Stockumites procedens ( Korn, 1984 ) Korn & Weyer, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2023.882.2177 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:67C909E4-C700-4F8D-B8CE-5FD9B2C5D549 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8184847 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03EA5C14-CA32-8573-FE35-FE98FEB183FB |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Stockumites procedens ( Korn, 1984 ) |
| status |
comb. nov. |
Stockumites procedens ( Korn, 1984) comb. nov.
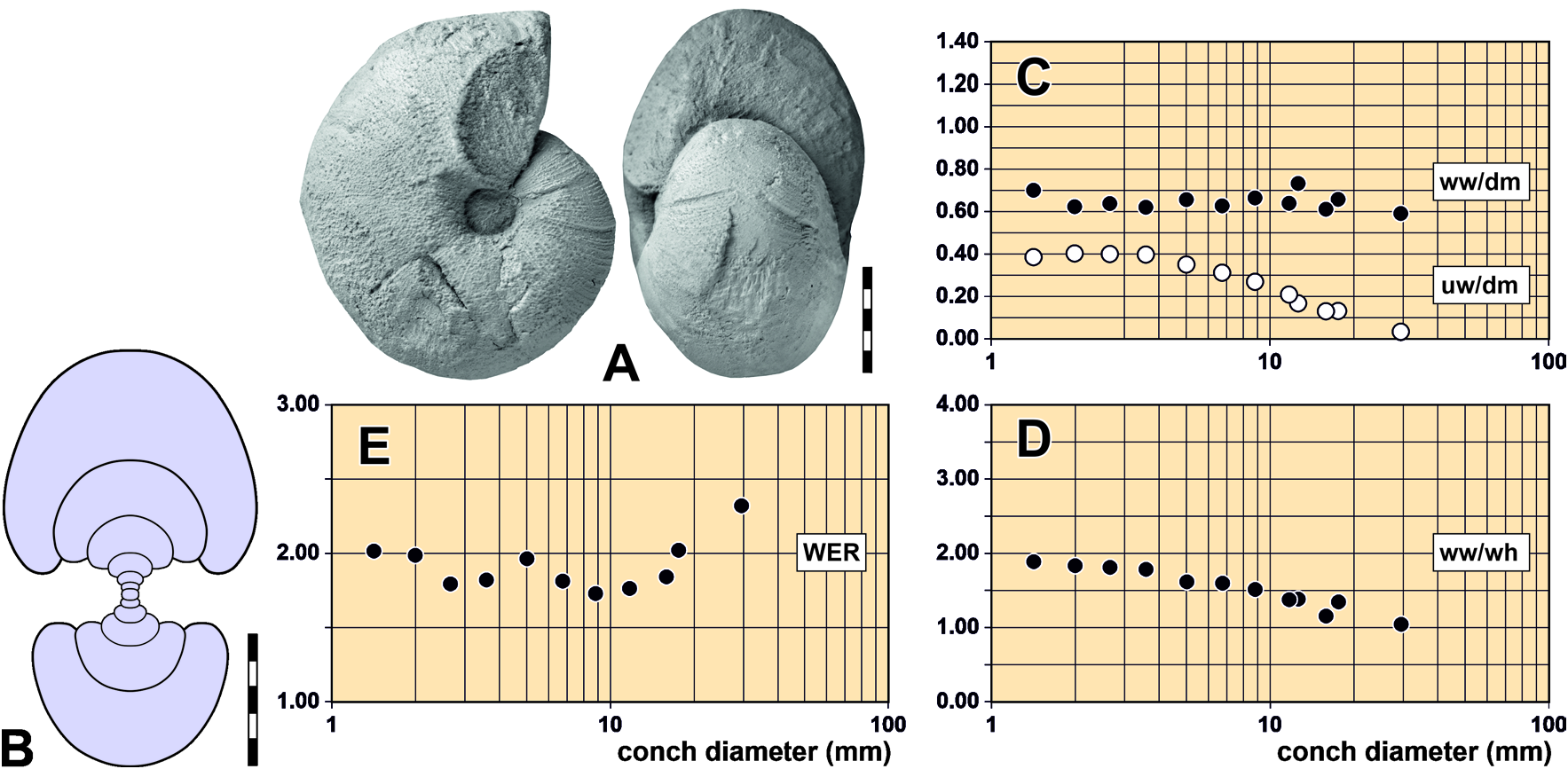
Fig. 36 View Fig ; Tables 30–31 View Table 30 View Table 31
Acutimitoceras procedens Korn, 1984: 80 , pl. 4 figs 24–25, text-fig. 5b.
Acutimitoceras procedens – Korn 1994: 47, text-figs 36b–c, 71f.
Acutimitoceras prorsum prorsum – Korn 1981: 519, text-figs 3a, 4a–d.
Diagnosis
Species of Stockumites with a conch reaching 40 mm diameter. Conch at 5 mm dm thinly pachyconic, subevolute (ww/dm ~0.65; uw/dm ~0.35); at 15 mm dm thinly pachyconic, involute (ww/dm ~0.65; uw/dm ~0.12); at 30 mm dm thickly discoidal, involute (ww/dm ~0.55; uw/dm ~0.00). Whorl profile at 30 mm dm weakly depressed (ww/wh ~1.05); coiling rate very high (WER ~2.35). Venter very broadly rounded, umbilical margin broadly rounded. Growth lines fine, with convex course in the middle growth stage and slightly biconvex course in the adult stage. Ornament with shallow constrictions on the shell surface; with coarse internal shell thickenings.
Material examined
Holotype
GERMANY • Müssenberg , trench 1; Hangenberg Limestone , bed 3c; Korn 1980 Coll.; illustrated by Korn (1984: pl. 4 fig. 24) and Korn (1994: text-fig. 36b); GZG.INV.131.
Paratypes
GERMANY • 1 specimen; Müssenberg, trench 1; Hangenberg Limestone, bed 3c; Korn 1980 Coll.; GZG.INV.132 • 3 specimens; same collection data as for preceding; SMF 43141 About SMF – SMF 43143 About SMF .
Additional material
GERMANY • 1 specimen; Rhenish Mountains , Oberrödinghausen, railway cutting; Hangenberg Limestone, bed 6b; Weyer 1993–1994 Coll.; MB.C.31088 .
Description
Holotype GZG.INV.131 is a very well preserved, complete specimen with 30 mm conch diameter. The conch is thickly discoidal (ww/dm = 0.58); it has a funnel-shaped umbilicus that is completely closed. The aperture is very high and leads to a coiling rate of WER = 2.34. The shell bears very fine, biconvex growth lines with only weakly developed lateral sinus. Four shell constrictions are developed at 90 degrees to each other, restricted to the venter and ventrolateral flank area.
The cross-section of the smaller paratype GZG.INV.132 has slightly wider whorls (ww/dm = 0.60) at 16 mm conch diameter. The umbilicus is still open at this stage (uw/dm = 0.12).
Specimen MB.C.31088 has a conch diameter of 17.5 mm ( Fig. 36A View Fig ) and shows the transition from the middle growth stage to the adult stage, which is characterised by a considerable increase in aperture height. The conch is thinly pachyconic with a slightly opened umbilicus (ww/dm = 0.66; uw/dm = 0.12) and a high coiling rate (WER = 2.02). The shell surface has initially rather coarse and lamellar but later fine growth lines, which extend with a convex arc across the flank and form a shallow subangular sinus on the venter. Weak shell constrictions extend parallel to the growth lines.
Remarks
Stockumites procedens can easily be distinguished from the other species of the genus by the very high coiling rate in the adult stage. With a value of about 2.35, it exceeds by far the rate (usually under 2.00) known from the other species. Another character to distinguish S. procedens from the other species of the genus is the development of shell constrictions, which extend across the venter with a subangular sinus.
| SMF |
Germany, Frankfurt-am-Main, Forschungsinstitut und Naturmuseum Senckenberg |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Stockumites procedens ( Korn, 1984 )
| Korn, Dieter & Weyer, Dieter 2023 |
Acutimitoceras procedens
| Korn D. 1994: 47 |
Acutimitoceras procedens
| Korn D. 1984: 80 |
Acutimitoceras prorsum prorsum
| Korn D. 1981: 519 |