Hippomenella, Canu and Bassler, 1917
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.12782/specdiv.29.99 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:EA59EB18-8759-401A-96E0-62C2E9896A94 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FC87AB-FFB5-FF8F-A881-F936B23CF601 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Hippomenella |
| status |
|
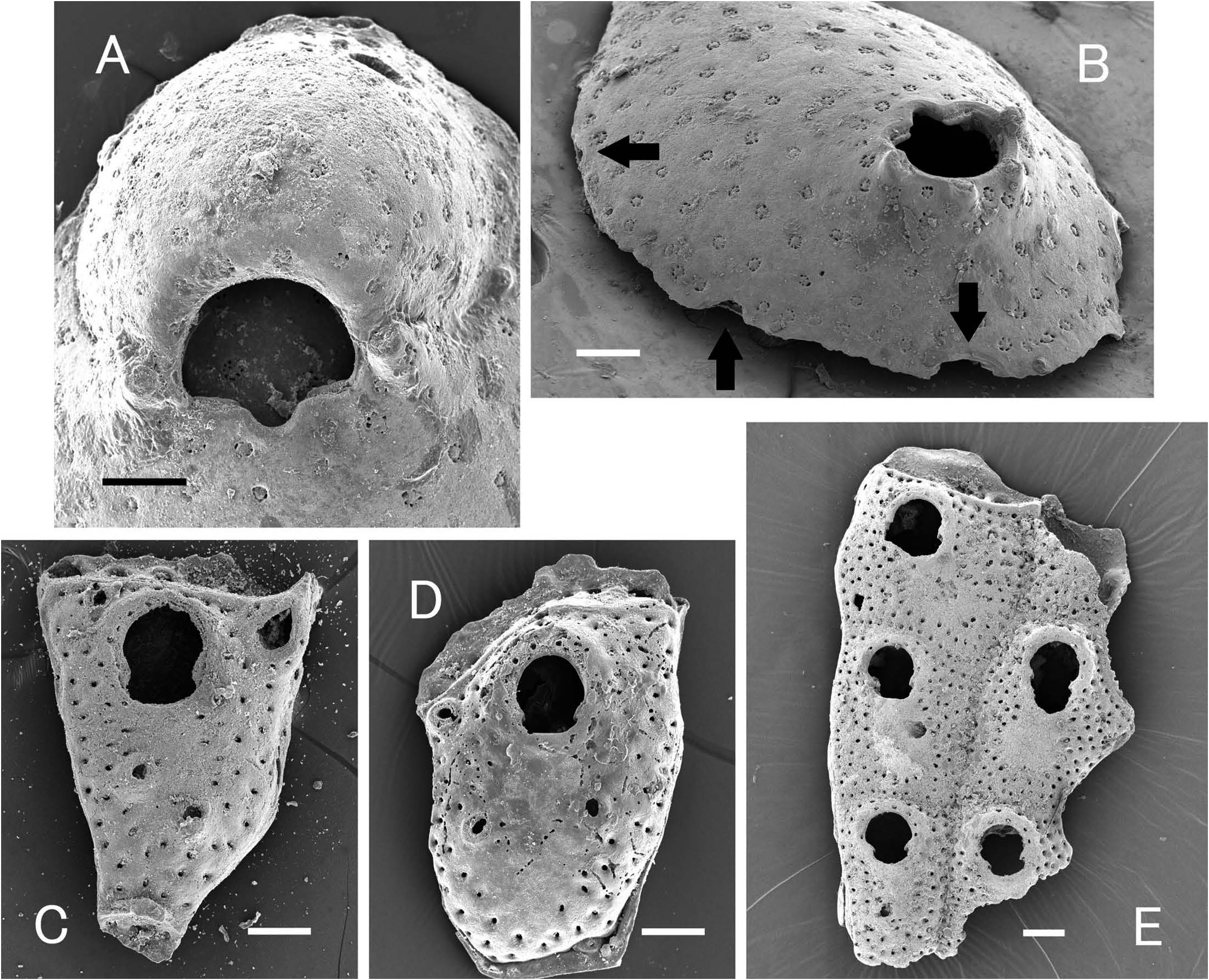
Hippomenella View in CoL (?) coronula ( Ortmann, 1890) ( Fig. 4C–E View Fig )
Diporula coronula Ortmann, 1890: 39 View in CoL , pl. 3, fig. 7. Hippomenella View in CoL (?) coronula View in CoL : Arakawa 1999: 79, pl. 9, fig. G. Hippomenella coronula View in CoL : Hirose 2010: 109, pl. 185, figs A–D;
Arakawa 2020b: 55.
Material examined. NMNS PA 20506 (fragment of colony A, and single zooids, B, C), Station 1748, R / V Hakurei-Maru cruise GH-80-2.
Measurements (in mm). NMNS PA 20506. Autozooids (6, 3): ZL, 0.85–1.18 (1.048 ± 0.129); ZW, 0.57–0.95 (0.809 ± 0.139); OrL, 0.24–0.31 (0.262 ± 0.023); OrW, 0.22– 0.25 (0.231 ± 0.015). Small frontal avicularia (8, 3): AvL, 0.11–0.13 (0.117± 0.008); AvW, 0.07–0.12 (0.086 ± 0.015)
Description. Colony encrusting. Zooids rectangular, or pentagonal to hexagonal, separated by furrows. Frontal shield imperforate in suboral area, with two to five rows of areolar pores. Orifice horseshoe-shaped, with broad poster separated from anter by proximomedially directed condyles. Oral spines five to seven. Small frontal avicularia generally two, sometimes absent ( Fig. 4E View Fig ); mandibular portion rounded or subtriangular, directed proximolaterally. One or two additional avicularia near distal corner of zooid, small, or large and elongate ( Fig. 4C, D View Fig ). Ovicell not found.
Distribution. Sagami Bay, depth 185 m ( Ortmann 1890); eastern Sagami Sea, depth 65–77 m and 132–172 m ( Hirose 2010); east of Boso Peninsula, depth 65 m (this study).
Remarks: My material comprises one colony fragment and two single zooids, but their zooidal characters correspond to those of the lectotype for H. coronula , studied by Hirose (2010). Hirose considered Ortmann’s species to be synonymous with H. spatulata Harmer, 1957 [= Lepralia tuberculara var. avicularis Livingstone, 1926 ; Hayward and Cook (1983) raised this taxon to species rank as H. avicularis ]. However, H. avicularis has a large avicularium with a markedly expanded tip ( Livingstone 1926; Harmer 1957; Powell 1967; Gordon and Hondt 1997); H. coronula , which shows gradual expansion of the avicularian tip, is a distinct species. For the same reason, the species from South Africa ( Hayward and Cook 1983) and from Korea ( Rho and Seo 1986) need to be restudied. I infer the Korean species as H. coronula , but the suboral imperforate area is narrower than in Japanese materials.
This species included in the species group of H. vellicata having proximally directed frontal avicularia and an ooecium with radially arranged pseudopores. These features do not coincide with the diagnosis of Hippomenella amended by Berning (2013).
| NMNS |
National Museum of Natural Science |
| R |
Departamento de Geologia, Universidad de Chile |
| V |
Royal British Columbia Museum - Herbarium |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Hippomenella
| Arakawa, Shinji 2024 |
Diporula coronula
| Hirose, M. 2010: 109 |
| Arakawa, S. 1999: 79 |
| Ortmann, A. E. 1890: 39 |