Pontopolycope orientalis, Padhye & Kulkarni & Pagni & Rabet, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.6620/ZS.2020.59-13 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8055862 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03EE878F-FF96-4709-728A-732D7D42FCA3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Valdenar |
|
scientific name |
Pontopolycope orientalis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Pontopolycope orientalis View in CoL View at ENA sp. nov. Tanaka,
Kondo and Ohtsuka ( Figs. 2–6 View Fig View Fig View Fig View Fig View Fig ) urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:
Type series: Holotype: adult male (NSMT-Cr 27373), right valve length 0.42 mm, height 0.34 mm, left valve length 0.44 mm, height 0.34 mm, soft parts mounted on one glass slide and valves preserved in one cardboard cell slide. Paratypes: 2 adult males (dissected on one slide and valves on SEM stab, NSMT-Cr 27374, 27375), 3 adult males (dissected on one slide and valves preserved in one cardboard cell slide, NSMT-Cr 27376 to 27378), 1 adult female (dissected on one slide and valves on SEM stab, NSMT-Cr 27379), and 3 adult females (dissected on one slide and valves preserved in one cardboard cell slide, NSMT-Cr 27380 to 27382); same collecting data with holotype.
Type locality: The holotype specimen was collected from a sea bottom consisting of coarse coral sand grains off of Nagannu Island, Okinawa Prefecture, southwestern Japan ( 26°14.339'N, 127°32.280'E) at a depth of 52 m on May 21, 2016. GoogleMaps
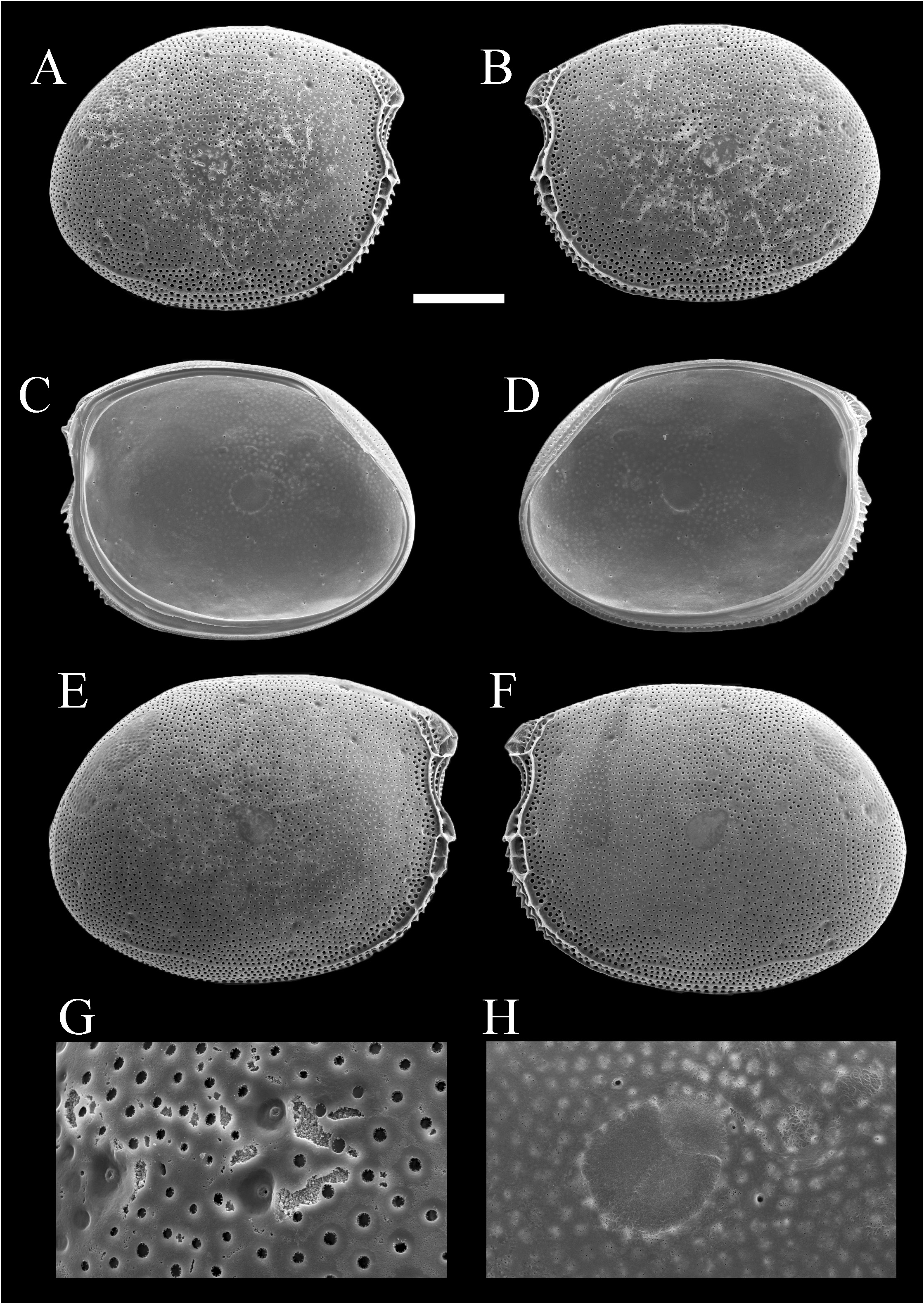
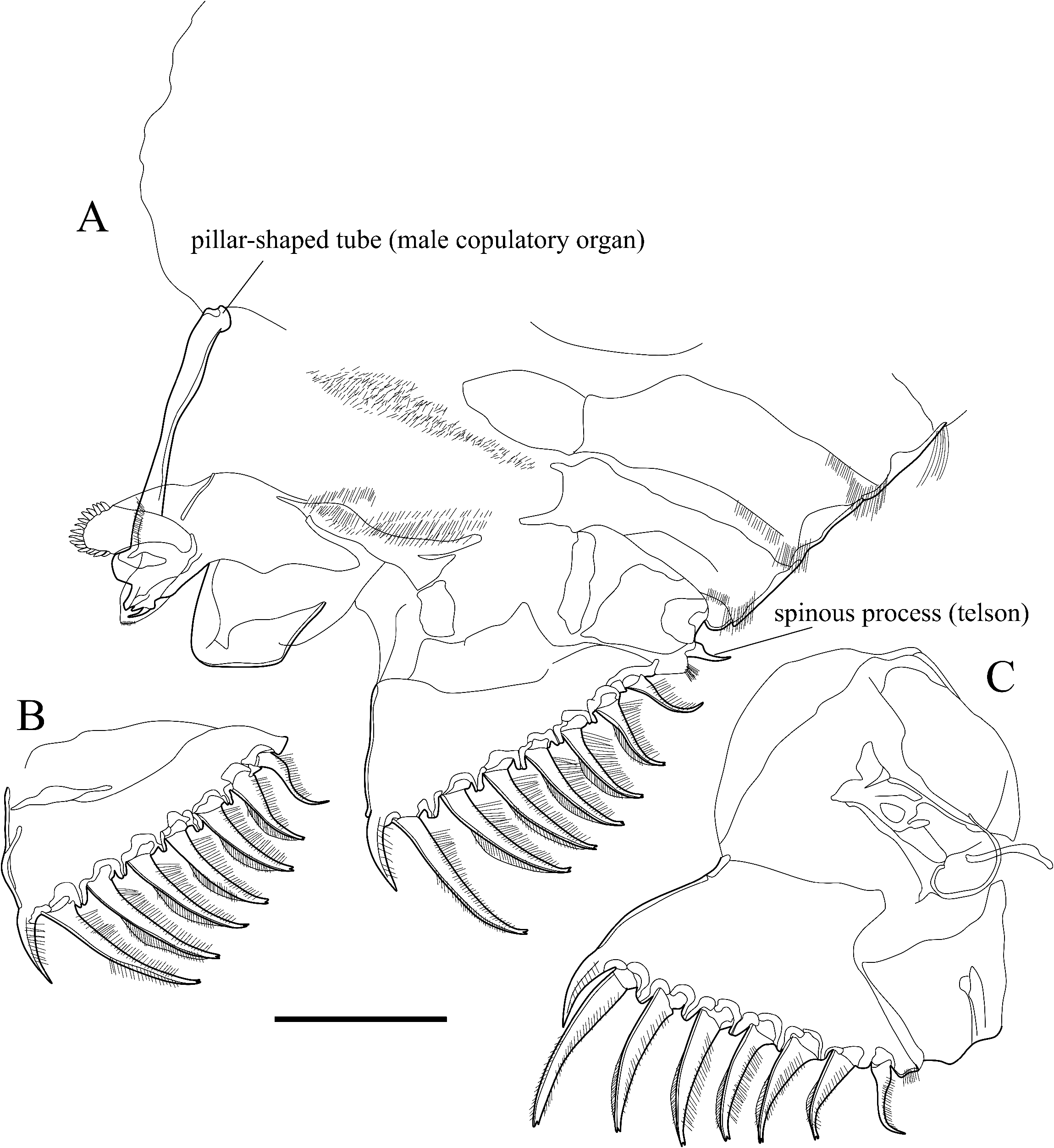
Diagnosis: Carapace circular in lateral view, with developed rostrum and concavity immediately ventral to rostrum of the anterior margin. Carapace surface covered with shallow pits. Carapace margin with serrations, along the anterior to posterior margin in left valve and anterior to ventral margin in right valve. Pore system consisting of shallow depression and a small dome with pore canal. Male copulatory organ consisting of a long pillar-shaped tube.
Description: (Measurements: Table 2 View Table 2 ). Adult male. ( Figs. 2A–D, G, H View Fig ; 3 View Fig ; 4E, F, H View Fig ; 5A–E View Fig ; 6A, B View Fig ).
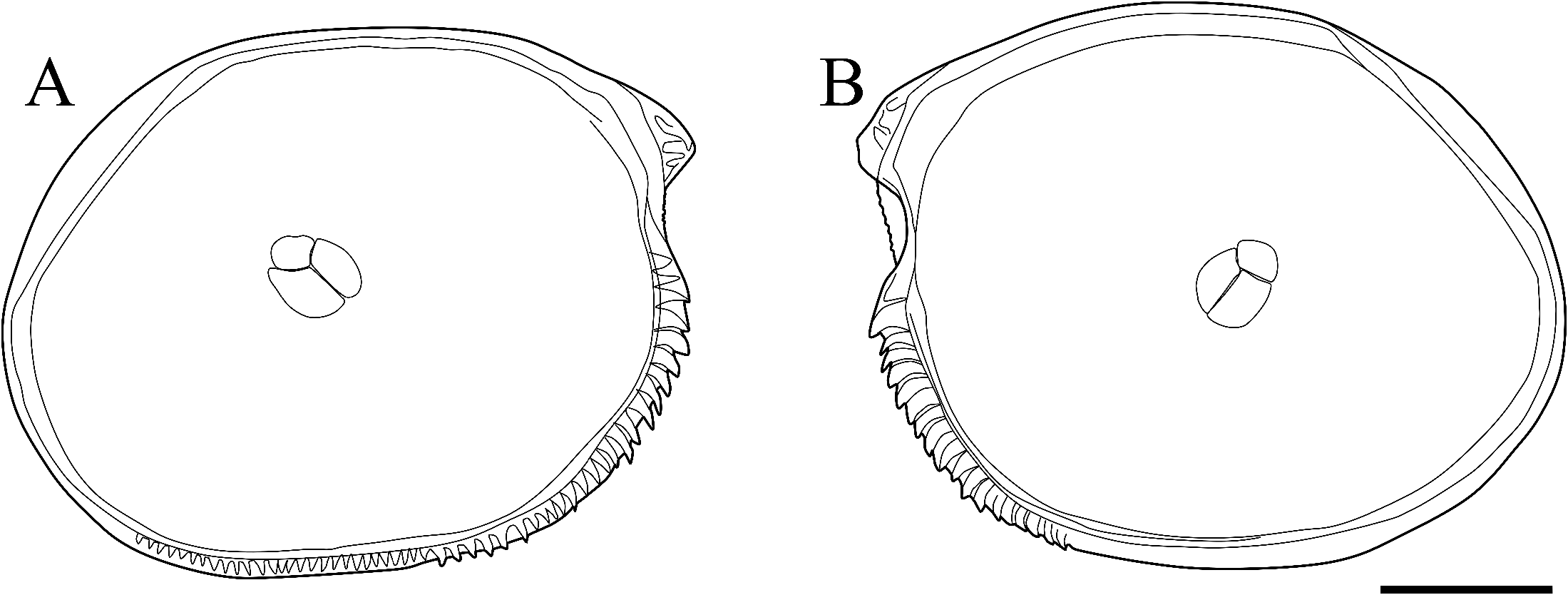
Carapace ( Figs. 2A–D, G, H View Fig ; 3 View Fig ): Circular in lateral view, with developed rostrum and concavity immediately ventral to the rostrum of anterior margin. Posterior end situated slightly near the ventral side. Surface covered with shallow pits ( Fig. 2A, B View Fig ). Along anterior to posterior margin in left valve and anterior to ventral margin in right valve with serrations ( Figs. 2C, D View Fig ; 3 View Fig ). Pore system consisting of a shallow depression and a small dome with pore canal ( Fig. 2G View Fig ). Adductor muscle scar consisting of three closely spaced scars ( Figs. 2C, D, H View Fig ; 3 View Fig ). Marginal infold with groove around internal marginal zone of postero-dorsal, anterior and ventral margins in right valve ( Fig. 2C View Fig ) and corresponding ridge in left valve ( Fig. 2D View Fig ). Hinge structure consisted of simple groove in right valve ( Fig. 2C View Fig ), and of corresponding bar in left valve ( Fig. 2D View Fig ).
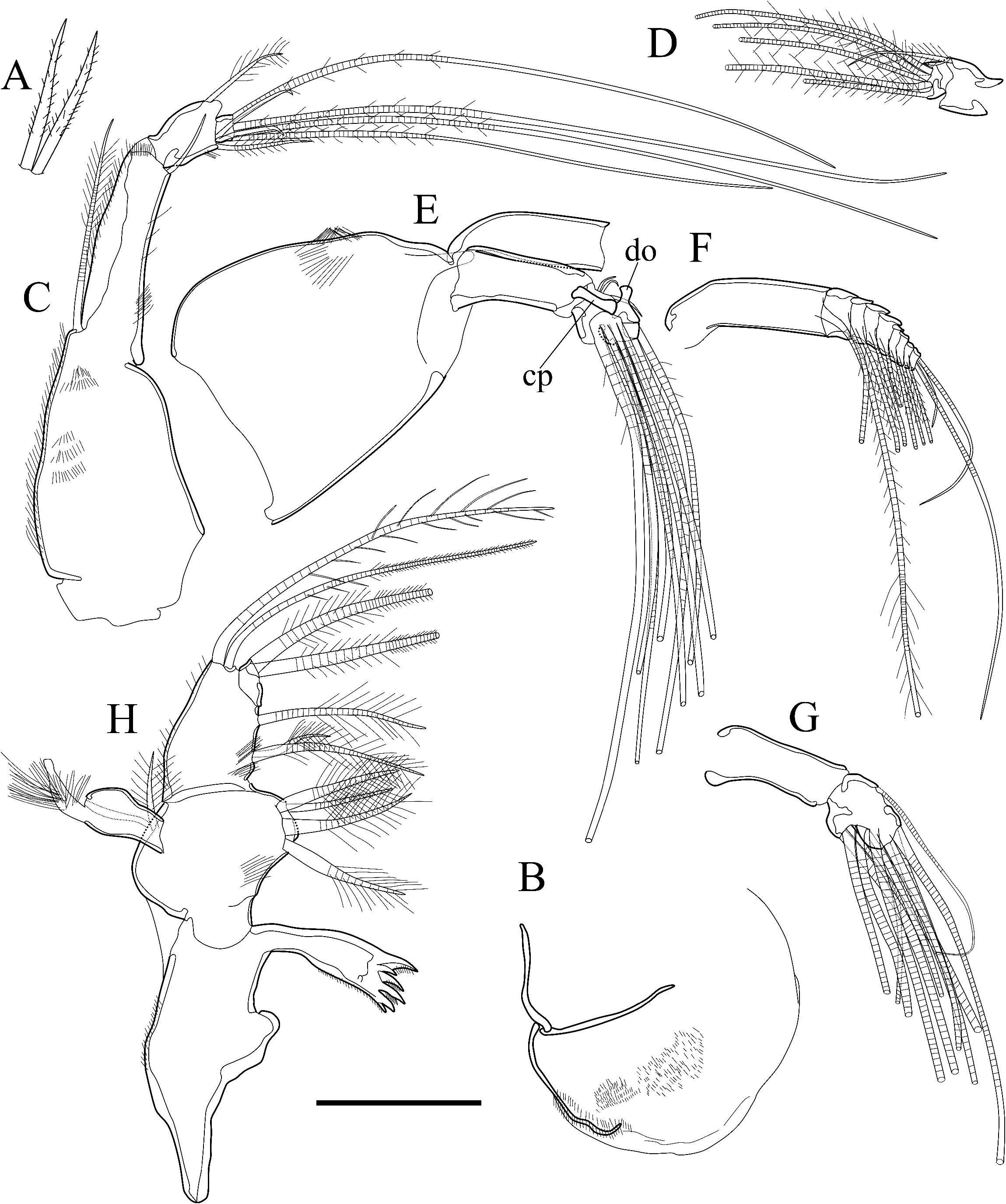
Bellonci organ ( Fig. 4A View Fig ): Two setulous seta.
Upper lip ( Fig. 4B View Fig ): Semicircular in lateral view, with fine setae on surface.
Antennula ( Fig. 4C View Fig ): Uniramous, four podomeres. First podomere with setulae on dorsal margin and lateral surface. Second podomere about four-fifths the length of first podomere, with one setulous annulated seta near dorso-proximal end, one simple seta on ventro-distal end, and setulae on dorsal and ventral middle margins and at dorso-distal end. Third podomere about one-fourth the length of first podomere, with one setulous seta at dorsal end and three setae consisting of one setulous annulated seta and two setae with curved tip on ventro-distal margin. Fourth podomere small, with four long setulous annulated setae.
Antenna ( Fig. 4E, F View Fig ): Biramous, with exopodite and endopodite consisting of nine and three podomeres, respectively. Basis triangular and tapering distally. Exopodite ( Fig. 4F View Fig ): first podomere about half lengths of basis; Second podomere about one-fifth the length of first podomere; podomere lengths decreasing in size from second to eighth, each podomere with one setulous annulated long seta, respectively; ninth podomere very small, with one long annulated, one medium annulated and one short simple setae at distal end. Endopodite ( Fig. 4E View Fig ): first podomere same length as first podomere of exopodite; second podomere about one-third the length of first podomere, with three simple setae along dorsal margin, one clavate process at proximal middle end, and five setulous annulated setae at distal end. Third podomere one-fifth the length of first podomere, with one dorsal outgrowth, and four setulous annulated setae at distal end.
Mandibula ( Fig. 4H View Fig ): Coxal endite with six teeth. Basis with four plumose annulated setae on ventral margin and one plumose seta at dorsal margin. Exopodite pear-shaped, with one thin broad setulous seta with blunt tip. Endopodite consisting of two podomeres. First podomere with three annulated plumose setae on ventral margin and two annulated setulous long setae at dorso-distal end. Second podomere very small, bearing two annulated plumose setae at distal end.
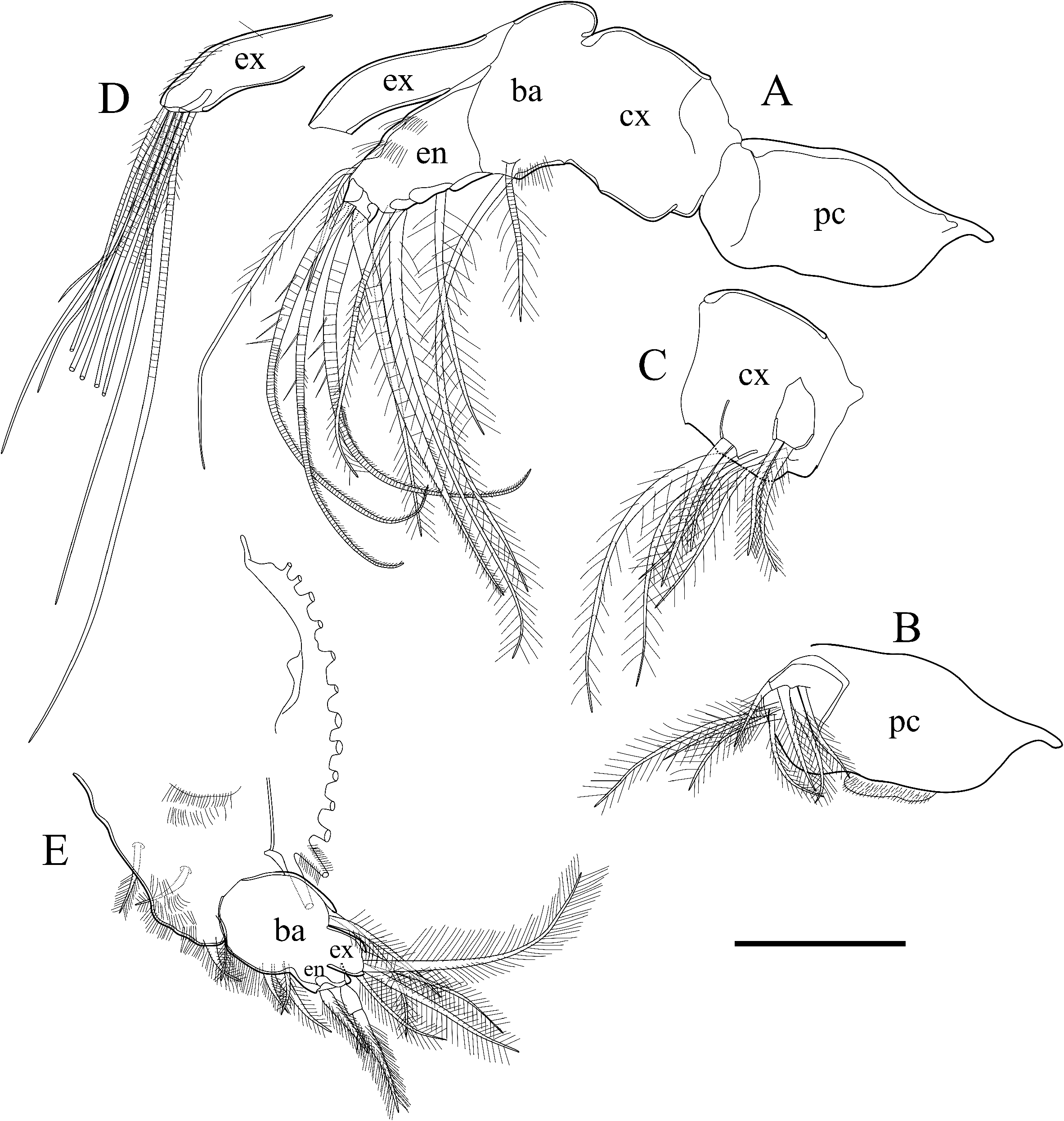
Maxillula ( Fig. 5A–D View Fig ): Precoxa ( Fig. 5A, B View Fig ) with eight annulated plumose setae. Coxa ( Fig. 5A, C View Fig ) with eight plumose setae on ventral side. Basis ( Fig. 5A View Fig ) rectangular with dorso-proximally hump in lateral view, with one plumose and one plumose annulated setae on ventral margin. First podomere of endopodite bare. Second podomere with one plumose seta on ventral margin. Third podomere with two setulous and one annulated setae at ventral margin, and two setulous setae at dorso-distal end. Fourth podomere with one setulous annulated seta, three annulated stout seta with spines on middle part and setulae on distal part. Exopodite ( Fig. 5D View Fig ) with setulae along dorsal margin, and 10 annulated setulous setae at distal end.
Fifth limb ( Fig. 5E View Fig ): Coxa bearing branchial plate (epipodite) with 13 long plumose setae, and two setulous short setae on dorso-lateral area and two setulous short setae at dorso-distal end. Basis with three setulous and two plumose setae on dorsal and ventral margin, respectively. Endopodite consisting of two podomeres. First podomere with one setulous stout seta. Second podomere cylindrical tapering proximally, with one setulous stout seta. Exopodite with four setulous setae.
Uropod ( Fig. 6A, B View Fig ): Each lamella with eight claws. Anterior-most claw small, with a row of fine setae on posterior margin. Anterior second to eighth claws with a row of setae on anterior and posterior margins, respectively.
Male copulatory organ and posterior body ( Fig. 6A View Fig ): Male copulatory organ arising from outer surface of body on left side of terminal trunk segment as a long pillar-shaped tube. A row of stout small setae on ventral margin. One spinous process (telson) at terminal end.
Adult female ( Figs. 2E, F View Fig ; 4D, G View Fig ; 6C View Fig ): Bellonci organ, mandibula, maxillula, fifth limbs, and upper lip similar to those of adult male.
Carapace ( Fig. 2E, F View Fig ): Carapace length and height slightly larger than adult male ( Table 2 View Table 2 ).
Antennula ( Fig. 4D View Fig ): Only third and fourth podomeres different from those of adult male. Third podomere about one-fourth the length of first podomere, with one setulous seta at dorsal end. Fourth podomere small, with five long setulous annulated setae.
Antenna ( Fig. 4G View Fig ): Only second and third podomeres of endopodite are different from those of adult male. Second podomere with one annulated seta on dorsal margin and six annulated setae at distal end. Third podomere one-sixth the length of first podomere with four annulated setae at distal end.
Uropod ( Fig. 6C View Fig ). Each lamella with eight claws.
DNA sequences: Three nucleotide sequences were obtained from the paratype (NSMT-Cr 27378): 28S (Accession no. LC528590 View Materials , 3217 bp), 18S (Accession no. LC528589 View Materials , 1794 bp), and CO1 (Accession no. LC528833 View Materials , 660 bp).
Etymology: The specific name orientalis (Latin, meaning in the east) refers to the first record of the living species of the genus Pontopolycope in the Indo-Pacific region.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |