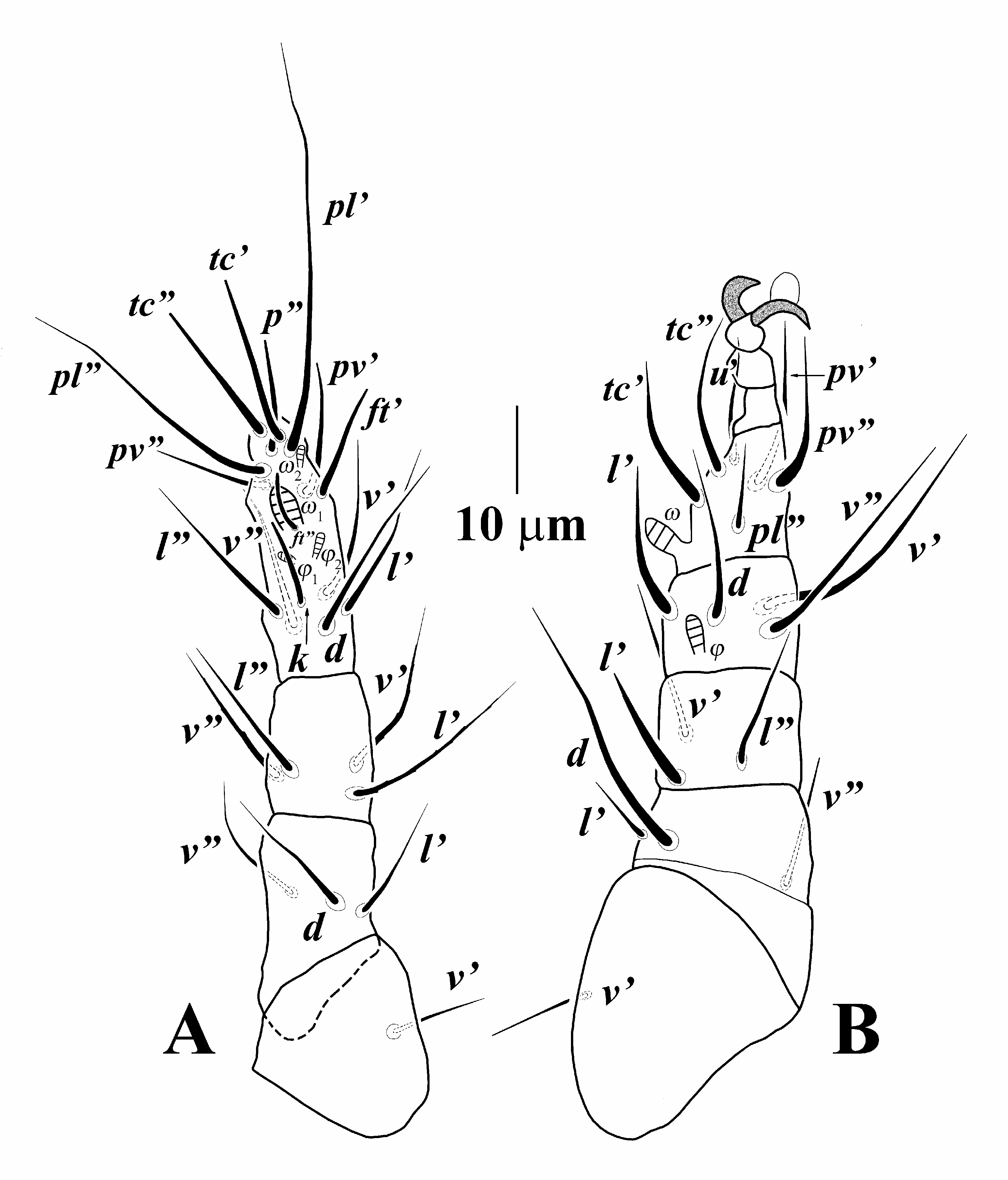
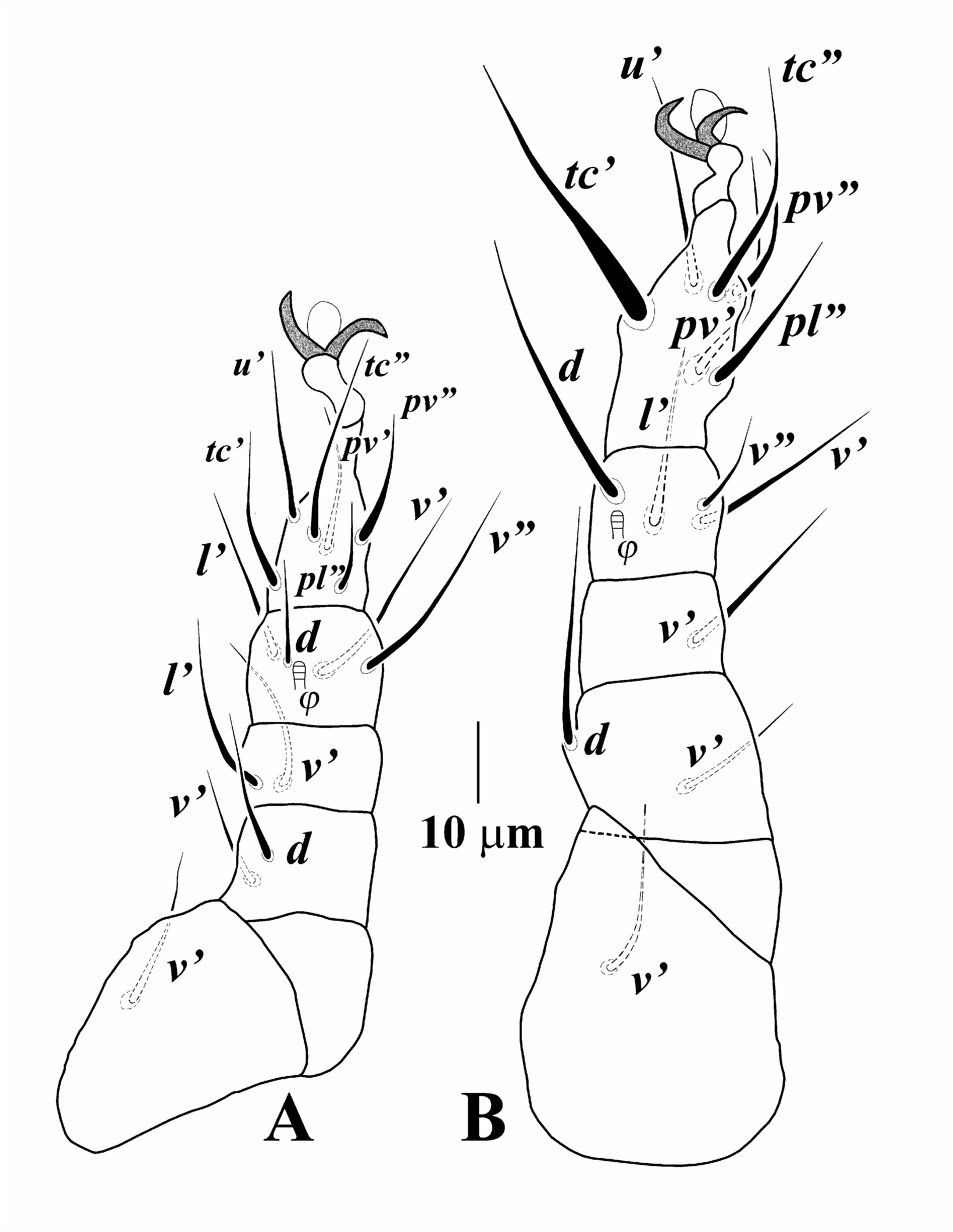
( Figures 1–3 View Figure 1 View Figure 2 View Figure 3 )
Diagnosis — The new species is characterized by posterior margin of tergites C and D with a distinct median incision; setae d, e and f blunt-ended; setae e not associated with ridge; distance d–d about 1.5 times longer than seta d; seta h 1 less than 1.5 times longer than h 2;
seta 4 a absent and seta ps 2 present; tibiotarsus I with four solenidia; all dorsal setae extending posterior border of their tergites; cupuli ia and ih rhombic.
