Stammericaris vincentimariae Bruno & Cottarelli, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2020.689 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:4E8B68C9-4F9F-4244-9A2C-192046753782 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4327931 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/AD8C5160-A007-4D29-974F-12925EAD0CA7 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:AD8C5160-A007-4D29-974F-12925EAD0CA7 |
|
treatment provided by |
Valdenar |
|
scientific name |
Stammericaris vincentimariae Bruno & Cottarelli |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Stammericaris vincentimariae Bruno & Cottarelli sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:AD8C5160-A007-4D29-974F-12925EAD0CA7
Figs 9–11 View Fig View Fig View Fig , 12a View Fig ; Tables 1–3 View Table 1
Diagnosis
Stammericaris vincentimariae Bruno & Cottarelli sp. nov. is characterized in males primarily by the presence of one seta on the 7 th antennular segment and by the morphology of the P4: the innermost spinule of the basis inner row is inserted transversally instead of longitudinally; the enp curved plate tip is bifid instead of pointy and the distal outgrowth is flattened instead of being a seta. Females are characterized by the enp P3 much shorter than half of the first corresponding exp-1. Both sexes are characterized by caudal rami with a strong apical pointed apophysis.
Etymology
The species epithet is the genitive of the Latin first names Vincentius and Maria (Vincent and Mary in English), the names of the son and daughter of one of the authors (RG), in recognition of the great
interest shown to speleology from their childhood onward and for participating in some of the collection campaigns.
Material examined
Holotype
ITALY • ♂; Cosenza Province, Cassano allo Ionio , Grotta dello Scoglio , pool 1; approximate coordinates 39°47′9.38ʺ N, 16°18′31.89ʺ E; 25 Apr. 2015; R. Grasso and M.T. Spena leg.; dissected and mounted on one slide labelled “ Stammericaris vincentimariae holotype: male”; NHMUK 2020.33 View Materials . GoogleMaps
Paratypes
ITALY • 2 ♂♂; same collection data as for holotype but pool 2; each dissected and mounted on one slide labelled “ Stammericaris vincentimariae paratype: male”; NHMUK 2020.34 View Materials to 2020.35 View Materials GoogleMaps • 1 ♂; same collection data as for preceding; dissected and mounted on one slide labelled “ Stammericaris vincentimariae paratype: male”; NHMUK 2020.36 View Materials GoogleMaps • 3 ♂♂; same collection data as for holotype; each dissected and mounted on one slide labelled “ Stammericaris vincentimariae paratype: male”; NHMUK 2020.37 View Materials to 2020.39 View Materials GoogleMaps • 1 ♀; same collection data as for holotype; dissected and mounted on one slide labelled “ Stammericaris vincentimariae paratype: female”; NHMUK 2020.40 View Materials GoogleMaps .
Description
Adult male
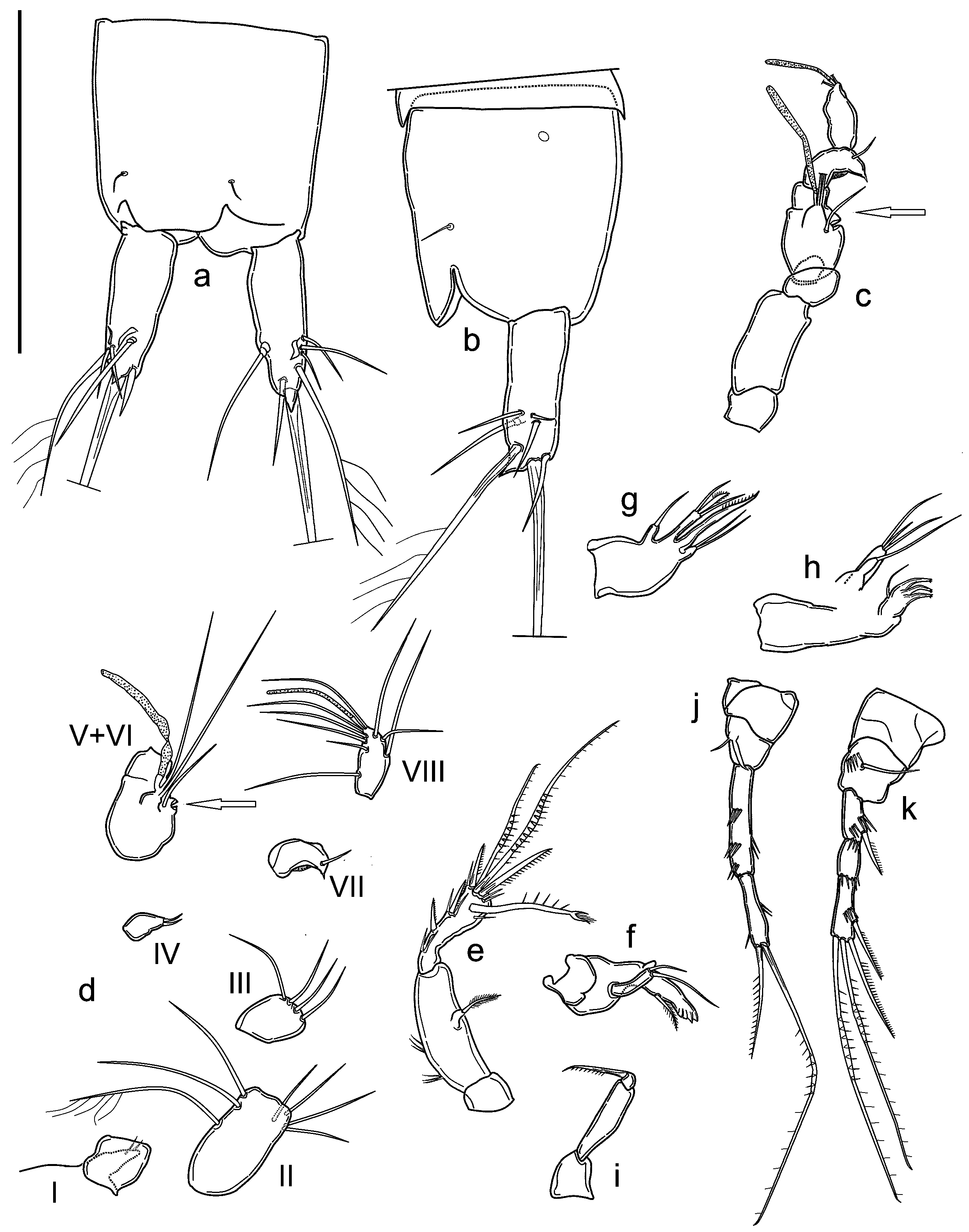
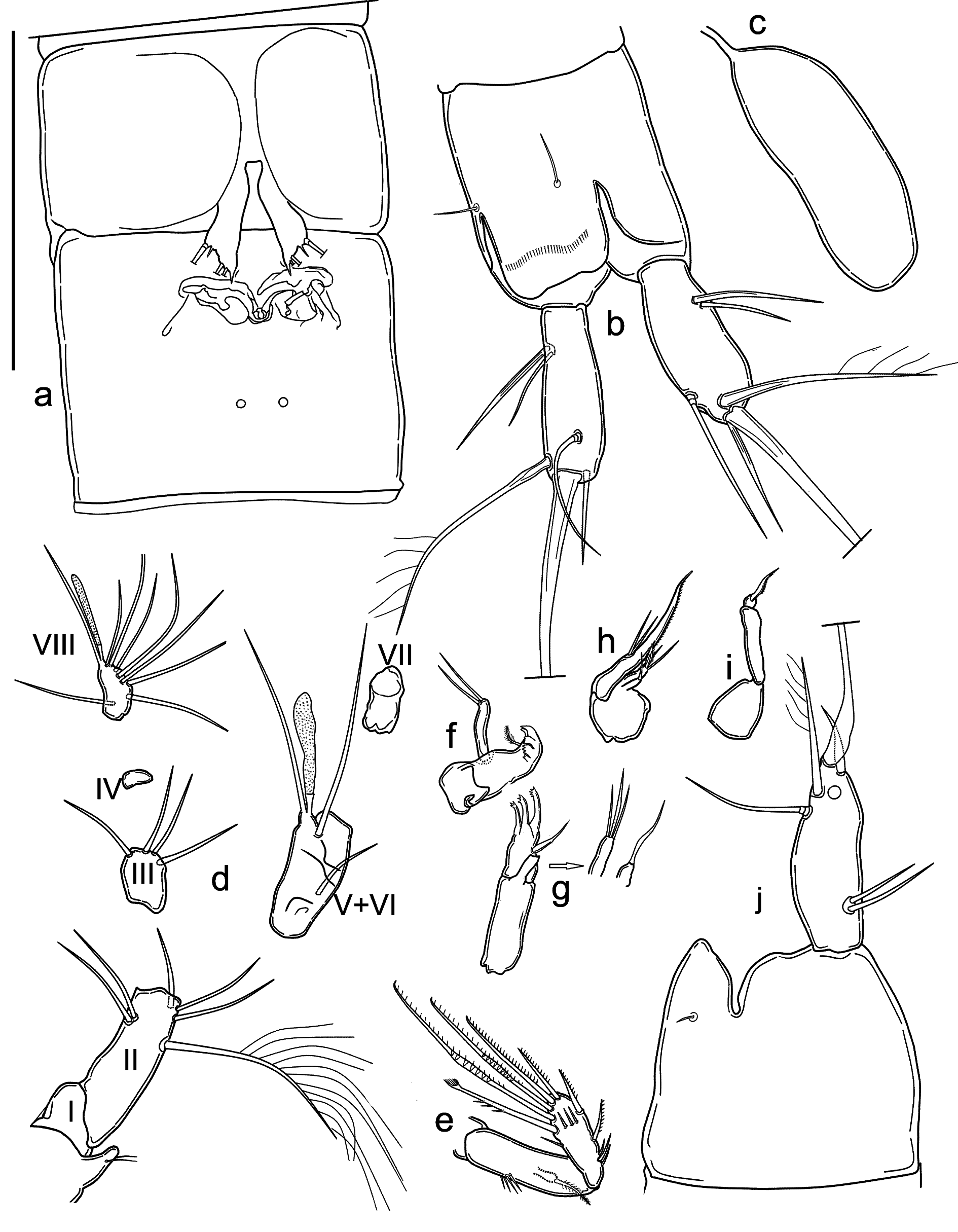
BODY. Unpigmented, nauplius eye absent. Total body length, measured from tip of rostrum to posterior margin of caudal rami (excluding caudal setae) from 295 to 334 µm, mean 310 μm (n = 5). Habitus cylindrical and slender, without any demarcation between prosome and urosome; prosome to urosome ratio: 0.80. Free pedigerous somites without any lateral or dorsal expansions, all connected by welldeveloped arthrodial membranes. Integument weakly sclerotized, without cuticular pits, ornamented with sensilla on all somites except preanal one. Cuticular windows on urosomites ( Figs 10j View Fig , 11a View Fig ) and cephalothorax not visible. Cephalothorax representing about 18 % of total body length. Anal somite ( Fig. 9 View Fig a–b) with pair of large dorsal sensilla at base of anal operculum, pair of cuticular lateral pores (one pore on each side) on proximal margin. Anal operculum ( Fig. 9 View Fig a–b) well developed, with straight distal margin. Anal sinus wide open. Spermatophore as in Fig. 10j View Fig .
CAUDAL RAMI ( Fig. 9 View Fig a–b). Shorter than anal somite, approximately cylindrical, with strong dorsal pointed apophysis, length to width ratio: 2.7. Anterolateral accessory seta (I) and anterolateral seta (III) subequal in length, posterolateral seta (III) short, all setae inserted together distally at ¾ length of caudal ramus. Outer terminal seta (IV) long and pinnate (length seta/length caudal ramus: 1.4), inserted subterminally; inner terminal seta (V) without fracture plane. Terminal accessory seta (VI) short (length seta/length caudal ramus: 0.6) and smooth. Dorsal seta (VII) articulate, inserted distally at ¾ length of the caudal ramus.
ROSTRUM ( Fig. 9d View Fig ). Small, not demarcated at base, almost reaching distal margin of first antennulary segment, ornamented with two dorsal sensilla.
A1 ( Fig. 9 View Fig c–d). Prehensile, eight-segmented, pocket-knife type sensu Schminke (2010). First segment short; second segment longest, with seven setae, the longest seta unipinnate; third segment with four distal bare setae; fourth segment reduced to small sclerite with two short setae; fifth segment enlarged with inner round expansion with deep incision (arrowed in Fig. 9 View Fig c–d) and one seta at base of distal tubercle with two long subequal setae and one large aesthetasc, reaching past end of eighth segment. Sixth segment bare, partially fused to previous one. Seventh segment with one small seta, distal anterior corner protruding as curved apophysis ending in tip. Eighth segment with seven setae and apical acrothek represented by two setae and slender long aesthetasc. Armature formula: 1-[0], 2-[1 uniplumose + 6 bare], 3-[4 bare], 4-[2 bare], 5-[3 bare + ae], 6-[0], 7-[1 bare], 8-[7 bare + (2 bare + ae)].
A2 ( Fig. 9e View Fig ). Coxa unarmed; allobasis with two transverse row of spinules on inner margin. Exp represented by small segment merged with allobasis, with bipinnate apical seta. Enp bearing two spines along inner margin, one short subdistal inner spine, one subdistal outer transformed seta, two geniculate setae and one spine apically, all spines unipinnate, all elements with long spinules near their insertions except proximalmost inner spines.
MDB ( Fig. 9f View Fig ). Coxal gnathobase with lateral pinnate short seta, cutting edge with apical teeth. Onesegmented palp, with two distal setae of different length.
MX 1 ( Fig. 9h View Fig ). Praecoxal arthrite with three apical curved robust spines apically denticled, one subdistal curved seta. Coxal endite long, with one apical seta. Basis cylindrical, with three distal bare setae. Enp and exp absent (fused to basis without trace).
MX 2 ( Fig. 9g View Fig ). Basis with two endites, proximal endite short, with one thin, bare seta; distal endite cylindrical, longer, armed apically with two subequal thin bare setae and one transformed, leaf-like pinnate seta; proximal endopodal segment drawn into apical unipinnate claw; distal endopodal segment with two long setae of equal length.
MXP ( Fig. 9i View Fig ). Subchelate, composed of small and unarmed syncoxa, basis slim and elongate, unarmed, 1-segmented enp fused to claw-like apical seta.
P1 ( Fig. 9 View Fig j–k). With smooth and small intercoxal sclerite; coxa bare. Basis large, armed with single slender seta on outer margin, and small seta and lamellar hook on inner margin of basis near enp insertion. Exp three-segmented, slightly shorter than enp; exp-1 with thin unipinnate spine on outer distal corner; exp-2 shortest and unarmed; exp-3 with two geniculate and one normal unipinnate apical setae, and one subapical unipinnate spine. Enp two-segmented; enp-1 longer than first two segments of corresponding exp, with one transversal row of spinules on outer margin, and three on inner margin. Enp-2 thinner and shorter than enp-1, with two spinules at ¼ of inner margin; long, geniculate unipinnate seta, and shorter unipinnate seta on apex.
P2 ( Fig. 10a View Fig ). With smooth and small intercoxal sclerite, three times as wide as long, with slightly concave distal margin. Coxa bare. Basis unarmed, with row of four spinules on outer margin. Exp three-segmented, exp-1 longest, with three transversal rows of spinules and transversal row of spinules proximal to strong distolateral bipinnate spine. Second and third segments of same length, exp-2 unarmed, with distal row of spinules; exp-3 armed with subapical outer unipinnate spine, apical bipinnate seta and unipinnate spine, ornamented with outer subapical spinules, distal row of spinules, and inner hyaline frill. Enp one-segmented, slightly longer than half length of corresponding exp-1, but reaching approximately to half length of exp-1, cylindrical, with subapical seta about as long as segment and three short apical spinules.
P3 ( Fig. 10 View Fig b–c). Intercoxal sclerite narrow and tall, trapezoidal, unornamented, with slightly concave distal margin. Coxa with two outer spinular rows. Basis robust, with long, slender, smooth outer seta and transverse spinule row above. Enp reduced to short seta. Exp-1 outer margin with one proximal group of two spinules, distal group of two large and two smaller spinules (almost divided into two groups). Exp-2 fused with exp-1, without ornamentation, prolonged into long apophysis slightly bent inwards, with pointed tip surrounded by hyaline membrane (arrowed in Fig. 10b View Fig ). Distal thumb represented by thin and pointed segment, shorter than apophysis.
P4 ( Fig. 10 View Fig g–h). Intercoxal sclerite smaller than in P1 or P2, with concave, smooth distal margin. Coxa with spinular row on outer margin. Basis armed with single slender seta on outer margin; ornamented with row of spinules at base of outer seta and pore. Row of three spinules of increasing size, slightly curved inwards aligned along inner margin, smaller one close to enp; one spiniform process on inner margin projecting inwards. Exp three-segmented, slender, all segments approximately of the same length; exp-1 with distolateral unipinnate spine; with transversal row of two spinules at ¼ of outer margin and below distolateral spine insertion, spinular row along distal margin; exp-2 unarmed, with spinular row along distal margin and two spinules at outer distal corner; exp-3 armed with outer unipinnate spine and long apical unipinnate seta, spine length less than ½ of seta length; ornamentation represented by row of apical spinules, row of spinules along distal outer margine, inner hyaline frill. Enp one-segmented and as long as first two segments of corresponding exp, represented by curved plate with bifid tip, carrying at outer border two outgrowths, distal one being long denticled lamella and proximal one plain small spiniform outgrowth.
P5 ( Figs 10 View Fig i–j, 11a). Fused to intercoxal sclerite; represented by two trapezoidal cuticular plates with long basipodal seta. Armature on free distal margin, from inner to outer: one spiniform process, three bare setae, outermost very short, remaining two subequal.
P6 ( Figs 10j View Fig , 11a View Fig ). Vestigial, fused into simple cuticular plate, unornamented and unarmed.
Adult female
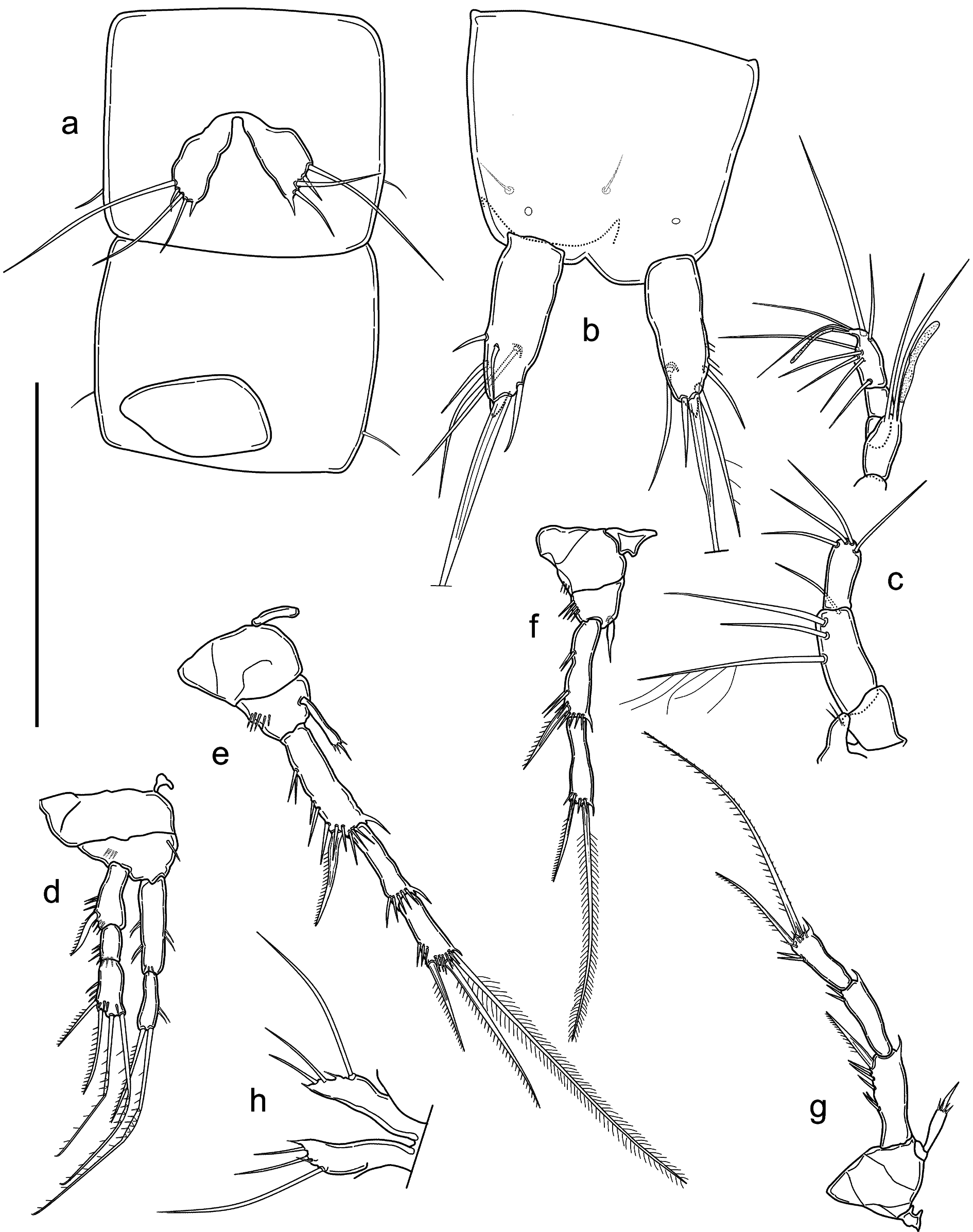
HABITUS. Cylindrical and slender, without any demarcation between prosome and urosome. Free pedigerous somites without any lateral or dorsal expansions, all connected by well-developed arthrodial membranes. Integument weakly sclerotized, without cuticular pits, ornamented with sensilla on all somites except preanal one. Cuticular windows on urosomites and cephalothorax not visible. Body length, excluding caudal setae, from 290 to 340 μm, mean 314 μm (n = 5), ornamentation of cephalothorax, somites, pigmentation and absence of nauplius eye as in male, except genital and first urosomite fused into double-somite. Cephalotorax representing about 19% of total body length. Prosome/urosome ratio: 0.80. Genital double-somite ( Fig. 12a View Fig ) without any trace of subdivision. Genital field ( Fig. 12a View Fig ) broader than tall, occupying anterior ventral ¼ of genital double-somite, with pair of ventrodistal pores; single genital aperture covered by fused vestigial sixth legs; median copulatory pore located medially at ¼ of double-somite length. Anal operculum and anal sinus ( Fig. 11b View Fig ) as in male.
CAUDAL RAMI ( Fig. 11b View Fig ). Shape, ornamentation and armature similar to those of male, length/width ratio: 3.3.
ROSTRUM, A2 AND ORAL APPENDAGES. As in male.
A1 ( Fig. 11c View Fig ). Seven-segmented, aesthetasc on fourth segment shorter than in male, reaching below end of seventh segment. First segment bare. Second segment longest. Apical acrothek represented by two setae of subequal length and slender aesthetasc. Armature formula: 1-[0], 2-[1 pinnate + 3 bare], 3-[4 bare], 4-[2 bare + ae], 5-[0], 6-[0], 7-[7 bare + (2 bare + ae)].
P1 ( Fig. 11d View Fig ). Intercoxal sclerite, coxa, basis ornamentation as in male, but with inner spiniform seta (lamellar hook missing), outer seta missing; exp and enp similar to those of male in shape, ornamentation and armature.
P2 ( Fig. 11e View Fig ). Intercoxal sclerite, coxa, basis and exp as in male. Enp similar in shape and ornamentation to that of male, but subapical seta shorter.
P3 ( Fig. 11f View Fig ). Intercoxal sclerite small, trapezoidal, with concave margin, bare. Coxa with outer spinular row. Basis with outer spinular row; exp two-segmented: exp-1 slightly longer than exp-2, with distolateral curved unipinnate spine, transversal row of spinules at ¼ and ¼ of outer margin, distal spinular row, hyaline frill on inner distal corner; exp-2 with subapical outer unipinnate spine and apical bipinnate seta, spine length about ¼ of seta, with distal spinular row and hyaline frill on inner distal corner. Enp represented by thin and pointed segment, much shorter than half of corresponding exp-1.
P4 ( Fig. 11g View Fig ). Intercoxal sclerite, coxa and exp as in male. Basis bare. Enp represented by thin cylindrical segment, slightly shorter than ½ the length of corresponding exp-1, ending in spiniform seta with spinules around the insertion.
P5 ( Figs 11h View Fig , 12a View Fig ). Fused to intercoxal sclerite, represented by cuticular plate more elongated than in male, with inner spiniform process shorter than in male, outer short setae transformed in spiniform process, remaining ornamentation represented by two setae, innermost shortest and long basipodal seta.
P6 ( Fig. 12a View Fig ). Vestigial, fused into simple cuticular plate, covering gonopore, unornamented and unarmed.
Variability
One male specimen with a distal row of three spinules on the outer margin of P3–Exp-1 ( Fig. 10d View Fig ). A second specimen with three spinules on one P3 ( Fig. 10e View Fig ) and one spinule on the other P3 ( Fig. 10f View Fig ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |