Callistocypris, SHORNIKOV, 1980
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1096-3642.2005.00185.x |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10545383 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E487A9-111F-6C2A-FF0B-CA3B6026D798 |
|
treatment provided by |
Diego |
|
scientific name |
Callistocypris |
| status |
|
GENUS CALLISTOCYPRIS SHORNIKOV, 1980 View in CoL
Type species: Callistocypris zlotini Shornikov, 1980 by original designation.
Diagnosis (modified after Shornikov, 1980)
Carapace small (0.3–0.5 mm long), wide in dorsal view, oval in lateral view. Caudal part of valves with postero-ventral locking system consisting of inner lists and selvage in RV, inner lists in LV. A2 with 1 very short natatory seta and 1 accompanying seta. T 1-palp with only 2 setae. Caudal ramus consisting of a slen- der ramus and 1 weak apical claw.
Additional features
Cp small (0.3–0.5 mm long), oval in lv, relatively wide in dv, LV overlapping RV on all sides, surface smooth except for a pitted central area and some ventral ridges, cms consisting of six scars, mandibular scars small, oval. Calcified inner lamella with 3 parallel inner lists, with an additional postero-ventral locking structure formed by diverging inner lists. Fused zone narrow, with few, straight pore canals. Hinge adont. Cms anteriorly consisting of 1 half-rounded row of 4 scars, posterior with 2 scars, all approximately of equal size. Eye simple.
Most appendages with a reduction in number and length of setae. A1 7-segmented, with only segments 1 and 2 fused. A2 with stout apical claws and relatively short z-setae; seta t4 claw-like, natatory setae reduced to 1 short (= accompanying seta) and 1 very short seta. Md palp with alpha-seta short and straight, beta-seta almost plate-like, gamma-seta a normal seta, 1 apical claw on terminal segment with basket-shaped apex. Mx1 palp with terminal segment carrying 2 weak claws and 2 setae. T 1-palp (female) with 1 long and 1 short apical seta. T 2 a stout walking limb, penultimate segment divided, with seta d1 absent, d2 of average length. T 3 a cleaning limb, terminal segment not fully fused with penultimate segment. CR reduced to a narrow, tapering ramus with 1 apical, seta-like claw.
Remarks
The LV is tightly connected to the RV at the posterodorsal side, to the extent that generally the LV broke at this spot during dissection. Therefore, we do not consider the structure illustrated in Figures 3 View Figure 3 , 6 View Figure 6 to be evidence for the existence of a posterior cardinal tooth on the RV.
CALLISTOCYPRIS MCKENZIEI SP. NOV.
( FIGS 1–3 View Figure 1 View Figure 2 View Figure 3 )
Type locality
Parque Estadual da Serra do Mar Núcleo Cunha- Indaiá , Municipality of Cunha, São Paulo State, Brazil. GPS coordinates: 23°14′03.5″S, 45°01′23.2″W. In moist leaf litter inside the forest, close to the Barracão waterfall of the Paraibuna river. Material collected 21.viii.2002 by RLP GoogleMaps .
Type material
Holotype: a dissected female, with valves stored dry in a micropalaeontological slide and dissected soft parts kept in a sealed slide (MZUSP 16339).
Paratypes: 8 females, dissected and stored like the holotype ( MZUSP 16340–47 View Materials ); 2 dissected females, with valves used for SEM and stored in micropalaeontological slides, and dissected soft parts kept in sealed slides ( MZUSP 16348 View Materials , 16349 View Materials ); 4 carapaces used for SEM and stored in micropalaeontological slides ( MZUSP 16350 View Materials , 16351 View Materials , 16342 View Materials , 16343 View Materials ) ; 45 females kept whole in ETOH ( MZUSP 16354 View Materials ) .
Additional material
Boracéia Biological Station , Municipality of Salesópolis , São Paulo State, Brazil. GPS coordinates: 23°38′16.9″S, 45°50′24.5″W. Inside the forest, near Pedreira’s swamp, in leaf litter at the foot of a rock wall. Material collected 02.iv.2003 by CEFR and RLP GoogleMaps .
15 females kept in toto in ETOH ( MZUSP 16355 View Materials ) .
Derivation of name
This species is named after the late Dr Ken McKenzie (Wagga Wagga, Australia), in recognition of his considerable contributions to crustacean research in general and ostracodology in particular. Ken was a grand man and a great scientist, always ready to help young students and established colleagues alike. Ken passed away in 2003; he will be greatly missed.
Diagnosis
Cp elongate in lv, smooth in lateral view, with ventral ridges weakly pronounced. RV caudally with selvage developing a single ridge, only inner list close to inner margin present; LV with 3rd inner list running halfway along caudal margin. A2 with 3 z-setae. Mx1-palp with 4 apical seta on distal segment.
Description
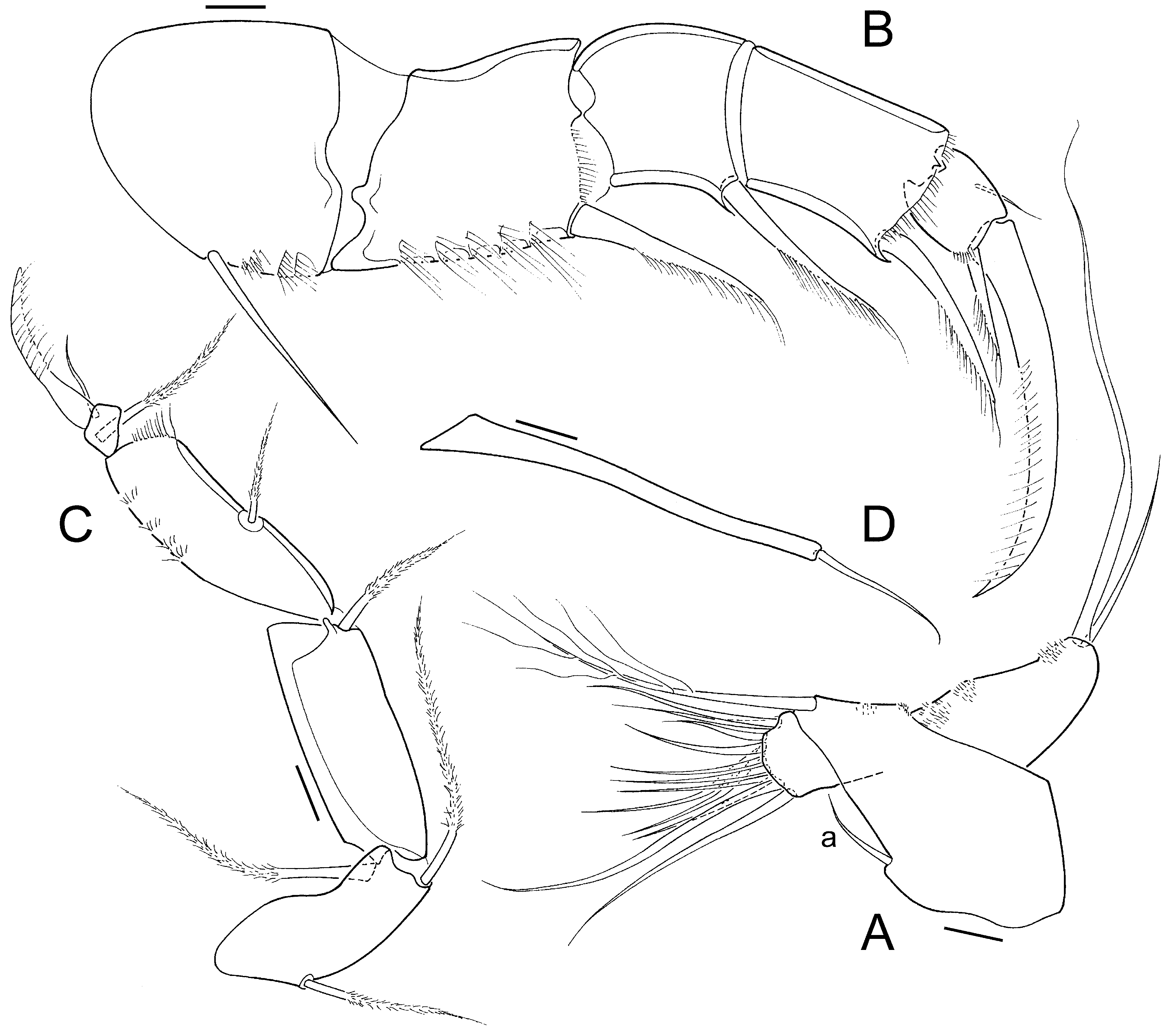
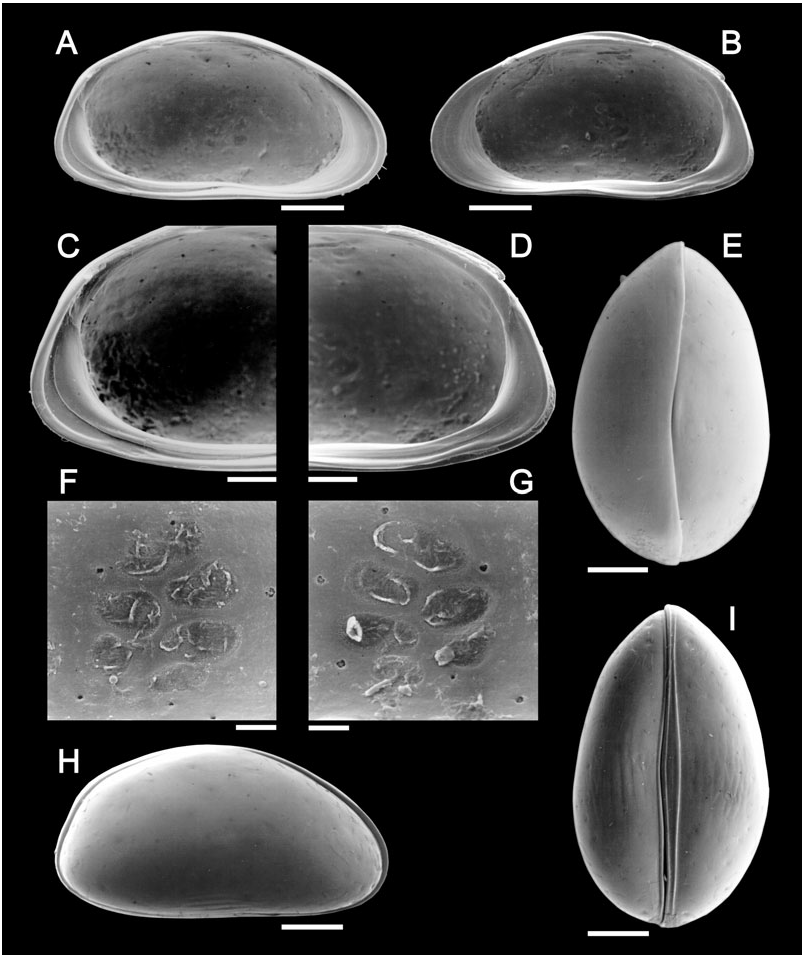
Cp elongated in lv ( Fig. 3F View Figure 3 ), with LV overlapping RV along anterior, posterior and most of ventral margins; in dv ( Fig. 3E View Figure 3 ), Cp with greatest width (c. half the length) situated in middle, anterior and posterior edges bluntly pointed. Valve surface generally smooth, in lv weakly pitted in the central part, in vv ( Fig. 3G View Figure 3 ) with weak central ridges. LV ( Fig. 3A, C View Figure 3 ) with well- developed anterior calcified inner lamella, posterior marginal structures complex, consisting of at least three inner lists, ventro-caudally with a shallow socket in the marginal inner list (il2), il3 running halfway up the caudal margin.
RV ( Fig. 3B, D View Figure 3 ) with wide anterior calcified inner lamella, posteriorly with well-developed selvage, latter postero-ventrally elevated into ridge (this ridge accommodated in socket of LV when valves closed); posterior inner margin of RV also elevated into list, no third il between selvage and il2.
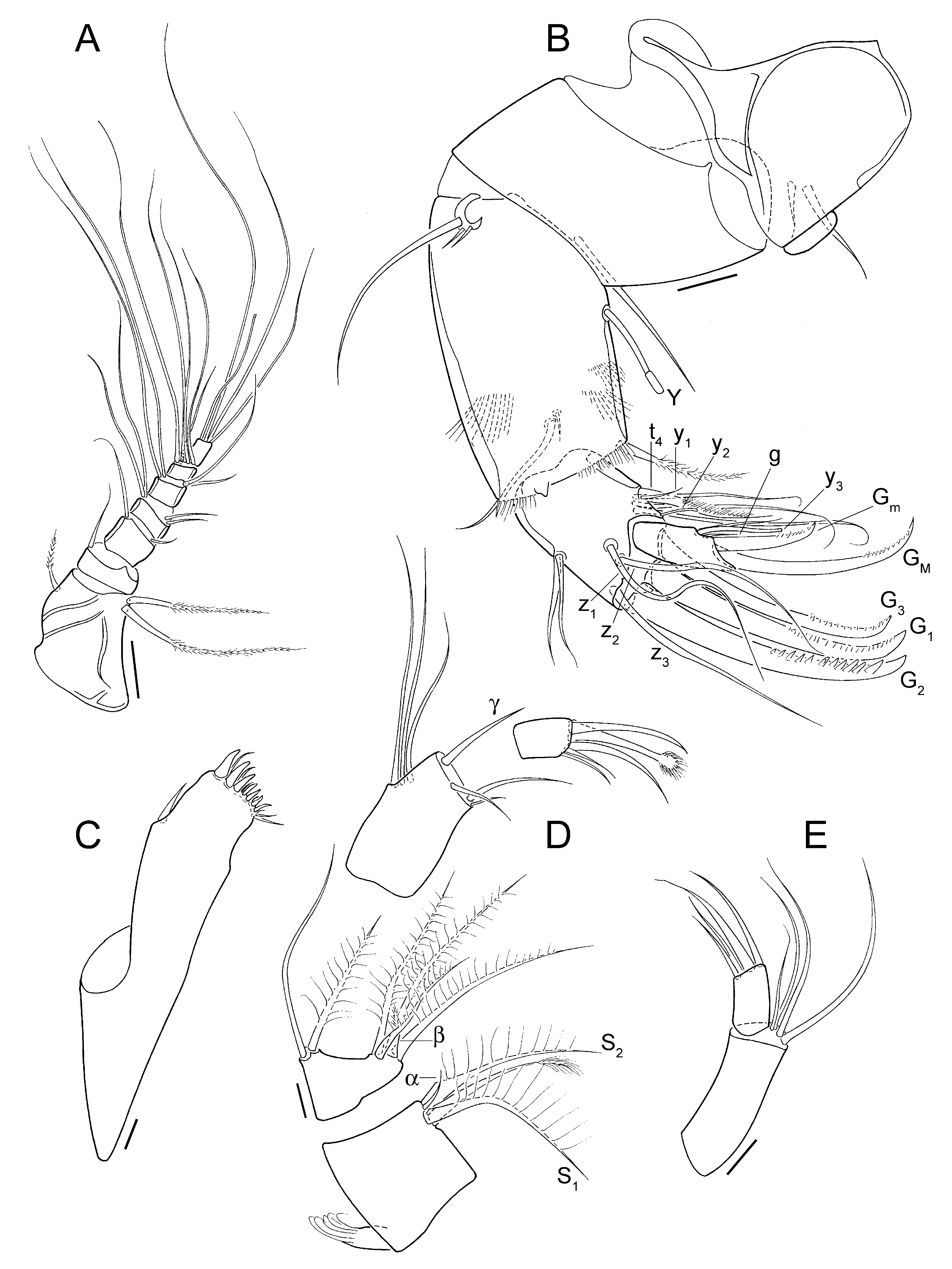
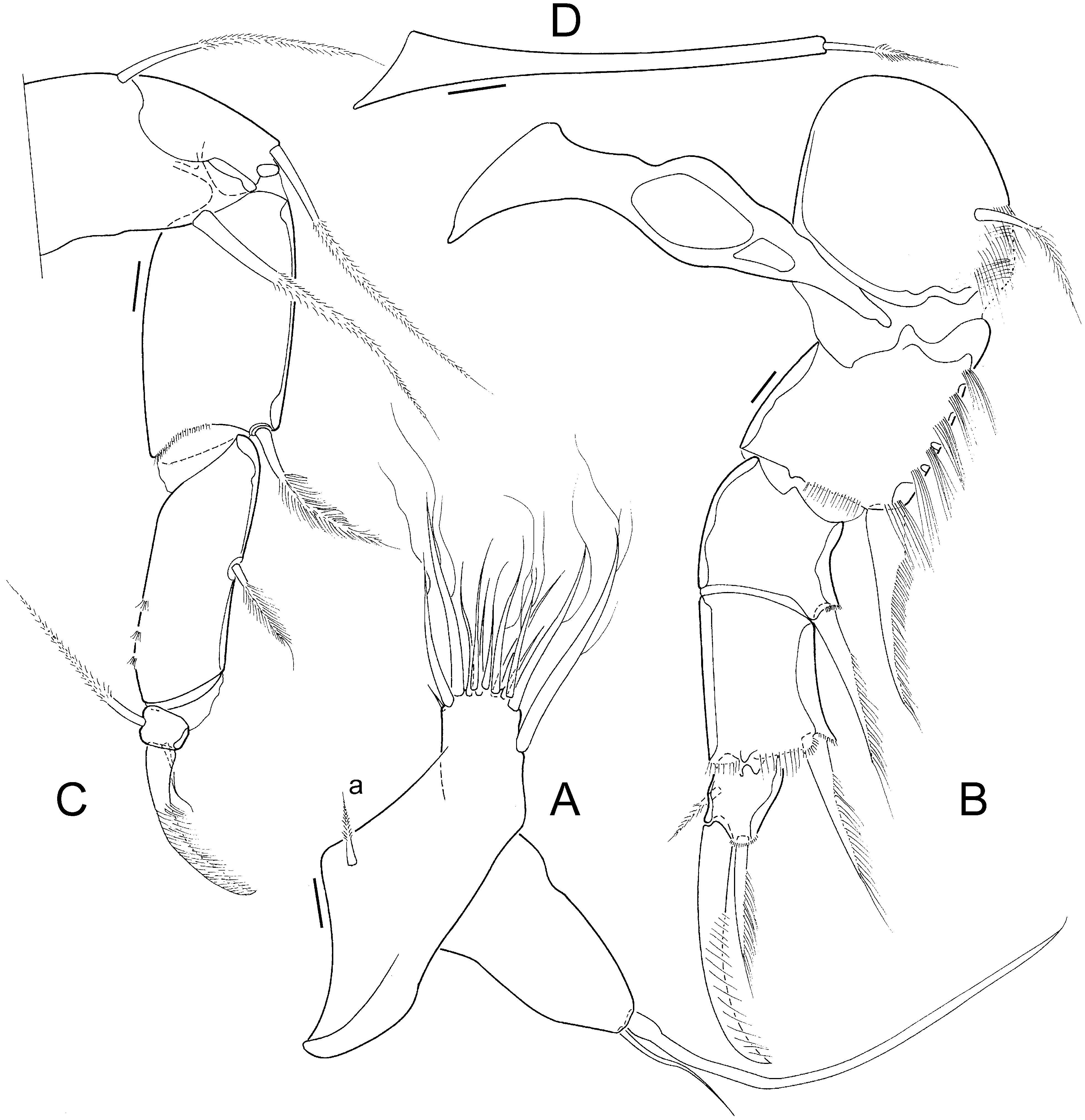
A1 ( Fig. 1A View Figure 1 ) 7-segmented; first segment (= fusion of first two segments) with 2 long, ventral and 1 shorter dorsal seta; third segment with 1 dorsal seta, Rome organ not detectable; fourth segment with 1 long dorsal seta (longer than three following segments) and 1 shorter ventral seta; fifth segment with 2 long dorsal and 2 unequal but shorter ventral setae; sixth segment with 2 long dorsal, and 1 long and 1 short ventral setae; seventh segment with 4 long and 1 intermediate setae; terminal segment with 2 long setae, 1 seta of intermediate length and 1 long aesthetasc, the latter in dorsal position.
