Rhinolophus sinicus, K. Andersen, 1905
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.7150/ijbs.5.659 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4329179 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E1850B-FFF8-FF91-D7FC-F89863A6FE33 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Rhinolophus sinicus |
| status |
|
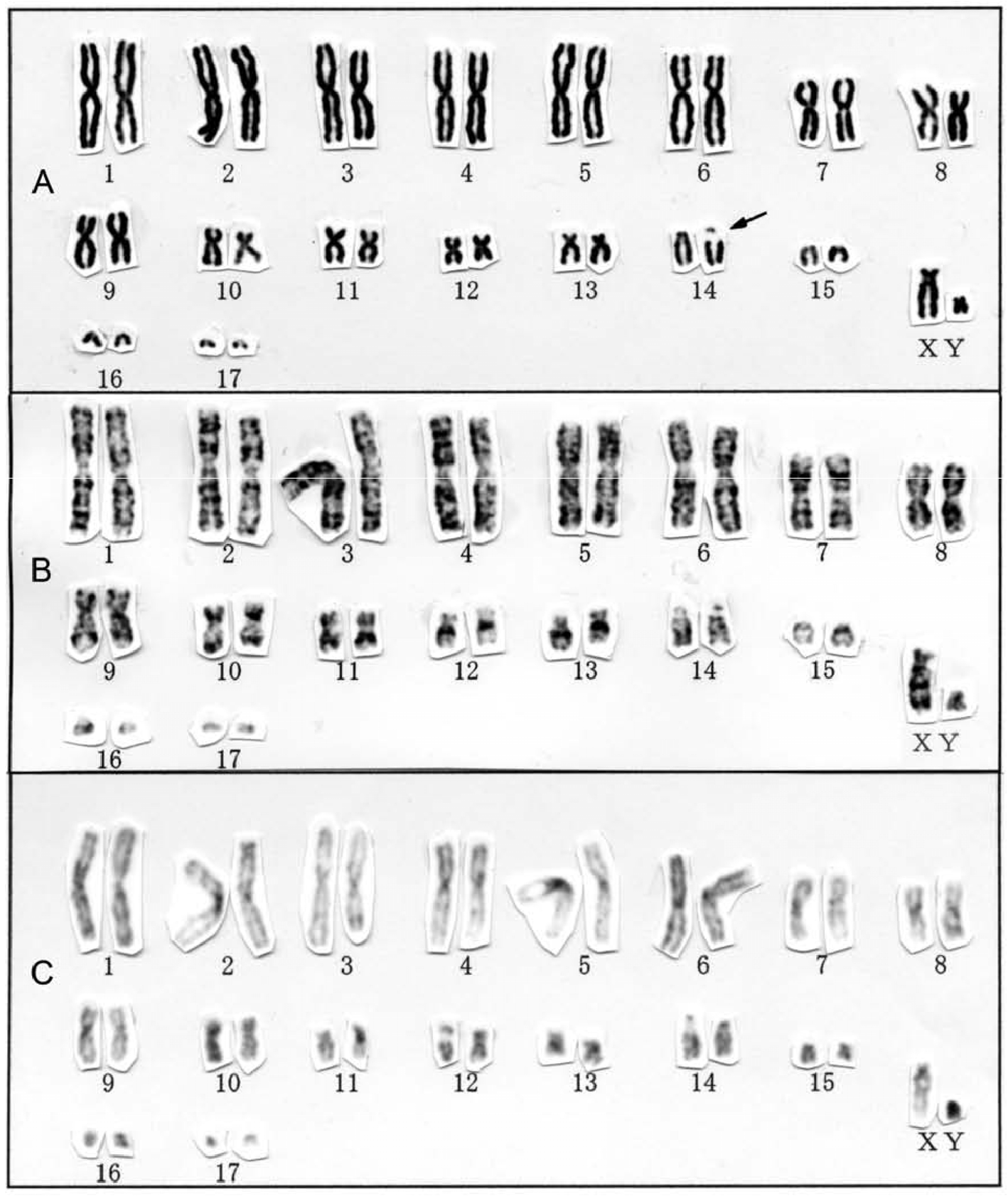
The karyotype of R. sinicus View in CoL
was 2n = 36, FN = 60 ( Fig. 3 View Figure 3 ), consisting of 13 large-to-small metacentric or submetacentric pairs and four medium-sized to small acrocentric pairs of autosomes, a medium-sized subtelocentric X chromosome, and a small subtelocentric Y chromosome. This species had a prominent secondary constriction involving one pair of medium-sized acrocentric chromosomes. The karyotype of R. sinicus from Hainan Island (2n = 36, FN = 60) does not differ from conspecific populations in the Chinese provinces of Anhui [ 6] (reported as R. rouxii sinicus ), Sichuan [ 14], and Guangdong [ 15] in conventional karyotype and that from "south-western China" also in G-banding pattern [ 17], but does differ from the 2n = 56, FN = 60 karyotype of R. rouxii reported from India and Sri Lanka [ 31]. These karyological differences between R. sinicus and R. rouxii support the view that these two taxonomically confused taxa both represent distinct species, as previously proposed [ 14, 15, 26].
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |