Stenus fujianensis Liu, Tang & Luo, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4375.1.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:12FBEFC0-1C13-4548-AA50-1679D016D090 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5998759 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E7878D-FFDC-E06C-DF8D-FA0EFBA97B34 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Stenus fujianensis Liu, Tang & Luo |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Stenus fujianensis Liu, Tang & Luo View in CoL , new species
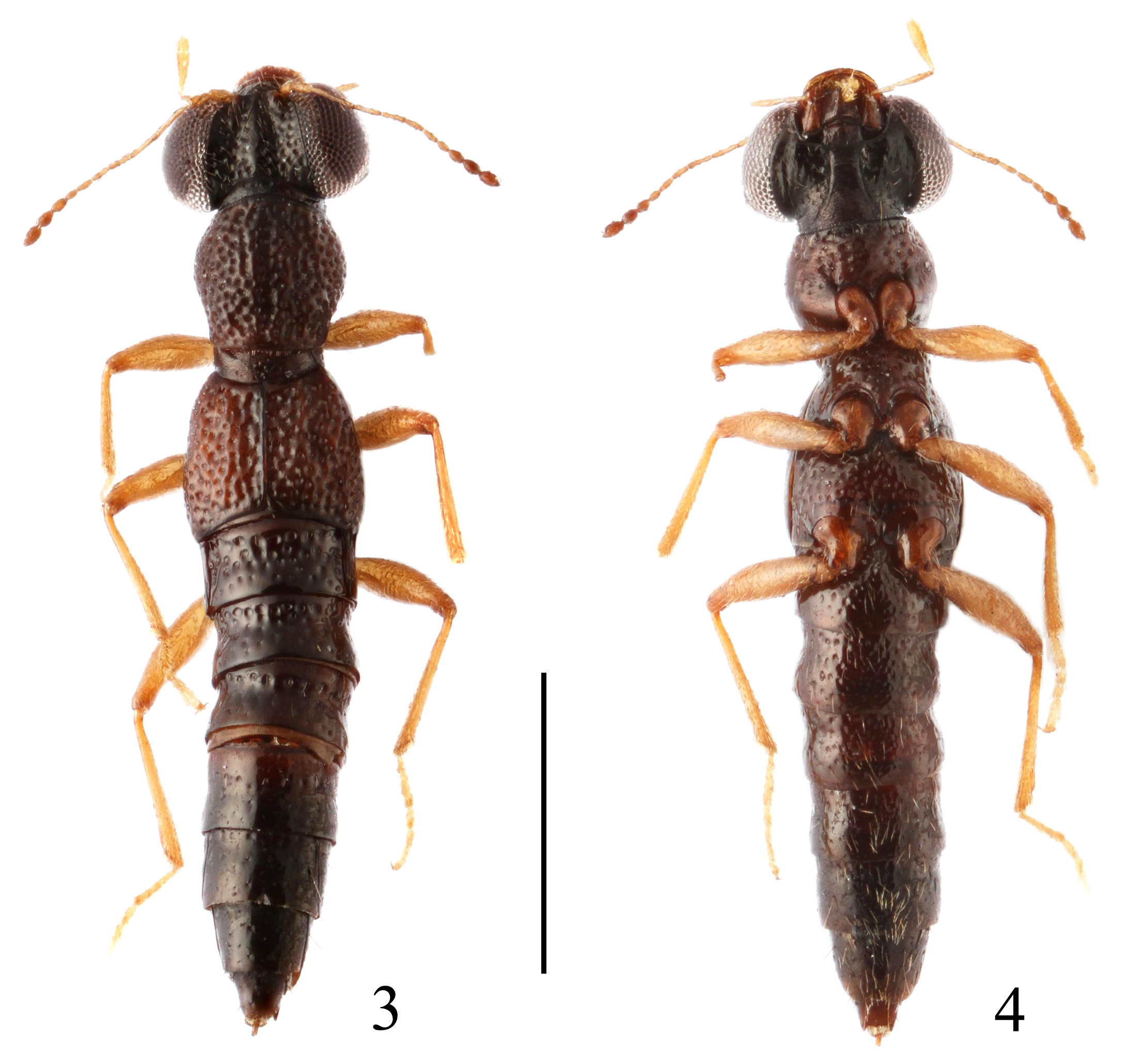
( Figs 3, 4 View FIGURES 3–4 , 15–20 View FIGURES 15–20 )
Material examined. CHINA: Fujian Prov. : Holotype: ♂, glued on a card with labels as follows: “ China Fujian Prov., Wuyishan City, Guadun N. R., 31.V.2012, alt. 1700–1800 m, P. & D. leg”. “ Holotype / Stenus fujianensis / Liu, Tang & Luo ” [red handwritten label] ( SHNU) . Paratypes: 5♂♂ 4♀♀, same data as for the holotype. ( SHNU, cPut) ; 2♂♂ 4♀♀, same data as for the holotype, but 1.VI.2012, PENG Zhong leg. ( SHNU).
Description. Brachypterous; head blackish, pronotum and abdomen dark brown, elytra reddish brown with margins and suture darker. Antennae, maxillary palpi and legs yellowish brown except antennal club infuscate. Labrum reddish brown.
BL: 3.2–3.4 mm, FL: 1.5–1.6 mm.
HW: 0.66–0.73 mm, PL: 0.51–0.54 mm, PW: 0.50–0.52 mm, EL: 0.52–0.57 mm, EW: 0.60–0.61 mm, SL: 0.40–0.43 mm.
Head 1.10–1.22 times as wide as elytra; interocular area with two deep longitudinal furrows, median portion convex, reaching the level of inner eye margins; punctures round, slightly larger and sparser on median portion than those near inner margins of eyes, diameter of large punctures about as wide as apical cross section of antennal segment II; interstices between punctures partially reticulated, mostly narrower than half the diameter of punctures except those along the midline of the convex median portion, which distinctly wider than the diameter of punctures. Paraglossae oval.
Pronotum 1.00–1.04 times as long as wide; disk uneven, with distinct median longitudinal furrow almost throughout; punctures confluent, of similar size to those of head; interstices between punctures distinctly reticulated, narrower than half the diameter of punctures except for those in the middle of the median longitudinal furrow, which may be as wide as diameter of punctures.
Elytra 0.90–0.95 times as long as wide; disk uneven, with sutural impression, humeral impression and posterolateral impression; punctures confluent, slightly larger than those on pronotum; interstices partially and indistinctly reticulated, distinctly smaller than half the diameter of punctures.
Legs with tarsomeres IV strongly bilobed.
Abdomen cylindrical; paratergites very narrow and almost impunctate, present only in segment III, tergites and sternites totally fused in segments IV–VI, posterior margin of tergite VII with indistinct apical membranous fringe; punctation of tergites III–VIII sparse and shallow, gradually becoming smaller posteriad; interstices smooth, mostly wider than diameter of punctures except those on basal impressions of tergites III–V, which may be distinctly narrower than half the diameter of punctures.
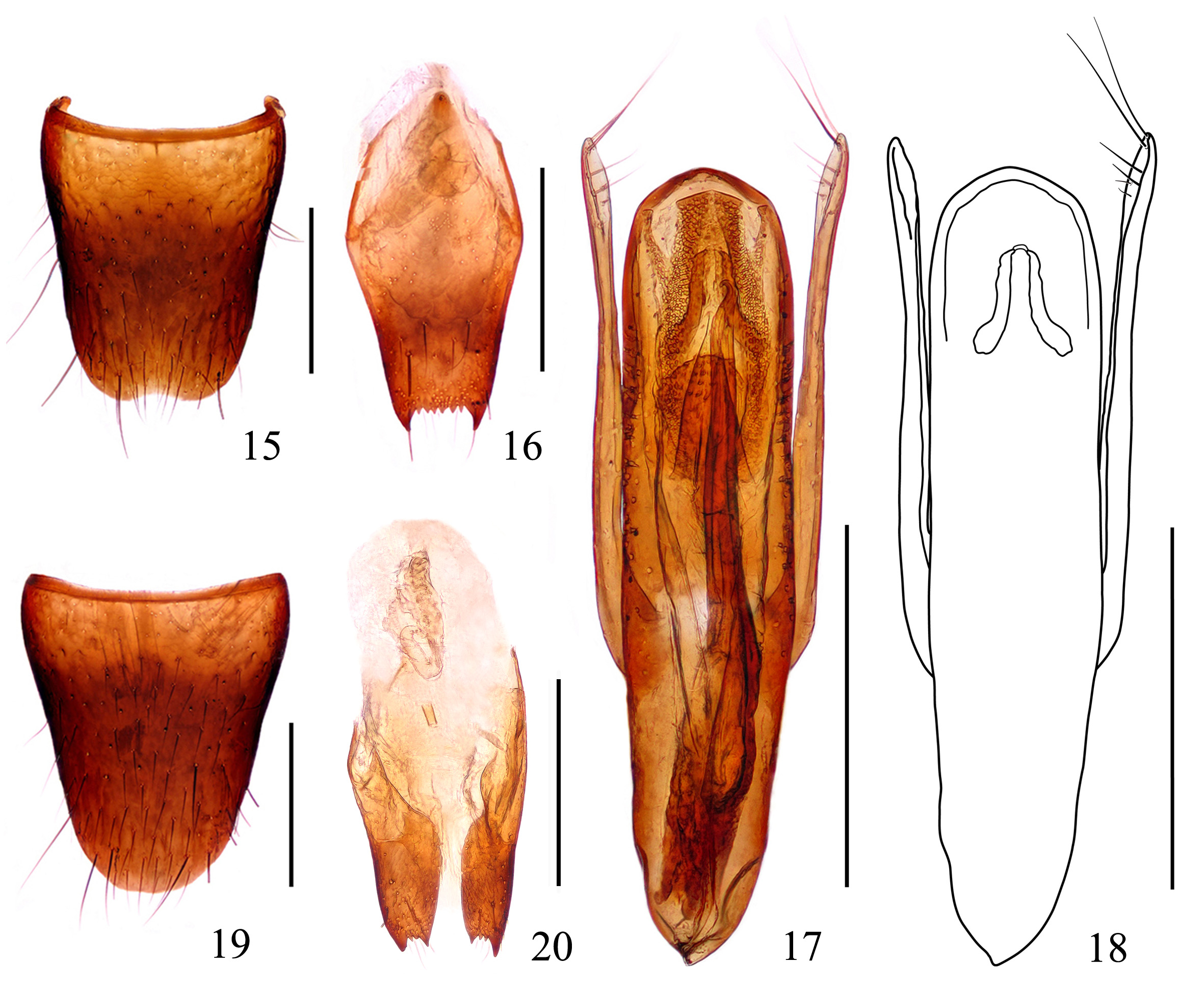
Male. Sternite VII with inconspicuous emargination at middle of posterior margin; sternite VIII ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 15–20 ) with shallow emargination at middle of posterior margin; sternite IX ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 15–20 ) with distinct apicolateral projections, posterior margin serrate. Aedeagus ( Figs. 17–18 View FIGURES 15–20 ) with apical sclerotized portion very short and broad; sclerotized expulsion clasps long, slender, median longitudinal bands triangular; copulatory tube very long, relative wide, apical tube strongly curved; parameres distinctly longer than median lobe, swollen at apical parts, each with 6–8 setae on apico-internal margins.
Female. Sternite VIII ( Fig. 19 View FIGURES 15–20 ) entire; spermatheca ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 15–20 ) strongly sclerotized with short basal duct.
Distribution. China (Fujian).
Remarks. The new species is similar to S. wuyanlingus Liu, Tang & Luo, 2017 from Zhejiang, but can be distinguished from the latter species by the larger size, smaller ratio of HW/EW (in S. wuyanlingus HW/EW: 1.21– 1.30), less confluent punctation of pronotum and different sexual characters.
Etymology. The specific name is derived from the type locality of this species.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |