Sotolensis, Menard & Schwartz, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4514.2.11 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:B6E01410-4422-46FD-A08B-140A35341DA7 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5970265 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/17388790-FFDF-FFC9-C9D9-3FB9FCD6F9FD |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Sotolensis |
| status |
gen. nov. |
Sotolensis gen. nov.
( Figs 1–5 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 )
Type species: Sotolensis keltoni sp. nov.
DIAGNOSIS: Recognized by small size, large eyes with posterior margin overlapping anterior margin of pronotum, deep punctation on posterior margin of pronotum, weakly developed tubercle on dorso-lateral margin of gonopore in males, presence of a supragenital bridge, and presence of modified dorsal surface of ventral labiate plate forming spines in females.
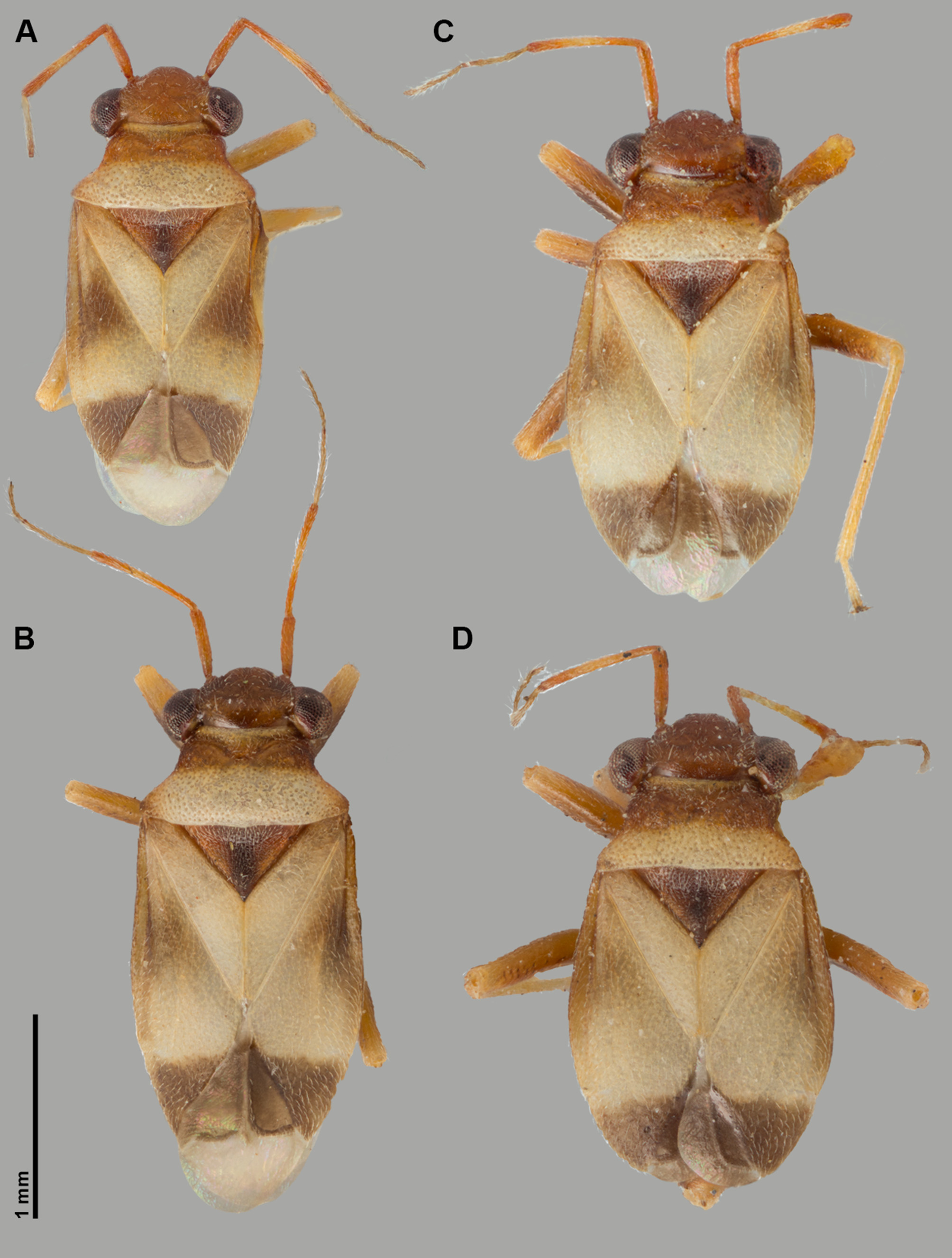
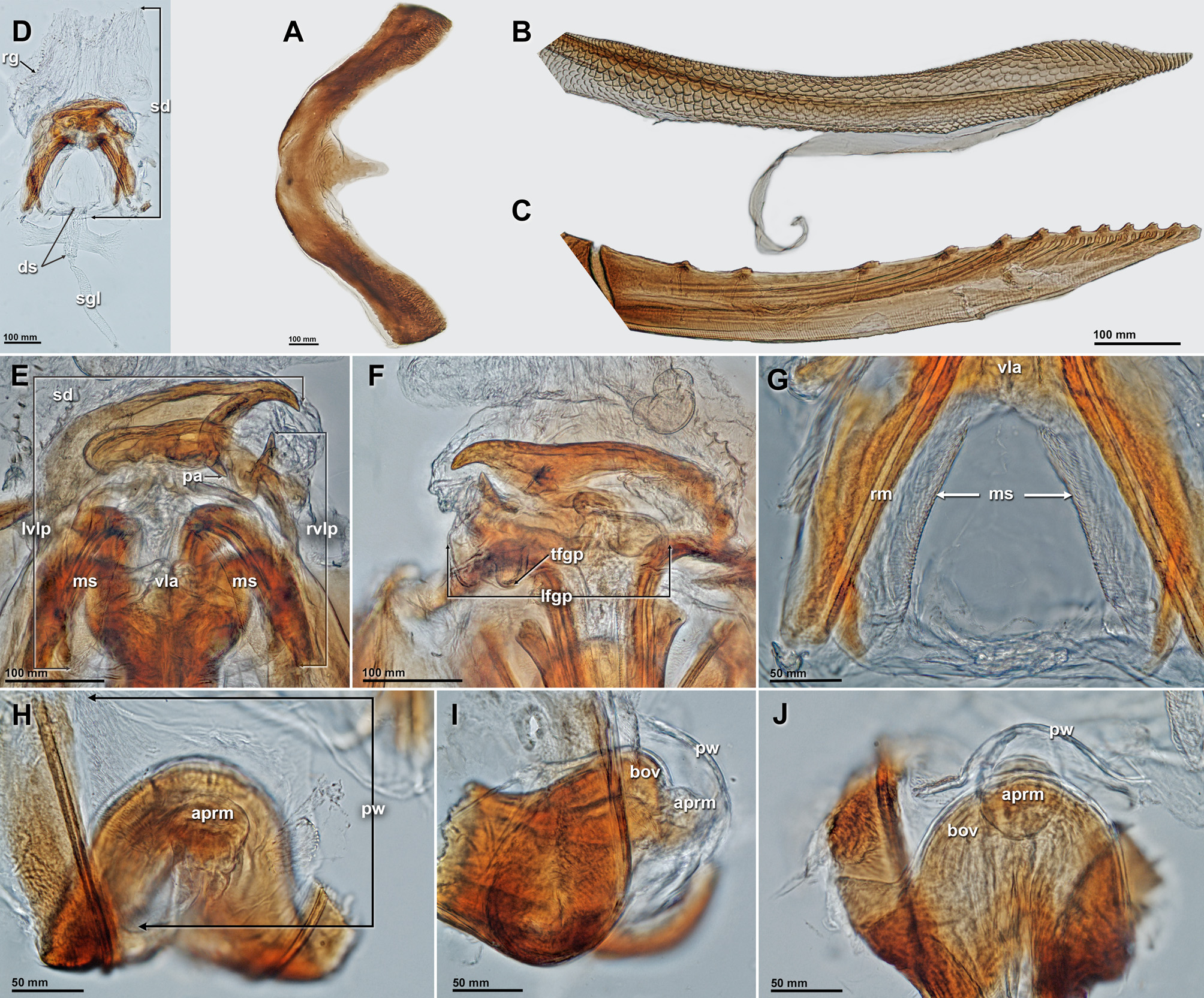
DESCRIPTION: MALE: COLORATION: Dorsum primarily castaneous with whitish-yellow and dark brown markings on pronotum and hemelytron, venter dark brown; clypeus and labrum brown ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 ); antennal segments I and II pale castaneous, segment II paler medially, or sometimes pale on apical one third; antennal segment III pale castaneous basally, dark castaneous distally; segment IV dark castaneous; pronotal collar yellowcastaneous, calli and area between calli dark castaneous, posterior lobe of pronotum cream, propleuron orangecastaneous; metepimeron pale brown to castaneous, remainder of thorax dark brown; mesoscutum and scutellum dark castaneous with dark longitudinal medial stripe; coxae and femora pale castaneous, tibiae yellow, tarsal segments pale yellow transitioning to dark brown towards claws; hemelytron primarily cream with anterior one third of clavus transitioning to darker brown, corium pale brown at base, dark brown medially, and approximately posterior one-third cream, costal margin primarily castaneous with posterior one-fourth lightening to cream, cuneus dark brown; membrane within cell dark brown, pale cream posteriad of cell, veins dark brown; pregenital abdominal segment dark brown. SURFACE AND VESTITURE: Head, pronotal collar, calli and anterior or pronotum smooth and weakly shiny; reminder of pronotum, scutellum and hemelytron matte; thoracic pleura and abdomen shiny, smooth to weakly rugose; head, pronotum, except anterior margin of collar, mesoscutum, scutellum, and base of clavus punctate; each puncture bearing a recessed seta. Dorsum and appendages with dense, relatively short, semi-adpressed pale simple setae ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ); thoracic pleura with a few similar setae; abdomen with dense simple setae; tibial spines absent, tibiae with dense pale simple setae only. STRUCTURE: Body short and parallel sided, macropterous. Head: ( Figs 2 View FIGURE 2 A–D) Comparatively large compared with body, nearly as long as wide and high, almost triangular in frontal view, clypeus and frons anterior to eyes prominent in lateral view; vertex broad and weakly convex; frons strongly convex; clypeus prominent, oriented ventroposteriorly, clearly differentiated from mandibular plates and labrum; mandibular plate broadly triangular; maxillary plate rectangular, twice as long as high; buccula short, merging behind base of labium; gula reduced, one half length of buccula; eyes small, less than half height of head in lateral view, not stylate, posterior margins projecting beyond collar and anterolateral margins of pronotum; antennal fossa located slightly above ventral margin of eye; antennal segment I thickest segment, narrowing just at joint with antennal fossa; antennal segment II thin with width increasing distally to match approximate width of first; segments III and IV filiform; labium thick, reaching to base of abdomen, segment IV short, nearly twice as long as broad at base, apically blunt. Thorax: ( Figs 2A, B View FIGURE 2 ) Pronotum trapeziform, lateral margins strongly concave, posterior angles rounded, posterior margin weakly convex; pronotal collar demarcated by flat surface anteriad of calli, nonpunctate portion of collar short and narrow, width approximately equal to diameter of antennal segments III or IV; calli weakly raised, not touching medially; posterior lobe of pronotal disc only slightly raised; peritreme of metathoracic scent-gland lanceolate, extended posteriorly along ventral margin of metapleuron; evaporative area reduced to narrow falciform area along dorsal margin of peritreme, with scalloped surface devoid of characteristic mushroom bodies ( Fig. 3B View FIGURE 3 ); separation between mesoscutum and scutellum denoted by short suture on extreme lateral margin; scutellum weakly bulbous at apex, somewhat depressed in middle. Legs: All femora comparatively short, cylindrical, hind femur not swollen; tibiae straight and rather short; hind femora with trichobothria (tb) deeply recessed, tuberculate and trichoma well developed ( Fig. 3C View FIGURE 3 ); tarsus three segmented, segments I–III almost equal in length, combined II and III slightly fusiform ( Fig 2D View FIGURE 2 ), III with long guard setae. Pretarsus: ( Figs 3D, E View FIGURE 3 ) Claw falcate, strongly and gradually curved (cl); inner surface of claw with large subquadrate pulvillus (pul), ventral surface with fringe of very small trichia; pulvillar comb of 5 relatively large trichia behind each pulvillus (pulcmb); parempodia asymmetrical, with outer parempodium reduced, shorter than inner (par) [of 9 pretarsi examined with SEM, all apices broken]. Hemelytron: Opaque, corium with nearly straight lateral margin, R+M vein weakly demarcated and terminating at approximate median of corium; costal vein indented at basal one-half of length; cuneus as long as wide; membrane with single cell not surpassing apex of cuneus. GENITALIA: Pygophore: Comparatively large, about half of abdomen, short, about twice as wide as long, with base partly retracted into abdominal segment VIII ( Fig. 3F View FIGURE 3 ); dorsal wall straight, with quadrate tergal process on posterior edge of aperture ( Fig. 4B View FIGURE 4 ); ventral wall strongly sloping and extending caudally; subgenital plate with internal process protruding medial to right paramere insertion ( Fig. 4B View FIGURE 4 ); left lateral margin of pygophore opening with weakly developed tubercle; supragenital bridge present ( Fig. 4B View FIGURE 4 ); aperture of genital capsule wide; plane of phallic structures turned slightly more than 20°. Parameres: Left paramere: Small, weakly scythe-shaped ( Figs 3E, F View FIGURE 3 , 4E View FIGURE 4 ). Right paramere: Large, long, L-shaped with the apex hook-like ( Figs 3E, F View FIGURE 3 , 4C, D View FIGURE 4 ), in repose placed behind tubercle of pygophore ( Fig 3E View FIGURE 3 ). Aedeagus: Small and simple; eversible, projecting ventrad through supragenital bridge. Phallobase: With well-developed capitate processes ( Fig 4F, G View FIGURE 4 ). Phallotheca: Dorsal and ventral walls sclerotized, ventral wall expanded apically, approximately twice as long as dorsal wall ( Fig 4G, H View FIGURE 4 ). Ductus seminis: Attached to middle of phallobase, proximal one third with rings, distal two thirds sclerotized, narrow, approximately as long as ventral wall of phallotheca, base swollen, apical portion needlelike, enclosed in thin transparent membrane projecting free of main endosomal membrane ( Fig 4 View FIGURE 4 F–H; mds); opening of secondary gonopore simple, without ring-like structure ( Fig 4G, H View FIGURE 4 ; 2 View FIGURE 2 °gp). Endosoma: (or vesica sensu Konstantinov 2000) Small, wrinkled, predominately membranous with apex sclerotized, cap-like ( Fig 4 View FIGURE 4 F–H; mpes).
FEMALE: COLORATION: Specimens with reduced membrane without dark median patch of coloration on corium. SURFACE AND VESTITURE: As in male. STRUCTURE: Hemelytron with varying degrees of wing membrane reduction and shortening of the cuneus ( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 B–D). GENITALIA: Posterior margin of sternite 7: With broad triangular projection, reaching posteriad one-half length of lateral margins ( Fig 5A View FIGURE 5 ). Dorsal wall of genital chamber: Dorsal sac: Membranous, small, pediculate, located posteriorly; anterior margin terminates even with posterior end of ventral labiate plates. Dorsal labiate plate and sclerotized rings absent. Lateral oviducts: Short, attached contiguously. Spermathecal gland: Attached posteriad of oviducts. Seminal depository: Posterior margin begins level with posterolateral margins of ventral labiate plate, continues anteriorly as thin clear membranous bag spanning length and width of sclerotized portion of bursa copulatrix, extending anteriorly for length equal to length of bursa copulatrix as slightly thicker winkled sac; lateral surface of anterior portion of seminal depository with two large thin rings with wavy border ( Fig 5D View FIGURE 5 ). Vestibular sclerites: Formed by strongly sclerotized, asymmetrical left and right sides of ventral labiate plate ( Fig 5E View FIGURE 5 ) and base of left first gonapophysis ( Fig 5F View FIGURE 5 ); apical portion of left ventral labiate plate with spinelike anterior and posterior apices; right ventral labiate plate with spinelike apex; base of left first gonapophysis with ventroposterior tubercle. Medial surface of rami membranous, extending ventroanteriad and forming thickened membranous border of vulva ( Fig 5G View FIGURE 5 ). Posterior wall: Membranous without interramal lobes or sclerites; covering anterior surface of ovipositor base and large sclerotized prominence on anterior surface of ovipositor base ( Fig 5 View FIGURE 5 H–J). Gonapophyses: First: Gradually tapering, with outer surface clothed with dense minute teeth. Second: Apically twisted, with peculiar row of large teeth on inner surface and finely dentate outer surface ( Fig 5B, C View FIGURE 5 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.