Grouvellinus nigerquadratus Freitag, Molls and Bouma, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2019.1709669 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3671822 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/052D87A1-586C-1318-FE9A-AC99FEEDFD1D |
|
treatment provided by |
Valdenar |
|
scientific name |
Grouvellinus nigerquadratus Freitag, Molls and Bouma |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Grouvellinus nigerquadratus Freitag, Molls and Bouma , sp. nov.
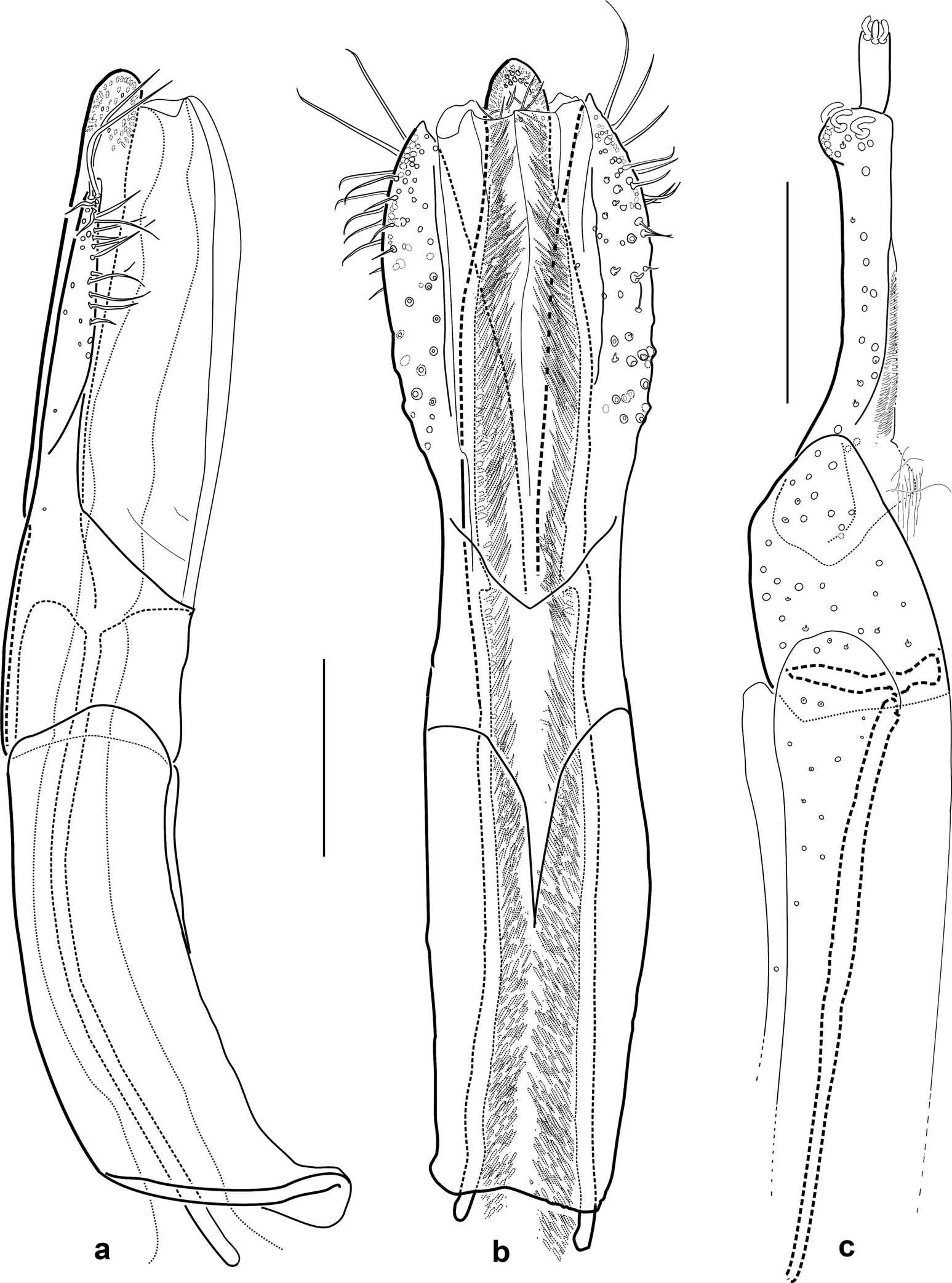
( Figures 3, 4 View Figures 2–5 , 10 View Figure 10 (a – c), 11(a – c))
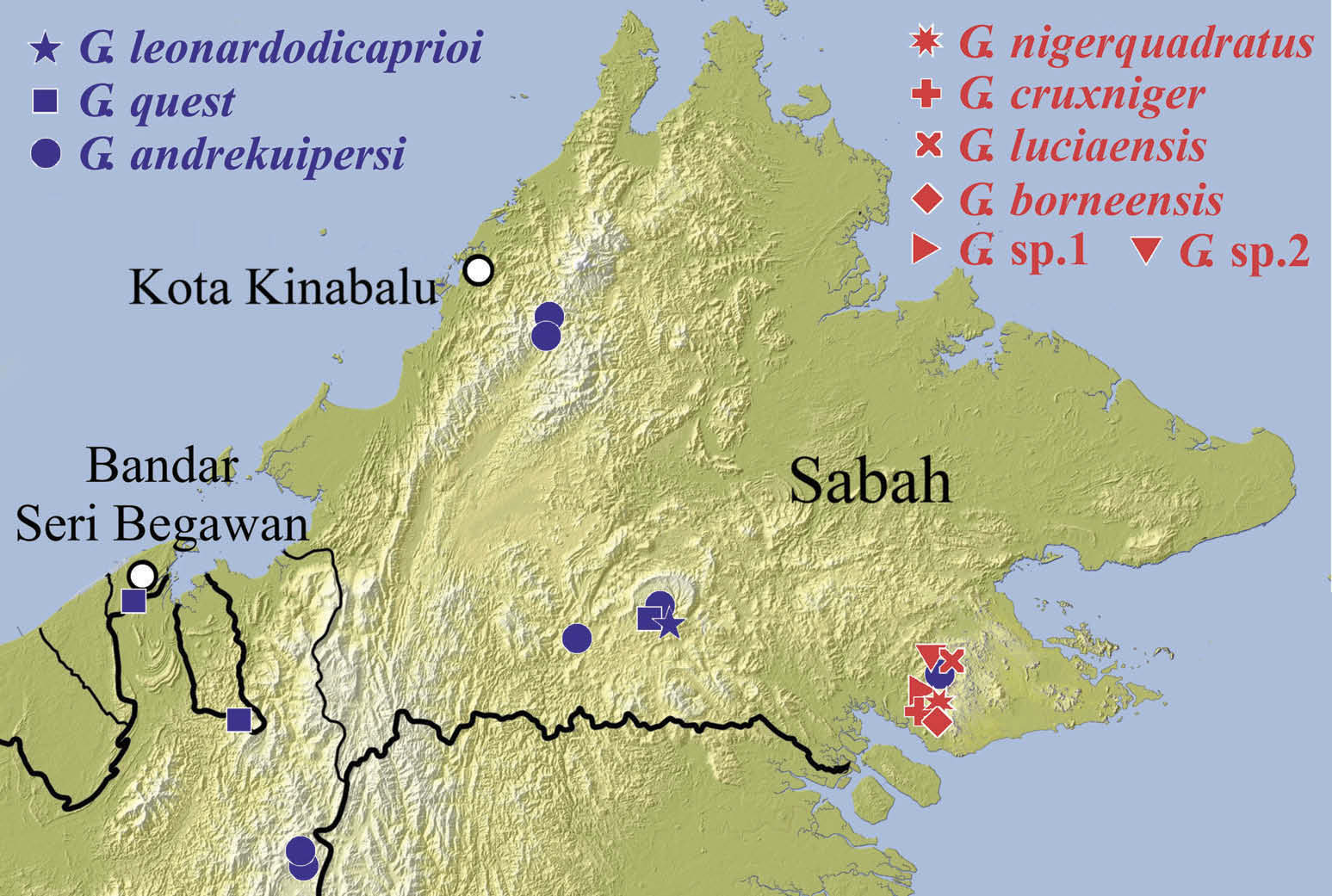
Type locality. Malaysia, Sabah (on Borneo Island), Tawau Hills Park, Tawau River, 4° 24 ʹ 14 ʹʹ N, 117°53 ʹ 35 ʹʹ E, 270 m a.s.l. ( Figure 1 View Figure 1 (e)).
Type material. Holotype 3 [H56] ( SP): ‘ MALAYSIA: Sabah: Tawau River; bottom gravel, run; primary forest; ca. 4°24 ʹ 14 ʹʹ N, 117°53 ʹ 35 ʹʹ E, 280 m a.s.l.; leg. Taxon Expedition participants 12. GoogleMaps
March GoogleMaps .2018 (1c)M ’, terminal parts of abdomen incl. aedeagus glued separately. Paratypes: 23, 1♀ [H16] (SP) same data as holotype; 2 exs. ‘ MALAYSIA: Sabah: Tawau River; rock surface, run; primary forest; ca. 4°24 ʹ 14 ʹʹ N, 117°53 ʹ 35 ʹʹ E, 280 m a.s.l. ; leg. Taxon Expedition participants 12.March.2018 ( 1g)M ’; 1♀ (SP) ‘ MALAYSIA: Sabah: Tawau River; rock surface, run; primary forest; ca. 4°24 ʹ 14 ʹʹ N, 117°53 ʹ 35 ʹʹ E, 280 m a.s.l.; leg. Taxon Expedition participants 12. March.2018 (1f)M ’ . Other material: 13, 1♀ (SP) same data as holotype; 13 (SP) ‘ MALAYSIA:
Sabah: Lucia River; rock surface, run; primary forest; ca. 4°28 ʹ 34 ʹʹ N, 117°55 ʹ 38 ʹʹ E, ca. 750 m a.s. l., leg. Taxon Expedition participants 10.March.2018 ( 6g)M ’.
Etymology
The epithet refers to the elytral colour pattern which appears like an oblique black square especially in pale specimens with distinct yellowish markings.
Description
Body elongate, males 1.50 – 1.55 mm, females 1.65 – 1.75 mm long (CL); males 0.74 – 0.78 mm, females 0.78 – 0.88 mm wide (EW), 2.0 times as long as wide (CL/EW).
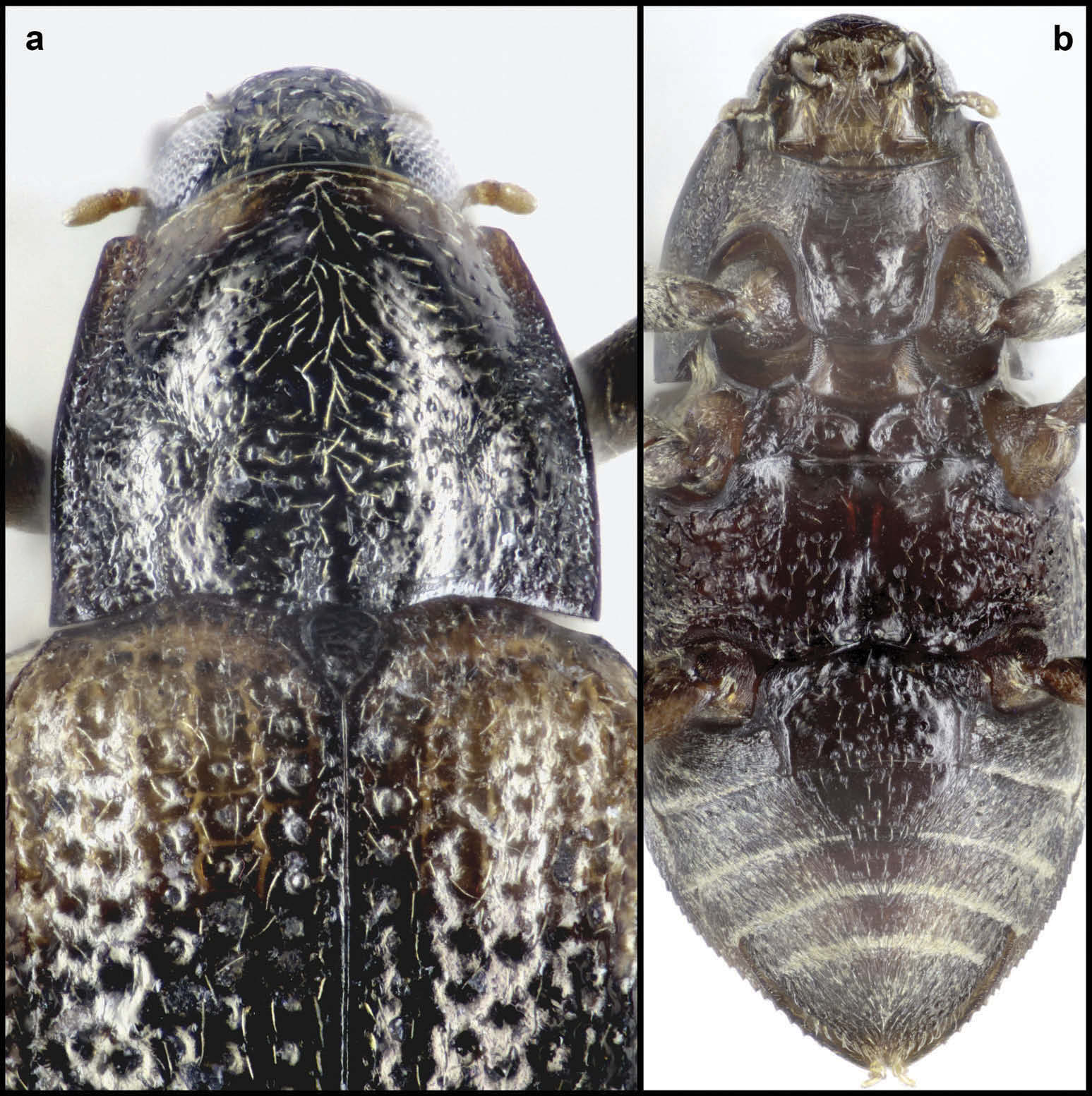
Dorsal colouration ( Figures 3, 4 View Figures 2–5 ) dominantly dark brown; pronotum black, anterior margin slightly paler, golden-brown; entire median transverse portion of elytra including disc dark brown; peripheral elytral portions with two pairs of more or less distinct, extended yellowish-brown spots; basal pair between lateral margin and first row of punctures subtrapezoidal; subapical spots between lateral margin and suture obliqueoval; coxae, femora and tibiae dark brown, areas near articulations usually slightly paler; tarsi and antennae golden brown; maxillary and labial palps dark brown; pubescence yellowish. Ventral side ( Figure 10 View Figure 10 (b,c)) dark brown.
Head ( Figure 10 View Figure 10 (a)) 0.35 – 0.39 mm wide (HW); ID 0.16 – 0.17 mm; frons, clypeus, and labrum moderately pubescent; punctures small; intervals medially flat and glabrous, laterally rugulose. Frontoclypeal suture straight, distinct. Eyes moderately large (eye diameter smaller than ID), slightly protruding. Antennae genus-typical, usually semicircularly folded around anteriolateral eye margin.
Pronotum ( Figure 10 View Figure 10 (a)) in males 0.48 – 0.50 mm, in females 0.48 – 0.54 mm long (PL); in males 0.57 – 0.61 mm, in females 0.61 – 0.67 mm wide (PW), wider than long (PL/PW), widest posterior 0 – 0.4, distinctly narrower than elytra, anteriorly attenuate; anterior margin slightly convex, anterior angles obtuse, rounded, slightly protruding; pronotal disc slightly vaulted; entire pronotum moderately densely punctate; punctures very small and shallowly impressed; setae moderately long; median carina absent; pair of short posteriomedian patches conspicuous; sublateral carinae short, rather indistinct; oblique impression moderately shallow and narrow, extending approximately anterior 0.3 – 0.7; laterobasal impression shallow; disc, entire anterior portion and portion between sublateral carinae and posterior-median patches glabrous; lateral submarginal area, laterobasal and oblique impressions rugose. Hypomeron very densely punctate.
Prosternum ( Figure 10 View Figure 10 (b)) moderately long; lateral portions appearing rugulose, with inconspicuous pubescence (plastron); anteriomedian portion inconspicuously transversely micro-reticulate, almost glabrous; prosternal process subtrapezoidal, slightly shorter than as wide at the base, medially somewhat irregularly impressed, rugulose; posterior margin convex; angles gently rounded. Scutellum ( Figure 10 View Figure 10 (a)) subtriangular, medially slightly impressed, glabrous.
Elytra ( Figures 3, 4 View Figures 2–5 ) elongate, moderately convex dorsally. EL: males 1.05 – 1.15 mm, females 1.15 – 1.24 mm; ca. 1.45 times as long as wide (EL/EW), widest at the middle, subparallel from anterior 0.2 to 0.6, subconical towards apices; apices moderately narrow, separately rounded; with eight longitudinal, slightly impressed rows of primary punctures; primary punctures regularly arranged, large (approximately as wide as intervals) and deeply impressed anterior of clivity and in anterolateral portions, small (0.1 – 0.3 times of intervals) and shallowly impressed apicad of clivity and at most basal portion; interstices slightly rugose; intervals with additional, very inconspicuous setiferous secondary punctures; pubescence yellowish, somewhat regularly arranged along intervals, consisting of sparse, large erected setae, and moderately large adpressed setae; interval 8 with distinct, interval 7 with indistinct serrate carinae; interval 2 neither carinate nor elevated; lateral elytral margin distinctly serrate (at least in basal half).
Mesoventrite ( Figure 10 View Figure 10 (c)) with two pairs of deep grooves, the median pair obliquely oval in males, subquadrate in females (somewhat varying in some specimens, see comments below). Metaventrite ( Figure 10 View Figure 10 (c)) with median groove and most anterior portion somewhat glabrous; remaining disc with irregularly uneven surface and moderately densely covered with setiferous tubercles; longitudinal impression moderately deep, widely impressed, reaching ca. posterior two-thirds in males, and one-half in females; portions adjacent to disc and coxae with irregular, rugose impressions, punctures and tubercles, but without any distinct hair patch; most lateral portions densely punctate and with plastron.
Ventrite 1 ( Figure 10 View Figure 10 (c)) with pair of longitudinal carinae; discs of ventrites 1 and 2 mainly glabrous, but with sparse regularly arranged long trichoid setae; ventrite 3 glabrous medially; lateral portions of ventrites 1 – 3 and almost entire ventrites 4 – 5 ( Figure 10 View Figure 10 (c)) densely covered with plastron and scattered, moderately long setae; the latter more dense at apex and lateral margins of ventrite 5.
Legs ( Figures 3, 4 View Figures 2–5 ) all approximately of the same length and slightly longer than body; tibiae longer than tarsi and femora; inner and outer ventral margin of all tibiae with longitudinal row or patch of long trichoid setae (in both sexes); faces of femora and tibiae very densely covered with plastron-like setae and some longitudinally arrange long trichoid or spine-like setae. Legs not conspicuously varying between sexes.
Aedeagus ( Figure 11 View Figure 11 (a,b)) ca. 590 μm long, medially ca. 105 μm wide. Base reaching basal 0.45 of total aedeagus length. Median lobe ca. 4.5 times as long as wide, moderately overreaching parameres, moderately conical towards broadly rounded apex in apical third. Ventral sac inflated ventrad, internally densely covered with long, thin spines that reach the apical opening. Parameres very slender (lateral view), laterally inflated (ventral view), apically conical, pointed (in both, ventral and lateral view), usually with slightly more than 10 trichoid setae in apical third, most of them at outer ventral face; most apical two setae longest and inserted at dorsolateral face, medioventral portion moderately densely covered with scattered very short, acute setae.
Ovipositor ( Figure 11 View Figure 11 (c)) total length ca. 570 μm; stylus ca. 42 μm long, straight with ca. three short sensilla; coxite ca. 280 μm long, moderately densely and evenly covered with very short, acute setae; proximal portion distinctly longer than wide and distinctly overlapping with slender distal portion, apically distinctly roundly broadened at outer margin and with three or more hook-like sensilla; valvifer 295 μm long, caudal portion slightly sclerotised and with a few scattered, very short, acute setae; fibula almost straight.
Differential diagnosis
Grouvellinus nigerquadratus sp. nov. is similar to G. andrekuipersi especially in the yellowish elytral patterns commonly observed in pale specimens, but the extension of these elytral patterns is usually larger in the new species. G. nigerquadratus sp. nov. can be distinguished from G. andrekuipersi by the generally slightly smaller size (CL 1.50 – 1.75 mm vs. 1.7 – 1.8 mm), the pronotum with obtuse anterior angles (vs. protruding acute angles), the large (approximately as large as interstices) and deeply impressed elytral punctures in striae 4 and 5 anterior of clivity. From all known Bornean Grouvellinus spp. it can be distinguished by its very slender aedeagus with apically distinctly pointed and laterally inflated parameres that are covered with very short, acute setae in medioventral portions. The species varies at least by 6.3% genetic distance (654 bp CO1 barcode) from the most similar Bornean congener G. cruxniger sp. nov.
Distribution
This species is known only from Tawau, Sabah, Borneo Island, namely the Tawau Hills Park ( Figure 18 View Figure 18 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |