Ochotona iliensis, Li Weidong & Ma Yong, 1986
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.6619785 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6620042 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E94121-1E48-FF73-FA31-F9B719942E80 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Ochotona iliensis |
| status |
|
Ili Pika
French: Pika de I'lli / German: lli-Pfeifhase / Spanish: Pica de li
Taxonomy. Ochotona iliensis Li Weidong & Ma Yong, 1986 View in CoL ,
“1-85Jé #5£5BL Ih LH PE BOER3200K4” (= western part ofJilimalale mountain altitude of 3200 m, Nilka County, Xinjiang, China) .
According to mtDNA, O. iliensis belongs to subgenus Conothoa. This recently found and distinctly colored species has not caused any taxonomic ambiguity. Monotypic.
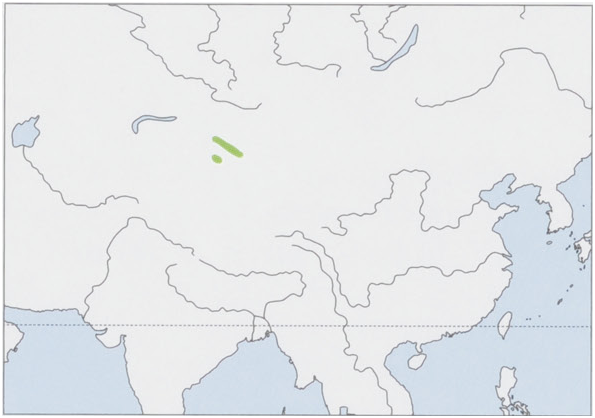
Distribution. Restricted to the Borohoro Shan (Nilka, Jinghe, Usu, Shawan, Hutubi, Urumqi, and Hejing counties) and Halke Shan (Kuga County) in E Tian Shan Range in NW Xinjiang, NW China. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 190-200 mm, ear 36-37 mm, hindfoot 42-43 mm; weight 200-250 g. The Ili Pika is a large pika. Dorsal fur is gray with rufous brown patches on forehead, and hindlegs and collar are the same color. Muzzle is light. Some specimens have rufous dorsal stripe. Ventral fur is gray. Ears are large, furred, rounded, and covered with long rufous hairs. Melanistic individuals occur. Seasonal variation in color is unclear. Skull is large, with widely confluent incisive and palatal foramens. Auditory bullae are large. Condylobasal lengths are 44-45 mm, skull widths are 24-25 mm, and skull heights are 17 mm. Distinct pelage color differentiates Ili Pikas from all other species of pikas.
Habitat. Rocky cliffs with holes, crevices, and piles of stones at elevations of 2800— 4100 m. The Ili Pika is a cliff-associated species.
Food and Feeding. The Ili Pika feeds on green plants and hoards hay in hay piles situated in rock niches.
Breeding. Breeding ofthe Ili Pika occurs in May-September. Reproductive rate is supposedly low.
Activity patterns. Ili Pikas are active around-the-clock. Activity changes seasonally. Spring and autumn are characterized by more nocturnal activity, while winter activity is mainly diurnal. General activity aboveground is very low.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. Judging from photographs,Ili Pikas have similar locomotion to ecologically close Chinese Red Pikas ( O. erythrotis ). Ili Pikas are asocial and occupy individual territories at low densities. Social interactions have never been observed. The Ili Pika is silent. Breeding chambersare situated inside hollows in rocky cliffs.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Endangered on The IUCN Red List. The Ili Pika declined dramatically in last 30 years, and its distribution has contracted by an estimated 70%.
Bibliography. Li Weidong & Ma Yong (1986), Li Weidong & Smith (2005, 2015), Li Weidong et al. (1993), Niu Yidong et al. (2004).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Ochotona iliensis
| Don E. Wilson, Thomas E. Lacher, Jr & Russell A. Mittermeier 2016 |
Ochotona iliensis
| Li Weidong & Ma Yong 1986 |