A2 ( Fig. 1B View Figure 1 ) 5-segmented. Exopodite consisting of 1 longer and 2 short setae. Endopodite 3-segmented; first segment with ventral aesthetasc Y of normal size, 1 ventro-apical seta with swollen base, 1 longer (= accompanying seta) and 1 minute (= natatory seta) subapical setae; second segment with 4 ventral t-setae (t4 claw-shaped) and 2 subequal, mediodorsal setae, z1–3 medium-length setae (almost reaching tips of endclaws); aesthetasc y1 inserted next to seta t4 resembling short seta; 3 large claws (G1–3) and aesthetasc y2; terminal segment minute, with claws Gm slightly longer than half of GM, aesthetasc y3 very basally fused with slightly longer accompanying seta and seta g less than half length of aesthetasc.
Md palp ( Fig. 1C, D View Figure 1 ) 4-segmented; first segment with respiratory plate with reduced number of short rays, ventro-apically with 2 large s-setae, accompanying seta with distal brush of setulae and short and narrow alpha-seta, with slightly widened base; second segment with 2 dorso-apical setae, 1 set with long setules, and ventro-apical group of 5 setae: 3 long and 1 of intermediate size, set with long setulae, and broad and hirsute beta-seta; third segment with 3 dorsolateral setae, 1 short and 1 longer ventro-apical setae, 1 medio-apical seta and dorso-apical gamma-seta; terminal segment with 3 claw-like setae and 2 shorter setae, longest claw-like seta ending in hirsute, spoonshaped apex.
Mx1 ( Fig. 1E View Figure 1 ) with 2-segmented palp, first segment with 4 apical setae on expanded distal corner, second segment elongated, tapering, with 2 large and 2 smaller apical setae. Three endites set with setae in various shapes and sizes, third endite with claws not serrate.
T 1 ( Fig. 2A View Figure 2 ) with short palp, with 1 long and 1 shorter apical setae; endite with c. 13 setae, unequal in length and number and length of setulae.
T 2 ( Fig. 2B View Figure 2 ) 5-segmented, stout and hirsute and set with setulae on first two segment; first segment (knee-segment) with large d2 seta; second to fourth segment each with stout, serrate apical claw-like seta; terminal segment with 1 long end-claw, 1 short, claw-like apical seta next to endclaw and 1 minute lateral seta.
T 3 ( Fig. 2C View Figure 2 ) 4-segmented, first segment with 3 setae; second segment with 1 apical seta, third segment (= fusion of segment 3 and 4) with 1 lateral seta; terminal segment not fused with previous segment, with 1 weakly sclerotized endclaw, 1 minute accompanying apical seta and 1 longer, reflexed, lateral seta.
CR ( Fig. 2D View Figure 2 ) reduced to narrow, tapering ramus with 1 apical, seta-like claw.
Male unknown.
Measurements (in µ m)
MZUSP 16353: L = 397, H = 201.
MZUSP 16351: L = 397, W = 224.
MZUSP 16349: LV: H = 387, L = 189; RV: L = 371, H = 188.
Remarks
The present species is morphologically closely related to C. zlotini from the Solomon Islands as described by Shornikov (1980). The differences observed in the valves are minimal (LV in the Brazilian population with slightly more pointed posterior margin and with anterior margin less broadly rounded), but there are a whole range of differences in the chaetotaxy: (1) A2 with 3 z-setae in C. mckenziei sp. nov., only 2 in C. zlotini ; (2) A2 with additional minute natatory seta in C. mckenziei sp. nov., not illustrated for type material of C. zlotini ; (3) A2 with claw GM shorter than G 1–3 in C. zlotini , equally long in C. mckenziei sp. nov.; (4) Md palp with alpha seta not described for C. zlotini ; (5) Md palp with 5 terminal setae in C. mckenziei sp. nov., only 4 in C. zlotini and with distal part of largest apical claw more spoon-shaped in C. mckenziei sp. nov.; (6) Mx1-palp with 4 seta on terminal segment in C. mckenziei sp. nov., only 3 in C. zlotini . Some of these features (alpha seta and terminal seta on Mdpalp) deal with very small structures, which could only be observed with the best contemporary microscopes, and these could have been missed in the description of C. zlotini . Others, however (e.g. number of z-setae on A2 and number of terminal setae on Mx1-palp), concern relatively large structures and could constitute genuine, specific differences; they are also included in the diagnosis of the present new species.
CALLISTOCYPRIS ROSSETTII SP. NOV.
( FIGS 4–6 View Figure 4 View Figure 5 View Figure 6 )
Type locality
Boracéia Biological Station , Municipality of Salesópolis , São Paulo State, Brazil. GPS coordinates: 23°38′16.9″S, 45°50′24.5″W. Inside the forest, near Pedreira’s swamp, in leaf litter at the foot of a rock wall. Material collected on 02.iv.2003 by CEFR and RLP. The species is thus far known only from its type locality GoogleMaps .
Type material
Holotype: a dissected female, with valves stored dry in a micropalaeontological slide and dissected soft parts kept in a sealed slide (MZUSP 16356).
Paratypes: a female dissected and stored like the holotype (MZUSP 16357); a dissected female, with valves used for SEM and stored in a micropalontological slide, and dissected soft parts kept in a sealed slide (MZUSP 16358); 3 carapaces used for SEM and stored in micropalaeontological slides (MZUSP 16359–61), 30 females kept in toto in ETOH (MZUSP 16362).
Derivation of name
Named after Dr G. Rossetti (Parma, Italy), in recognition of his significant contributions to the taxonomy of Darwinulidae and of (semi-) terrestrial ostracods.
Diagnosis
Cp arched in lateral view, wider in dv, relatively large (L = c. 0.5 mm). Valves with pitted central area in lv, with pronounced ventral ridges. RV caudally with selvage dividing in ventral and central ridge, with additional inner list in between submarginal list and selvage; LV with third inner list only running along ventral margin. A2 with 3 z-setae. Mx1-palp with 4 apical seta on distal segment.
Description
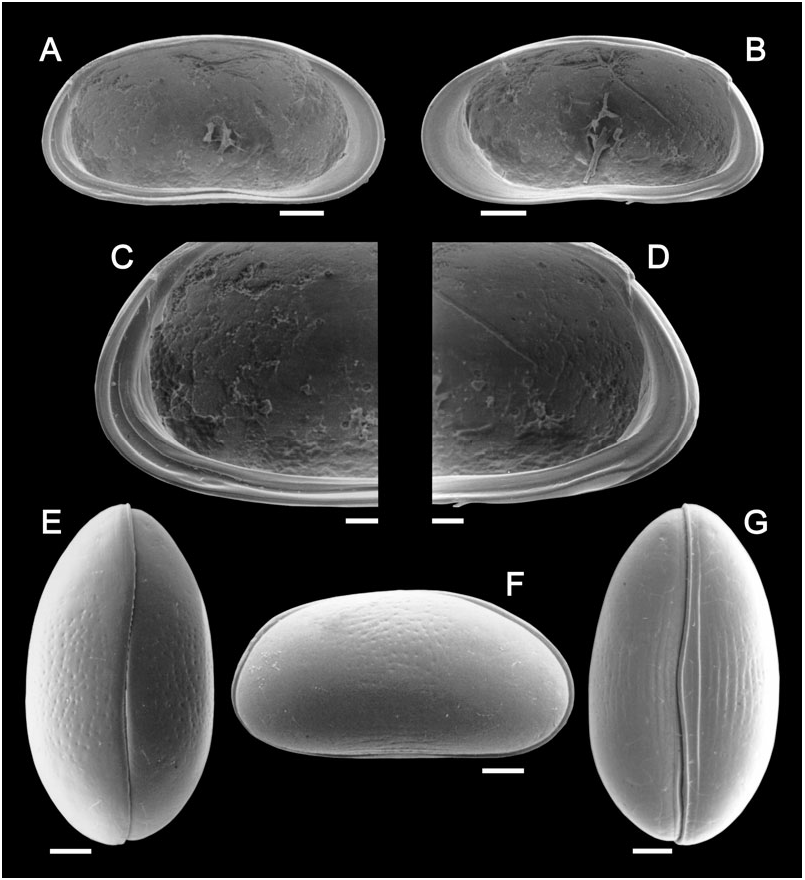
Cp ( Fig. 6H View Figure 6 ) considerably larger than the previous species, and more highly arched in lv; LV overlapping RV along anterior, posterior and most of the ventral margins; in dv ( Fig. 6E View Figure 6 ), Cp with greatest width (L/H ratio = 1.67) situated well behind middle, anterior and posterior edges bluntly pointed. Valve surface laterally pitted, especially in centre, ventral side ( Fig. 6I View Figure 6 ) with 6–7 longitudinal ridges.
LV ( Fig. 6A, C, F View Figure 6 ) with well-developed anterior calcified inner lamella, posterior marginal structures complex, consisting of at least 3 inner lists, ventrocaudally with shallow socket in marginal inner list (il1); proximal inner list (il3) only running ventrally, not along caudal margin.
RV ( Fig. 6B, D, G View Figure 6 ) with wide anterior calcified inner lamella, posteriorly with well-developed selvage, the latter postero-ventrally splitting into ventral and more dorsally directed ridge, the latter being accommodated in socket of LV when valves closed; posterior inner margin of RV elevated into list (il2), third list (il3) being present between selvage and il2. In vv ( Fig. 6I View Figure 6 ) LV with strong outer list along the entire margin, more developed than in C. mckenziei .
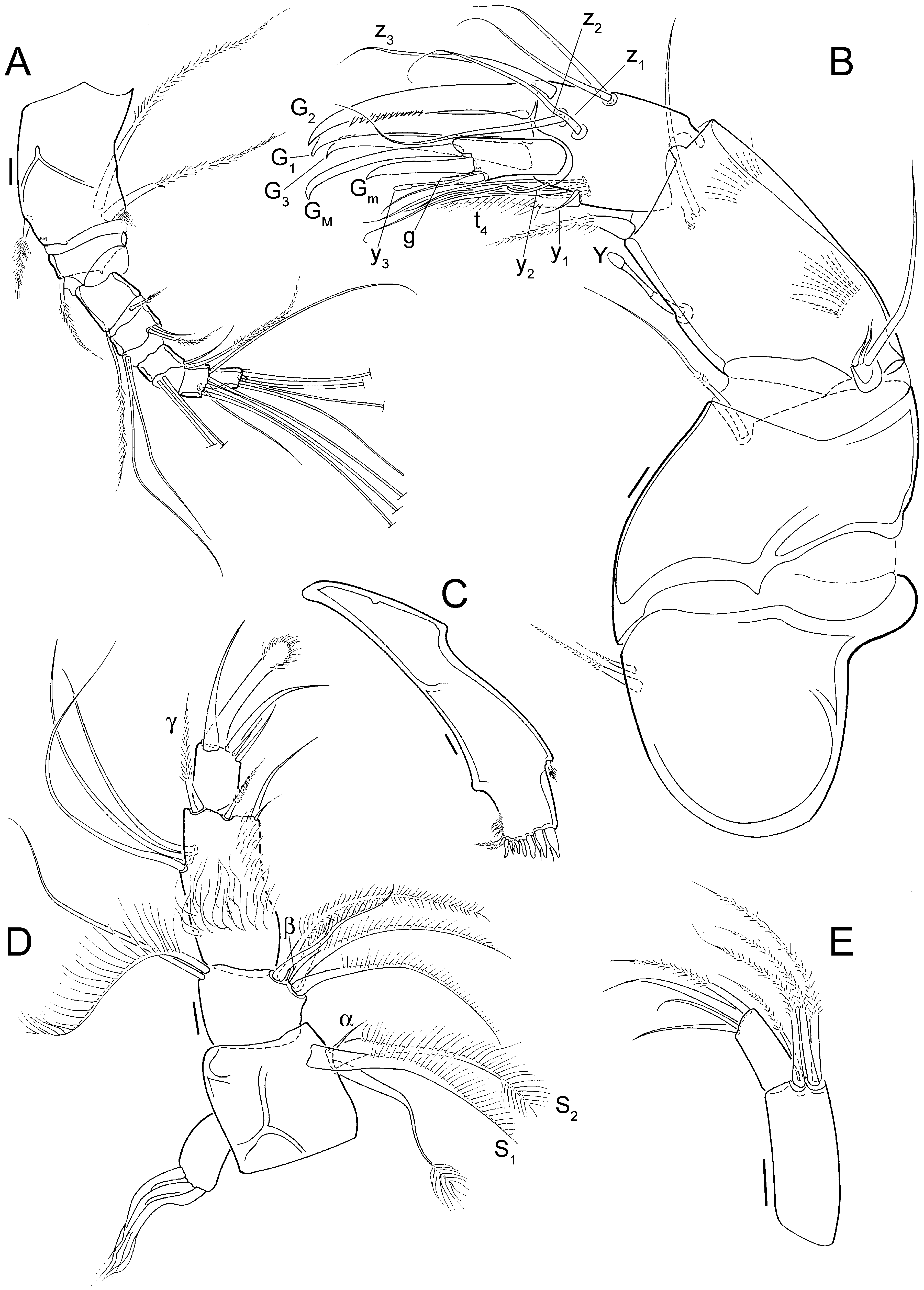
A1 ( Fig. 4A View Figure 4 ) 7-segmented; first segment (= fusion of first 2 segments) with 2 long, ventral setae and 1 shorter dorsal seta; third segment with 1 dorsal seta, Rome organ not detectable; fourth segment with 1 long dorsal seta (longer than 3 following segments) and 1 shorter ventral seta; fifth segment with 2 long dorsal and 2 unequal but shorter ventral setae; sixth segment with 2 long dorsal, and 1 long and 1 short ventral setae; seventh segment with 4 long and 1 intermediate setae; terminal segment with 2 long setae, 1 seta of intermediate length and 1 long aesthetasc in dorsal position.
A2 ( Fig. 4B View Figure 4 ) 5-segmented. Exopodite consisting of 1 longer and 2 short setae. Endopodite 3-segmented; first segment with ventral aesthetasc Y of normal size, 1 ventro-apical seta and 1 longer (= accompanying seta) and 1 minute (= natatory seta) subapical setae; second segment with 4 ventral t-setae (T4 clawshaped) and 2 medio-dorsal setae, z1–3 mediumlength setae (reaching tips of endclaws); aesthetasc y1 inserted next to seta t4 resembling short seta; 3 large claws (G1–3) and an aesthetasc y2; terminal segment minute, with claw Gm about half length of GM, aesthetasc y3 very basally fused with slightly longer accompanying seta and seta g less than half length of aesthetasc.
Md palp ( Fig. 4C, D View Figure 4 ) 4-segmented; first segment with respiratory plate carrying unknown number of rays, ventro-apically with 2 large s-setae, accompanying seta with distal brush of setulae and short and narrow alpha-seta; second segment with 2 dorso-apical setae, 1 set with long setules, and ventro-apical group of 5 setae: 3 long and 1 of intermediate size, set with long setulae, and broad and hirsute beta-seta; third segment with 3 dorso-lateral setae, 1 short and 1 longer ventro-apical setae, 1 medio-apical seta and dorso-apical gamma-seta; terminal segment with 3 claw-like setae and 2 shorter setae, longest claw-like seta ending in a hirsute, spoon-shaped apex.
Mx1 ( Fig. 4E View Figure 4 ) with 2-segmented palp, first segment with 4 apical setae on expanded distal corner, second segment elongated, tapering, with 2 large and 2 smaller apical setae. Three endites set with setae in various shapes and sizes, third endite with claw not serrated.
T1 ( Fig. 5A View Figure 5 ) with short palp, with 1 long and 1 shorter apical setae; endite with 12–13 setae, unequal in length and setulation.
T2 ( Fig. 5B View Figure 5 ) 5-segmented, stout and hirsute and set with brushes or setulae on first 2 segments; first segment (knee-segment) with relatively large d2 seta; second to fourth segments each with stout, serrate apical claw-like seta; terminal segment with 1 long end-claw, 1 short, claw-like apical seta next to endclaw and 1 minute lateral seta.
T3 ( Fig. 5C View Figure 5 ) 4-segmented, first segment with 3 setae; second segment with 1 apical seta, third segment (= fusion of segments 3 and 4) with 1 lateral seta; terminal segment not fused with previous segment, with 1 weakly sclerotized endclaw, 1 minute accompanying apical seta and 1 longer, reflexed, lateral seta.
CR ( Fig. 5D View Figure 5 ) reduced to a narrow, tapering ramus with 1 apical, seta-like claw.
Male unknown.
Measurements (in µ m):
MZUSP 16359: L = 517, H = 275.
MZUSP 16361: L = 506, W = 312.
MZUSP 16360: L = 513, W = 319.
MZUSP 16358: LV: L = 506, H = 264; RV: L = 493, H = 260.
Remarks
Callistocypris rossettii sp. nov. differs from C. mckenziei sp. nov. mainly in size (it is considerably larger) and shape (less elongated), but also in structures of the valve margins: in the RV, an additional caudal inner list (il3) is present in C. rossettii sp. nov. (absent in C. mckenziei sp. nov.) and in the LV, the il3 runs only ventrally in C. rossettii sp. nov., while this list runs up to halfway along the caudal margin in C. mckenziei sp. nov.
The chaetotaxy is largely similar in the two Brazilian Callistocypris species and only small differences occur, e.g. length ratio of the 2 dorsal seta on the fifth and the sixth segments of A1, length ratio of Gm and GM on A2, etc.
| RV |
Collection of Leptospira Strains |
| T |
Tavera, Department of Geology and Geophysics |
| MZUSP |
Museu de Zoologia da Universidade de Sao Paulo |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.