Chloropepla, Stal, 1867
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1163/1876312X-04401002 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3665157 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03EFB13F-FFBD-FF92-FFCB-FBF66E75FAEB |
|
treatment provided by |
Tatiana |
|
scientific name |
Chloropepla |
| status |
|
Key to Chloropepla species
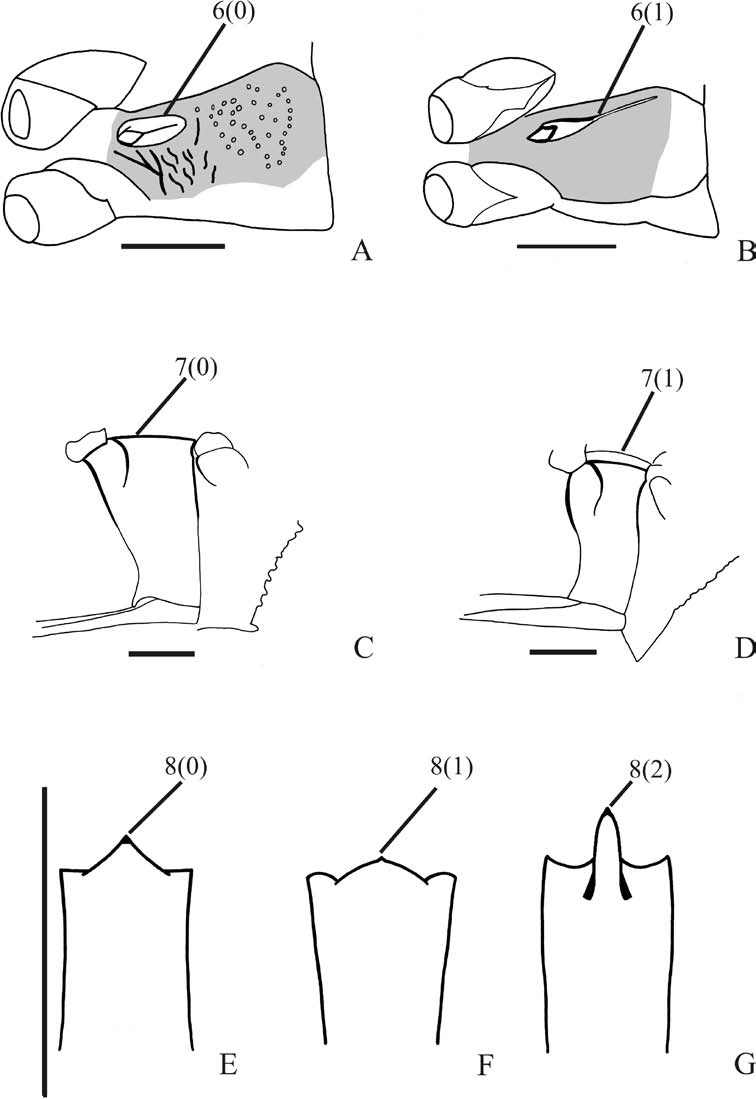
1 Humeral angles produced into spines ( Fig. 1C View Fig ) ................................................. 2
- Humeral angles acute but not produced into spines ( Fig. 1E View Fig )............................ 4
2 Humeral angles outlined in black ( Fig. 1D View Fig )....................................................... 3
- Humeral angles not outlined in black ( Fig. 1C, E View Fig ) .......................................... 12
3 Lateral margin of each jugum uniformly convex towards apex ( Fig. 1A View Fig ), bordered in black; dorsum of each tibia outlined in black ................ C. aurea ( Pirán, 1963)
- Lateral margins of juga sinuous ( Fig. 1B View Fig ), not bordered in black; dorsum of tibia not outlined in black .............................................. C. pirani Grazia-Vieira, 1971
4 Apices of femora with conspicuous spine ( Fig. 2G View Fig ) ........................................... 5
- Apices of femora with reduced spine ( Fig. 2F View Fig ) ................................................... 6
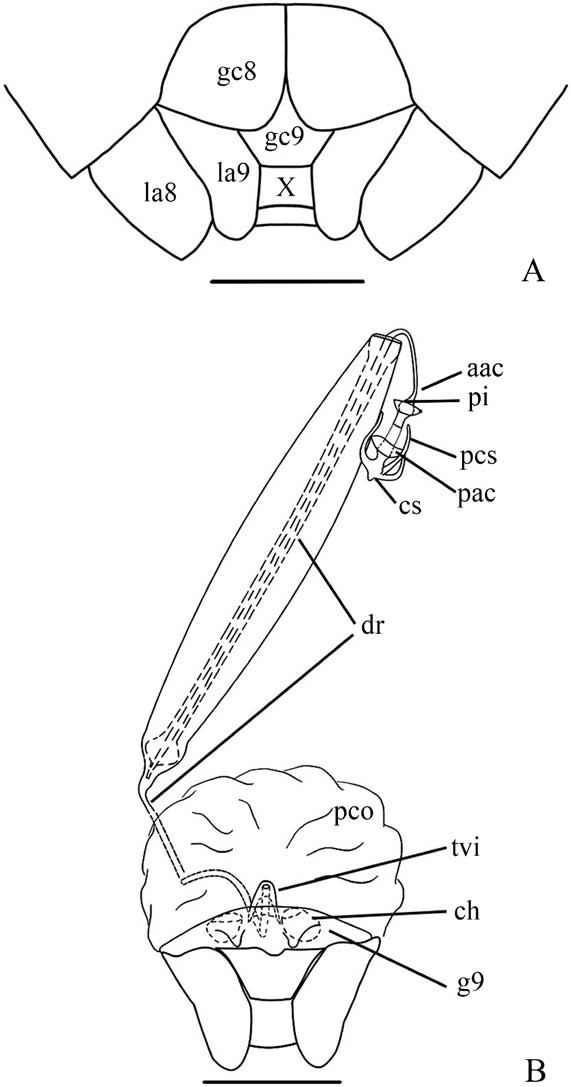
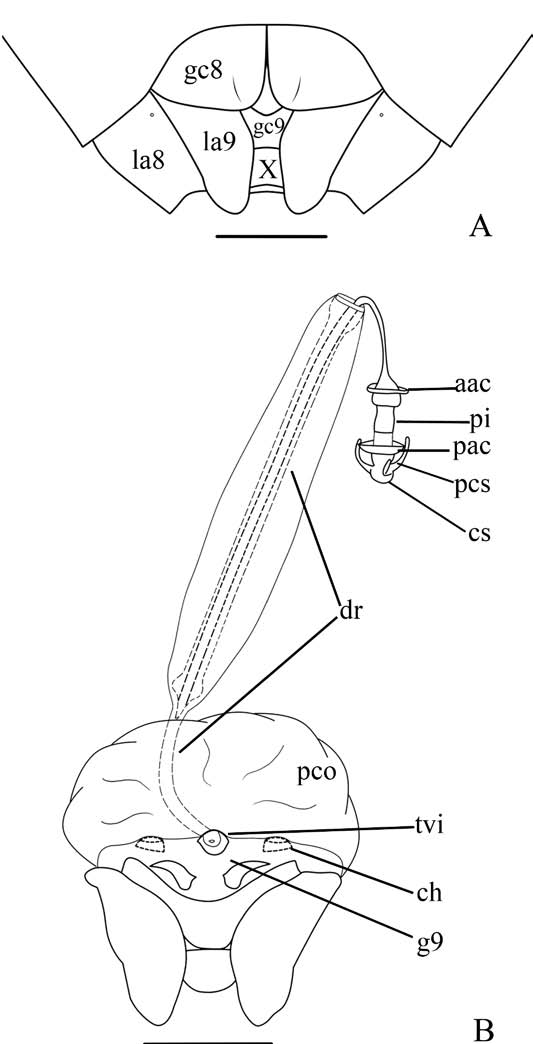
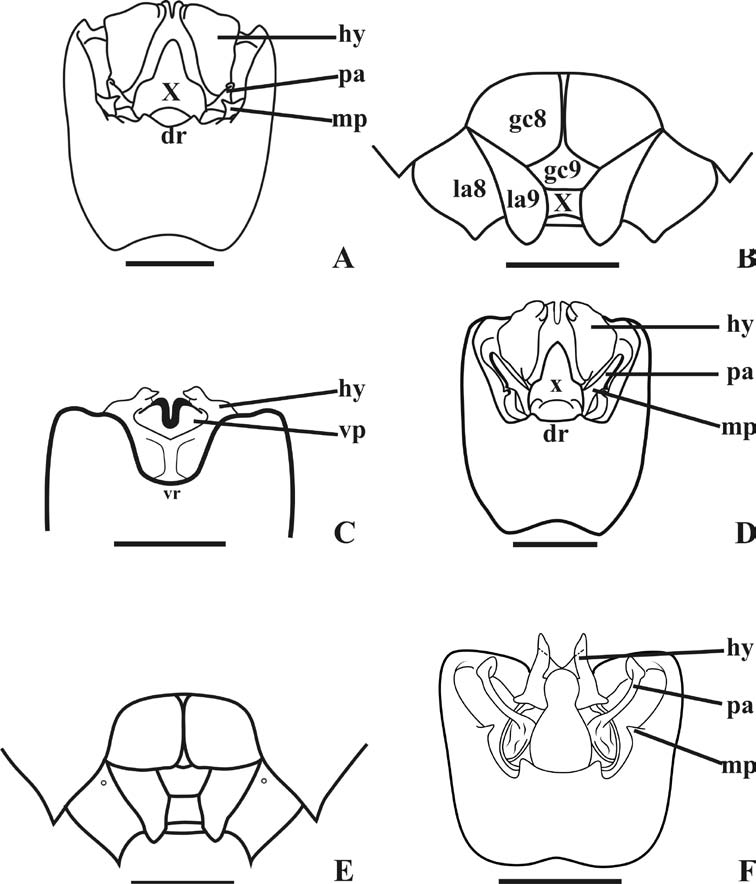
5 Hypandrium with 1+ 1 broad expansions flanking segment X, each expansion bearing an elongated outgrowth on dorsal surface ( Fig. 11A View Fig ); posterior margin of gonocoxites 9 straight ( Fig. 12A View Fig ) ...................................... Chloropepla rideri sp.n. - Hypandrium with 1 +1 narrow expansions flanking segment X, without outgrowth on dorsal surface ( Fig. 8A View Fig ); posterior margin of gonocoxites 9 convex ( Fig. 8B View Fig ).......................................... C. paveli Grazia, Schwertner & Greve, 2008
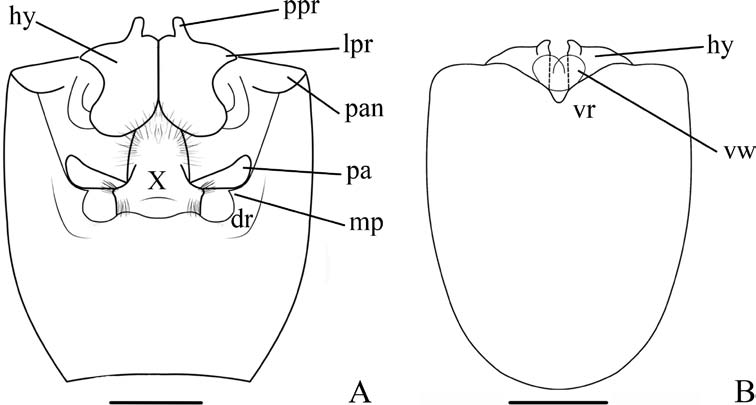
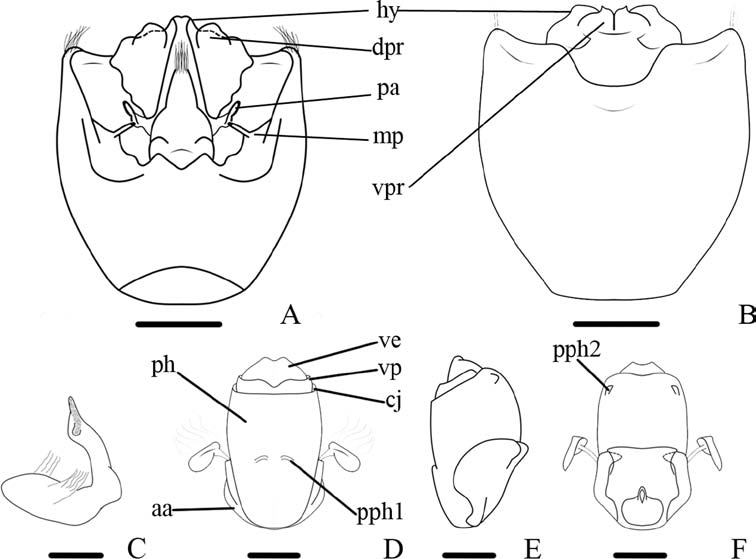
6 Medial excavation in ventral rim of pygophore “V”-shaped ( Fig. 4F View Fig ); marginal process of dorsal rim of pygophore triangular ( Fig. 4A, B View Fig ); gonocoxites 9 strongly convex, with lateral margins nearly parallel ( Fig. 16A View Fig ) ....................................... 7
- Medial excavation in ventral rim of pygophore “U”-shaped ( Fig. 4G View Fig ); marginal process of dorsal rim of pygophore digitiform ( Fig. 4C-E View Fig ), gonocoxites 9 slightly convex, with lateral margins convergent ............................................................ 8
7 Apex of hypandrium rounded, without process ( Fig. 8C View Fig ); apex of laterotergites 8 and 9 acute ( Fig. 8D View Fig ) .......................................................... C. lenti Grazia, 1968
- Apex of hypandrium with 1+1 narrow, rectangular process ( Fig. 15A View Fig ); apex of laterotergites 8 and 9 obtuse ( Fig. 16A View Fig ) ................................. C. costaricensis sp.n.
8 Humeral angles outlined in black ...................................................................... 9
- Humeral angles not outlined in black.............................................................. 10
9 Dorsal expansions of hypandrium broad, with 1 +1 laminar processes with quadrangular form along dorsal surface, near apex ( Fig. 17A View Fig ) ...... C. caxiuanensis sp.n.
- Dorsal expansion of hypandrium narrow. Without process on dorsal surface ( Fig. 4E View Fig )............................................................... C. rolstoni Grazia-Vieira, 1973
10 Ventral process of hypandrium digitiform ( Fig. 8F View Fig )........ C. dollingi Grazia, 1987
- Ventral process of hypandrium bilobate ( Fig. 8G View Fig ) ........................................... 11
11 Ventral surface of hypandrium mesially bearing 1+ 1 laminar process, oblique to the longitudinal axes of the hypandrium ( Fig. 8G View Fig ); parameres short, not reaching the margin of pygophore ( Fig. 9A View Fig ); posterior margin of gonocoxites 8 strongly angulate ( Fig. 9B View Fig ).................................. C. tucuruiensis Grazia & Teradaira, 1980
- Ventral surface of hypandrium without mesially process ( Fig. 9C View Fig ); parameres long, almost surpassing the margin of pygophore ( Fig. 9D View Fig ); posterior margin of gonocoxites 8 slightly convex.............. C. stysi Grazia, Schwertner & Greve, 2008
12 Width at base of gonocoxites 9 almost 2.5 times the width at apex; laterotergites 8 with triangular apices ( Fig. 14A View Fig ); males unknown ............................................ .......................................................................... C. luteipennis ( Westwood, 1837)
- Width at base of gonocoxites 9 nearly two times the width at apex; laterotergites 8 strongly acute at apices, almost spine like ( Fig. 9E View Fig ); pygophore strongly excavated dorsally, reducing the dorsal wall of pygophore to nearly half of the total length of pygophore; parameres long, surpassing segment Xin length ( Fig. 9F View Fig ) ................. ............................................................................................ C. vigens ( Stål, 1860)
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.