Bakerdania tadjikistanica, Khaoustov & Homidov, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.22073/pja.v12i4.81979 |
|
publication LSID |
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A5A18372-BF57-4C63-9863-4A6904486AAA |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10943893 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/184A87F6-FFD3-0B41-42E6-FCD3D1BDFE82 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Bakerdania tadjikistanica |
| status |
sp. nov. |
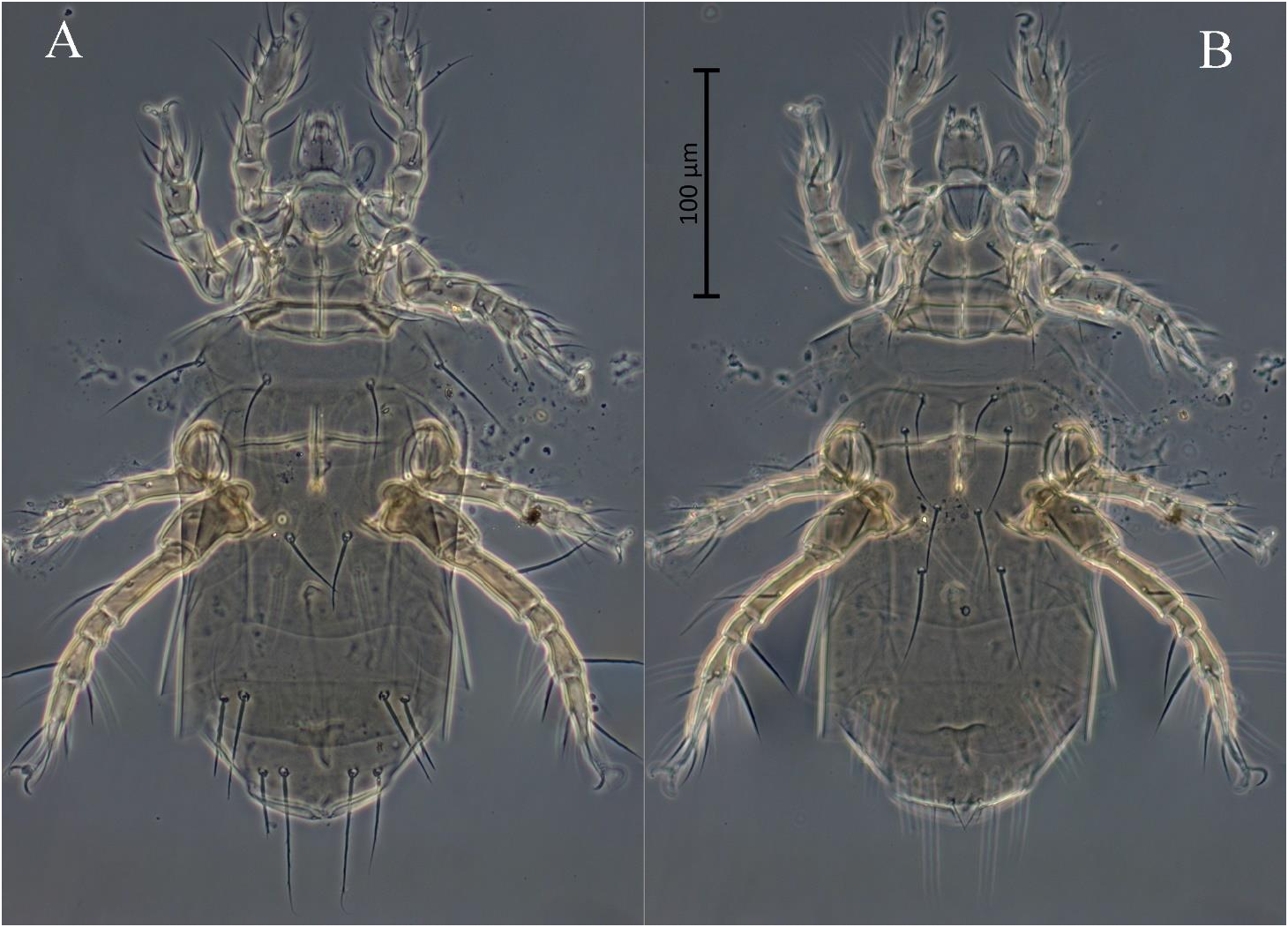
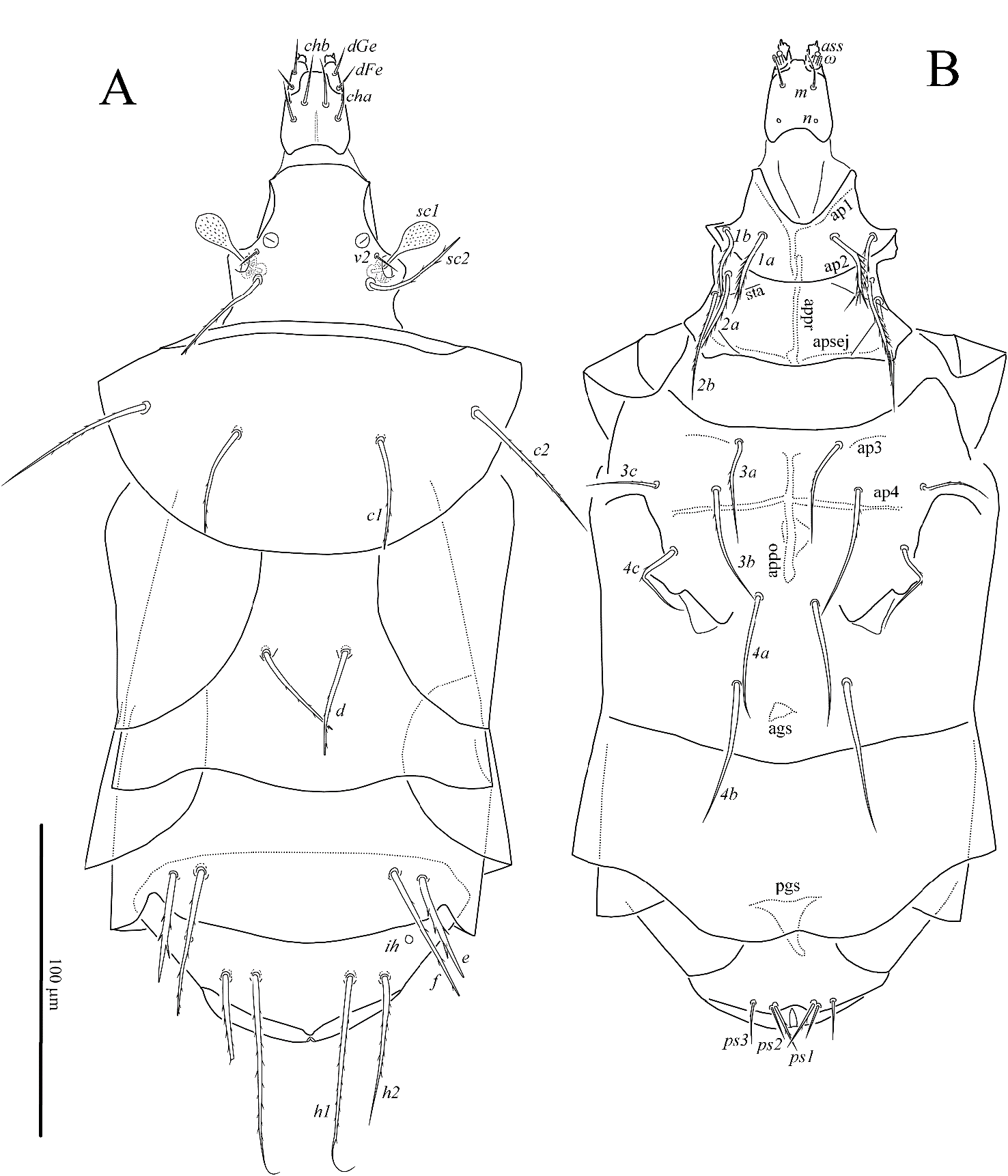
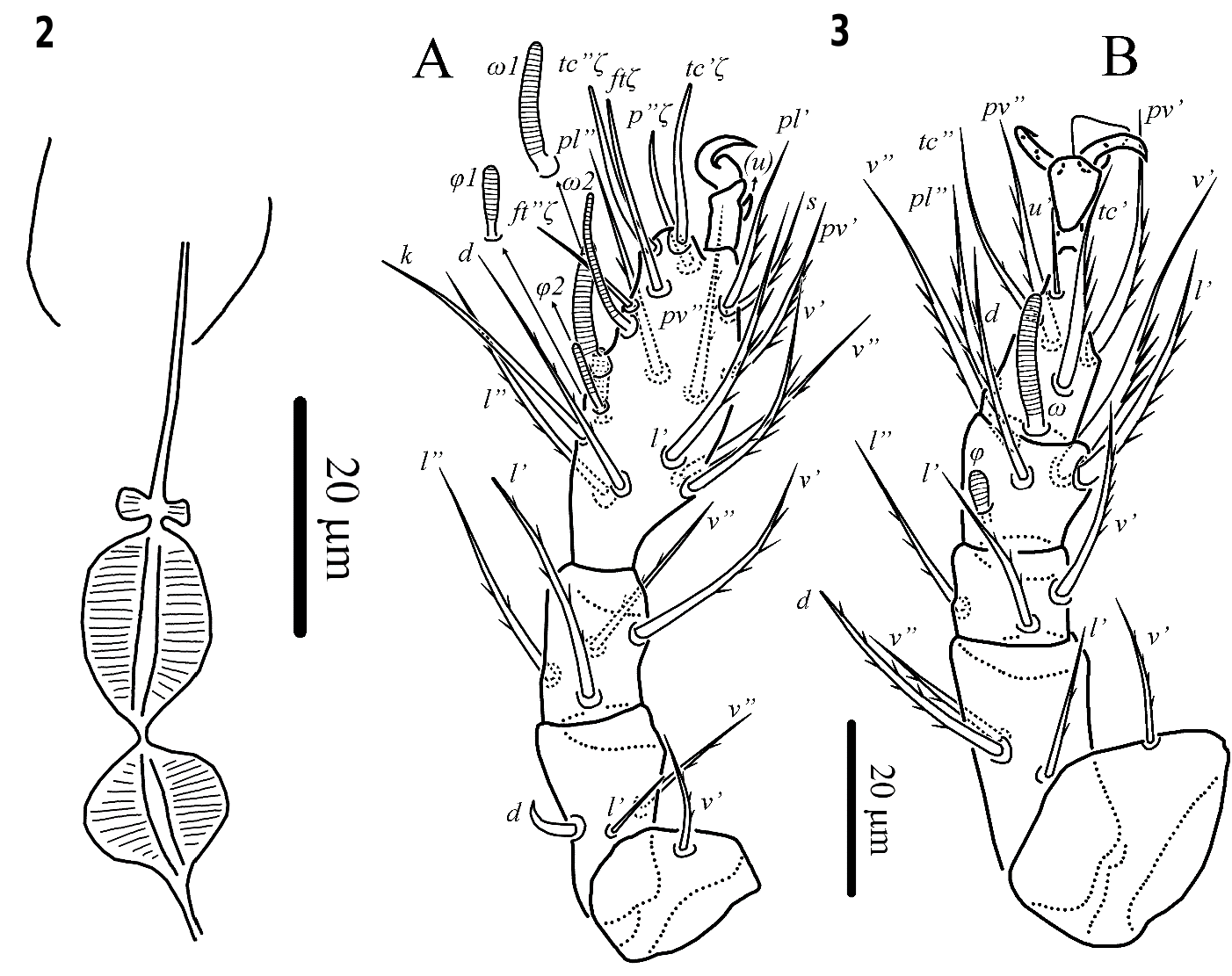
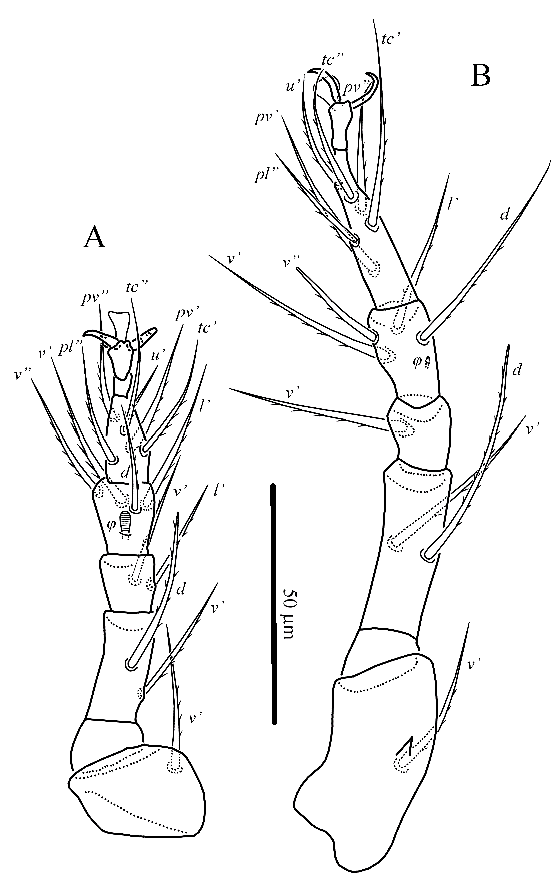
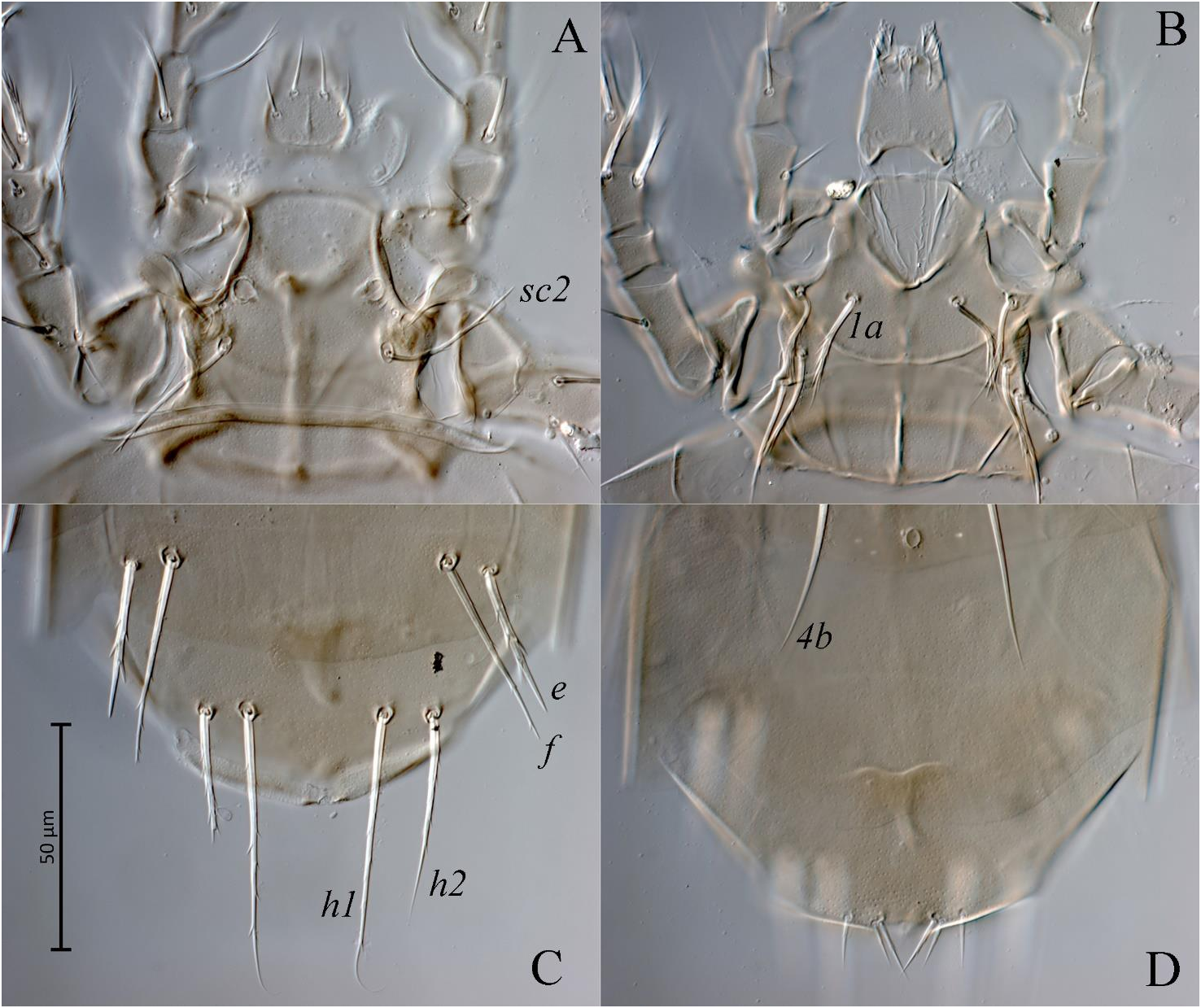
Bakerdania tadjikistanica sp. nov. ( Figs. 1–6 View Figure 1 View Figures 2–3 View Figure 4 View Figure 5 View Figure 6 )
http://zoobank.org/ urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:
Diagnosis
Pretarsus IV short; claws on tarsi III and IV subequal in length. Setae sc2, c1, d, e, and f blunt-tipped, other dorsal setae pointed; setae e slightly thickened, with several strong blunt barbs. Setae h1 distinctly longer than f. Setae ps2 and ps3 clearly separated. Seta pl” on tarsus IV pointed. Solenidia ω1 and ω2 on tarsus I subequal in length.
Description (n = 3)
FEMALE. Length of idiosoma 280 (315–325), maximum width 140 (145–150).
Gnathosoma ( Figs. 1 View Figure 1 , 2 View Figures 2–3 , 6A, B View Figure 6 ) – Length of gnathosomal capsule 28, width 22. Gnathosomal capsule with well-developed dorsal median apodeme. All gnathosomal setae smooth and pointed. Length of setae: cha 12, chb 14, dFe 7, dGe 10, m 11; palpal tibiotarsus with tiny eupathid-like seta and well developed blunt tibial claw distally; palpal solenidion baculiform, almost as long as accessory setigenous structure ( ass). Subcapitulum with a pair of round alveolar pits n in posterior half. Pharyngeal pumps tripartite, joined together and situated on long oesophagus ( Fig. 2 View Figures 2–3 ); pump 1 small, bow-shaped; pumps 2 and 3 oval in shape, pump 2 slightly longer than pump 3; all pumps weakly transversely striated.
Idiosomal dorsum ( Figs. 1A View Figure 1 , 5A View Figure 5 , 6A, C View Figure 6 ) – Stigmata small, round, located anteromesad bases of setae v2 and associated with long tracheal trunks typical for the genus. All dorsal sclerites with small puncta ( Figs. 6A, C View Figure 6 ). Trichobothria clavate, weakly barbed, with rounded apex. Setae v2 smooth, needle-like, other dorsal setae barbed; setae sc2, c1, d, e, and f blunt-tipped, other dorsal setae pointed; setae e slightly thickened, with several strong blunt barbs ( Fig. 6C View Figure 6 ). Cupules ia on tergite D not evident; cupules ih on tergite H small, round. Bases of setae e and f clearly separated. Lengths of dorsal setae: v2 8 (8), sc2 34 (33–37), c1 35 (35–38), c2 53 (52–57), d 33 (32–36), e 35 (34–36), f 47 (45–50), h1 69 (67–70), h2 48 (49–50). Distances between setae: v2–v2 38 (36–40), sc2–sc2 36 (34–37), c1–c1 46 (47–50), c1–c2 31 (28–30), d–d 25 (25), e–f 9 (9–10), f–f 61 (61–65), h1–h1 30 (30–32), h1–h2 10 (11).
Idiosomal venter ( Figs. 1B View Figure 1 , 5B View Figure 5 , 6B, D View Figure 6 ) – All ventral plates with small puncta ( Figs. 6B, D View Figure 6 ). Ap1 well developed and joined with appr; ap2 well developed, joined with appr; apsej well developed and joined with appr; sta represented by a pair of short oblique lines directed from base of setae 2b to ap2; ap3 weakly developed, linear, not joined with appo; ap4 joined with appo, exceeding bases of setae 3b; appo well developed; ap 5 absent. All ventral setae pointed; all setae of anterior sternal plate strongly barbed, setae 3a, 3b, 3c, 4c and ps1 weakly barbed, other ventral setae smooth. Bases of setae ps2 and ps3 separated. Posterior margin of posterior sternal plate convex in middle part; posterior margin of aggenital plate concave in middle part. Ags bell-like, pgs large, inverted subtriangular. Lengths of ventral setae: 1a 29 (26–30), 1b 28 (26–30), 2a 34 (33–36), 2b 35 (33–37), 3a 33 (33–35), 3b 43 (45), 3c 30 (22), 4a 42 (39–43), 4b 49 (48–52), 4c 31 (32), ps1 17 (15–17), ps2 12 (10–12), ps3 13 (13–14).
Legs ( Figs. 3 View Figures 2–3 , 4 View Figure 4 ) – Leg I ( Fig. 3A View Figures 2–3 ). Leg setation: Tr 1 ( v’), Fe 3 ( d, l’, v”), Ge 4 ( l’, l”, v’, v”), TiTa 16(4) ( d, l’, l”, v’, v”, k, tc’, tc”, ft’, ft”, p”, pl’, pl”, pv’, pv”, s, ω1, ω2, φ1, φ2). Lengths of solenidia ω1 15 (14–15), ω2 17 (16–17), φ1 9 (8–9), φ2 8 (8–9); ω1 digitiform, φ1 clavate; φ2 baculiform; ω2 uniformly thin and slightly curved. Setae k and eupathidia ft’, ft”, tc’, tc”, p” blunt-tipped and smooth; seta d of femur hook-shaped; seta v” of femur weakly blunt-tipped and barbed, other leg setae barbed and pointed. Tarsal claw pointed, situated on long pretarsus; setae ( u) modified into spiniform structure located near basal part of claw. Leg II ( Fig. 3B View Figures 2–3 ). Leg setation: Tr 1 ( v’), Fe 3 ( d, l’, v”), Ge 3 ( l’, l”, v’), Ti 4(1) ( d, l’, v’, v”, φ), Ta 6(1) ( pl”, tc’, tc”, pv’, pv”, u’, ω). Solenidion ω 16 (15–16) digitiform, solenidion φ 6 (6) clavate. Seta u’ of tarsus smooth, other leg setae barbed; seta d of femur weakly blunt-tipped, other leg setae pointed. Tarsal claws curved and thickened basally; empodium flipper-shaped. Leg III ( Fig. 4A View Figure 4 ). Leg setation: Tr 1 ( v’), Fe 2 ( d, v’), Ge 2 ( l’, v’), Ti 4(1) ( d, l’, v’, v”, φ), Ta 6 ( pl”, tc’, tc”, pv’, pv”, u’). Solenidion φ 5 (5) clavate. Seta u’ of tarsus smooth, other leg setae barbed; seta d of femur weakly blunt-tipped, other leg setae pointed. Tarsal claws and empodium as on tarsus II. Leg IV ( Fig. 4B View Figure 4 ). Leg setation: Tr 1 ( v’), Fe 2 ( d, v’), Ge 1 ( v’), Ti 4(1) ( d, l’, v’, v”, φ), Ta 6 ( pl”, tc’, tc”, u’, pv’, pv”). Solenidion φ 3 (3) tiny, weakly clavate. All setae barbed; setae d of femur and v” of tibia weakly blunt-tipped, other leg setae pointed. Tarsus IV short, with short pretarsus; tarsal claws as long as on tarsi II and III, without basal thickenings; empodium as on tarsi II and III; femur IV shorter than combined length of tibia and tarsus. Trochanter with short dorsal spiniform projection.
Male and larva unknown.
Type material
Holotype female, Tajikistan, Vahdat District , 2360 m a.s.l., 26 May 2022, soil in mountain pasture, 38° 51' 40.5" N, 69° 00' 14.2" E, coll. A.A. Khaustov; paratypes: 2 females, same data. GoogleMaps
Differential diagnosis
The new species is most similar to Bakerdania plinthos Mahunka , described from Tunisia ( Mahunka 1978), in having claws on tarsus IV as long as on tarsi II and III; tarsus IV relatively short, pretarsus not elongate; bases of setae ps2 and ps3 separated and in having similar length and shape of idiosomal setae. The new species differs from B. plinthos in having alveoli of setae e and f clearly separated (alveoli of setae e and f contiguous in B. plinthos ) and in having solenidia ω1 and ω2 of tibiotarsus I subequal in length (solenidion ω1 about 1.5 times longer than ω 2 in B. plinthos ). The new species is also similar to Bakerdania taymyrica Khaustov, 2008 in having similar shape of dorsal idiosomal setae. The new species differs from B. taymyrica in having setae ps3 clearly separated from ps2 ( ps2 and [ s3 contiguous in B. taymyrica ); setae e with several strong barbs (setae e smooth in B. taymyrica ); and setae h1 distinctly longer than f (setae f and h1 subequal in length in B. taymyrica ).
Etymology The name of the new species tadjikistanica refers to its geographical distribution in Tajikistan.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |