Siphonolaimus japonicus, Julia, Zograf, Yulia, Trebukhova & Olga, Pavlyuk, 2015
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3911.1.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:1F69EB9B-62F6-4D27-B773-749F292E4A05 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5628417 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F1A458-FFEB-7C7E-FF4D-F953B7B3FEE9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Siphonolaimus japonicus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Siphonolaimus japonicus sp. n.
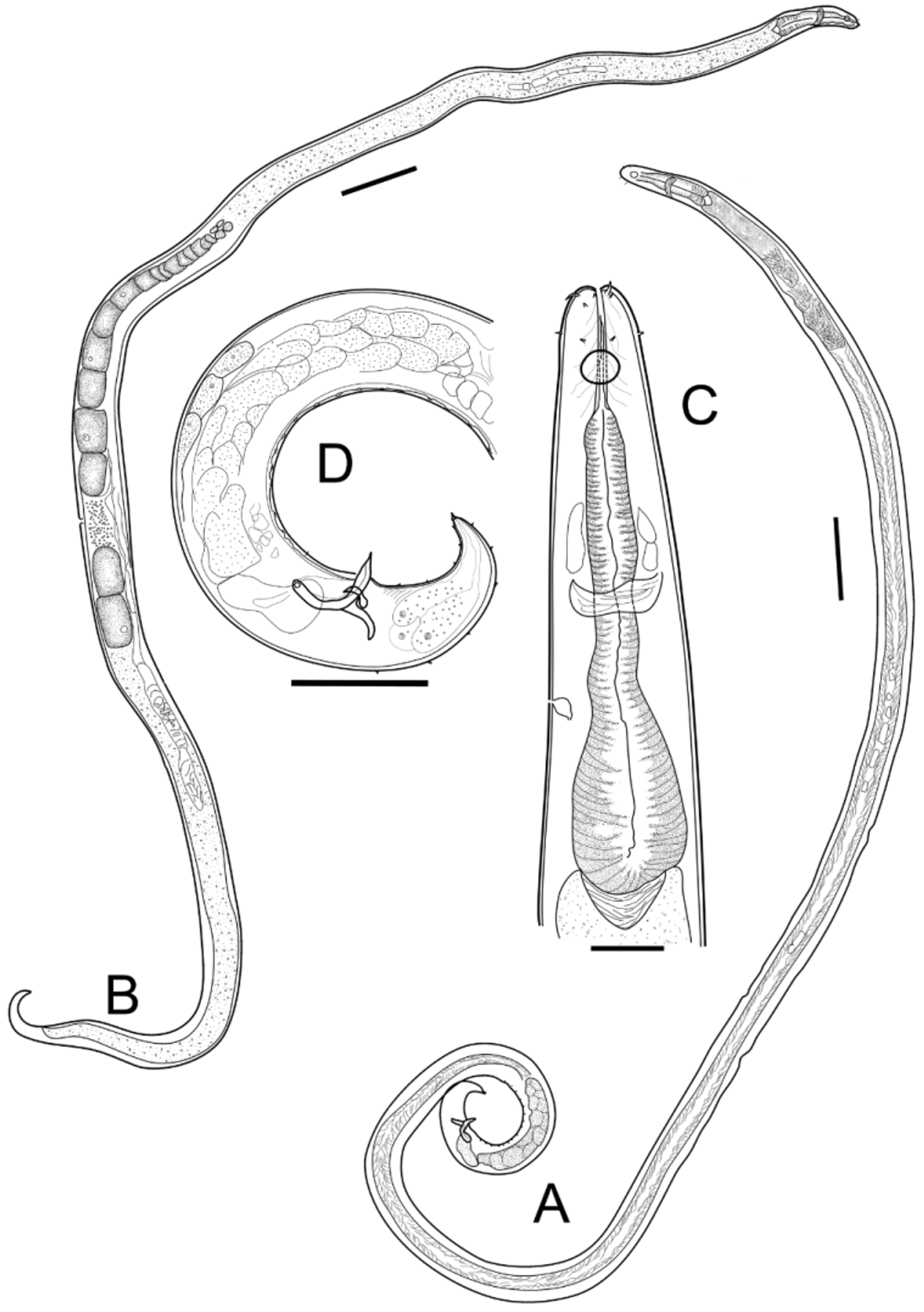
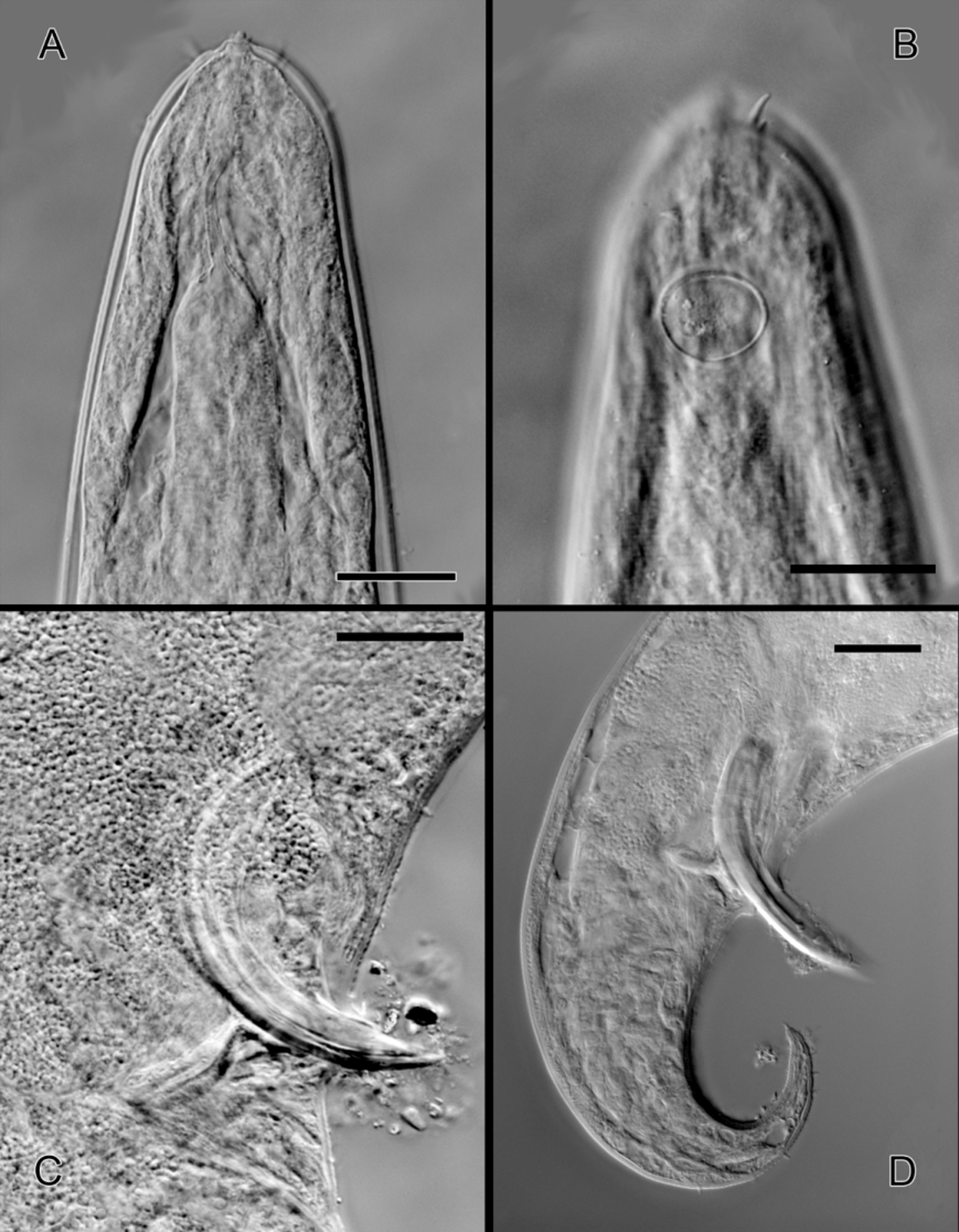
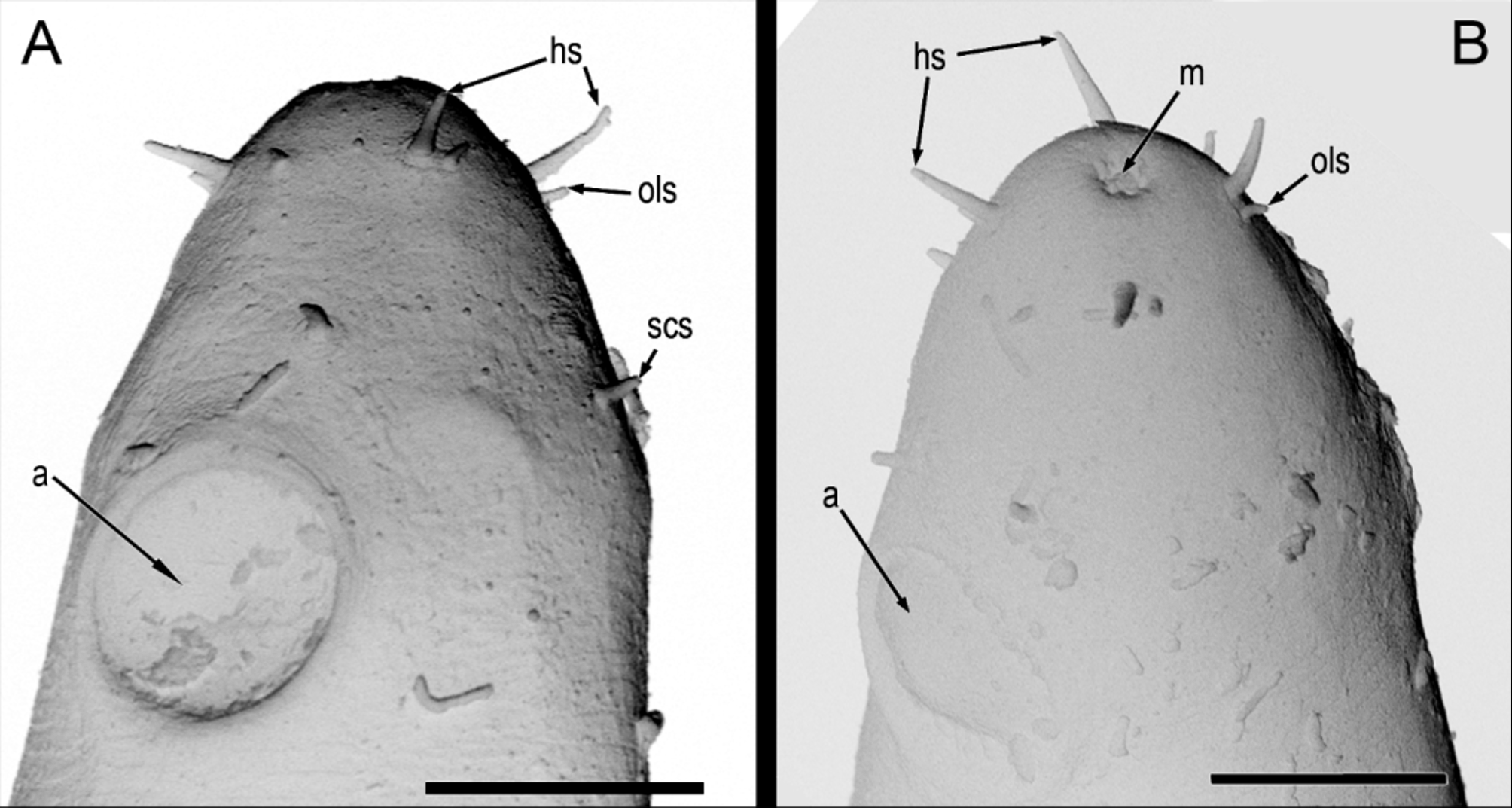
( Figs 2–4 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 )
Measurements. Table 1.
Material examined. Holotype male: deep-sea (the Sea of Japan), from 3358 m sampled with box-corer, found in silt-clay, 0–5 cm profile, collected by Trebukhova Yu.A. on August, 17th 2010. Slide is kept in Museum of A.V. Zhirmunsky Institute of Marine Biology, Vladivostok, Russia (N MIMB 28871).
Paratypes: five females and seven males ( MIMB 28872, MIMB 28873 and MIMB 28874): same collection data.
Siphonolaimus japonicus sp. n. Halichoanolaimus brandtae sp. n.
gender ♂ ♂ ♀ ♂ ♂ ♀ hοlοtype hοlοtype
54.9 49.5 ± 4.1 34 ± 2.84 14.8 17.1 ± 1.4 12.6 ± 2.3 (44.9-54.9) (31.7-37.9) (14.8-18.5) (11-14.2) 18.7 19.6 ± 0.6 19,2 ± 1,3 6.5 6.3 ± 0.2 6.7 ± 0.5 (18.7-20.2) (17.5-20.6) (5.9-8.8) (6.3-7.1) 33.4 31.1 ± 1.7 26.1 ± 3.4 7.5 7.9 ± 0.5 6.5 ± 0.03 (29.4-33.4) (20.8-29.3) (7.5-8.8) (6.4-6.5) 2.2 2.2 ± 0.1 4.4 ± 0.7 4.8 4.1 ± 0.5 3.9 ± 0.1 (2-2.3) (3.3-5.3) (3.6-4.8) (3.8-3.9) 4192.2 4181.4 ± 146.3 4217.3 ± 352.5 1673.8 1617 ± 48.3 1718.8 ± 120.3 (4038.9-4394.7) (3671-4520) (1552.3-1673.8) (1633.7-1803.9) 125.5 134.8 ± 9.7 (125.5-148.8) 162.9 ± 14.9 224.1 205.1 ± 17.1 265.7 ± 20.2 (148-182) (181.6-224.1) (251.4-280) 76.4 84.7 ± 5.3 128.2 ± 7.4 112.9 95.6 ± 10.1 137.9 ± 15.4 (76.4-90.3) (119.11-137.2) (88.3-112.9) (127-148.7) 31.9 31 ± 3 29.7 ± 2.6 57.1 50.9 ± 3.9 59 ± 3.4 (26.4-33.5) (26.81-33.73) (46.5-57.1) (56.6-61.4)
amph D 13.1x16.6 13.1 ± 0.8 x 14.6 ± 1.2 13.3 ± 1.1 x 12.2 ± 0.5 20.33x16.28 19.26 ± 0.7 x 14.1 ± 1.4 19.2 ± 0.02 x 12.5 ± 1.7
hd, % 40.9 42.7 ± 6.1 (39-53.5) 41.3 ± 4.3 (35.5-45.5) 35.6 37.8 ± 1.9 32.5 ± 1.2 (35.9-39.9) (31.3-33.9)
.b.e. 22.5 23.8 ± 1.6 26.7 ± 2.7 15.8 13.9 ± 1.5 11.2 ± 2.7 (22-25.5) (24.5-31.3) (11.9-15.8) (9.3-13.1)
.d. 56.8 62.4 ± 5.3 37.9 ± 5.4 47.1 49.8 ± 1.7 68.4 ± 7.3 (56.8-71) (34-46.7) (47.1-51.7) (63.3-73.6) 2.2 2.3 ± 0.4 2 ± 0.4 3.6 3.1 ± 0.6 6.78 (2-3) (1.4-2.6) (2.34-3.6)
5.4 5.2 ± 0.5 5.1 ± 0.3 1.85 3.37 (4.7-5.9) (4.8-5.5)
.b.e. 132.6 136.1 ± 2.9 (132.9-138.4) 137.4 ± 13.4 131.8 133.2 ± 4.6 118.8 ± 15.1 (119.8-151.2) (128.6-139) (108.1-129.5) 40.8 38.1 ± 3.7 38.4 ± 6.1
(32-40.6) (29.7-46.1)
......continued on the next page Siphonolaimus japonicus sp.n. Halichoanolaimus brandtae sp.n.
gender ♂ ♂ ♀ ♂ ♂ ♀
hοlοtype hοlοtype
BCH 32.3 41.2 ± 5.3 43.1 ± 8.3
(32.4-46.1) (37.2-49)
99.6 101.7 ± 11.7 (86.7-119.4) 94.3 ± 6.5 114.5 107 ± 5.3 118.7 ± 33.9
(88.7-101.5) (102.7-114.5) (94.7-142.7) L 224.7 213.4 ± 9 219.6 ± 8.1 258.8 256.4 ± 3.5 256.8 ± 1.5
(201.2-224.7) (209.8-230.1) (251.6-260.5) (255.7-257.9) e.b.d. 73.4 70.3 ± 3 74.1 ± 4.4 112.9 95.6 ± 10.1 119.4 ± 14.4
(66.9-73.4) (67.9-79.3) (88.3-112.9) (109.2-129.6)
spic 74.2 72.2 ± 4.1 92.1 81.8 ± 6.9
(65.6-76) (74.2-92.1)
1.3 1.2 ± 0.1 1.9 1.6 ± 0.2
(1-1.3) (1.5-1.9)
L 25.1 26.8 ± 3.2 53.3 47.9 ± 4.1
(23.8-31.1) (42.6-53.3)
128.8 ± 7.1 x 100.37 ± 4.2 85.01 x 81.97
2965.8 ± 295.9 854.9 ± 72.9
(2539.5-3285.7) (806.3-909.5) % 70.3±2.2 49.9 ± 0.8
(68.3-74) (49.4-50.4) AGL 2059.3 100.8 138.6 ± 26.9 132.9 ± 13.9
(100.8-161.4) (123-142.7) PGL 212.7 156.1 ± 65.6 124.4 ± 24.7
(99.6-212.7) (107-141.9)
456.2 437.7 ± 81.8 48 51.4 ± 2.7
(379.9-495.6) (47.3-54.7)
Description. Adult males: Body long, cylindrical, tapered to both extremities, 4181±146 Μm long, head diameter 11–12 Μm and 15% of diameter at the posterior end of pharynx.
Cuticle finely striated, striation not visible under light microscope. Head rounded. Anterior sensillae arranged in three separated circles: six inner labial papillae (difficult to observe), six outer labial setae (2.2 Μm long) and four cephalic setae (5 Μm long or 45% of head diameter). Sub-cephalic setae 3 Μm long, positioned slightly anterior to the amphid.
Amphids circular, 13–14 Μm diameter or 40–42% of corresponding body diameter, 22–26 Μm from anterior body end. Buccal cavity with cuticularized axial spear, 38–40 Μm or 16–17% of pharynx length. Pharynx 201–230 Μm long, muscular, slightly narrowed at the level of nerve ring; posterior end forming an elongated bulbus. Cardia present, small. Nerve ring at 86–119 Μm from anterior body end or 44% of the pharynx. Renette cell posterior to the cardia. Secretory-excretory pore visible, 132–138 Μm or 59% of pharynx length from anterior end. Intestine filled with small opaque black granules. Nerve ring at 47% of the total pharynx length from anterior end. Single outstretched anterior testis to the left of intestine. Spicules paired, curved, 1.3 anal diameters in length. Long gubernaculum with dorso-caudal apophysis. Fifteen small tubular supplements, supplementary field 437 µm long. Tail length 12% of total body length. Tail conical. Seven to nine short setae in the tail region. Three caudal glands.
Adult female: Similar to male. Single anterior outstretched ovary. Vulva at 70% from the anterior end. Two fertilized eggs in uterus. Females index c’ twice that of male (4.4 vs 2.2).
Juvenile. Not found.
Diagnosis and relationships. Siphonolaimus japonicus sp. n. is mainly characterized by the short anterior sensillae, long body (3670–4500 Μm), buccal cavity with axial spear, and length of the spicules. It differs from all other congeneneric species by the number of supplements (fifteen) and diameter of amphid (40-42% of correcponding body diameter).
Siphonolaimus japonicus sp. n. is similar to S. smetti Chen & Wincx, 2000 and S. auratus Wieser, 1956 but differs in morphometrics ( Table 2 View TABLE 2 ). The new species is distinguished from S. smetti by the short anterior sensilla and subcephalic setae (2.2, 5.4 and 3.3 µm vs 1–2, 6 and 7 µm) and longer spicules (72 µm vs 55 µm). It is twice the length of S. smetti (4200 µm vs 2200 µm) and index c is bigger than that in S. smetti (33 vs 21). Siphonolaimus japonicus sp. n. differs from S. auratus by the shorter anterior sensillae (2.2, 5.4 and 3.3 µm vs 3, 12, and 9 µm) and longer spicules (72 µm vs 62 µm). The amphid of S. japonicus sp. n. is smaller than that of S. auratus (13 µm vs 17 µm or 41% c.b.d. vs 50% c.b.d.). From both species, S. japonicus sp. n. differs by the number of supplements (15 in S. japonicus n. sp., 5–8 in S. smetti and 26–30 in S. auratus ).
Etymology. The species name refers to the locality where it was found (The Sea of Japan).
Remarks. We consider the genus to have twenty one valid species (including the new species). There are five species inquirendae.
Siphonolaimus pachyderma Wieser, 1954 , Siphonolaimus elongatus (= Southernia elongata ) ( Schuurmans Stekhoven, 1950), and Siphonolaimus tenius Steiner, 1922 known from juveniles we regarded as species inquirenda. Siphonolaimus anticomoides ( Allgen, 1933) (= Chromagaster anticomoides Allgen, 1933 ) known from one female we regarded as species inquirenda. Siphonolaimus falklandiae Allgen, 1959 is described from two strongly wound males and must be considered a species inquirenda (Pastor de Ward, 1989). Siphonolaimus granulatus ( Allgen, 1929) was transferred back to genus Spirina (Wieser, 1954) . Siphonolaimus pellucidus Allgen 1932 is doubtful species that has been referred as Araeolaimus s. str. by Chitwood (1936) and later considered as Southerniella by Wieser (1956).
TABLE 2. Morphometric features (in Μm unless dimensionless) of Siphonolaimus japonicus sp. n. compared with S. smetti Chen & Vinx, 2000 and S. auratus Wieser, 1956.
| Measurements | S. japonicus sp. n. | S. smetti Chen & Vinx, 2000 S. auratus Wierser, 1956 |
|---|---|---|
| SL | 49.5 | 40–45 35–40 |
| amph D | 13.1 | 12–13 17 |
| spic | 72.2 | 54–55 62 |
| s’ | 1.2 | 1.4–1.6 1.5 |
| gub L | 26.8 | 24–29 22.5 |
| N sup | 15 | 5–8 26–30 |
| OLS | 2.3 | 1–2 3 |
| CSL | 5.2 | 6–7 12 |
| BL | 4181 | 2400 3400 |
| a | 49.5 | 52.5 57 |
| b | 19.6 | 12.7 18 |
| c | 31.1 | 20.8 28 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Siphonolaimus japonicus
| Julia, Zograf, Yulia, Trebukhova & Olga, Pavlyuk 2015 |
S. smetti
| Chen & Wincx 2000 |
Siphonolaimus falklandiae
| Allgen 1959 |
S. auratus
| Wieser 1956 |
Siphonolaimus pachyderma
| Wieser 1954 |
Spirina
| Wieser 1954 |
Siphonolaimus anticomoides (
| Allgen 1933 |
Chromagaster anticomoides
| Allgen 1933 |
Siphonolaimus pellucidus
| Allgen 1932 |
Siphonolaimus granulatus (
| Allgen 1929 |
Siphonolaimus tenius
| Steiner 1922 |