Synergus kawakamii Tang & Melika
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3999.4.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:CB6127D2-DF5B-4F86-A3D9-6A2F9DBD021C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5628686 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E887CE-5C37-FFCC-FF45-C12AA3FCF9BC |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Synergus kawakamii Tang & Melika |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Synergus kawakamii Tang & Melika , new species
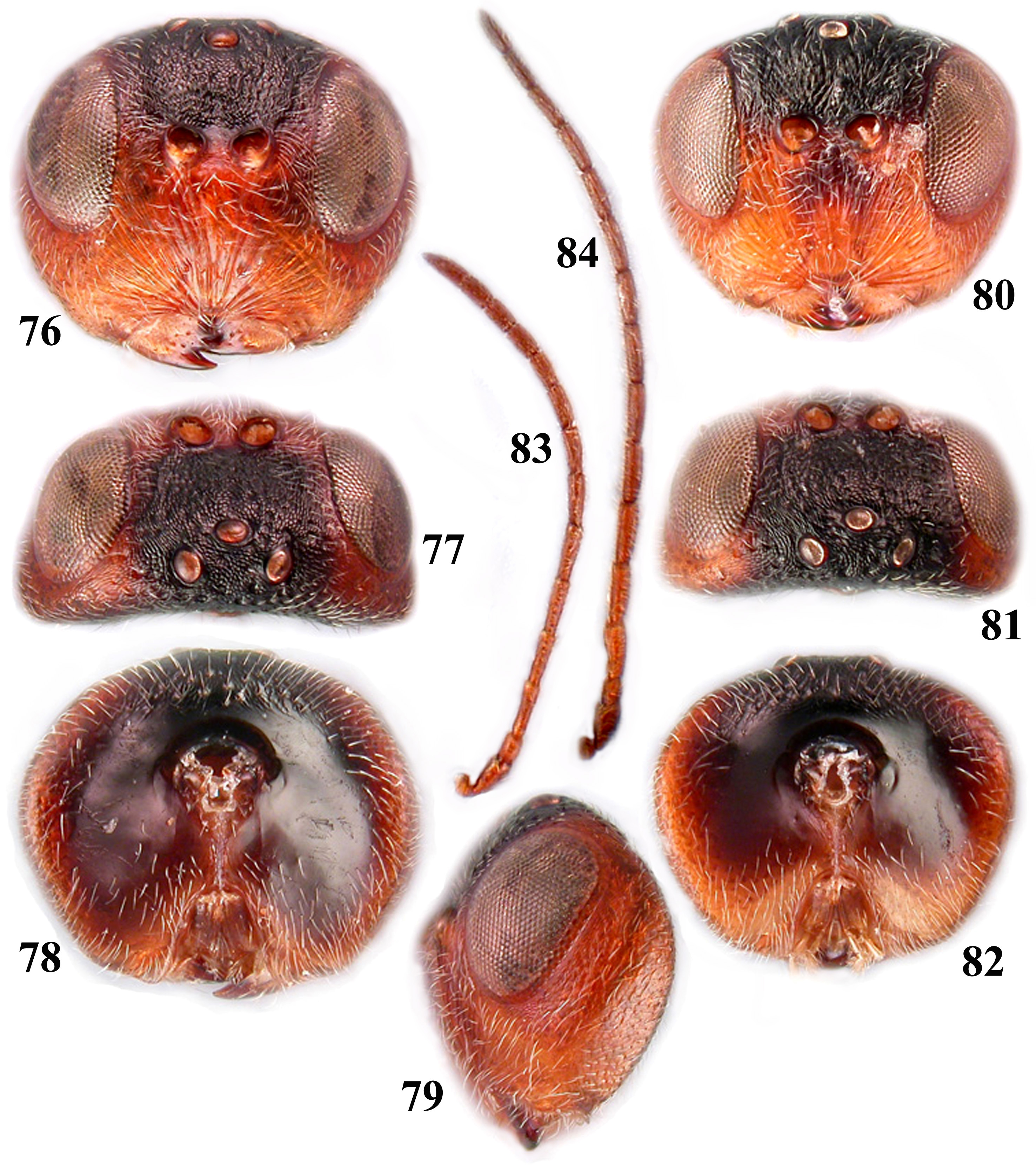
Figs 76 View FIGURES 76 – 84 –90
Type material. HOLOTYPE female: TAIWAN, Hualien Co, on Castanopsis kawakamii , exirregular spheric galls. One female and 4 male PARATYPES, with the same labels as the holotype.
The female holotype, 2 male paratypes are deposited in NCHU, 1 female and 2 male paratypes in PHMB.
Etymology. The species is named after the host plant species, Castanopsis kawakamii Hayata , which from the host galls were collected.
Diagnosis. In S. kawakamii the radial cell of the fore wing is open (Fig. 88) and thus most closely resembles Synergus castaneus Pujade-Villar, Bernardo & Viggiani, 2013 which is the only known Eastern Palaearctic Synergus species with an open radial cell of the fore wing ( Pujade-Villar et al. 2013). However, in S. castaneus R1 and Rs do not reach the wing margin, head entirely black, frontal carina indistinct, not reaches lateral ocellus, antenna with indistinctly separated F12, F1 nearly 1.5–2.0 times as long as F2; first metasomal tergite with strong longitudinal parallel rugae (well-illustrated in Pujade-Villar et al. 2013), while in S. kawakamii R1 and Rs reach wing margin, and R1 partially running along the wing margin (Fig. 88), head light brown, frontal carina distinct, reaches lateral ocellus ( Fig. 76–82 View FIGURES 76 – 84 ), female antenna with distinct 12 flagellomeres, F1 nearly equal F2 ( Fig. 83 View FIGURES 76 – 84 ); first metasomal tergite with very delicate indistinct longitudinal parallel rugae (Fig. 89).
FIGURES 85–90. Synergus kawakamii , new species, female: 85, mesosoma, lateral view, 86, mesoscutum, dorsal view, 87, mesoscutellum, dorsal view, 88, fore wing, part, 89, 1st metasomal tergite (petiole), dorsal view, 90, metasoma, lateral view.
Description. FEMALE. Head light brown with dark brown frons, interocellar area and postocciput; mesosoma black to dark brown; antenna light brown, mouthparts, maxillary and labial palps yellowish; legs yellowish brown with darker coxae; wings with pale brown venation, metasoma dark brown to reddish brown.
Head delicately coriaceous, rounded, nearly as broad as high in frontal view; slightly broader than mesosoma, 1.8 times as broad as long in dorsal view. Lower face and malar space with relatively dense white setae; frons with only few scattered setae; gena behind eye, postgena, occiput and vertex with some setae; posterior areas aside hypostoma with denser setae. Eye 1.6–1.8 times as high as length of malar space. Malar sulcus absent, delicate striae radiating from clypeus and reach eye. Clypeus very small, alutaceous, slightly impressed, ventrally straight, not emarginate; epistomal sulcus and clypeo-pleurostomal line indistinct; anterior tentorial pit small, distinct. Lower face with distinct numerous striae radiating from clypeus and extending to lower level of torulus and eye.
Frons uniformly delicately coriaceous laterally of narrow distinct frontal carina, with numerous small deep punctures; interocellar area with micropunctures. Transfacial distance same length as height of eye; distance between eye and antennal torulus equal to diameter of torulus; diameter of torulus 1.2 times as long as distance between toruli. POL almost as long as OOL and 2.1 times as long as LOL; OOL 1.7 times as long as length of lateral ocellus. Vertex narrow, shiny with some dull striae and punctures. Occiput alutaceous, with some striae; occipital carina absent. Gena broadened behind eye in frontal view, smooth, delicately coriaceous, with white setae. Postgena smooth. Postgenal bridge reduced to long, narrow median strip; postgenal sulci united well before reaching hypostoma; posterior tentorial pit distinct, area around occipital foramen well-impressed, smooth. Antenna with 12 flagellomeres, pedicel 1.7 times as long as broad, F1 2.0 times as long as pedicel; F1=F2=F3, F12 nearly 1.3 times as long as F11; placoid sensillae on F4–F11, invisible on F1–F3.
Mesosoma 1.2 times as long as high in lateral view. Pronotum coriaceous, laterally with some rugae, area between them weakly coriaceous or almost smooth; sides of pronotum rounded in dorsal view; lateral pronotal carina present, weak. Propleuron alutaceous, with some transverse striae in lower half. Mesoscutum with white setae, slightly broader than long measuring along anterior edge of tegulae, uniformly transversely rugose. Notaulus complete, slightly broadened posteriorly, with smooth bottom; anterior parallel line very indistinct, hardly traceable; parapsidal line narrow, extending to 2/3 of mesoscutum length; distinct parascutal carina present only along tegula; median mesoscutal line extending to 2/3 of mesoscutum length. Dorsoaxillar area very finely coriaceous, with micropunctures; lateroaxillar area joins dorsoaxillar area at an acute angle. Mesoscutellum 1.3 times as broad as long in dorsal view, not emarginated along sides, uniformly dull rugose, with dense white setae. Scutellar foveae transverse, with coriaceous bottom, separated by broad median carina, well-delimited posteriorly. Mesopectus with parallel longitudinal striae. Metapleural sulcus reaches posterior margin of mesopectus in upper 1/3 of its height. Propodeum entirely uniformly delicately coriaceous, with short white setae; lateral propodeal carinae distinct, uniformly thin, nearly parallel; central propodeal area delicately coriaceous, without striae. Metascutellum indistinct, much shorter than ventral impressed area; metanotal trough smooth, without setae; propodeal spiracle transversely ovate, with strong raised carina along anterior border. Nucha with distinct longitudinal parallel rugae.
Fore wing veins brown or light brown venation; margin with long cilia; radial cell partially open, 2.5 times as long as broad; Rs and R1 straight, reach wing margin, R1 on short distance running along wing margin, areolet present. Legs with short white setae, tarsal claws with distinct basal lobe.
Metasoma longer than head+mesosoma and slightly longer than high from lateral view. First metasomal tergite with very delicate indistinct longitudinal parallel rugae. Syntergite with few white setae anterolaterally, smooth, glabrous, posterodorsally straight, slightly incised, micropunctures on posterior edge of syntergite very indistinct, hardly or not traceable. Subsequent tergites and hypopygium micropunctate; prominent part of ventral spine of hypopygium very short and slender, with very few short white setae ventrally. Body length 2.7–3.1 (n =2).
MALE. Similar to female but head yellowish, much lighter than in female; antenna with 13 flagellomeres, F1 slightly curved and broadened apically, less broadened basally, 1.1–1.2 times as short as F2; placoid sensillae on F3–F11. Body length 2.6–2.8 mm (n = 3).
Biology. This species was reared from undescribed irregular spheric galls on Castanopsis kawakamii .
Distribution. Currently known from Taiwan only (Hualien county).
Taxonomic comments. Synergus kawakamii is the first known Synergus species reared from galls on Castanopsis . Saphonecrus hupingshanensis Liu, Yang & Zhu , is the only known Saphonecrus species which associates with Castanopsis and it is also possible that induces its own gall (Liu et al. 2012).
| NCHU |
National Chung Hsing University |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |