Glyphidops (Glyphidops) filosus ( Fabricius, 1805 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11606/1807-0205/2020.60.19 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F98782-FFC8-FFF7-FFEF-FDF17F03FB80 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Glyphidops (Glyphidops) filosus ( Fabricius, 1805 ) |
| status |
|
Glyphidops (Glyphidops) filosus ( Fabricius, 1805) View in CoL
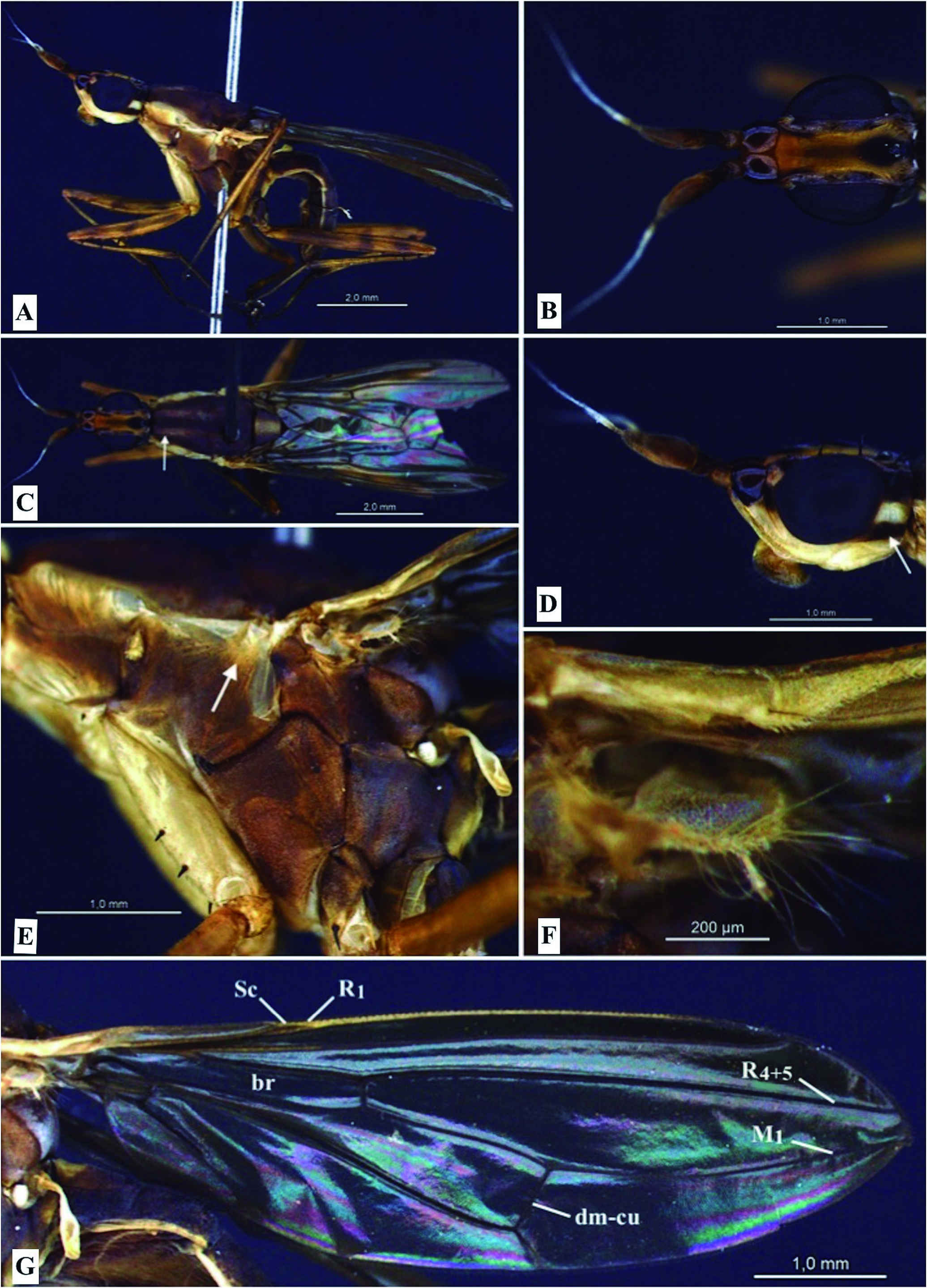
Male: Body length 8,0- 9,6 mm ( Fig. 2A View Figure 2 ). Head elongated sideways, length varying between 1,5-1,7 mm ( Fig. 2B View Figure 2 ). Ocellar triangle slightly prominent, surrounded by black oval spot at the frontal vitta posterior portion. Frontal vitta yellowish, narrow and long with longitudinal central concavity. Fronto-orbital plate brownish and with 3-4 setae, when present, the fourth seta is significantly lower than the others. Outer vertical seta divergent, inner vertical seta convergent and postocellar seta strongly convergent. Head in lateral view with one brownish stripe at the posterior portion, length 0,4-0,6 mm and width 0,1-0,2 mm ( Fig.2D View Figure 2 ).Strong genal seta.Postgena with setulae. Antennal base shiny brown with length 0,3-0,4 mm and width 0,2-0,3 mm. Scape brown with yellowish base, length 0,2-0,3 mm and width 0,1-0,2 mm, with setulae at the anterior portion. Pedicel dark brownish with inner process yellowish, length 0,4-0,6 mm and setulae all around the structure. First flagellomere lanceolate, yellowish at the posterior portion and brownish at the middle-anterior region, length 0,4-0,6 mm, covered with setulae. Arista yellowish at the posterior region, with white pubescence along the structure, length 1,1-1,5 mm.
Thorax: Pronotum and mesonotum with two lighter brownish longitudinal stripes separated by one darker medial stripe, which has the same color of the thorax ( Fig. 2C View Figure 2 ). Anterior notopleural seta absent and posteri- or seta present. Supra-alar seta absent and postalar seta present. Scutellum wider at the anterior portion and thinner distally, with one wide yellow longitudinal stripe. Proepisternum with lighter color than the pleura, with short anteroventral seta. Anepisternum dorsally lighter than the pleura ( Fig. 2E View Figure 2 ). Katerpisternum with 1-2 setae.
Legs: Fore coxa yellowish with three setae,in frontal view two lateral and one distal near the trochanter. Fore femur with 8-14 spines at the ventral portion. Mid coxa with brownish color and two lateral setae. Mid femur with 2-3 lateral spines at the anterior portion and six distal spines at the ventral portion. Hind coxa with two lateral setae, femur with 5-6 spines at ventral portion. Femora with yellowish-brown coloration and subtle brownish stripes. Tibia with a pair of distal spurs.
Wing: Length 6,1-7,0 mm. Basicosta with small seta at the apex. Sc and R₁ veins very close to each other, with slight bifurcation near the costal vein. R₄₊₅ and M₁ are convergent. The br cell is open in the wing basal portion and dm-cu vein is lightly concave. Fringe of yellowish setae on the calyptra edge ( Fig. 2F View Figure 2 ). Dorsal portion with slightly darkened coloration ( Fig. 2G View Figure 2 ). Halter whitish-yellow.
Abdomen: Tergites usually with dark brownish coloration, yellowish just in some specimens. Sternites yel- lowish.Tergite I-V covered with a thin layer of small black setulae, tergite VI and epandrium with longer apical setae. Epandrium shiny with brownish coloration and paler than the rest of the abdomen.
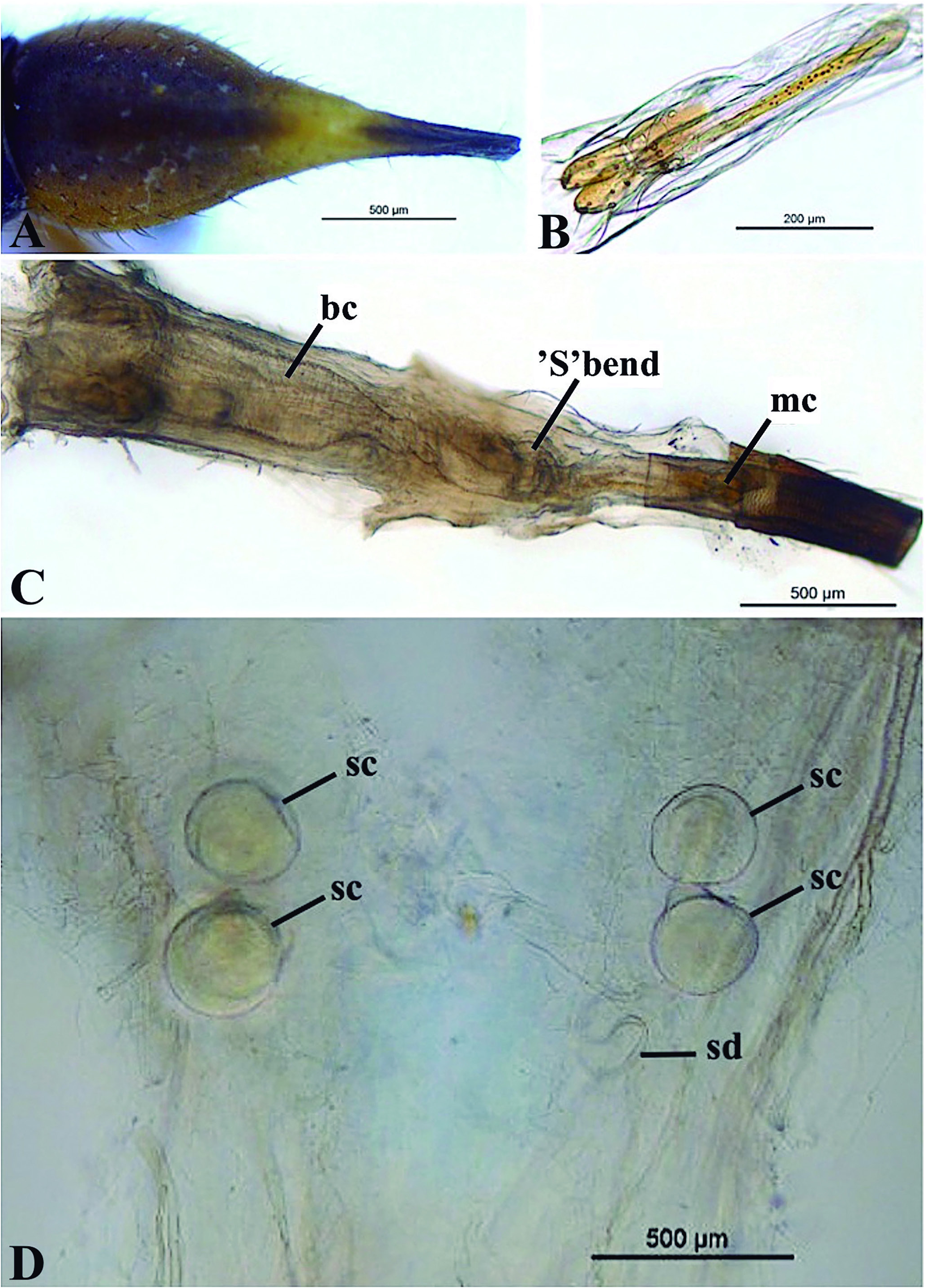
Female: Similar to male, except: length 7,4-9,1 mm. Postocellar seta convergent or parallel in some specimens. Scutellum with thin yellow longitudinal stripe and with stronger coloration. Katepisternum without seta. Fore coxa with one distal seta near the trochanter. Mid femur with three lateral setae at the anterior portion and 6-7 distal spines at the ventral portion. Hind femur with 8-9 spines at the ventral portion. Ventral portion of the abdomen with coloration like the dorsal portion.Tergites I-V with few setae. Oviscape dorsally darkish-brown and ventrally yellowish, with short and sparse setulae along the structure ( Fig. 5A View Figure 5 ).
Male and female terminalia
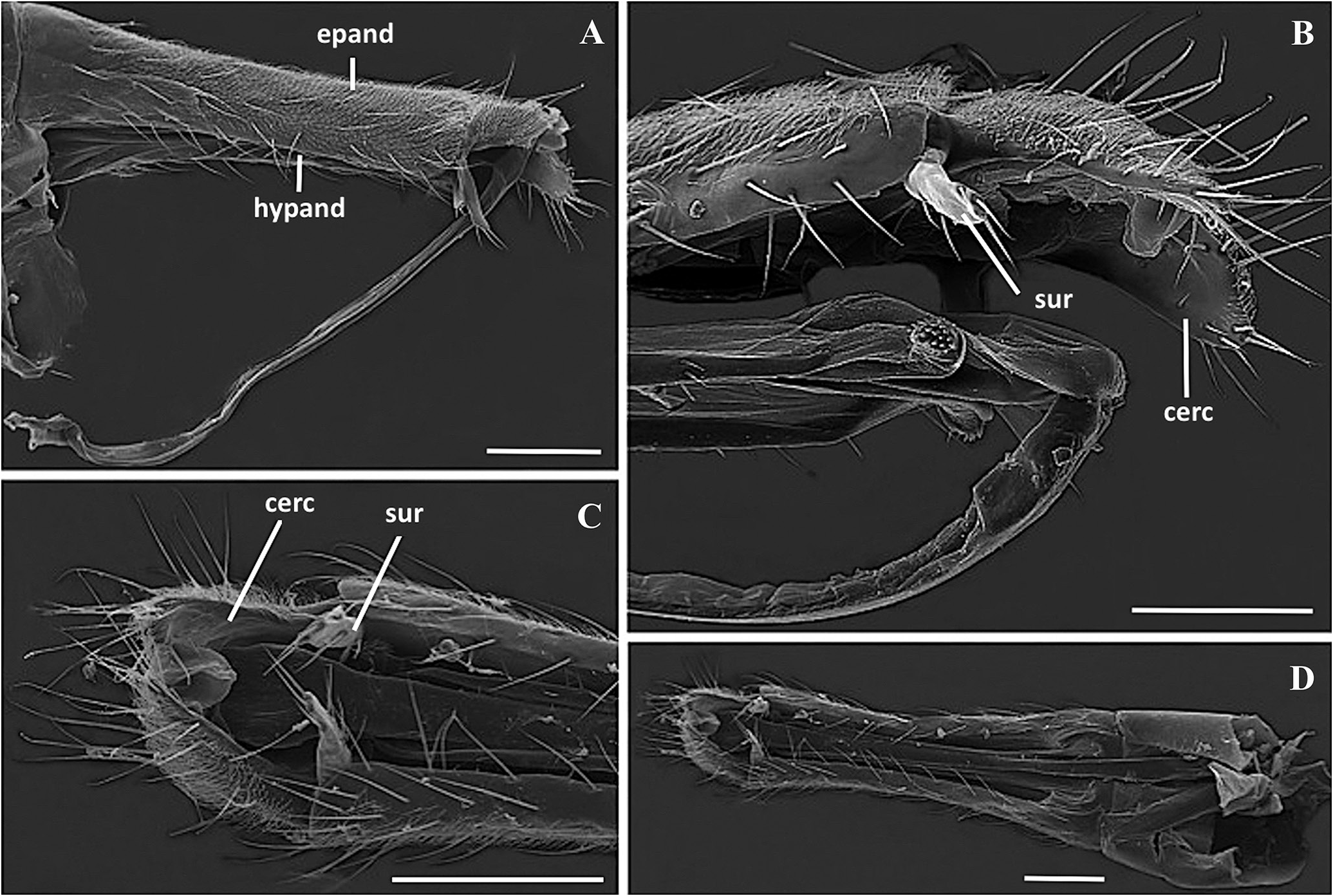
Aczél (1961) described briefly the male and female terminalia of the species Glyphidops (Glyphidops) filosus . In the description of male terminalia, the mentioned structures were cerci, syntergite 7 + 8 and epandrium, with the respective measures of length. The structures of female terminalia were the characteristics of oviscape, like coloration and measures of length. In Sepúlveda et al. (2014) the structures of male terminalia mentioned were syntergite 7 + 8 and coloration of the epandrium, and for females the oviscape coloration and measurements of the length.
Male Terminalia: Length 0,9-1,2 mm. Epandrium and hypandrium yellowish and long, with short setae ( Fig. 3A View Figure 3 ). Cerci and surstyli with sparse setae ( Fig. 3B View Figure 3 ); cerci with apical process turned ventrally ( Fig. 3 View Figure 3 C-D, Fig. 4A View Figure 4 ). Aedeagus long with three sections, basal, middle and distal ( Fig. 4B View Figure 4 ); bifid, with division appearing in the apical region of the distal section ( Fig.4C View Figure 4 ).The basal and middle sections have a complex hinge between them ( Fig. 4D View Figure 4 ). Basal section with lateral arms with short apical spines and long pregenital muscles ( Figs. 3B View Figure 3 , 4D View Figure 4 ). Middle section with one spine at the anterior portion. Distal section with spines at the apical portion. Aedeagal apodeme at the posterior portion of the basal section of aedeagus.
Female terminalia: Length 1,4-2,3 mm. Ovipositor with modified cerci in its distal portion. Modified cerci have an approximate length of 0,5 mm, yellowish, bifurcated and with setae at the apex in the posterior portion ( Fig. 5B View Figure 5 ). Ovipositor leads to the tube that passes through the ‘S’ bend and connects with the bursa copulatrix. Bursa copulatrix connects to ducts of the spermatheca,followed by the four spermathecal capsules ( Fig. 5C View Figure 5 ). Spermathecal capsules are spherical structures ( Fig. 5D View Figure 5 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |