Astatometopon, Campodonico, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1515/aemnp-2017-0053 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:16AAF1F8-E042-4DA8-92BE-3FD433A80425 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4643888 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FA878F-FFD2-FFA2-FE2E-E133FEB3FB68 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Astatometopon |
| status |
gen. nov. |
Astatometopon View in CoL gen. nov.
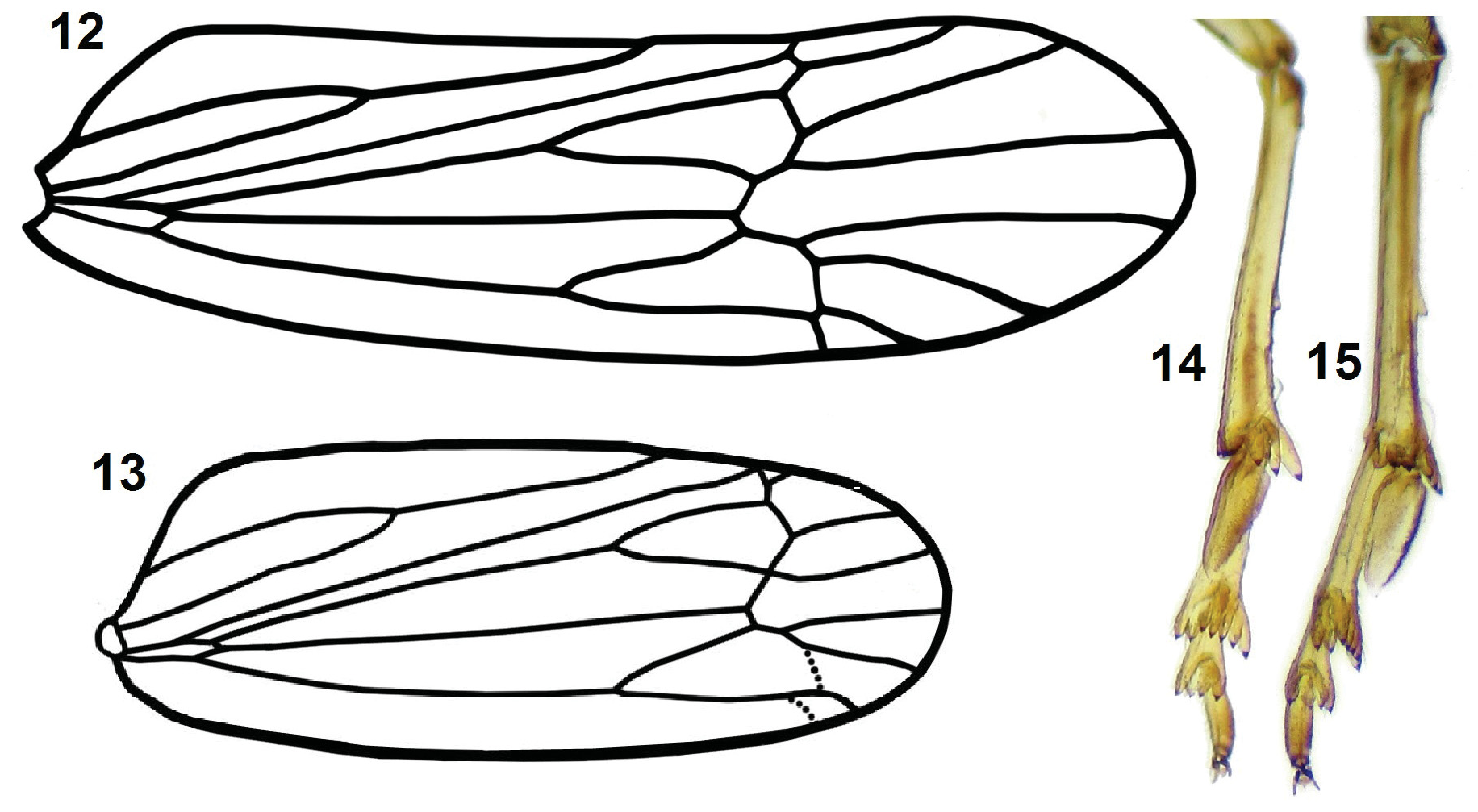
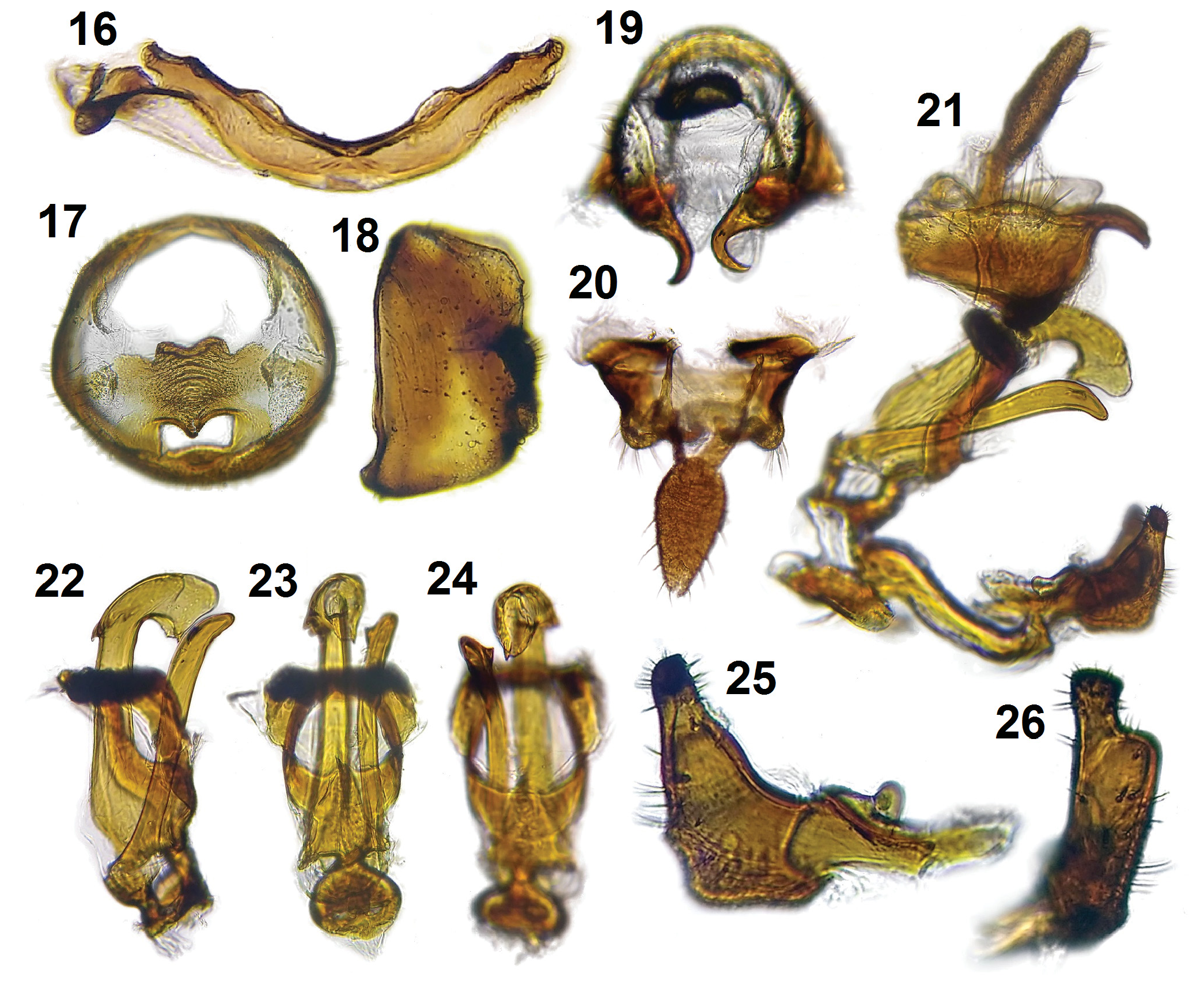
( Figs 1–32 View Figs 1–11 View Figs 12–15 View Figs 16–26 View Figs 27–32 )
Type species. Astatometopon sakakibarai View in CoL sp. nov., here designated.
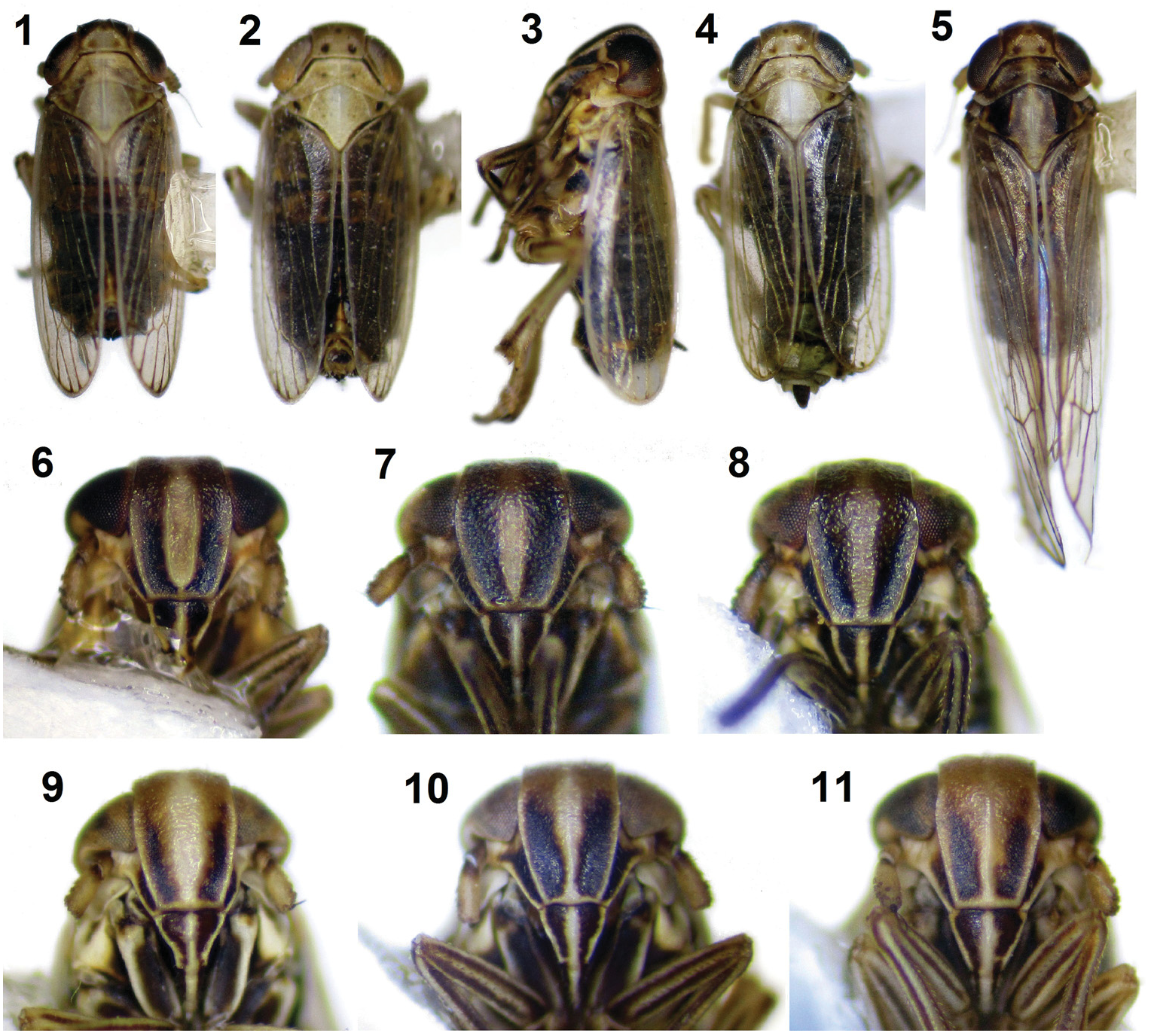
Description. General body shape ( Figs 1–5 View Figs 1–11 ) oblong, slightly more than twice longer than wide.
Head ( Figs 1–11 View Figs 1–11 ) wider than or subequal in width to pronotum. Macrocoryphe ( Figs 1–2, 4–5 View Figs 1–11 ) quadrangular, wider than long; apex rounded; anterior side and posterior margin almost equal in width; posterior margin, in dorsal view, medially positioned at anterior half of eyes; coryphe composed by two pentagonal cells enclosed by carinae. Fastigium ( Fig. 3 View Figs 1–11 ) smoothly curved. Superior side of eumetope ( Figs 6–11 View Figs 1–11 ) wider than its inferior margin; carinae of metope fading on fastigium, then subparallel and converging on lower margin of eumetope; carinae sometimes weak, absent, or reduced to a single carina. Clypeus ( Figs 6–11 View Figs 1–11 ) tricarinate. Rostrum reaching mesocoxae. Antennae ( Figs 6–11 View Figs 1–11 ) with scape shorter than pedicel.
Thorax ( Figs 1–5 View Figs 1–11 ). Pronotum ( Figs 1–2, 4–5 View Figs 1–11 ) subtrapezoidal, wider posteriorly; posterior margin bisinuate; median carina distinct; lateral carinae curved laterally behind eyes, not reaching posterior margin. Mesonotum ( Figs 1–2, 4–5 View Figs 1–11 ) with median and lateral carinae distinct; median carinae fading at scutellum; scutellum transversely striated.
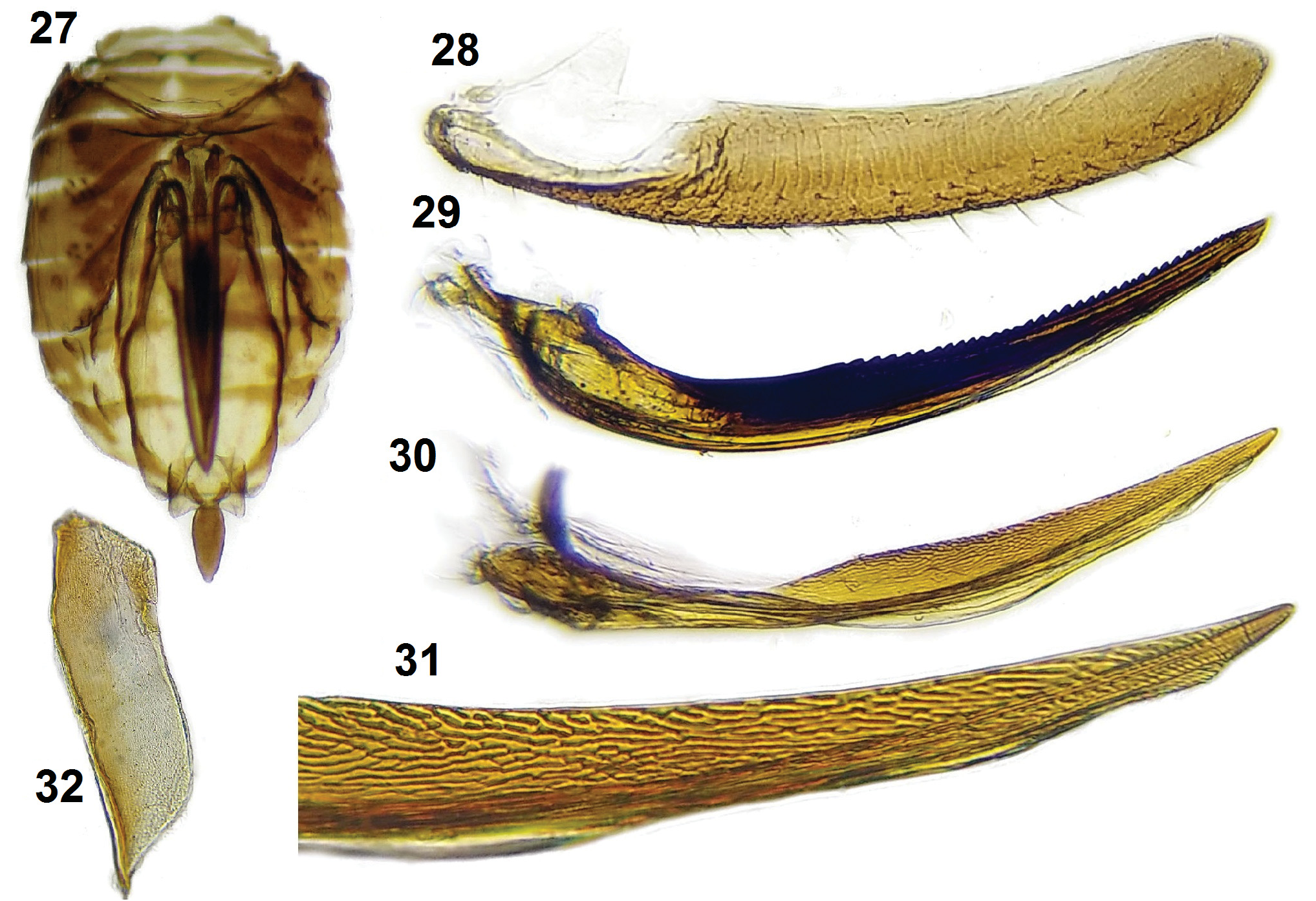
Legs. Metatibiae ( Figs 14–15 View Figs 12–15 ) with one lateral tooth near tibiofemoral articulation and another one near middle of its length. Calcar ( Fig. 14 View Figs 12–15 ) without teeth on its hind margin.
Male abdomen. Sternum I ( Fig. 16 View Figs 16–26 ) with apodemes short and directed dorsocaudad. Pygofer ( Figs 17–18 View Figs 16–26 ), in lateral view, higher than long; opening with no ventral processes; diaphragm strong, with armature. Segment X ( Figs 19–21 View Figs 16–26 ) wider than long, with pair of posteroventral processes. Segment XI ( Figs 19–21 View Figs 16–26 ) longer than segment X. Phallus ( Figs 21–24 View Figs 16–26 ) asymmetrical, with conspicuous porrect process arising from base. Suspensorium ( Figs 21–24 View Figs 16–26 ) ring-like, projected caudally over phallus. Styles ( Figs 25–26 View Figs 16–26 ) short, not surpassing height of diaphragm, narrowed at apex.
Differential diagnosis. See discussion.
Etymology. Combination of the Greek words αστατος (= astatos, inconstant) and μέτωπον (= metopon, forehead) in reference to the inconstant carination of the metope in the eumetope. Gender neuter.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Fulgoroidea |
|
Family |