Xestia
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.1215.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:B89D6B58-561B-48A5-B7D7-51B5C30B93CC |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2254ED3C-BF54-FFE8-5A77-FD1B36BE4D95 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Xestia |
| status |
|
25. Xestia View in CoL cnigrum (Linnaeus)
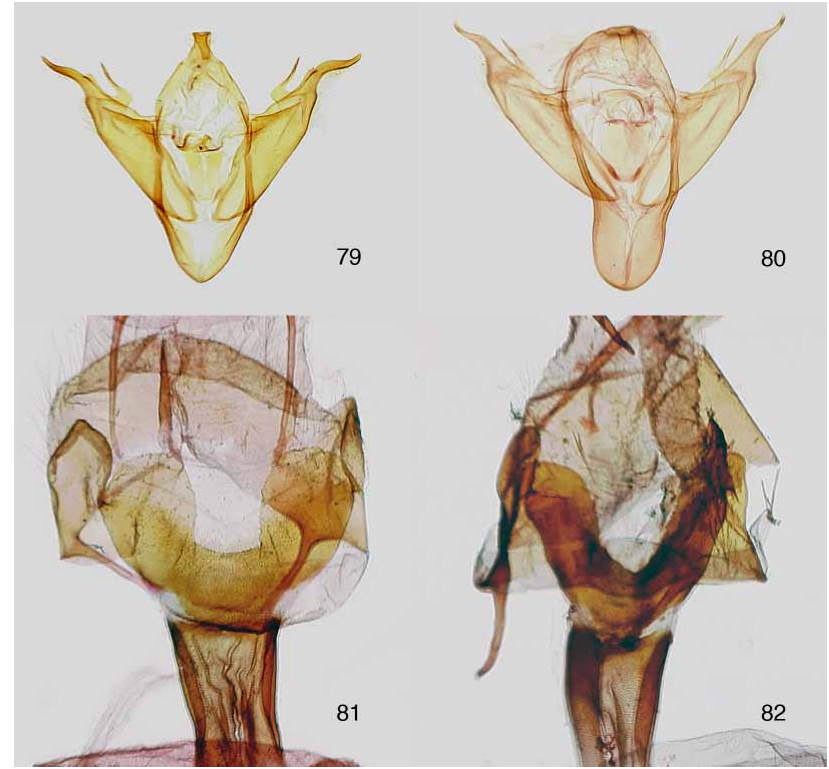
( Figs. 66, 81 View FIGURES 79–82 )
Identification: Forewing length 14.0–18.0 mm. Xestia cnigrum and X. dolosa Franclemont are very similar and difficult to separate. The forewing length is less in X. cnigrum than in X. dolosa . Habitats are also different; X. cnigrum prefers more disturbed areas like abandoned orchards and farmland, whereas X. dolosa is associated with rich deciduous forests ( Lafontaine 1998). The best character for separating these species is in the shape of the ostium bursae in the female genitalia, which is Ushaped with parallel sides in X. cnigrum ( Fig. 81 View FIGURES 79–82 ) and Vshaped in X. dolosa ( Fig. 82 View FIGURES 79–82 ).
Flight period: There are two generations per year from early May to July and from July to early October ( Lafontaine 1998).
Collected localities: This species is not yet recorded in the Park, but it is likely to occur there.
General distribution: This is a widespread species occurring from coast to coast across Canada and the northern United States to western Alaska . It occurs in the Rockies from Montana to southern Arizona and New Mexico. In the East it ranges from Maine to North Carolina ( Lafontaine 1998). The collections from GSMNP are new records for the state of Tennessee .
Larval hosts: Larvae have been reared on Indianpipe ( Monotropa uniflora L., Monotropaceae ), raspberry ( Rubus idaeus L., Rosaceae ), and common plantain ( Plantago major L., Plantaginaceae ) ( McCabe 1991). It was not until 1980 that X. cnigrum was considered a different species from X. dolosa Franclemont. Based on habitat, other hosts probably attributed to X. cnigrum include apple ( Malus sp. , Rosaceae ), barley ( Elyhordeum sp. , Poaceae ), corn ( Zea mays L., Poaceae ), clover ( Trifolium sp. , Fabaceae ), and tobacco (Nicotania sp., Solanaceae ) (Rings, et al. 1992).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.