Bavia insularis, Malamel, Jobi J., Sankaran, Pradeep M. & Sebastian, Pothalil A., 2015
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4007.4.11 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:FCDDDD58-4B1D-4684-ADF0-3F63A64E064C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6097036 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03DC87B1-FFD8-D51A-FF68-FED9FEF2FD2E |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bavia insularis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
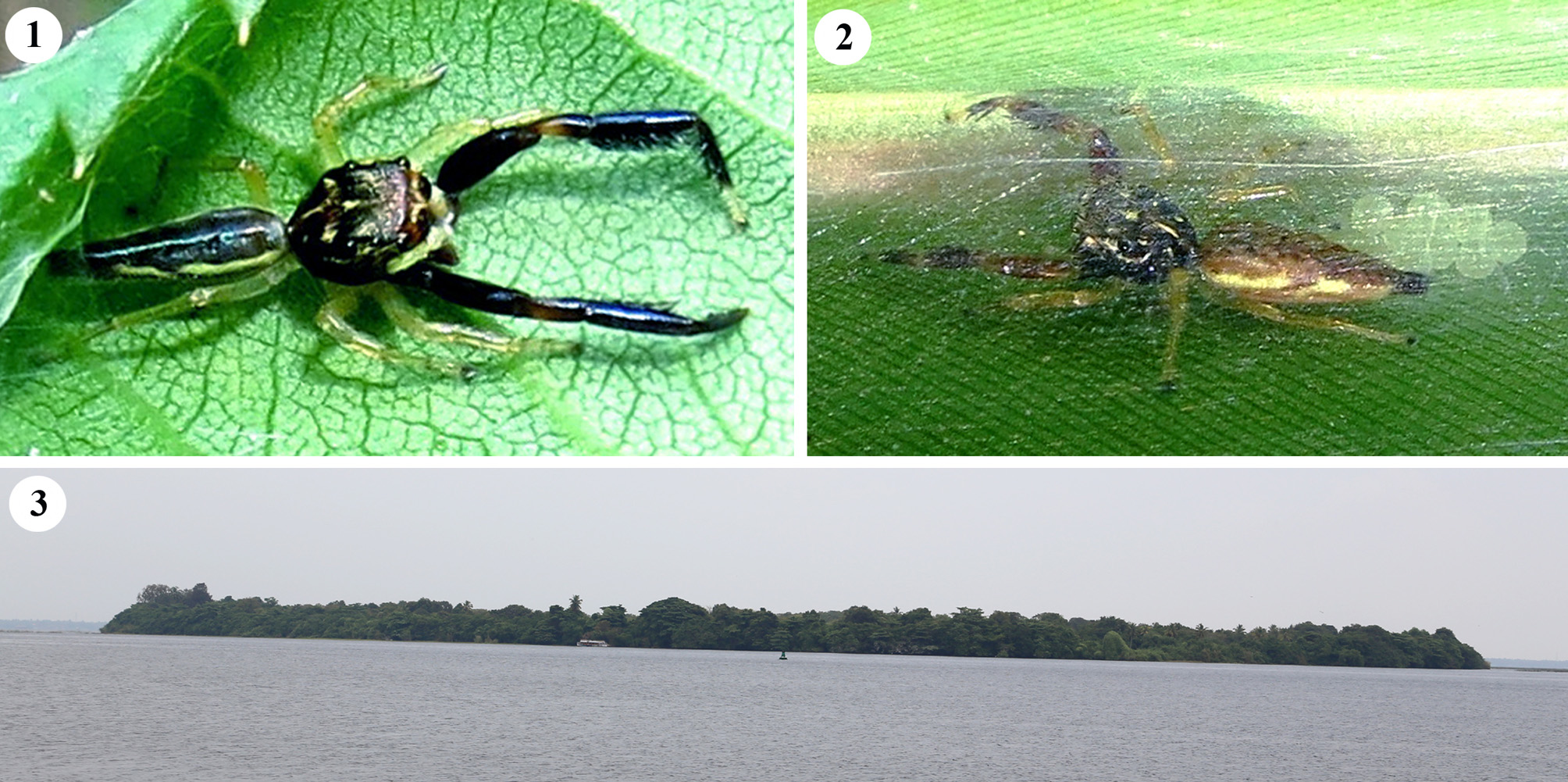
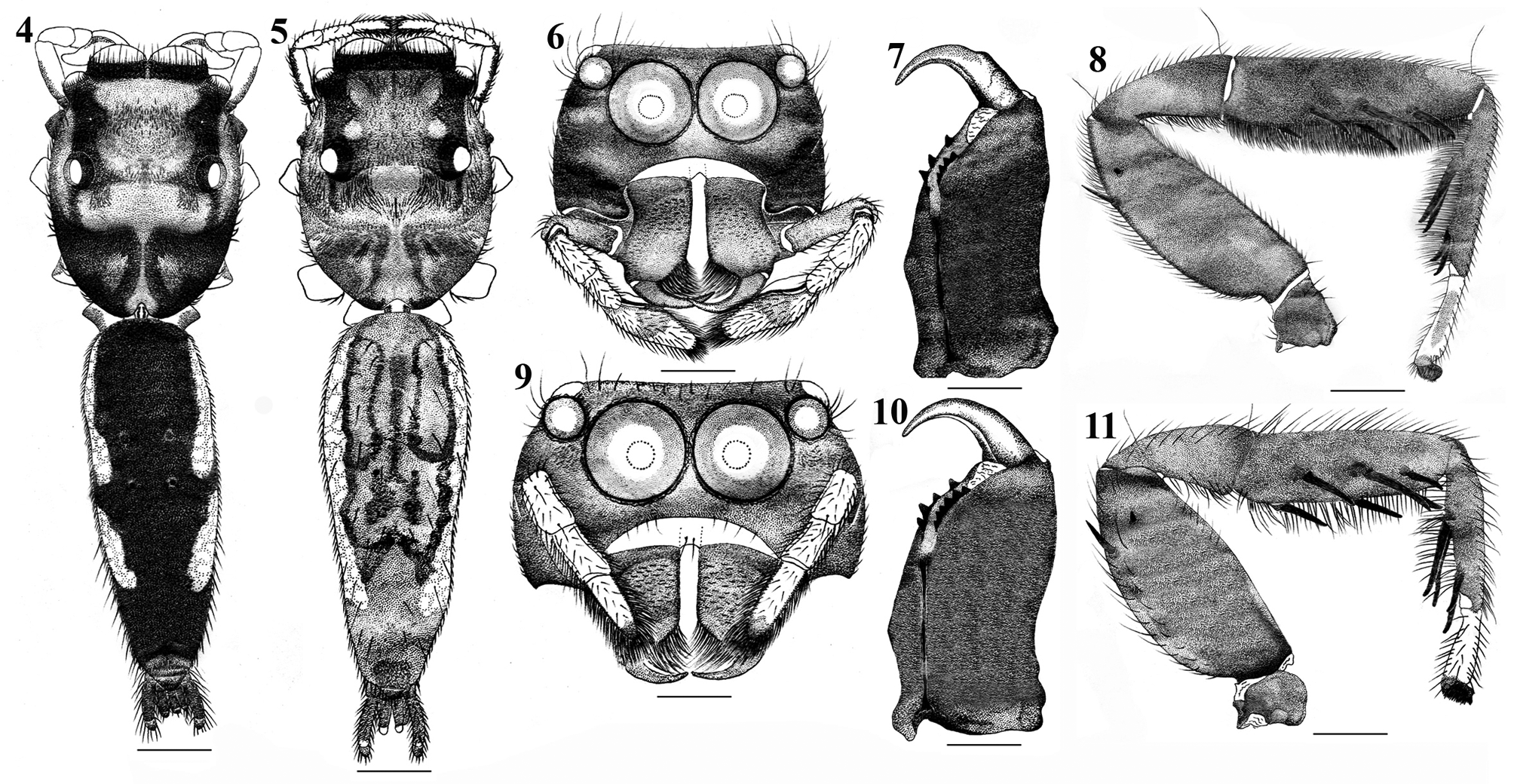
Bavia insularis View in CoL sp. nov.
Figs 1–2 View FIGURES 1 – 3 , 4–20 View FIGURES 4 – 11 View FIGURES 12 – 20
Type material: Holotype: Male ( ADSH 856501) from Pathiramanal Island, 9o37'07.11''N, 76o23'04.95''E, Alappuzha, Kerala, India, 0 m alt., 27 March 2015, M.S. Pradeep & M.J. Jobi leg., from foliage by hand. Paratypes: 3 males, 6 females ( ADSH 856502), same data as holotype.
Additional material examined: INDIA, Kerala: Ernakulam, Karukutty, 10o13'37.11''N, 76o22'30.08''E, 22 m alt.: 2 males, 2 females ( ADSH 856503), Simi leg., 22 January 2013, by hand. Kottayam, Edappady in Palai, 9o42'35.62''N, 76o42'48.42''E, 27 m alt.: 2 females ( ADSH 856504), 18 February 2013, M.S. Pradeep leg., from Colocasia sp. foliage, by hand. Trivandrum, Kallara near Kilimanoor, 9o42'21.45''N, 76o28'35.59''E, 14 m alt.: 1 male ( ADSH 856505), 21 February 2015, Karthika leg., by hand.
Diagnosis. Males are most similar with those of B. thorelli Simon, 1901 , but can be recognized for having a broad RTA with sinuous tip ( Fig 17 View FIGURES 12 – 20 ; B. thorelli with narrow, pointed RTA, as in Żabka 1988, fig 53). Females are similar to those of B. annamita Simon, 1903 , but can be distinguished by a deep, medial pocket and by the indistinct spermathecae ( Figs 18–19 View FIGURES 12 – 20 ; pocket shallow and wide and spermathecae distinctly globular in B. annamita , as in Żabka 1988, fig 51).
Description. Male (holotype, Figs 1 View FIGURES 1 – 3 , 4, 6–8 View FIGURES 4 – 11 , 12–17 View FIGURES 12 – 20 ). Prosoma brownish-black. Iridescent scales on prosoma and leg I. Clypeus, chelicerae, fangs, labium, maxillae brownish-black. Sternum yellowish-brown with brown margin. Chelicerae with four promarginal and five short, fused retromarginal teeth ( Fig 7 View FIGURES 4 – 11 ). Leg I robust, brownish-black; distal half of patella and entire tibia and metatarsus provided ventrally with bunch of black hairs, the ones on tibia prominent; tibia and metatarsus bear paired heavy ventral spines ( Fig 8 View FIGURES 4 – 11 ); all other legs yellowish. Opisthosoma long, tubular, black, provided dorso-laterally with longitudinal, discontinuous band of chalk-white spots ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 4 – 11 ). Spinnerets black. Body length 8.35. Prosoma length 3.30, width (at the middle) 2.78. Opisthosoma length 5.05, width (at the middle) 1.82.
Eyes diameter: AME 0.74. ALE 0.32. PME 0.11. PLE 0.32. Eye interdistances: AME–AME 0.04. AME–ALE 0.05. ALE–PME 0.44. PME–PLE 0.43. PME–PME 1.76. PLE–PLE 1.79. Clypeus height at AME 0.36, at ALE 0.95 ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 4 – 11 ). Length of chelicerae 1.07. Measurements of palp and legs: Palp 3.38 [1.38, 0.70, 0.41, 0.89], I 10.41 [2.88, 1.68, 2.81, 2.01, 1.03], II 6.32 [2.00, 1.10, 1.27, 1.29, 0.66], III 5.56 [1.83, 0.97, 0.81, 1.30, 0.65], IV 7.24 [2.33, 1.00, 1.41, 1.82, 0.68]. Leg formula: 1423. Pedipalp as in Figs 12–17 View FIGURES 12 – 20 .
Female (paratype, Figs 2 View FIGURES 1 – 3 , 5, 9–11 View FIGURES 4 – 11 , 18–20 View FIGURES 12 – 20 ). In all details like male except the followings: Prosoma brownish. Clypeus, chelicerae, fangs, labium, maxillae, spinnerets brownish. Chelicerae with four promarginal and six retromarginal teeth ( Fig 10 View FIGURES 4 – 11 ). Leg I robust, brownish; tibia and metatarsus bear paired heavy ventral spines ( Fig 11 View FIGURES 4 – 11 ). Opisthosoma long, tubular, greenish-gray; provided dorsally with characteristic pattern ( Fig 5 View FIGURES 4 – 11 ); dorso-laterally with longitudinal, continuous band of chalk-white spots. Body length 8.41. Prosoma length 3.29, width (at the middle) 2.66. Opisthosoma length 5.12, width (at the middle) 1.94. Eyes diameter: AME 0.70. ALE 0.30. PME 0.12. PLE 0.43. Eye interdistances: AME–AME 0.06. AME–ALE 0.08. ALE–PME 0.31. PME–PLE 0.28. PME–PME 1.66. PLE–PLE 1.69. Clypeus height at AME 0.19, at ALE 0.77 ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 4 – 11 ). Length of chelicerae 0.87. Measurements of palp and legs: Palp 2.45 [0.99, 0.50, 0.31, 0.65], I 7.23 [2.13, 1.26, 1.76, 1.40, 0.68], II 5.44 [1.76, 0.99, 1.08, 1.05, 0.56], III 4.89 [1.60, 0.89, 0.73, 1.10, 0.57], IV 6.59 [2.15, 0.93, 1.27, 1.68, 0.56]. Leg formula: 1423. Epigyne as in Figs 18–20 View FIGURES 12 – 20 .
Variation. Male: Body length 6.54–8.35 (n = 7). Female: Body length 8.07–8.41 (n = 10)
Etymology. The specific epithet is a Latin adjective and refers to the nature of the type locality of the new species (insula = island).
| ADSH |
Arachnology Division, Sacred Heart College |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |