Litinium australis, Martelli, Antonela, Russo, Virginia Lo, Villares, Gabriela & Pastor De Ward, Catalina T., 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4250.4.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:F15232E9-A0DF-4A72-94EE-40ACB7277A3C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5623731 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/086E8792-EA6C-F029-6AC4-FAE6FC3FFF54 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Litinium australis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Litinium australis sp. n.
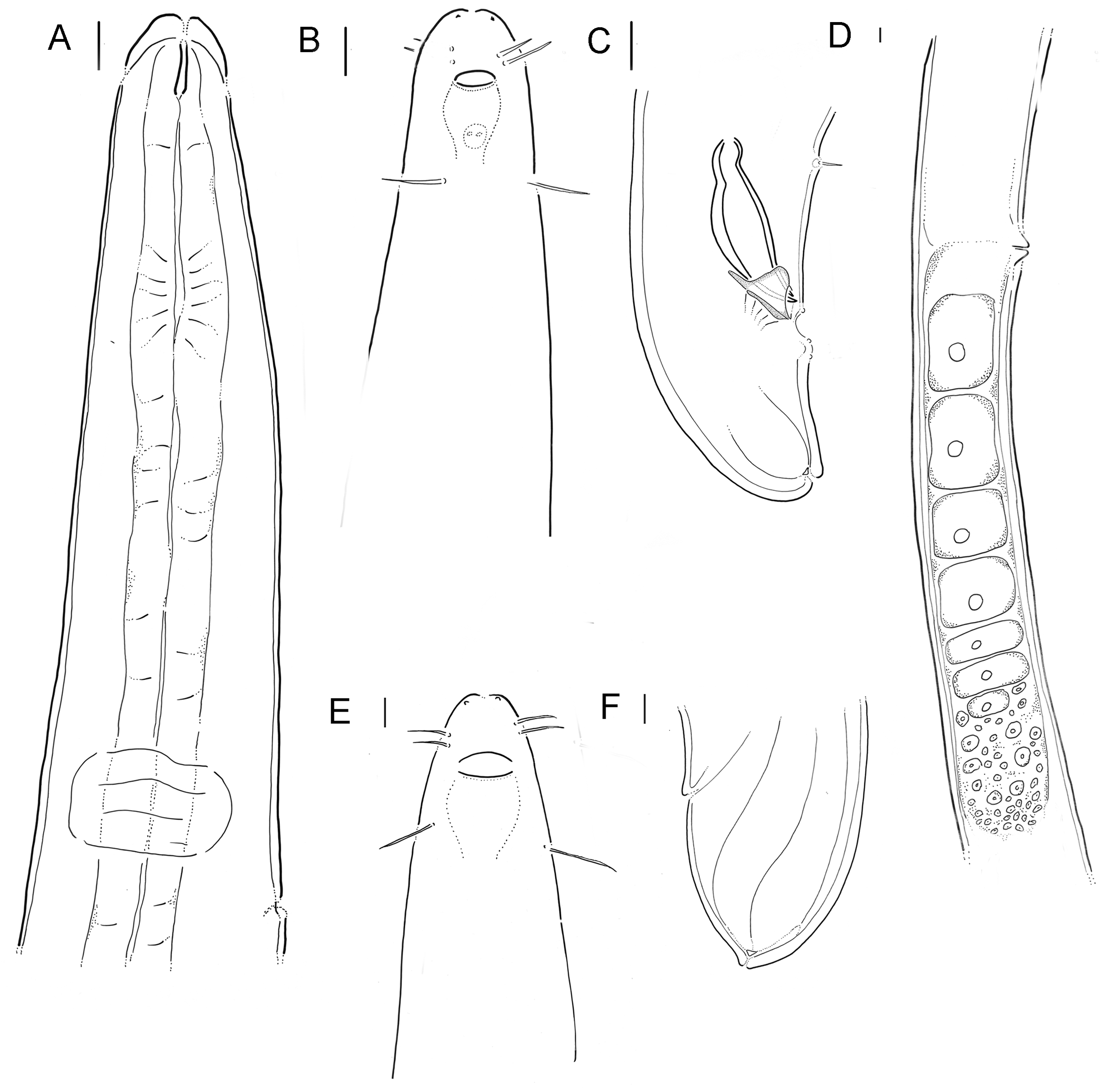
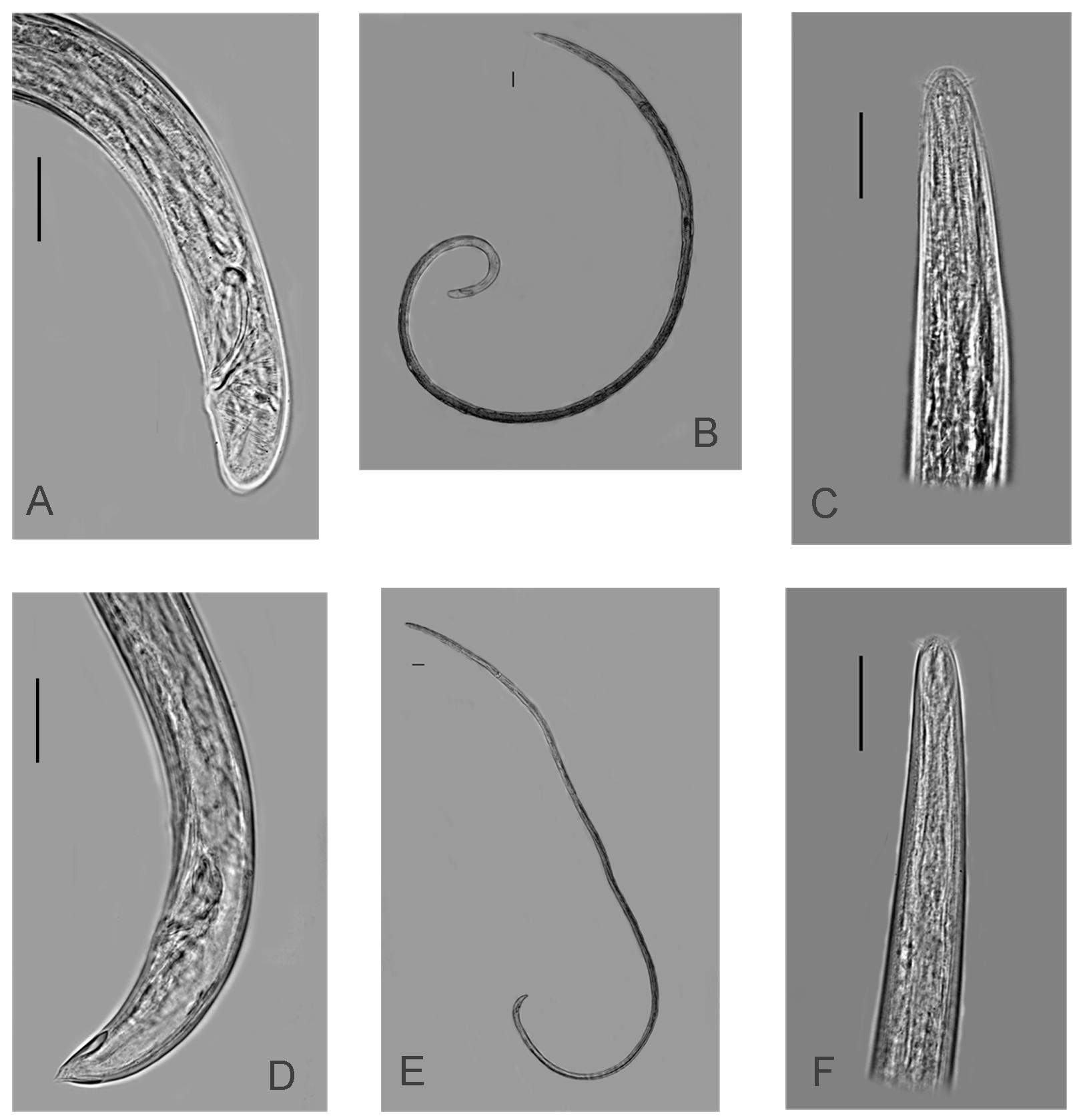
( Figures 2 View FIGURE 2 & 4 View FIGURE 4 (A–C); Table 1 View TABLE 1 )
Systematic position. Oxystominidae Chitwood, 1935 : Oxystomininae Chitwood, 1935 : Litinium Cobb, 1920
Type material. Holotype: adult male. Registration number CNP-NEM 1528; type locality: San José gulf; coordinates: 42°21’S, 64°08’W; sublittoral, mud sediments (59.8 m water depth). Collected by C.T. Pastor de Ward, 22 August 1984.
Paratype: adult female. Registration number CNP-NEM 1529. Same data as holotype.
Other material: One male and one juvenile. Registration number MACN-In 40898. Same data as holotype.
Etymology. In reference to the name of the sailboat, El Austral, with which the sample was collected.
Measurements. See Table 1 View TABLE 1 .
Description. Male (holotype): Cylindrical body, tapering slightly towards the anterior end (L = 2495 µm). Cuticle smooth. Somatic setae not seen. Buccal cavity small and narrow. Cephalic sensilla present in 6 + 6 + 4 circles. Six inner labial setae, 3.2 µm long, and six outer labial setae, 4 µm long. A crown of four cephalic setae (4 µm in length) at 2 c.d. from anterior end. Amphid and amphidial pouch conspicuous, situated 4 µm from anterior end. Amphidial fovea 6 µm wide and 9 µm long. Cephalic diameter 11 µm at level of amphid. Amphid width about 55% of the corresponding head diameter. Excretory pore located at 31 µm (3.9 c.d.) from anterior end.
Pharynx cylindrical (315 µm long), ending in a small weakly-developed bulb (18 µm in diameter). Body diameter at the base of pharynx 27 µm.
Reproductive system diorchic, testes opposed. Anterior and posterior testes situated to the left of the intestine. Spicules equal in length, 34 µm long, arcuate and cephalated (1.6 abd). Gubernaculum tubular, corpus 13 µm long, with apophysis, and capitulum 5 µm long. At least four precloacal organs observed, with one seta in each. The two closest to the cloaca are more conspicuous and the others are tiny. The first precloacal organ lies 32 µm anterior to the cloaca and has a seta 3 µm long. The other precloacal organs are 93 µm, 120 µm and 202 µm from the cloaca, each one with a 3 µm long seta. Tail short and round, 29 µm long, without caudal capsule.
Female (paratype): Female larger (L = 3455 µm) but similar to male in general body shape. One posterior ovary located on the right side of intestine, antidromously reflexed. Vulval orifice ventral, located at 20% of body length. Uterus and oviduct 2675 µm long and the antidromously reflexed ovary 200 µm in length. Vagina short and not thickened.
Differential diagnosis. Litinium australis sp. n. is characterized by the first and the second crown of setae of differing lengths, rounded tail, gubernaculum with apophysis, and by the presence of four precloacal papillae.
Litinium australis sp. n. resembles, in the similar shape and length of the tail (short and rounded): L. aequale , L. curticauda , L. obtusilobus , L. profundum , L. quangi , L. volutum and the recently-transferred species L. egregius , L. paramontemari , L. pirum and L. setosus . L. australis differs from L. aequale , L. curticauda , L. profundum , L.
quangi , L. egregius , L. paramontemari and L. setosus in the number of precloacal organs. L. pirum and L. volutum have as many precloacal organs as L. australis , which differs from these species, and from L. obtusilobus , in amphid shape and size and in length of the inner and outer labial setae.
TABLE 1. Measurements (µm) of Litinium australis sp. n.
| Holotype | Paratype | Paratype | Paratype | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Male | Juvenile | |
| n | - | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| L | 2495.00 | 3455.00 | 2880.00 | 2935.00 |
| a | 95.96 | 90.92 | 102.86 | 97.83 |
| b | 7.92 | 8.97 | 6.62 | 7.62 |
| c | 86.03 | 107.97 | 99.31 | 91.72 |
| Anterior cephalic setae, length | 3.20 | 3.50 | 3.50 | 3.00 |
| Posterior cephalic setae, length | 4.00 | 3.50 | 4.50 | 3.50 |
| Sub-cephalic setae, length | 4.00 | 4.50 | 4.00 | 4.50 |
| Cephalic diameter | 8.00 | 8.50 | 8.50 | 8.00 |
| Cs% | 50.00 | 41.18 | 52.94 | 43.75 |
| Amphid from anterior end | 4.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 | not seen |
| External amphid width | 6.00 | 6.00 | 6.00 | - |
| External amphid length | 9.00 | 10.00 | 9.50 | - |
| Bd at amphid level | 11.00 | 10.00 | 11.00 | - |
| Amph% | 54.55 | 60.00 | 54.55 | - |
| Nerve ring from anterior end | 140.00 | 140.00 | 190.00 | 117.00 |
| Oesophageal bulb diameter | 18.00 | 31.20 | 28.00 | 23.00 |
| Bd at oesophageal bulb level | 27.50 | 37.00 | 34.50 | 29.00 |
| Pharynx length | 315.00 | 385.00 | 435.00 | 385.00 |
| Maximum body diameter | 26.00 | 38.00 | 28.00 | 30.00 |
| Anterior end to anus, distance | 2466.00 | 3423.00 | 2851.00 | 2903.00 |
| Anal body diameter | 21.00 | 28.00 | 23.00 | 25.00 |
| Tail length | 29.00 | 32.00 | 29.00 | 32.00 |
| c’ | 1.38 | 1.14 | 1.14 | 1.28 |
| Spicule length | 34.00 | - | 29.00 | - |
| Gubernaculum length | 13.00 | - | 12.00 | - |
| Vulva from anterior end | - | 700.00 | - | - |
| Vulva from anterior end/L (%) | - | 20.26 | - | - |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.