Eurytoma rufipes Walker, 1832
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5252/z2011n3a3 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E487A7-AF51-2767-0625-FF136B60FE09 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Eurytoma rufipes Walker, 1832 |
| status |
|
Eurytoma rufipes Walker, 1832 View in CoL
MATERIAL EXAMINED. — Ex Xestophanes brevitarsis : Spain. La Coruña, Arins, 17.VII.2003, J. L. Nieves leg (n = 2). Ex X. potentillae : Spain. Madrid, Cotos de Monterrey, 24. VI.2004, J. F. Gómez leg (n = 16, of which 1 specimen MNHN-EY 6413). — Tarragona, Colldejou, 14.VIII.2003, J. L. Nieves leg (n = 6).
DESCRIPTION
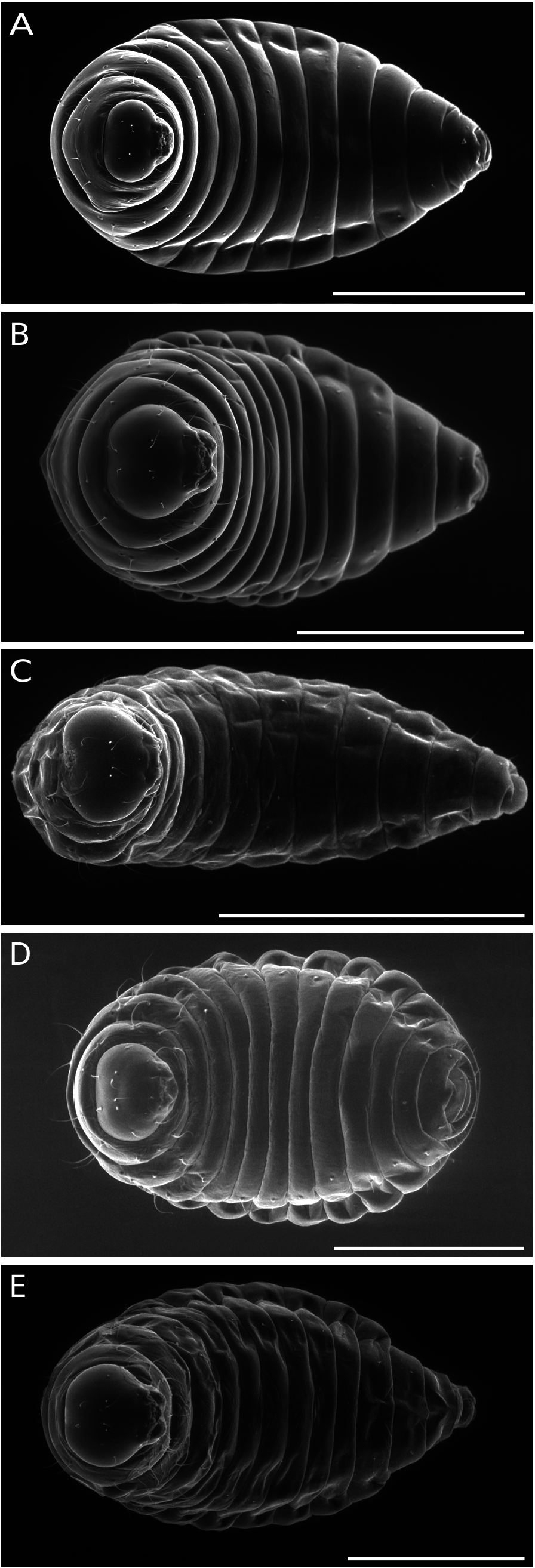
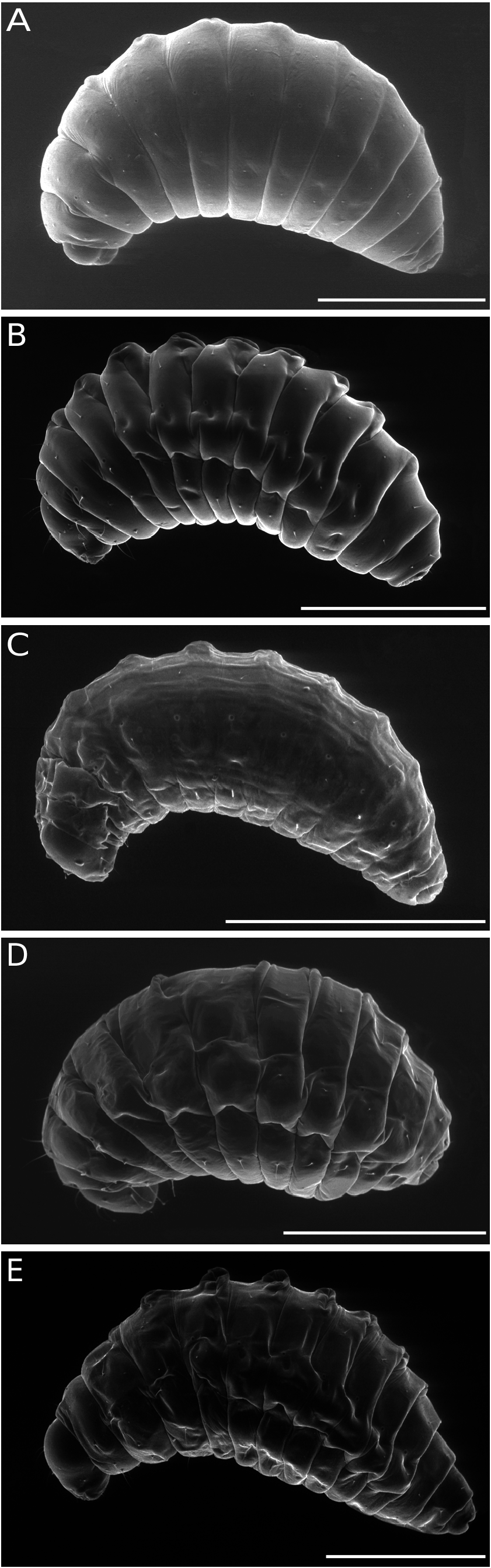
n = 24, body length 1.7 mm (range 1.2-2.4;); body width 0.9 mm (0.3-1.3) ( Figs 6A View FIG ; 8A View FIG ); body barrelshaped, tapering posteriorly, widest at segments 1-3; ratio L/W = 1.74; ventral margin of body segments slightly convex; anterodorsal protuberances present from second thoracic segment to the eighth abdominal and not protruding beyond the dorsal margin of body segments ( Fig. 8A View FIG ).
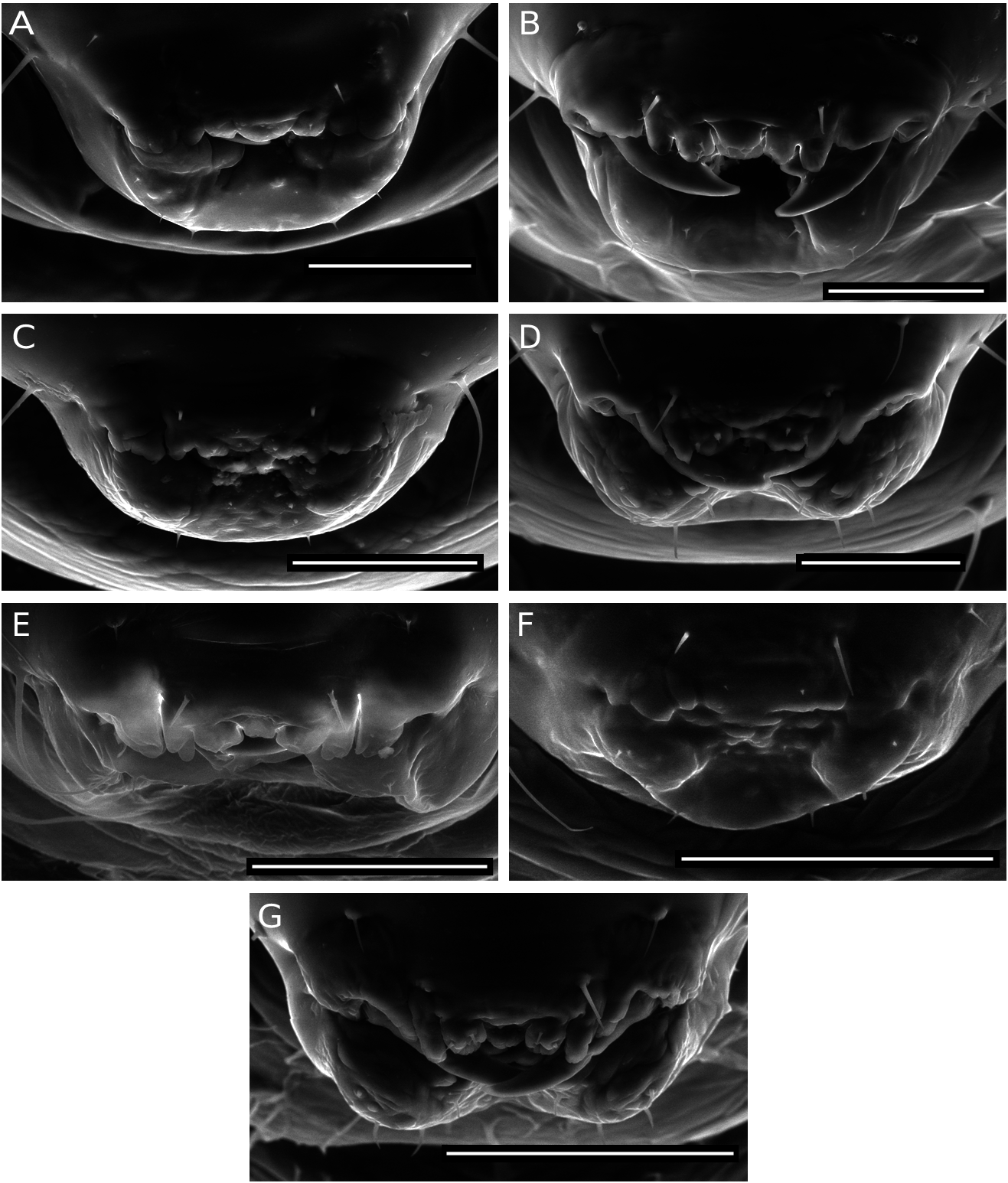
Antero-medial setae of the antennal area situated slightly below the antennae; antero-medial setae of vertex situated more or less midway between anterior margin of vertex and the antennae ( Fig. 10B View FIG ); ratios SA/LAA = 0.2 and SA/DAV = 1.4; dorsallabral setae as long as clypeal setae; ventral margin of clypeus with a distinct suture; labrum with slight divisions limited to apical part of labrum, showing a pair of lateral flaps and five poorly differentiated lobes; maxillary palps conspicuous ( Fig. 12C View FIG ).
Mandibles with two teeth, exposed in part, with the tip of the first tooth visible ( Fig. 12C View FIG ); ratio L/W 1T = 1.93; outer margin of first tooth strongly convex, tip moderately recurved; apex of the second tooth straight, directed upwards in the same direction as the first tooth, and more or less acute; inner margin of mandible, from the base of second tooth, forming a small projection relatively separated from the base of the second tooth ( Fig. 13I View FIG ).
BIOLOGY
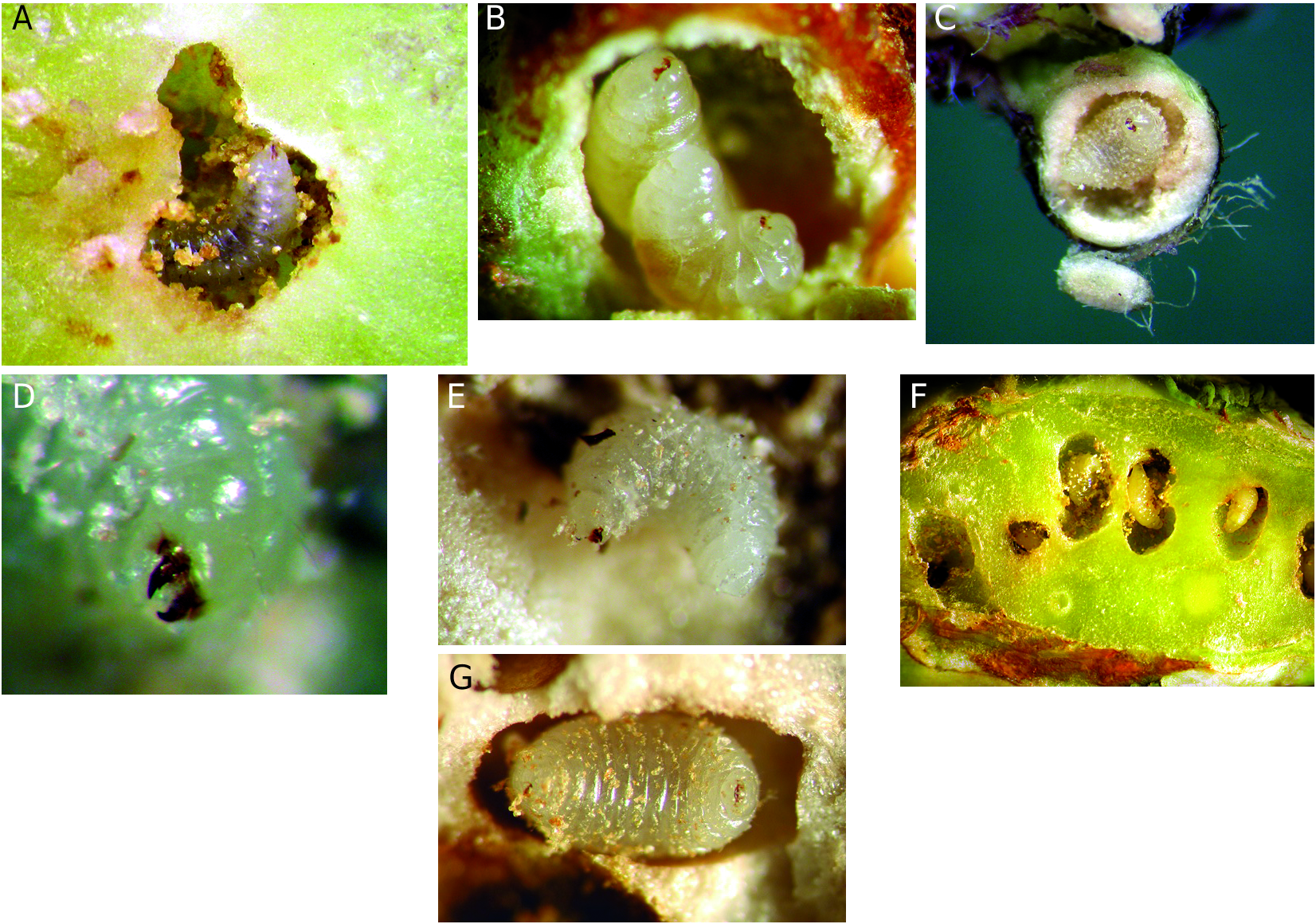
This is an ectoparasitoid associated with galls of Xestophanes brevitarsis (Thomson, 1877) and X. potentillae (Retzius, 1783) , both developing in runners on different species of Potentilla (Rosaceae) . Univoltine and oligophagous, attacking the gallinducing cynipid larva ( Fig. 15B View FIG ). Fully-grown larvae overwinter inside the gall and the adults emerge in synchrony with the development of new Xestophanes galls.
REMARKS
The larvae of E. rufipes is similar to the larvae of E. mayri and E. pediaspisi in terms of the position on the head of the antero-medial setae of vertex, and by the presence of only slight apical divisions on the medial part of the labrum. They differ from other larvae in having mandibles with a small projection on the inner margin at the base of the second tooth.
| VI |
Mykotektet, National Veterinary Institute |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.