Description — Female. Length of body (including gnathosoma) 236 (229–241), width 121 (118–125).
Gnathosoma ( Figs 1A & B View Figure 1 )– gnathosomal capsule elongated, dorsally with one pair of cheliceral setae, cha 11 (10–11). Palpal femorogenu with subequal setae dFe 5 (5–6) and dGe
7 (6–8). Gnathosoma ventrally with one pair of subcapitular setae m 11 (10–11). Pharyngeal system well sclerotized ( Fig. 1C View Figure 1 ), including three pumps, pump 2 developed with transversely striate and pumps 1 and 3 vestigial.
Idiosomal dorsum ( Fig. 1A View Figure 1 ) – Body elliptic, all tergites smooth; stigmata oval and associated with thin tracheal trunks; all dorsal setae smooth; setae d, e and f blunt-ended,
other dorsal setae pointed; prodorsal shield with elliptic stigmata, trichobothria with long stem, clavate and sparsely barbed, setae sc 2 36 (32–37); tergite C with two pairs of setae c 1 21
(20–24) and c 2 32 (30–35), setae c 2 longer than c 1, posterior border of tergites C and D with distinct median incision; tergite D with setae d 18 (17–19), and cupuli ia rhombic and situated postero-laterad setae d; tergite EF with two pairs of setae e 14 (13–14) and f 23 (21–24), bases of setae e not associated with linear ridge; tergite H with setae h 1 21 (20–22), h 2 16 (15–16),
cupuli ih rhombic and situated posteriad setae h 2; distance h 1 – h 1 subequal to h 1 – h 2; all dorsal setae reach to posterior border of their tergites. Distances between dorsal setae: sc 2 – sc 2 37
(35–39), c 1 – c 1 45 (41–48), c 2 – c 2 80 (79–83), c 1 – c 2 22 (20–23), d–d 31 (30–32), e–e 80 (76–84),
e–f 11 (10–12), f –f 45 (44–48), h 1 – h 1 18 (18–20), h 2 – h 2 57 (54–58), h 1 – h 2 19 (19–20).
Idiosomal venter ( Fig. 1B View Figure 1 ) – Apodemes 1 (ap1) and 2 (ap2) well developed and joined with prosternal apodeme (appr), sejugal apodeme (apsej) thick, well sclerotized and joined with appr; all ventral plates smooth; all ventral setae pointed and smooth; setae a 4absent; anterior margin of posterior sternal plate straight, without lobe; apodemes 3 (ap3) extending beyond bases of setae 3 a; apodemes 4 (ap4) short and reaching to bases of setae b 3; apodemes 5 absent; posterior margin of posterior sternal plate tripartite; coxal field I with setae a 1 11 (11–12), 1 b 16 (15–17); coxal field II with setae 2 a 11 (11–12), 2 b 11 (10–12); coxal field III with setae
3 a 14 (13–14), 3 b 11 (9–11), 3 c 16 (16–18); coxal field IV with setae 4 b 14 (13–15) and 4 c 11 (11–12), setae 1 b and 3 c subequal and longest on idiosomal venter; pseudanal plate with setae ps 1 17 (16–18), ps 2 9 (8–9) and ps 3 31 (30–34).
Legs ( Figs 2 View Figure 2 , 3 View Figure 3 ) – Leg I ( Fig. 2A View Figure 2 ). Thinner and shorter than other legs. Setal formula: (number of solenidia in parentheses): Tr1–Fe3–Ge4–TiTa15 (4). Tibiotarsus I with seta k
and five other blunt-ended eupathidial setae p (, tc , tc , ft and ft ), solenidion ω 1 6 (6–7) digitiform, solenidion ω 2 3 (3–3) baculiform, solenidion φ 1 3 (2–3) weakly clavate, φ 2 3 (2–3) baculiform, setae pl and pl whip-like; genu with three barbed setae and seta l smooth; femur with setae d, v and l subequal. Leg II ( Fig. 1B View Figure 1 ). Setal formula: Tr1–Fe3–Ge3–Ti4(1)–Ta6(1). Tarsus with sickle-like simple claws, solenidion ω 4 (3–4) digitiform, seta pl shortest on tarsus I; tibia with solenidion φ 3 (2–3) weakly clavate, setae v and v subequal and longer than two others; genu with setae l thickened; femur with setae l and d, shortest and longest setae on legII, respectively; trochanter with seta v as long as v on first leg. Leg III ( Fig. 3A View Figure 3 ). Setal formula: Tr1–Fe2–Ge2– Ti4(1)–Ta6. All leg setae smooth and pointed; tibia with solenidion φ 3 (2–3) digitiform, seta l shorter than three others; genu with two subequal setae l and v ; femur divided into basi- and telofemur with seta d longer than seta v ; trochanter with seta
v longer than femoral seta v . Leg IV ( Fig. 3B View Figure 3 ). Setal formula: Tr1–Fe2–Ge1– Ti4(1)–Ta6. Setae tc thickened; tibia with solenidion φ 3 (2–3) digitiform, seta v on tibia and tc on tarsus are shortest and longest on leg IV, respectively; genu with seta v as long as seta v on tibia; femur divided into basi- and telofemur with seta v longer than d; trochanter with seta v longer than v on femur.
Male and larva. Unknown.
Differential diagnosis — The new species is most similar to Premicrodispus spinosus Hosseininaveh & Hajiqanbar, 2015 by seta 4 a absent, seta ps 2 present, seta ps 3 longer than
ps 1 and seta ps 1 longer than ps 2, setae d and f blunt-ended, but differs in having tarsi and tibiae II and III with simple setae (tarsi and tibiae II and III with spine-like setae P in. spinosus ) and seta e with no linear ridge (setae e associated with a linear ridge in P. spinosus ). On the other hand, the new species is similar to P. tenuisetus Khaustov, 2006 and P. novaezealandicus Khaustov and Minor, 2020 by absence of setae 4 a and presence of setae ps 2, but differs from them by setae d, e and f blunt-ended (setae d, e and f pointed in P. tenuisetus ), setae e shorter than f (setae e longer than f in P. novaezealandicus and subequal with f in P. tenuisetus ),
setae e not associated with ridge (setae e associated with well-developed oblique ridges in P. tenuisetus ), pump 3 of pharyngeal system reduced (pump3 of pharyngeal system ovate in P. novaezealandicus and P. tenuisetus ), seta ps 1 two times longer than ps 2 (seta ps 1 and ps 2 subequal in P. novaezealandicus ), seta ps 3 longer than ps 1 and seta ps 1 longer than ps 2 (setae
ps 3 and ps 1 subequal and longer than seta ps 2 in P. tenuisetus ), posterior border of tergites
C and D with distinct median incision (posterior border of tergites C and D straight P. in novaezealandicus and P. tenuisetus ).
Type material — Female holotype (VRSS-20190812-1) and 5 female paratypes, in a vial containing Lucanus ibericus Motschulsky, 1845 (Col.: Lucanidae ). The hosts were captured by a light trap from Alangdareh forest, with Hornbeam trees Carpinus (spp.) and Oak trees ( Quercus spp. ), Gorgan town, Golestan province, northern Iran, 36.46°N, 54.26°E, altitude,
408 m., coll. V. Rahiminejad, 12 August 2019.
Etymology — The name of the new species refers to its sampling site, the city of Gorgan, northern Iran.
| V |
Royal British Columbia Museum - Herbarium |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |