Hylekobolus rufus Wesener, 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.3897/zookeys.19.221 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C473F9F6-1AE7-4B3F-B17F-CA1C2709010C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3791463 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/DA4510C8-7395-4FC6-B2E5-4FD125250FB4 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:DA4510C8-7395-4FC6-B2E5-4FD125250FB4 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Hylekobolus rufus Wesener |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Hylekobolus rufus Wesener View in CoL , sp. n.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:DA4510C8-7395-4FC6-B2E5-4FD125250FB4
Material examined: 14 ♂, 8 ♀, 1 imm. Holotype: 1 ♂ (60 mm long), FMMC 8188 , Province Fianarantsoa, PN Midongy, Mt. Papango , 3.5 km SW Befotaka, rainforest, 1250 m, 23°50.3’ S, 46°57.5’ E, leg. S. Goodman, 2–7.XI.1997 GoogleMaps . Paratype: 1 ♀, FMMC 8188 , same data as holotype GoogleMaps ; 1 ♂, 1 imm., FMMC 6172 , Province Fianarantsoa, PN Midongy, Mt. Papango , 2.5 km SW Befotaka, rainforest, 875 m, 23°50.1’S, 46°57.8’E, leg. S. Goodman, 26–31.X.2003, pitfall trap GoogleMaps .
Other material examined: 2 ♂, 1 ♀, FMMC W092 , Province Toliara, Vohimena Eastern Slope, Enato , rainforest, 24°53’0.25” S, 46°59’2.77” E, leg. T. Wesener et al., 27.V.2007 GoogleMaps ; 2 ♂, MNHN, Province Fianarantsoa, Tolongoina, route d’Ifanadiana , Fort Carnot , 21°33’ S, 47°31’ E, Rec. Blanc, 18.V.1964 GoogleMaps ; 1 ♂, MNHN, Province Fianarantsoa, Befotaka (p. de Farafangana), 600 m, Région montagneuse boisée, 23°49’ S, 46°59’ E, leg. entrée 17–1927, R. Decary, 10.VIII.1926 GoogleMaps ; 7 ♂, 6 ♀, CAS NoNumber, Province Fianarantsoa, PN Ranomafana , Talatakely , 21°14.9’ S, 47°25.6’ E, leg. C. Griswold et al., 19–30.IV.1998 GoogleMaps .
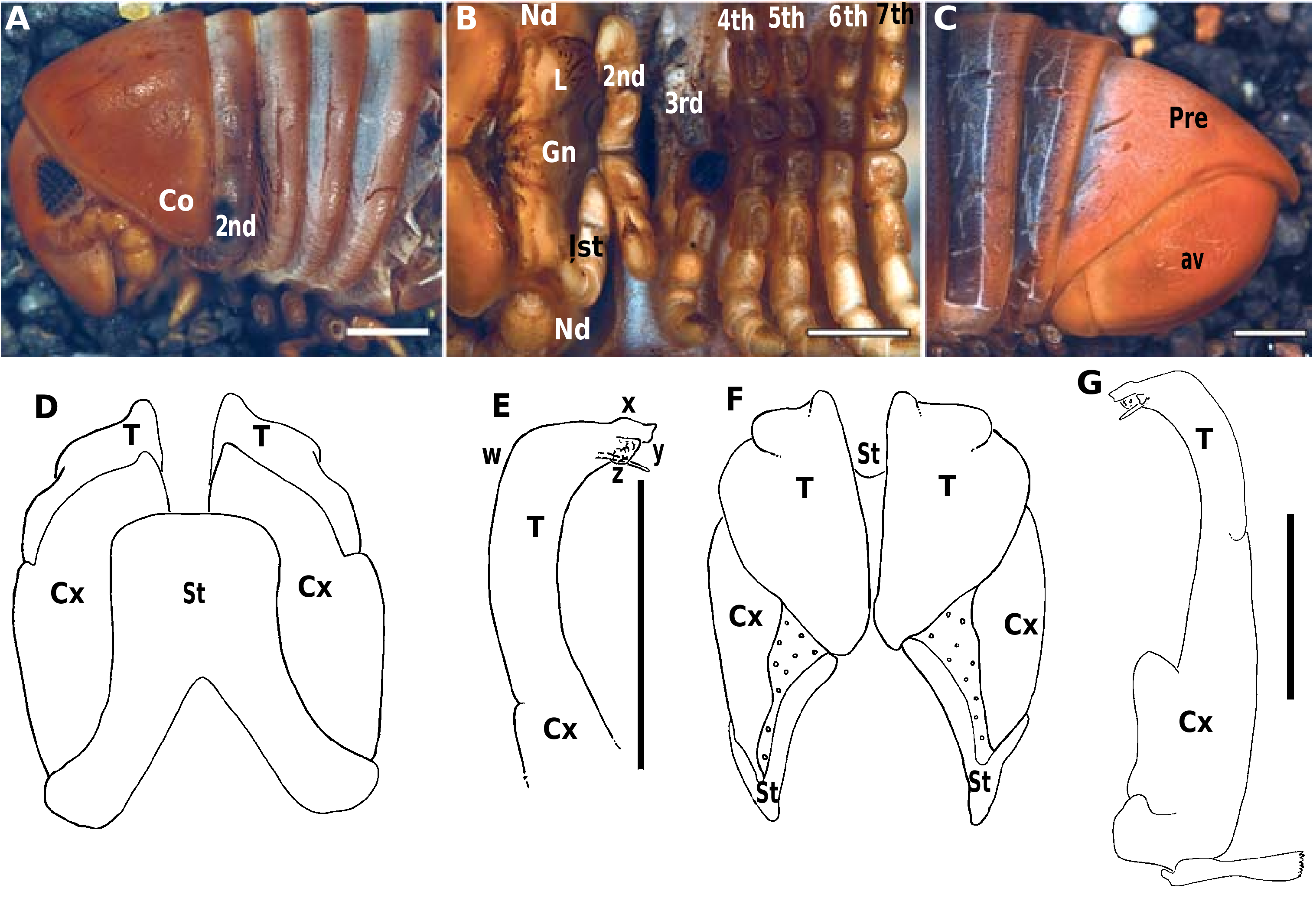
Differential diagnosis: H. rufus differs from all other Hylekobolus species in a unique combination of characters: collum red ( Fig. 56A View Figure 56 ), posterior gonopod at lateral margin (w) lacking projection, apical process (x) wide ( Fig. 56E View Figure 56 ).
Description. Measurements: males with 50–52 rings, 55–65 mm long, 4.1–4.8 mm wide. Females with 50 or 51 rings, circa 63 mm long, 5.7 mm wide.
Coloration in numerous samples affected by alcohol. Head, collum, antennae, legs, metazonites of body rings and posterior part of telson including anal valves and subanal scale red ( Figs 56A, C View Figure 56 ). Anterior part of body rings and telson dark grey ( Figs 56A, C View Figure 56 ). Eyes with 32–34 ocelli ( Fig. 56A View Figure 56 ).
Anterior gonopod sternite basally wide, completely rectangular, apically even slightly wider than basally ( Fig. 56D View Figure 56 ). Mesal process of coxite wide and only slightly protruding ( Fig. 56D View Figure 56 ). Apical process of telopodite large and well-rounded. Retrorse margin wide, projecting above telopodite margin ( Fig. 56F View Figure 56 ) but not protruding basally of apical process ( Fig. 56F View Figure 56 ).
Posterior gonopods telopodite bent 90° ( Fig. 56G View Figure 56 ). Lateral margin without a projection (w, Fig. 56E View Figure 56 ). Apical process (x) wide ( Fig. 56E View Figure 56 ). Membranous lobe (y) large and
rectangular ( Fig. 56E View Figure 56 ). In posterior view, an additional small, sclerotized lobe present apically of membranous lobe ( Fig. 56G View Figure 56 ). Projection of sperm canal (z) straight, as long as apical process ( Fig. 56G View Figure 56 ).
Distribution and ecology: H. rufus is the Hylekobolus species with the largest area of distribution. It occurs in Southeastern Madagascar from the eastern slopes of the Vohimena range, Midousy Mountains up to Tolongoina ( Fig. 54 View Figure 54 ).
Etymology: rufus , adjective, refers to the reddish colour pattern ( Fig. 56A View Figure 56 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |