Medaeops potens, Mendoza, Jose Christopher E. & Ng, Peter K. L., 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.191629 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6215187 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03DB2709-FFAB-E16A-FF48-F9F2BF6CFC1D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Medaeops potens |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Medaeops potens View in CoL new species
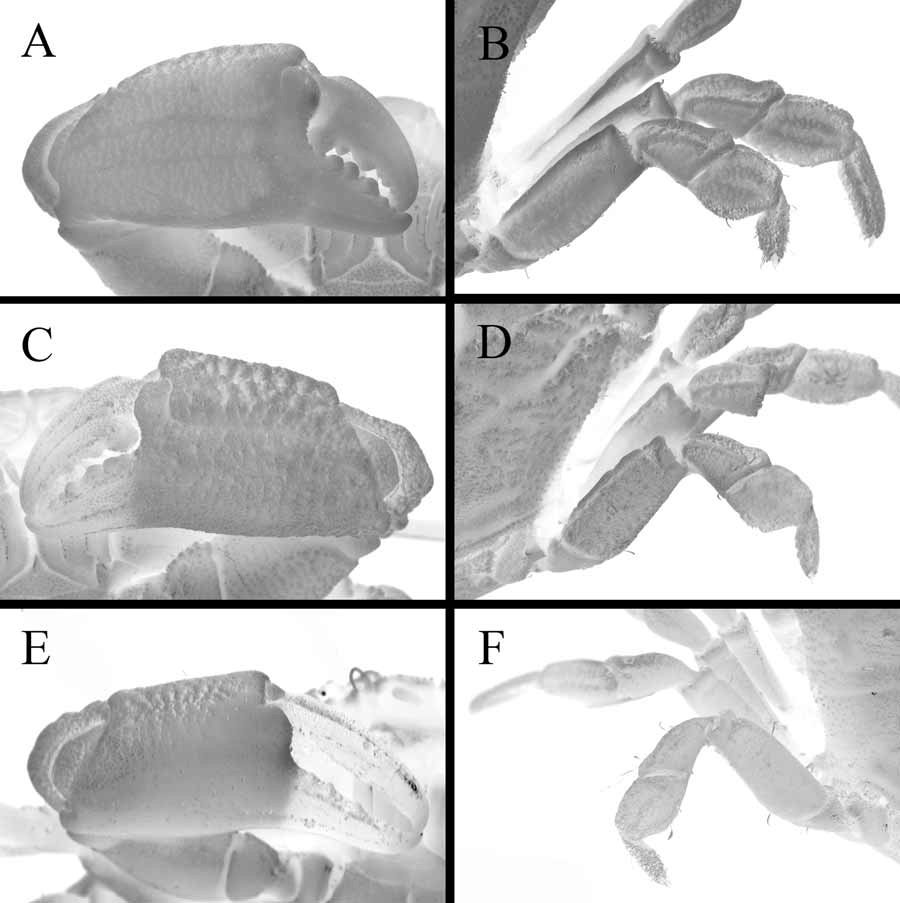
( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 ; 3A, B; 4)
Material examined. Holotype male, 32.9 x 21.3 mm ( ZRC 2009.0811), trash basket at Unit 6, 0.44 km from main Kapar Power Station, 3°06’47.02”N, 101°19’06.89”E, water intake from depth of 7.0 m, Klang Strait, Selangor, Malaysia, coll. Azila Azhar, 25–27 June 2004.
Paratypes: 3 males, 22.5 x 14.6 mm, 28.5 x 18.5 mm, 31.2 x 20.4 mm ( ZRC 2009.0812), same data as holotype.
Comparative material. Medaeops edwardsi Guinot, 1967 : holotype male, 25.4 x 16.9 mm (MNHN- B9448), Malabar Coast, India, coll. J.-J. Dussumier (no date); paratype female, 25.7 x 17.1 mm (MNHN- B9447), probably Madagascar (no collector or date).
Medaeops granulosus ( Haswell, 1882) View in CoL : lectotype female (dry), 15.7 x 10.8 mm (AM P40834, ex. MacLeay Museum, Sydney), Port Denison, Queensland, Australia ( type status hereby designated); 2 males (dry), 21.5 x 14.4 mm, 22.8 x 15.2 mm, (AM G5573), 2 females, 18.3 x 12.3 mm, 20.3 x 13.4 mm (AM P194), Port Denison, Queensland, Australia; 2 males, 18.8 x 12.4 mm, 20.7 x 14.6 mm, 3 females, 15.3 x 10.6 mm – 20.7 x 14.4 mm (ZRC 1965.11.10.46-50), reef at Lindeman Island, Queensland, Australia, coll. M. Ward, May 1934.
Medaeops neglectus ( Balss, 1922) View in CoL : 1 male, 17.2 x 11.5 mm, 1 female, 15.1 x 10.3 mm (MNHN-B6534), stn. 137, 4º38.8’S, 39º21.7’E, Shimoni, Kenya, coll. A. J. Bruce, 20 Oct. 1971.
Diagnosis. Carapace ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 A, B) depressed, 1.5 times broader than long, regions well defined; 2M partially divided longitudinally, lateral lobe larger than medial lobe, medial lobe fused with 1M; 3M prominent anteriorly, becoming indistinct posteriorly, 4M indistinct; 1L, 2L, 3L fused; 4L fused with third anterolateral tooth; 5L, 6L low but distinct; dorsal regions of carapace granulose at edges, becoming less so medially; granules evidently arranged as transverse rows on 2M, closely, randomly packed on anterior edges of carapace, scattered elsewhere. Front narrow, about 0.2 times carapace width, bilobed, projecting well beyond supraorbital margins; lobes truncate, separated by narrow slit, anterior margins straight. Supraorbital margin granular, short, separated from frontal lobes by deep, U-shaped incision; with small, triangular, internal orbital tooth; without obvious external orbital tooth; not clearly meeting anterolateral margin. Inferior orbital angle granular, with distinct, triangular tooth on medial end. Orbits small, width 0.07 times carapace width. Anterolateral margin convex, with 4 triangular teeth, first feeble, second, third broadly triangular, sometimes bifurcated, fourth acutely triangular, at point of maximum carapace width; anterior-most part not clearly meeting orbital margin, descending instead towards buccal frame. Posterolateral margin almost straight, convergent posteriorly. Central portion of posterior carapace margin slightly concave, with distinct row of spherical granules immediately anterior to it.
Eyes with short eyestalks, distal edge with cornea lined with small granules; corneas well developed ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B). Antennules ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B) folding transversely and obliquely. Basal antennal segment subrectangular, finely granular, filling orbital hiatus; long flagellum arising from distal margin, reaching well beyond outer edge of orbit. Central region of posterior margin of epistome ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B), concave, with median notch; separated from lateral regions by lateral notch on either half. Anterior region of endostome without oblique ridges; endopod of first maxilliped narrow. Outer surface of third maxillipeds ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B, C) granular. Merus subquadrate, with slight extension of anteroexternal angle, median length about half that of ischium, with 2 shallow depressions on either side of low, submedian, granular ridge; margins almost straight, lined with small granules. Ischium subrectangular, inner margin with short, stiff setae; with deep, longitudinal sub-median groove; separated from basis by feeble suture. Exopod granular, tapering toward distal end which just reaches anterior edge of merus, flagellum long.
Surface of thoracic sternum ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 C) granular, sparsely pitted, glabrous, with elongated anterior region. Sternites 1, 2 completely fused into triangular plate, separated from sternite 3 by distinct transverse suture. Sternites 3, 4 completely separated by distinct transverse suture intersected medially by deep, median, longitudinal depression (i.e. median line) on sternite 4. Sterno-abdominal cavity deep, press button of male abdominal locking mechanism on sternite 5, near suture with sternite 6; anterior end only reaching to imaginary line joining middle of coxae of P2s.
Chelipeds, ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 A, 3A) subequal. Merus rugose on external surface, slightly longer than carpus, with distinct row of granules on convex dorsal margin. Carpus similarly rugose on external surfaces, short, inner margin with spinose tooth. External surface of palm of chelae with reticulate pattern of pits, becoming more pronounced near upper margins; upper margin straight, finely granular; central portion of lower margin convex; inner surface similarly pitted. Major chela with fingers stout, distinctly shorter than palm, with rounded, incurving tips; fixed finger slightly deflexed with submarginal groove on external surface, cutting margin with 6 or 7 teeth throughout length; dactylus curved, with submarginal groove on external surface, cutting margin with large, subproximal, molariform tooth, 5 or 6 other teeth throughout length, with depression near point of articulation with palm to receive rounded ankylosity on distal margin of palm. Minor chela similar, dactylus without subproximal, molariform tooth.
P 2–5 ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 A, 3B) relatively short, stout, dorsal surfaces finely rugose, pitted or granular; P2, P3 longest, coxa-to-dactylus length 0.9 times carapace width. Meri subrectangular, median length about 2.1 times maximum width, anterior margins cristate. Carpi widening distally; anterior margins cristate, with submedian granular ridge. Propodi subrectangular; tomentose along anterior, distal, posterior margins, with stiff setae on posterior margin; with granular ridge along anterior margin (more prominent on P2–P4), and 2 wide, shallow, parallel grooves on dorsal surface. Dactyli straight, slightly longer than propodi (except in P5, where slightly shorter), tomentose; terminating distally in curved chitinous claw.
External surface of male abdomen ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 C) granular proximally, smooth distally; central regions of somites raised. Somite 1 much wider than long, covered with spherical granules, anterior margin concave. Somite 2 much wider than long, anterior margin concave, posterior margin convex; with larger, spherical granules on lateral regions. Somites 3–5 immovably fused, vestigial sutures seen as shallow depressions; lateral margins markedly concave; external surface of somite 3 rugose with granular posterolateral margins, external surface of somites 4, 5 smooth. Somite 6 subrectangular, longer than telson, greatest width about 1.1 times median length, lateral margins distinctly concave, distolateral angles well produced. Telson semicircular, basal width about 1.4 times median length, and about as long as somite 6.
G1 ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 A–D) moderate in length, stout, curving laterally, tapering distally into spatulate lobe; with several, terminally plumose setae near distal end; distal two-thirds covered with short spines primarily along medial margin; lateral margin with weak keel in central region; basal region wide, with a few plumose setae. G2 ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 E) about half length of G1, curving medially, terminal process recurved.
Etymology. The epithet of this species, potens (adjective, Latin, powerful), is an allusion to the type specimens being found in the vicinity of a power plant (Kapar Power Station).
Habitat. The specimens were collected from the trash basket at one of the intake points of Kapar Power Station, and were presumably sucked into the station from the immediately surrounding area. The station is located on a mudflat surrounded by mangrove forests, and the crabs were only obtained at the intake point from which Unit 6 of the power station drew its water at a depth of 7.0 m.
Remarks. The new species clearly agrees with the diagnosis of Medaeops sensu Guinot (1967) , particularly with regard to the following features: 1) the anterolateral margin does not end at the external orbital angle but instead goes down to meet the buccal cavity; 2) the carapace does not have a prominent 4M region; 3) the fingers of the chelae are relatively short and stout; 4) the ambulatory legs are relatively short; 5) the merus of the third maxilliped is subquadrate and does not have a well produced anterolateral angle; 6) the lacinia of the first maxilliped is narrow and does not reach the median of the endostome; and 7) the male G1 has a keel on its lateral margin and several long, terminally plumose setae near the distal end.
Medaeops potens View in CoL new species is morphologically most similar to M. granulosus ( Haswell, 1882) View in CoL , primarily on the meri and carpi of the ambulatory legs having cristate anterior margins ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 A, 2A, 3B, D). The new species can be distinguished from M. granulosus View in CoL by the following features: 1) the anterior half of the carapace is much shorter than the posterior half ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 A) (anterior half as long as posterior half in M. granulosus View in CoL , Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2. A – C ); 2) the dorsal surface of the carapace is flattened ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B) (more convex in M. granulosus View in CoL , Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2. A – C ); 3) the front is much more produced, exceeding well beyond the supraorbital margin ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 A) (less produced, barely exceeding supraorbital margin in M. granulosus View in CoL , Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2. A – C ); 4) the ratio of the fronto-orbital width and the maximum carapace width is much less compared to that of M. granulosus View in CoL ; 5) the anterolateral teeth are more prominent, particularly the last tooth ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 A) (less prominent, last tooth reduced in M. granulosus View in CoL , Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2. A – C ); 6) the dorsal and external surfaces of the palm of the chela have a less eroded appearance ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3. A, B ) (much eroded, with distinct cavities in M. granulosus View in CoL , Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3. A, B C); and 7) the male G1 has a weaker keel, smaller spines and a broader terminal lobe ( Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4 A–D) (more prominent keel, larger spines and narrower terminal lobe in M. granulosus View in CoL ( Fig. 5A, B View FIGURE 5. A, B ).
The new species is similar to M. neglectus ( Balss, 1922) View in CoL , and M. edwardsi Guinot, 1967 View in CoL , in having a proportionately flatter carapace, relatively less prominent carapace regions and generally smoother dorsal and external surfaces on the palm of the chelae. Medaeops potens View in CoL new species is easily distinguished from both species, however, by the cristate condition of the anterior margins of the meri and carpi of the ambulatory legs ( Figs. 3B, 3 View FIGURE 3. A, B F). Furthermore, it can be distinguished from M. neglectus View in CoL by: 1) the more produced front ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 A) (less produced in M. neglectus View in CoL , Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2. A – C ); 2) the more prominent anterolateral teeth, particularly the last ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 A) (less produced in M. neglectus View in CoL , Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2. A – C ); and 3) the male G1, which is relatively longer, more slender and armed with fewer, shorter spines ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 A–D) (male G1 shorter, stouter, with longer and more spines in M. neglectus View in CoL , Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5. A, B C, D).
| ZRC |
Zoological Reference Collection, National University of Singapore |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
InfraOrder |
Brachyura |
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Euxanthinae |
|
Genus |
Medaeops potens
| Mendoza, Jose Christopher E. & Ng, Peter K. L. 2009 |
M. edwardsi
| Guinot 1967 |
Medaeops neglectus (
| Balss 1922 |
M. neglectus (
| Balss 1922 |
Medaeops granulosus (
| Haswell 1882 |
M. granulosus (
| Haswell 1882 |