Megacalanus ohmani, Bradford-Grieve, Janet M., Blanco-Bercial, Leocadio & Boxshall, Geoffrey A., 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.293480 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:BCDF8F6F-B8B4-4A9D-A8B8-7EDCEF1100BE |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6029162 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FC3969-BB51-FF89-01BE-66D2FD69065F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Megacalanus ohmani |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Megacalanus ohmani n. sp.
( Figs 9 View FIGURE 9 , 17–23 View FIGURE 17 View FIGURE 18 View FIGURE 19 View FIGURE 20 View FIGURE 21 View FIGURE 22 View FIGURE 23 )
Type locality. 5.350o S, 133.583o E.
Material examined. Indopac VIII, Stn 6, IKMT, 0–2 0 96 mwo, 33♀ (9.5–11.0 mm), 8♂, holotype female 11.0 mm, paratypes.
Type specimens. Deposited in the collection of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography , California: Holotype female: PIC- 140409 -0004-HT; Paratype male: PIC- 140409 -0005-PT; Paratype lot of 33 females and 7 males PIC- 140409 -0006-PT.
Morphological description. Following description based on holotype and paratype from Indopac VIII, Stn 6. As for genus with following specific level features.
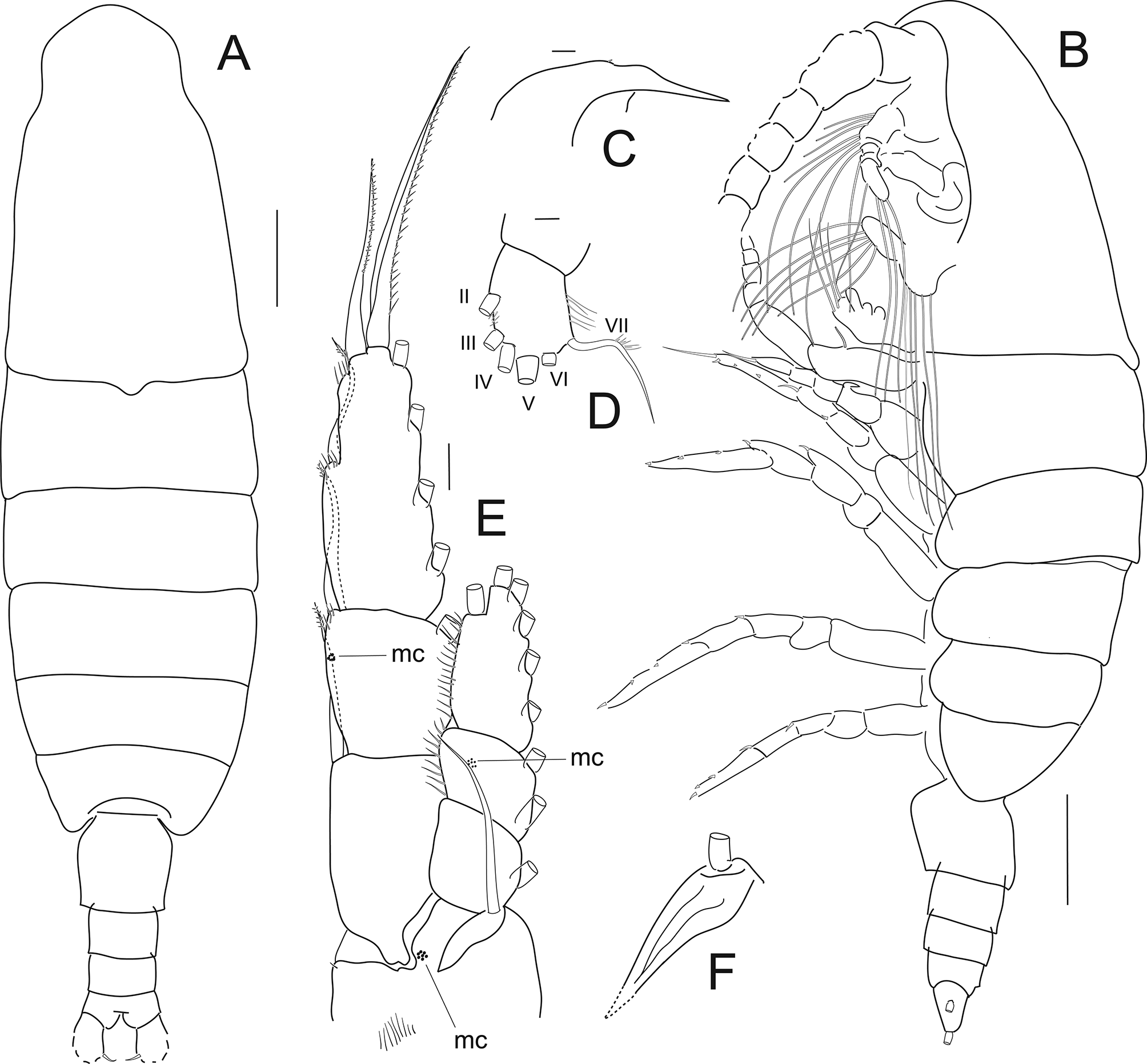
Female ( Figs 17–20 View FIGURE 17 View FIGURE 18 View FIGURE 19 View FIGURE 20 ). Total length 11.0 mm (mean 10.4 mm, range 9.5–11.0 mm, n=10). Head bluntly rounded, posterior corners of pedigerous somite 5 with short bluntly rounded posterior borders extending one quarter of distance along genital double-somite in dorsal view and only as far as genital bulge of genital double-somite in lateral view, posterior borders appearing rounded in dorsal view.
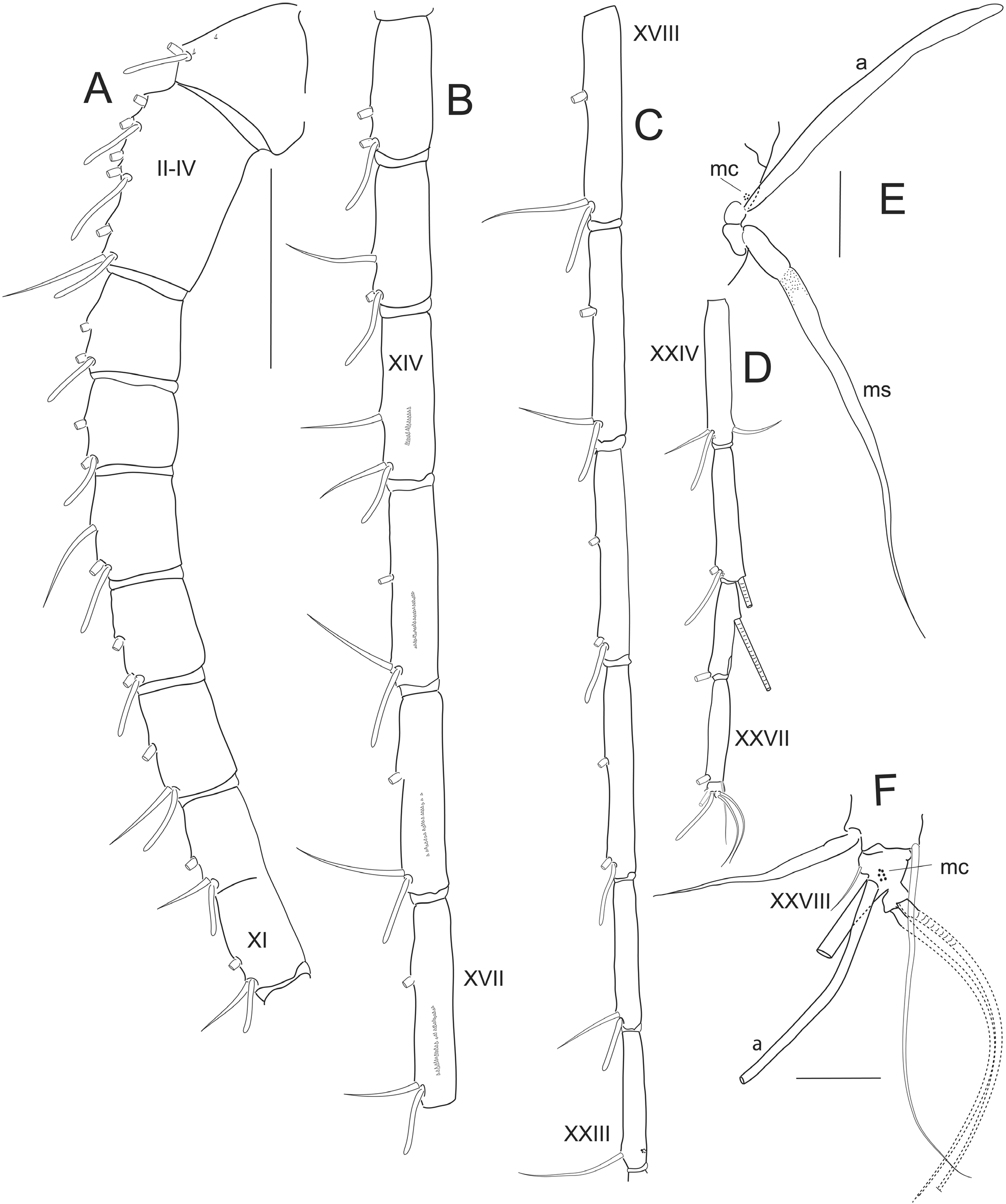
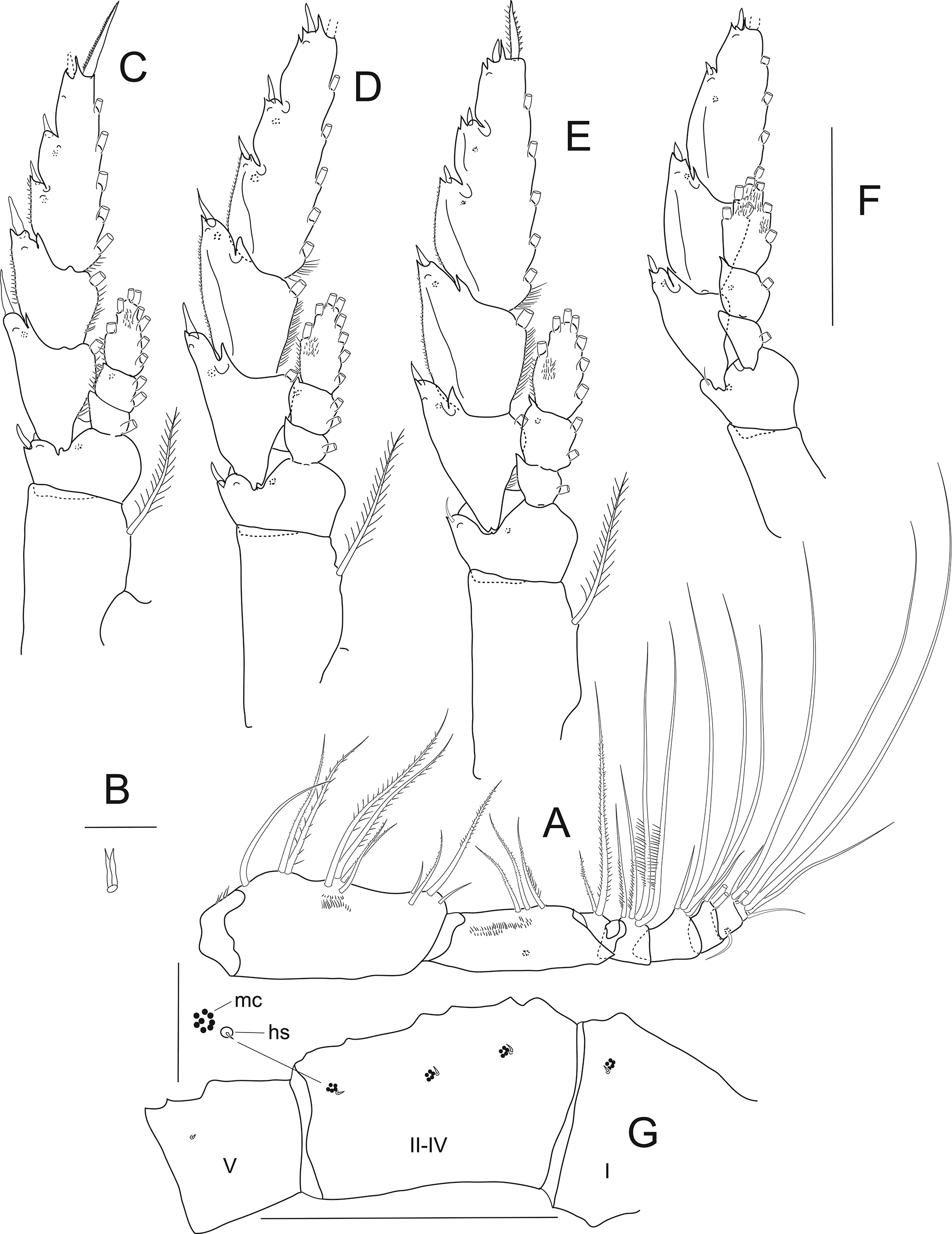
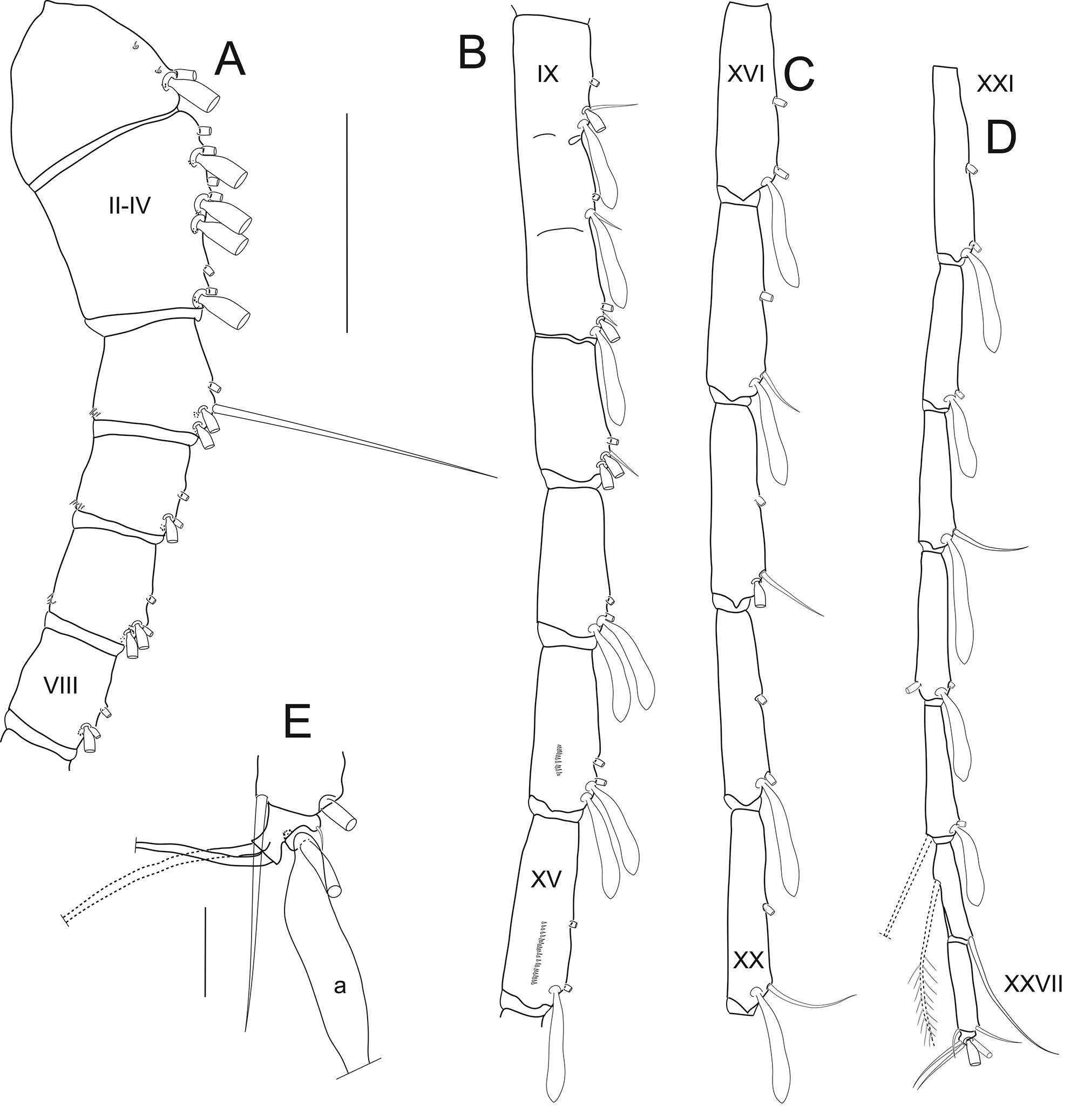
Antennule ( Fig. 18 View FIGURE 18 ) segment length (µm) as follows. Measurements taken along posterior border of each segment but two (posterior (shortest) and anterior) measurements taken of ancestral segment I. I (441, 691); II–IV (765); V (376); VI (371); VII (418); VIII (418); IX (483); X–XI (928); XII (654); XIII (666); XIV (787); XV (938); XVI (951); XVII (968); XVIII (1020); XIX (1020); XX (1012); XXI (1005); XXII (708); XXIII (651); XXIV (691); XXV (658); XXVI (431); XXVII (503); XXVIII (67). Dorsal surface of segments I–V each with very small hair sensillum of which those on segments I–IV each accompanied by macula cribrosa ( Fig. 20 View FIGURE 20 G); ventral surface of ancestral segments XIV to XVII with distal row of 19/20, 31/31, 30/36, 30/30 teeth, respectively ( Fig. 18 View FIGURE 18 B); ancestral segments XV and XVI smooth, without distoposterior row of blunt teeth.
Leg 1 ( Fig. 17 View FIGURE 17 E, F) outer spines on exopod segments 1 and 2 extending only slightly beyond base of following, more distal spine and exopod segment 2 has macula cribrosa located at distal one third from base of distolateral spine on lateral border.
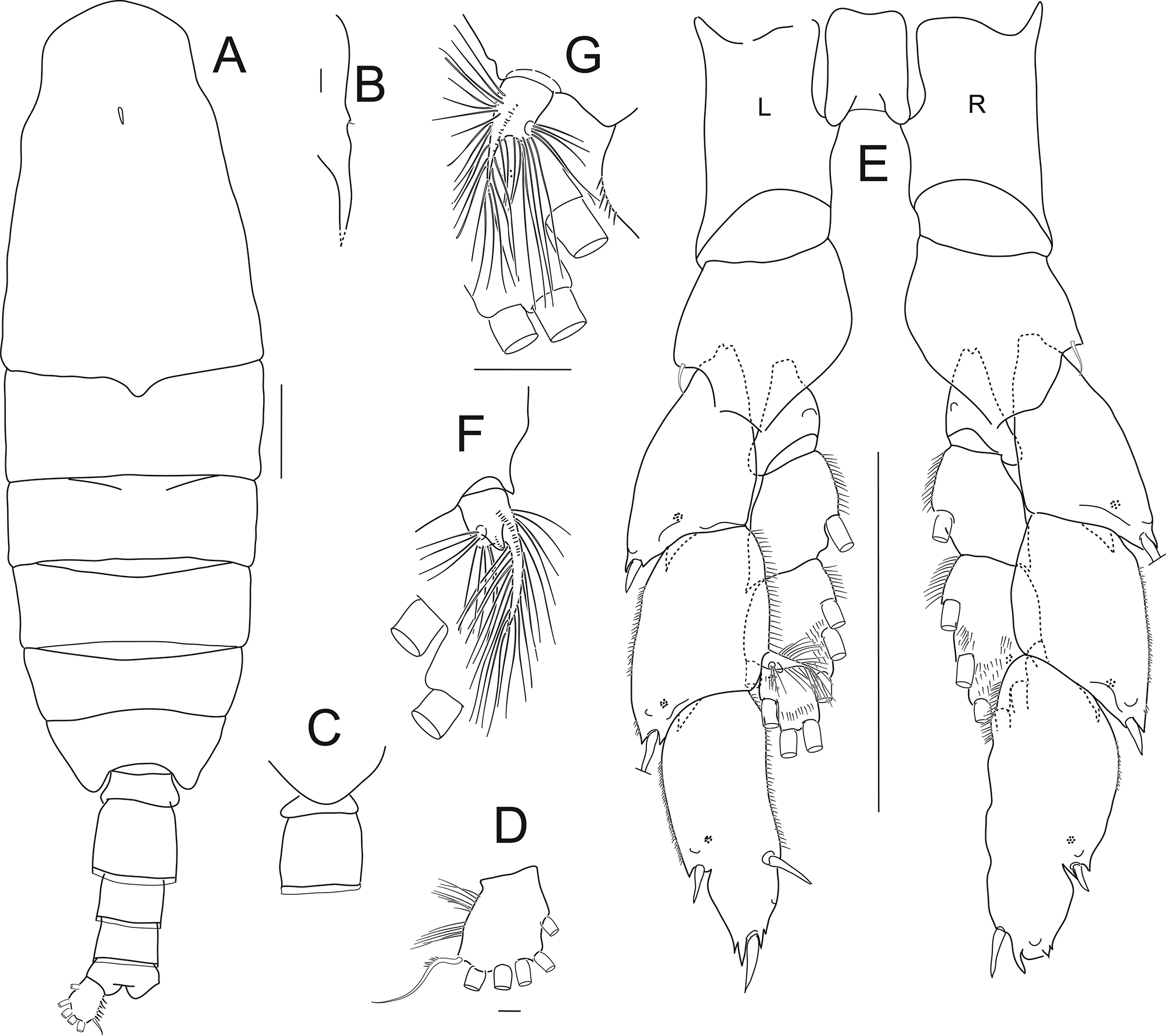
Male ( Figs 21–23 View FIGURE 21 View FIGURE 22 View FIGURE 23 ). Total length 10.7 mm. Anterior margin of head bluntly rounded in dorsal view.
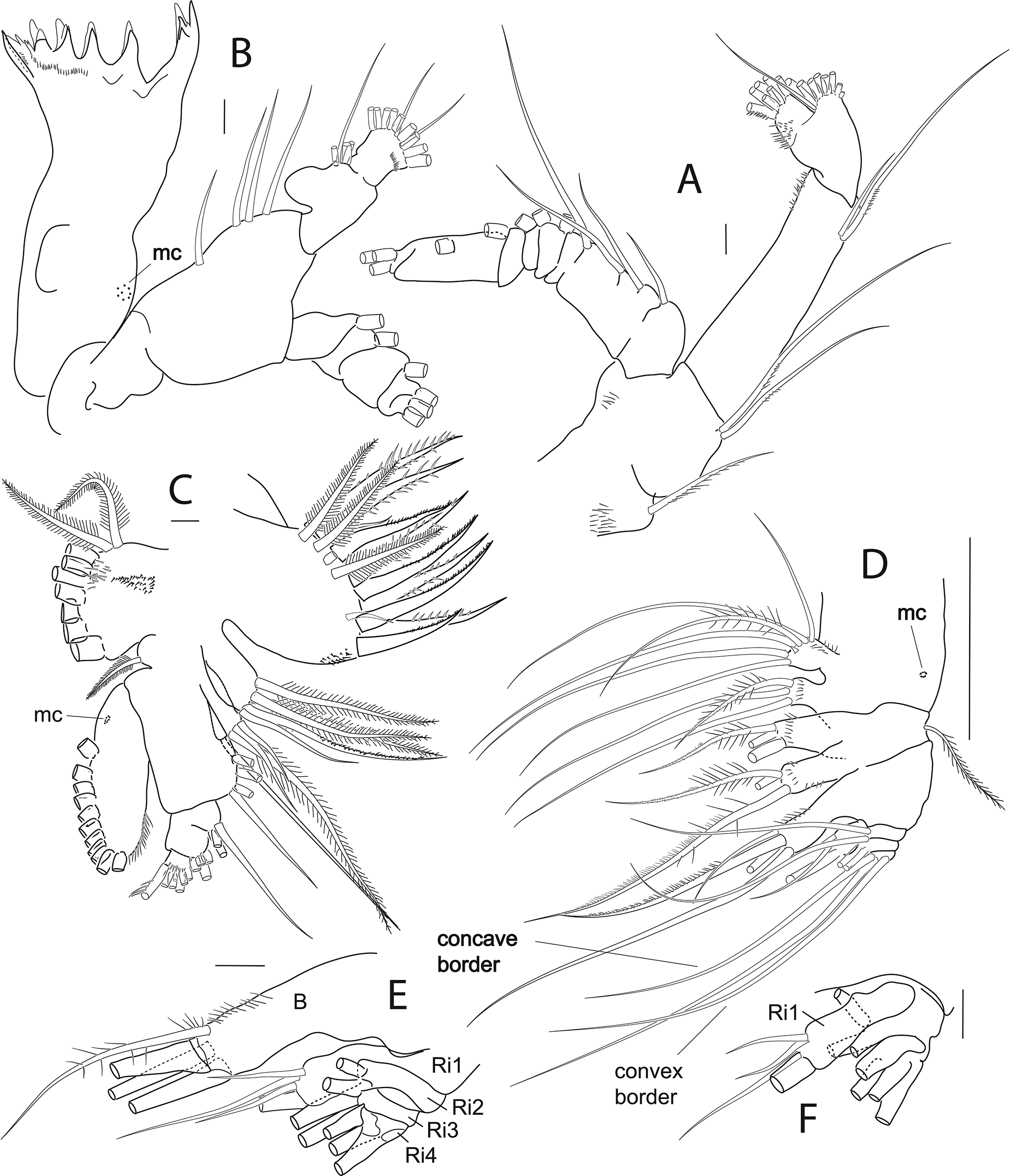
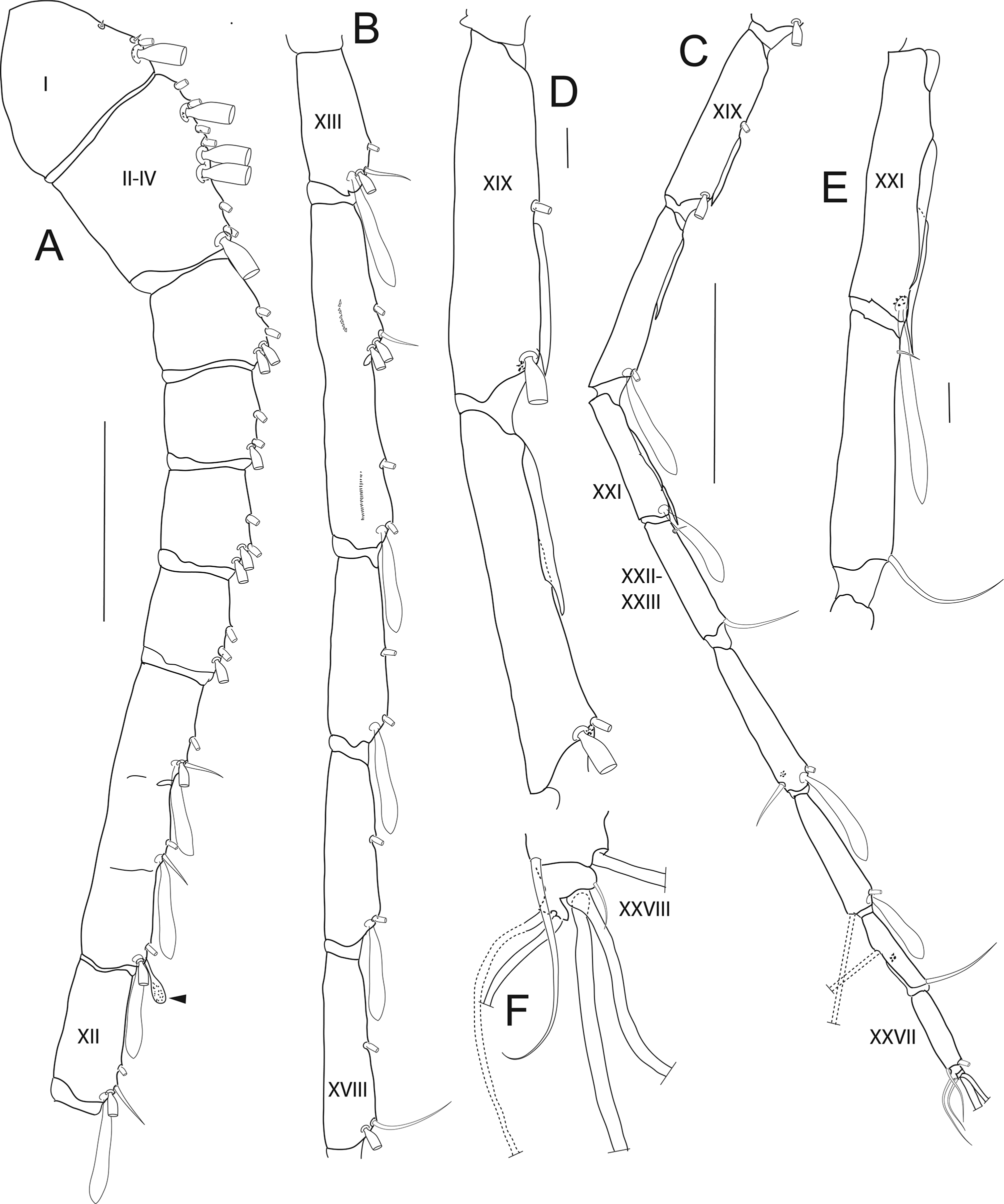
Right antennule ancestral segment XI with distal clavate (club-shaped) seta (indicated by arrow) ( Fig. 23 View FIGURE 23 A); ancestral segment XIX with 1 fused gripping element extending beyond base of aesthetasc, 1ms, 1a ( Fig. 23 View FIGURE 23 C, D); and segment XXI with 2 long overlapping gripping elements (proximal element with tip extending to base of aesthetasc, distal element extending well beyond distal border of segment), 1a ( Fig. 23 View FIGURE 23 C, E). Left antennule ( Fig. 22 View FIGURE 22 ) with clavate seta broken off ancestral segment XI in figured specimen leaving setal vestige, but present in other specimens.
Leg 5 inner distal border of basis without setules, left leg 5 exopod segment 2 specialised seta with basal part longer than wide and lash longer than basal part ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 E–G). Right exopod segment 3 inner border with series of hyaline ridges along distal two thirds, proximal one third lined with fine setules ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 E).
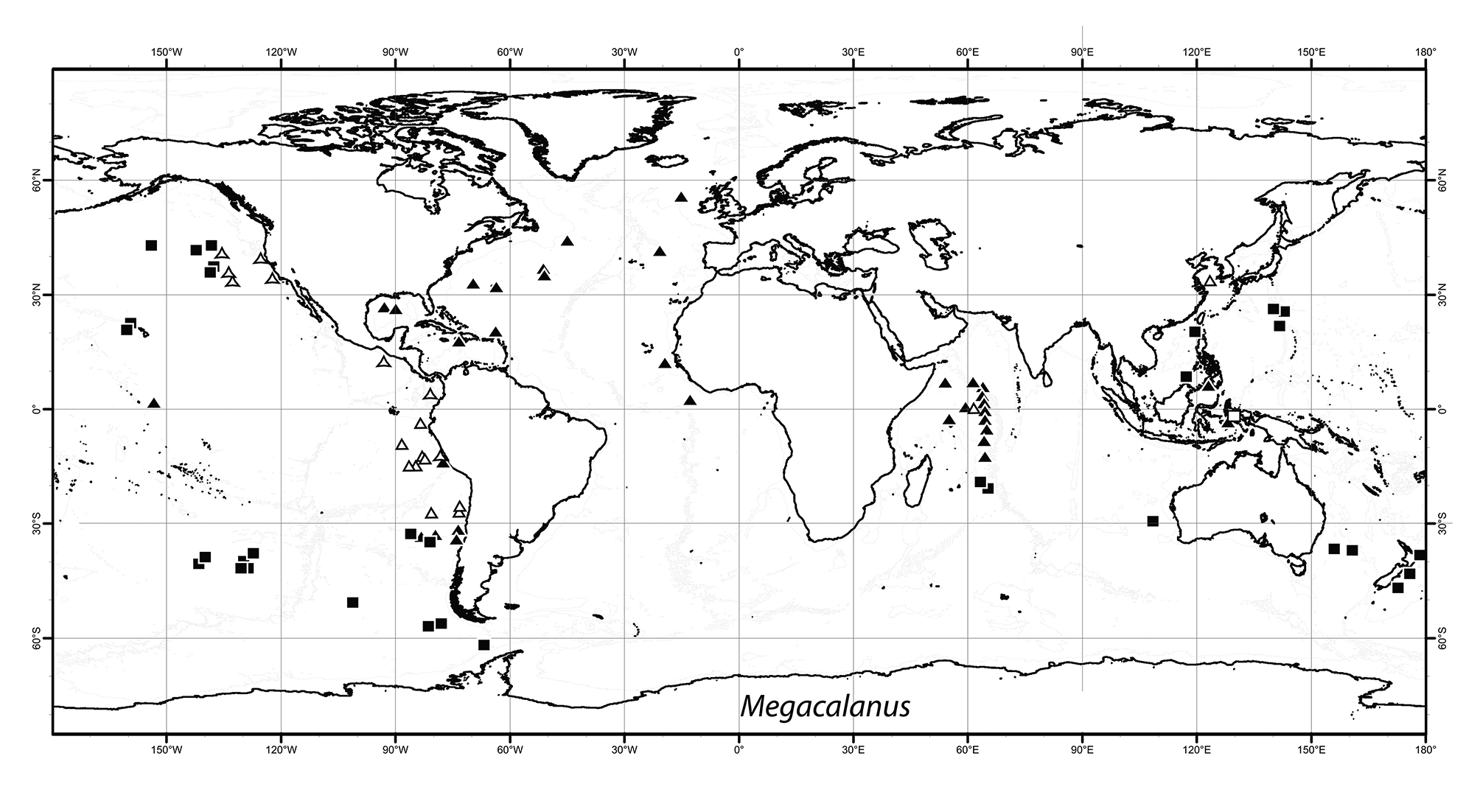
Distribution. Megacalanus ohmani is a bathypelagic species known so far only from east of Irian Jaya ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 , Table 1 View TABLE 1 ).
Species comparisons. Female of M. ohmani n. sp. and M. ericae n. sp. are similar in that ancestral segments XV and XVI of the antennule have a smooth distoposterior border ( Table 7). Females (and males) of these two species may be distinguished by the shape of the posterior borders of pedigerous somite 5: in M. ohmani n. sp. these borders are short and round and in M. ericae n. sp. longer and triangular. Male M. ohmani n. sp. is easily distinguished from males of all other species by the pair of overlapping fused gripping elements on right antennule ancestral segment XXI and the inner border of the right leg 5 exopod segment 3 which is setulose only on the proximal one third and has a series of hyaline ridges along the remainder of the inner border — no other species has these features.
The specialised seta on the male left leg 5 exopod segment 2 is similar to that of M. princeps and M. frosti n. sp. but differs from the Pacific species M. ericae n. sp. which has a much stumpier specialised seta with a lash that is shorter than the basal part. Leg 1 of M. ohmani n. sp. has two unique features: the outer spines on exopod segments 1 and 2 extend only slightly beyond base of following, more distal spine (in the other species these outer spines are longer); and exopod segment 2 has the macula cribrosa located at distal one third from base of distolateral spine on lateral border (whereas in the other species the macula cribrosa is situated close to the base of the outer border spine and on the anterior surface).
Etymology. This species has been named for Professor Mark Ohman who made available the extensive collection of Megacalanidae from the Scripps Institution of Oceanography ( USA) collection of pelagic invertebrates, on which this work is partly based.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.